瞬态统计能量分析法中动态响应误差分析
宋海洋,于开平,李向阳,韩敬永
(哈尔滨工业大学 航天学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001)
瞬态统计能量分析法中动态响应误差分析
宋海洋,于开平,李向阳,韩敬永
(哈尔滨工业大学 航天学院,黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001)
统计能量分析方法能够有效预示舰船和车辆等结构的高频振动及噪声。本文通过建立两子结构耦合模型,利用差分法研究了瞬态统计能量分析中参数误差对子结构响应能量的影响,同时给出了参数误差与所导致能量误差的关系函数。结果表明:对于外载荷直接激励的子结构,内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子的误差都会导致被预示总能量的减小。对于外载荷间接激励的子结构,内损耗因子的误差会导致峰值能量的减小,而耦合损耗因子的误差会导致峰值能量的增加。本文内容对改进动力学系统数值模型以及提高结构振动和噪声预示精度有一定的帮助。
瞬态统计能量分析;参数误差;能量误差
0 引 言
解决复杂结构振动和噪声问题的方法包括有限元法、边界元法、模态分析法、波动分析法、阻抗导纳功率流法、结构声强法和统计能量分析法,其中统计能量分析法是目前公认的解决复杂结构高频振动问题最有效的方法。经过几十年的研究和探索,统计能量分析方法不但在理论上有了创新和突破,而且已经成功地应用到了船舶[1-3]和车辆[4]等领域来解决复杂结构的振动和噪声问题。
采用瞬态统计能量分析法进行动力学系统环境预示需要确定结构 2 个基本参数:内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子。这 2 个参数的准确估算对结构响应的预示和数值仿真结果的精度有重要的影响。其中内损耗因子是衡量系统阻尼特性、决定振动能量耗散的重要参数。耦合损耗因子是统计能量分析中表征耦合系统间能量交换的重要参数。目前除了一些简单结构的内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子可以从理论上推得,比较复杂的结构的内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子只能通过实验测量来得到[5-8]。然而内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子在很多情况下是 10–2~10–4数量级的小数,在实际工作中要对这些小数进行运算和测量很困难,故这些参数的测量结果经常存在不同程度的误差。
本文基于 2 个耦合子结构所组成的系统,分析了瞬态统计能量分析法中参数误差对子结构能量的影响,给出了参数误差与所导致能量误差的关系函数,对改进动力学系统数值模型及提高数值模拟的精度有很大的帮助。
1 瞬态统计能量分析中参数误差对子结构能量影响
1.1 内损耗因子误差对子结构能量的影响
两子结构耦合的统计能量分析模型如图 1 所示,瞬间能量平衡方程可写为:
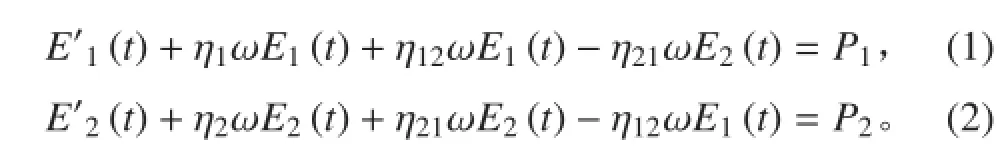
其中:Ei(t)(i=1,2) 是带宽 Δω 内随时间变化的总能量,代表总能量对时间的一阶导数,ηi(i=1,2) 是子结构 i 的内损耗因子,代表子结构 i 与子结构 j 间的耦合损耗因子,ω 为分析带宽Δω 的中心频率。现给子结构 1 施加一个短时的脉冲激励力,那么子结构 1 的初始能量为而子结构 2 的初始能量为 0 且输入功率 P1=P2=0。
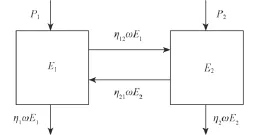
图 1 两子结构的统计能量分析模型Fig. 1 SEA model for two coupled subsystems
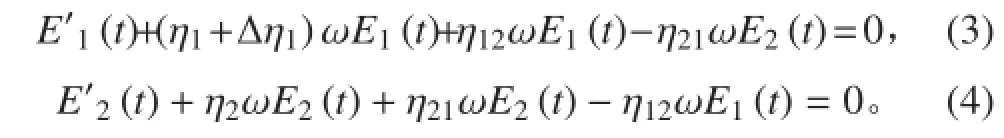
采用拉普拉斯变换方法可得两子结构随时间变化的能量表达式为:
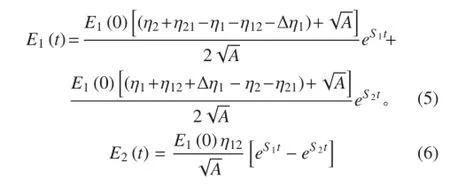
其中:
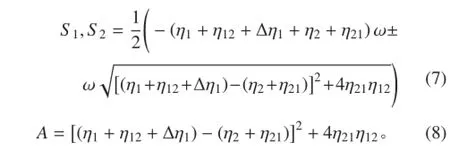
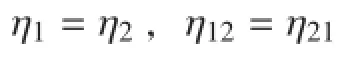
① 当两子结构满足时,将式(5)整理后得:
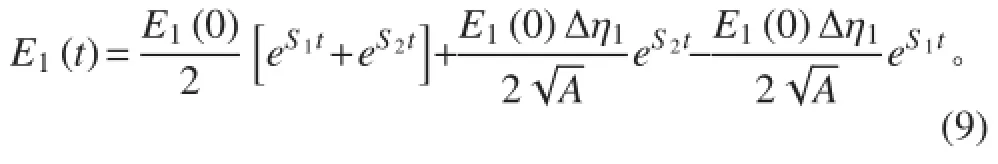
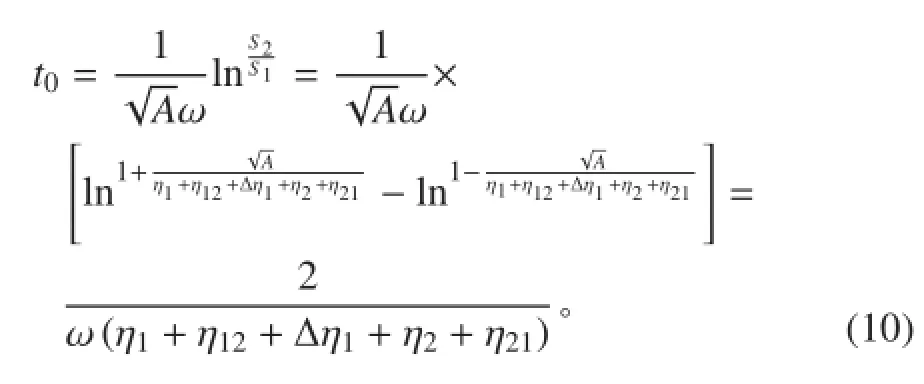
将式(10)代入式(6)中可得子结构 2 的峰值能量为
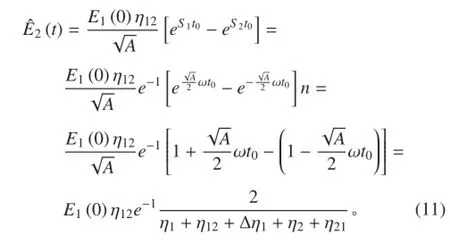
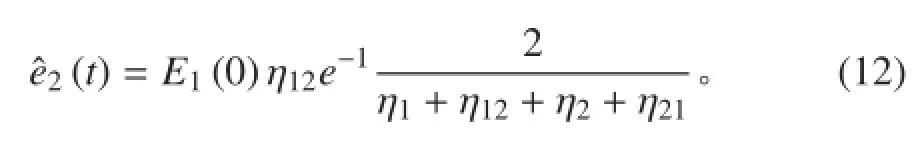
那么子结构 2 峰值能量的相对误差为
1.2 耦合损耗因子误差对子结构能量的影响
其中:
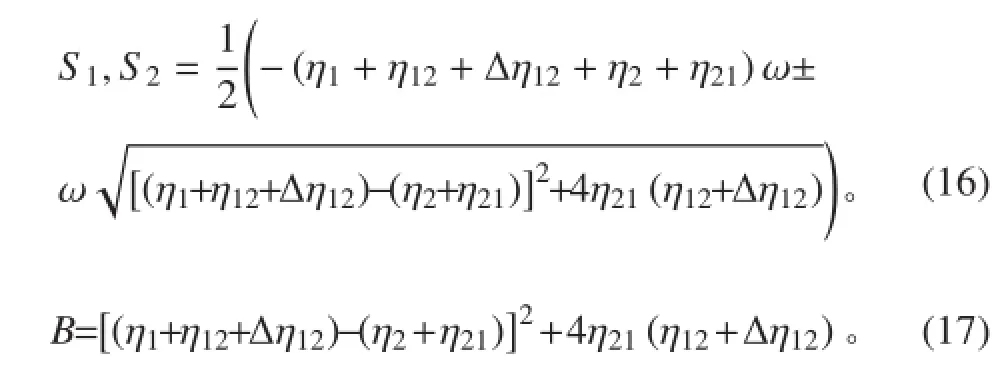

② 通过计算可得到子结构 2 的峰值能量为
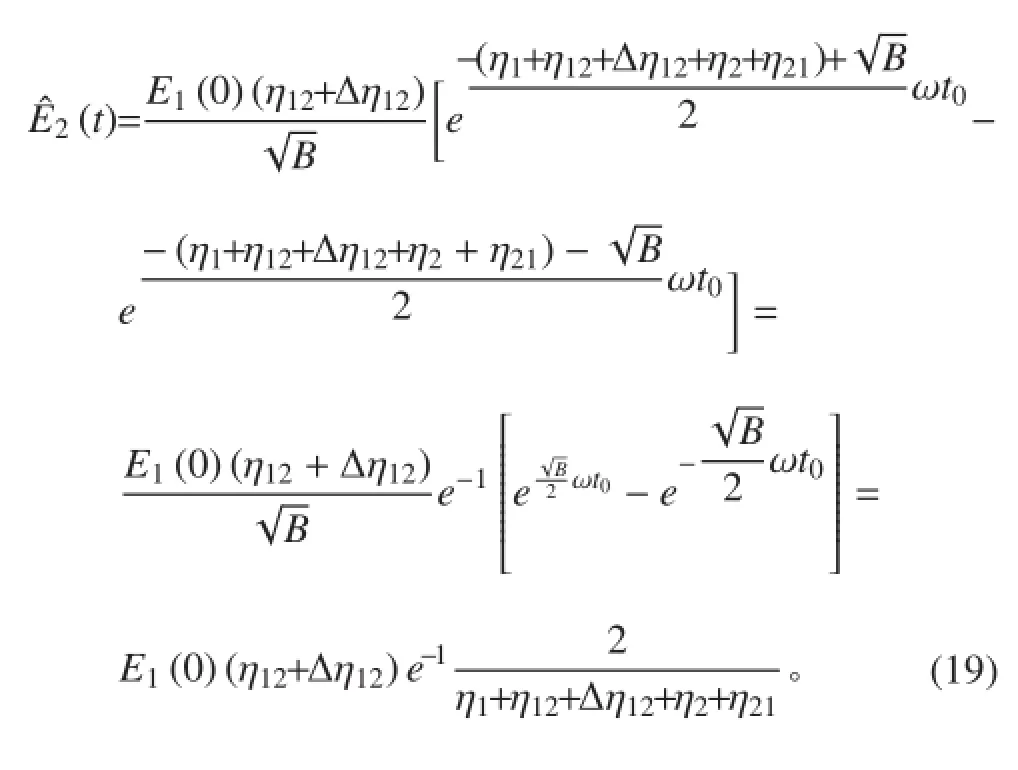
得子结构 2 的峰值能量为
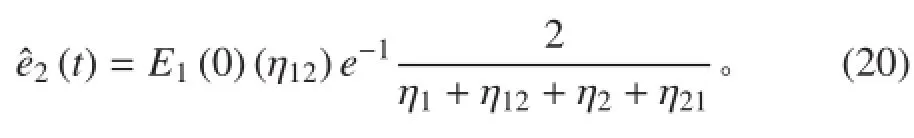
子结构 2 峰值能量的相对误差为
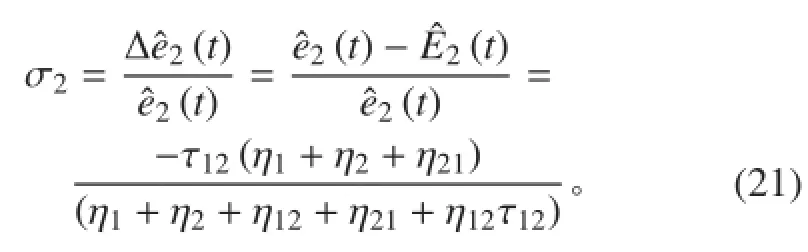
2 计算实例
如图 2 所示,系统由两块相互垂直并铆接的钢板组成,并且两块钢板的其他边界条件是自由的。钢板的密度为 7 800 kg/m3。板 1 的长度为 0.42 m,宽度为0.36 m,厚度为 0.01 m。板 2 的长度为 0.42 m,宽度为0.36 m,厚度为 0.004 5 m。以上2块钢板的内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子已经在文献[9]中由实验测量得到,表 1展示了两板在中心频率 f=2 000 Hz 时测量的内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子。

图 2 两板耦合系统Fig. 2 Two-plate coupling structural system
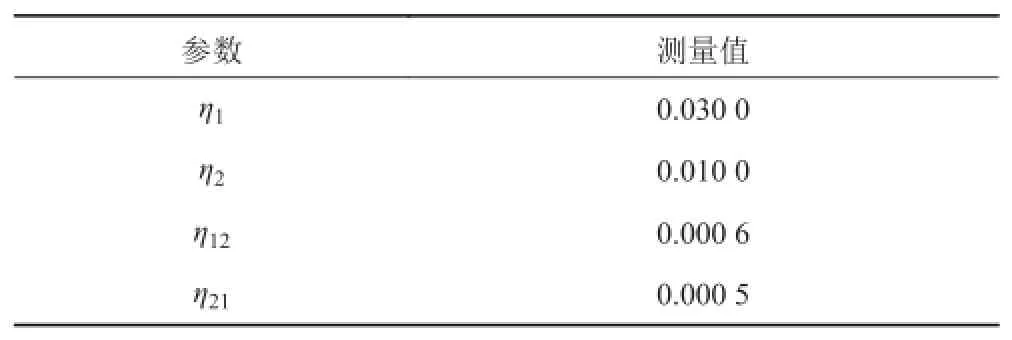
表 1 两板在中心频率 f = 2 000 Hz 时内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子测量值Tab. 1 Measured values of damping loss factors and coupling loss factors at f = 2 000 Hz
现对板 1 施加一个短时的脉冲激励,使板 1 具有初始能量 E1(0)=1 kJ,通过式(13)和式(21)可以得到板 2 的峰值能量相对误差和板 1 参数相对误差的关系曲线,如图 3 和图 4 所示。

图 3 板 2 的峰值能量相对误差与板 1 内损耗因子相对误差关系Fig. 3 The relation between peak energy error of plate 2 and damping loss factor error of plate 1
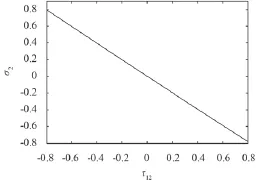
图 4 板 2 的峰值能量相对误差与板 1 耦合损耗因子相对误差关系Fig. 4 The relation between peak energy error of plate 2 and coupling loss factor error of plate 1
图 3 表明增大板 1 的内损耗因子,将引起板 2 峰值能量的降低,因为增加的阻尼过多消耗了板 1 的能量,导致传递到板 2 的能量减少。图 4 表明增加板 1对板 2 的耦合损耗因子,实际增大了板 1 对板 2 能量的传递,导致板 2 峰值能量的增加。因此精确确定内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子尽量减少测量误差对瞬态统计能量分析中结构能量的预示精度有较大的影响。
3 结 语
本文从两耦合子结构所组成系统的能量平衡方程入手,借助拉普拉斯变换研究了瞬态统计能量分析法中参数误差对子结构总能量的影响,同时给出了参数误差与所导致能量误差的关系函数。对于外载荷直接激励的子结构,内损耗因子和耦合损耗因子的误差都会导致总能量的减小。对于外载荷间接激励的子结构,内损耗因子的误差会导致峰值能量的减小,而耦合损耗因子的误差会导致峰值能量的增加。不同于稳态统计能量分析理论,在瞬态统计能量分析中,求解 3 个及以上子结构组成的系统的精确能量解是很复杂的,后续需要更多数学方法的发展和引进,本文内容对于 2 个以上的子结构组成的复杂系统将有一定参考意义。
[1]HYNNá P, KLINGE P, VUOKSINEN J. Prediction of structureborne sound transmission in large welded ship structures using statistical energy analysis[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,1995, 180(4): 583–607.
[2]邵亮. 统计能量法在船舶舱室噪声预报中的应用[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2012, 34(5): 98–100, 107. SHAO Liang. Prediction and research of ship cabin noise with statistical energy analysis[J]. Ship Science and Technology,2012, 34(5): 98–100, 107.
[3]YAYLADERE B C, ÇALIŞKAN M. Prediction of noise levels within a submerged vessel by statistical energy analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 20th International Congress on Sound & Vibration. Bangkok, Thailand: ICSV, 2013: 66–71.
[4]CHEN S M, WANG D F, LEI Y F. Automotive interior noise prediction based on single sound cavity using statistical energy analysis method[J]. Noise & Vibration Worldwide, 2011,42(11): 36–43.
[5]程广利, 朱石坚, 伍先俊. 统计能量分析法及其损耗因子确定方法综述[J]. 船舶工程, 2004, 26(4): 10–15. CHENG Guang-li, ZHU Shi-jian, WU Xian-jun. A summary of statistical energy analysis method and its loss factor’s determination[J]. Ship Engineering, 2004, 26(4): 10–15.
[6]叶敏, 郎作贵, 郝志勇. 复杂系统振动能量平衡方程中SEA参数的测定[J]. 内燃机学报, 1998, 16(4): 469–474. YE Min, LANG Zuo-gui, HAO Zhi-yong. The determination of vibration energy balance sea system parameters in a complex structure[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 1998, 16(4): 469–474.
[7]盛美萍, 王敏庆, 孙进才, 等. 非保守耦合系统的等效内损耗因子[J]. 声学学报, 1997, 22(6): 555–561. SHENG Mei-ping, WANG Min-qing, SUN Jin-cai, et al. Equivalent internal loss factors for non-conservatively coupled systems[J]. Acta Acustica, 1997, 22(6): 555–561.
[8]盛美萍, 王敏庆, 孙进才. 非保守耦合系统的耦合损耗因子[J].声学学报, 1999, 24(5): 550–556. SHENG Mei-ping, WANG Min-qing, SUN Jin-cai. The coupling loss factors of non-conservatively coupled systems[J]. Acta Acustica, 1999, 24(5): 550–556.
[9]MAO B Y, XIE S L, XU M L, et al. Simulated and experimental studies on identification of impact load with the transient statistical energy analysis method[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2014, 46(2): 307–324.
Analysis on dynamic response error in transient
SONG Hai-yang, YU Kai-ping, LI Xiang-yang, HAN Jing-yong
(Department of Astronautical Science and Mechanics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China)
Statistical energy analysis (SEA) method has been recognized as a powerful tool in predicting the highfrequency sound and vibration of ship structures and vehicles. In the transient statistical energy analysis framework, this paper applies the difference method to investigate the effect of parameters error on structural total energy. Meanwhile, the function relation of parameters error and caused energy error is also provided. The following results can finally be shown. For the subsystem that is directly excited by an external load, the error of the damping loss factors and coupling loss factors will result in the decrease of structural total energy. For the subsystem that is indirectly excited, the error of damping loss factors can lead to the decreasing of structural peak energy, while the error of coupling loss factors will result in the increase of structural peak energy. The content of this paper can provide some help for improving the dynamics model and predicted accuracy of sound and vibration.
transient statistical energy analysis;parameter error;energy error
V415.4
A
1672 – 7619(2016)04 – 0038 – 04
10.3404/j.issn.1672 – 7619.2016.04.008
2015 – 07 – 02;
2015 – 09 – 20
国家自然科学基金 资助项目(11372084)
宋海洋(1986 – ),男,博士,研究方向为高频振动和噪声环境的预示。

