赣北景德镇韧性剪切带两类剪切指向及其构造意义
徐先兵,汤 帅,林寿发.中国地质大学(武汉)地球科学学院,武汉,430074.Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences,University of Waterloo,Ontario NL 3G,Canada
赣北景德镇韧性剪切带两类剪切指向及其构造意义
徐先兵1,汤 帅1,林寿发2
1.中国地质大学(武汉)地球科学学院,武汉,430074
2.Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences,University of Waterloo,Ontario N2L 3G1,Canada
摘要:景德镇韧性剪切带位于新元古代江南造山带的核部,其构造变形特征和形成时代对华南新元古代至早古生代构造演化具有重要的制约意义。景德镇韧性剪切带呈北东向展布,全长约180 km,最大出露宽度为~7 km。通过详细的野外地质调查和室内定向薄片鉴定,在景德镇韧性剪切带中识别出了两期韧性走滑构造变形,并研究了其运动学指向和形成时的温压条件。早期构造变形表现为左旋韧性走滑兼逆冲作用,形成温度为420~530℃,差应力为40~300 MPa;晚期变形主要表现为右旋走滑,形成温度为300~420℃,差应力为120~350 MPa。结合前人资料,景德镇韧性剪切带左旋走滑兼逆冲作用形成于新元古代造山作用的晚期(810~800 Ma),是由同造山挤压到后造山伸展调整的结果;而右旋走滑形成于早古生代,是华南早古生代陆内造山作用的产物。
关键词:运动学指向;温压条件;景德镇韧性剪切带;江南造山带;华南
First author:XU Xianbing,Ph.D.,E-mail:xbxu2011@cug.edu.cn;bingge1018@gmail.com
江南造山带是扬子与华夏地块新元古代俯冲-碰撞拼合的产物,发育不同类型的蛇绿岩、大量的花岗闪长岩以及强烈的韧性变形(白文吉等,1986;Shu et al.,1991,1994;Charvet et al.,1996;Shu and Charvet,1996;Li et al.,2003;Wu et al.,2006;董树文等,2010;张彦杰等,2011;Li et al.,2013;Zhang et al.,2012,2013;周效华等,2014)。区域上,景德镇韧性剪切带向南西与九岭南缘的南昌—万载韧性剪切带相连,向北东与皖南伏川蛇绿混杂岩带相连,共同构成宜丰—景德镇—歙县剪切带(江西省地矿局,1984;张彦杰等,2011,2012;Wang et al.,2013a)。目前,对北东走向的宜丰—景德镇—歙县韧性剪切带的运动学和形成时代还存在争论。对于其运动学指向,存在由北向南逆冲(张彦杰等,2012)、由南向北逆冲(周新民和王德滋,1988;徐备等,1992;Chu and Lin,2014)、左旋走滑(Shu et al.,1991;舒良树等,1995;陈伯林等,1998)以及右旋走滑(李德威和卢宇,1991;陈伯林等,1998;Chu and Lin,2014)之争。对于韧性变形的形成时代,一种观点认为景德镇韧性剪切带是新元古代弧后盆地关闭的产物(张彦杰等,2011,2012;Wang et al.,2013a;周效华等,2014);另外一种观点则认为其是早古生代陆内造山作用的产物(Shu et al.,1991;徐备等,1992;Chu and Lin,2014)。
地质和地球物理资料表明宜丰—景德镇—歙县韧性剪切带是超壳断裂(江西省地矿局,1984;张彦杰等,2011,2012;王鹏程等,2015),其不仅是新元古代弱变形的双桥山群和强变形溪口岩群的分界线(楼法生等,2003;张彦杰等,2010a,b),还控制着晚古生代至早中生代萍乐坳陷和晚中生代高安盆地的形成和演化(江西省地矿局,1984;钟南昌,1992)。因此,景德镇韧性剪切带的研究对江南造山带新元古代-早古生代构造演化具有重要的制约意义。本文通过对景德镇韧性剪切带详细的野外地质调查和室内定向薄片的研究,探讨了剪切带的几何学、运动学以及年代学,为江南造山带新元古代和早古生代造山作用的研究提供了详实的资料。
1 地质背景
江南造山带东段是指由南侧NEE向萍乡—江山—绍兴断裂带、东侧NNE向东乡—德兴蛇绿混杂岩带和NE向歙县伏川蛇绿混杂岩带以及北侧江南断裂带所围限的皖南—赣北地区(图1)(Xu et al.,2015;徐先兵等,2015)。其主要由新元古代浊积岩、花岗闪长岩以及基性-超基性岩组成(江西省地矿局,1984;Li et al.,2003;Wu et al.,2006;Wang et al.,2008,2013b;Zhao et al.,2011;周效华等,2012,2014;Yin et al.,2013;Xu et al.,2014)。
景德镇韧性剪切带位于江南造山带东段的核部,其西起于鄱阳湖东岸,沿北东方向经鄱阳、景德镇、浮梁、休宁,止于晚中生代黄山盆地西缘,全长约180 km(图2)。剪切带沿走向呈舒缓波状展布,在浮梁县王港乡至瑶里镇分散成三条北东向近平行的小型剪切带,由北至南分别为猫儿颈—桃岭韧性剪切带、大背坞—金村韧性剪切带以及下坞—瑶里韧性剪切带。小型剪切带出露宽度250~1500 m不等,景德镇韧性剪切带出露最大宽度为~7 km。
景德镇韧性剪切带卷入的岩石主要为新元古代浊积岩和基性-超基性岩,且被早白垩世花岗岩所侵位,主要由超糜棱岩、糜棱岩以及糜棱岩化岩石组成,与围岩呈渐变过度关系。景德镇韧性剪切带面理主要由定向排列的石英条带和黑云母组成,以高角度倾向SE或NW,倾角为60°~90°(图3A);线理主要由显著拉长的石英斑晶和绢云母组成,以低角度向NE倾伏为主,倾伏角为15°~35°(图3B)。构造要素特征指示景德镇韧性剪切带主要表现为韧性走滑特征,但有明显地逆冲分量。
2 运动学分析
详细的野外地质调查表明,景德镇韧性剪切带中发育大量运动学指向的标志,如不对称褶皱(图3C)、不对称旋转碎斑(图3D)以及S-C组构等。宏观的运动学标志指示景德镇韧性剪切带以左旋走滑为主。
通过对67块定向薄片的系统观察,在景德镇韧性剪切带鉴别出了两类运动学指向,即左旋走滑和右旋走滑。这两类运动学指向不仅发育在整个剪切带中,而且还发育在同一个定向薄片之中(图4)。系统的观察表明,右旋走滑标志包括压力影构造(图4A)、不对称旋转碎斑(图4C,E,G)、S-C组构以及云母鱼构造等;左旋走滑标志包括压力影构造(图4B),不对称石英旋转碎斑(图4D,F,H)以及云母鱼构造。
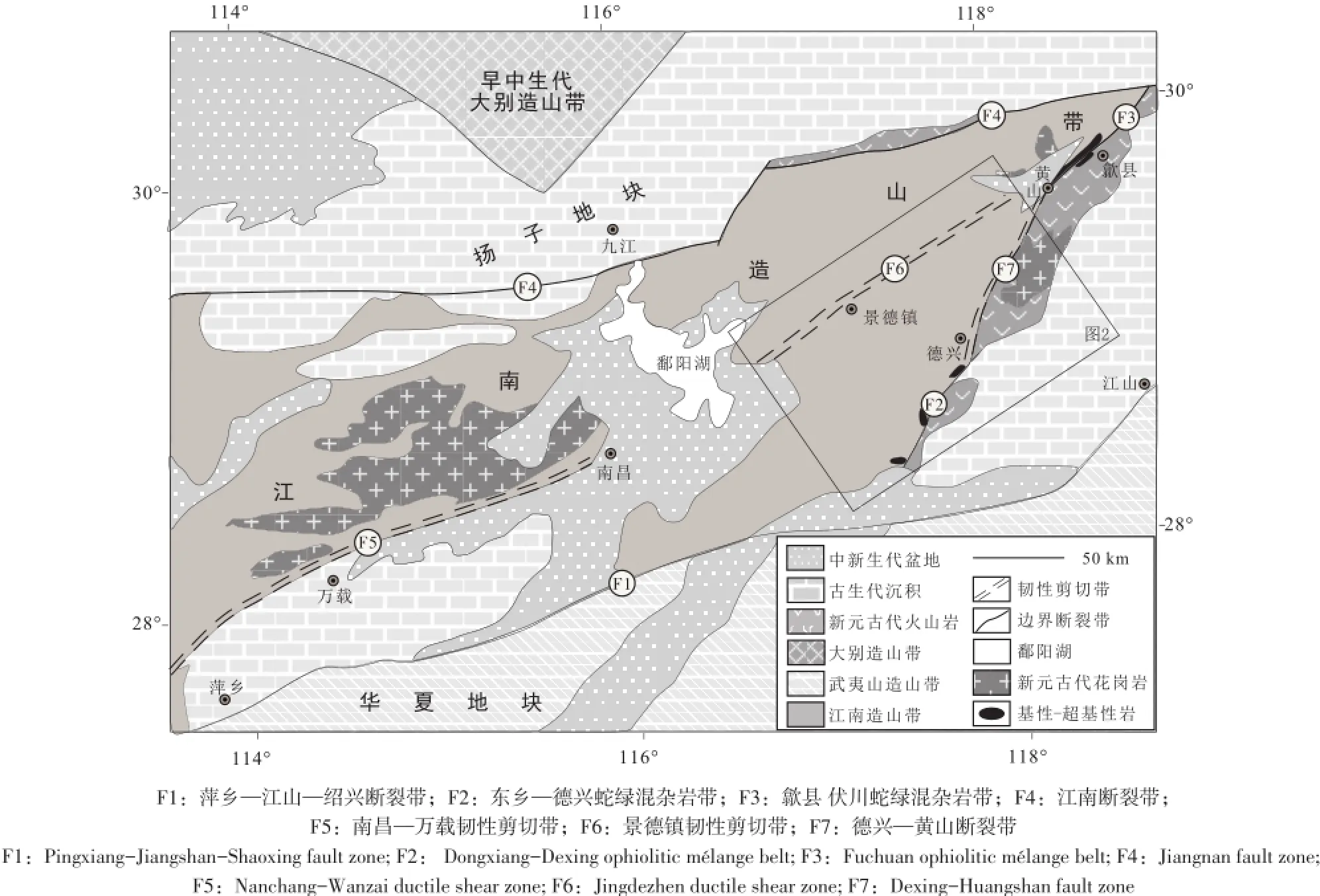
图1 江南造山带东段地质简图Fig.1 Sketch map of the eastern Jiangnan Orogen
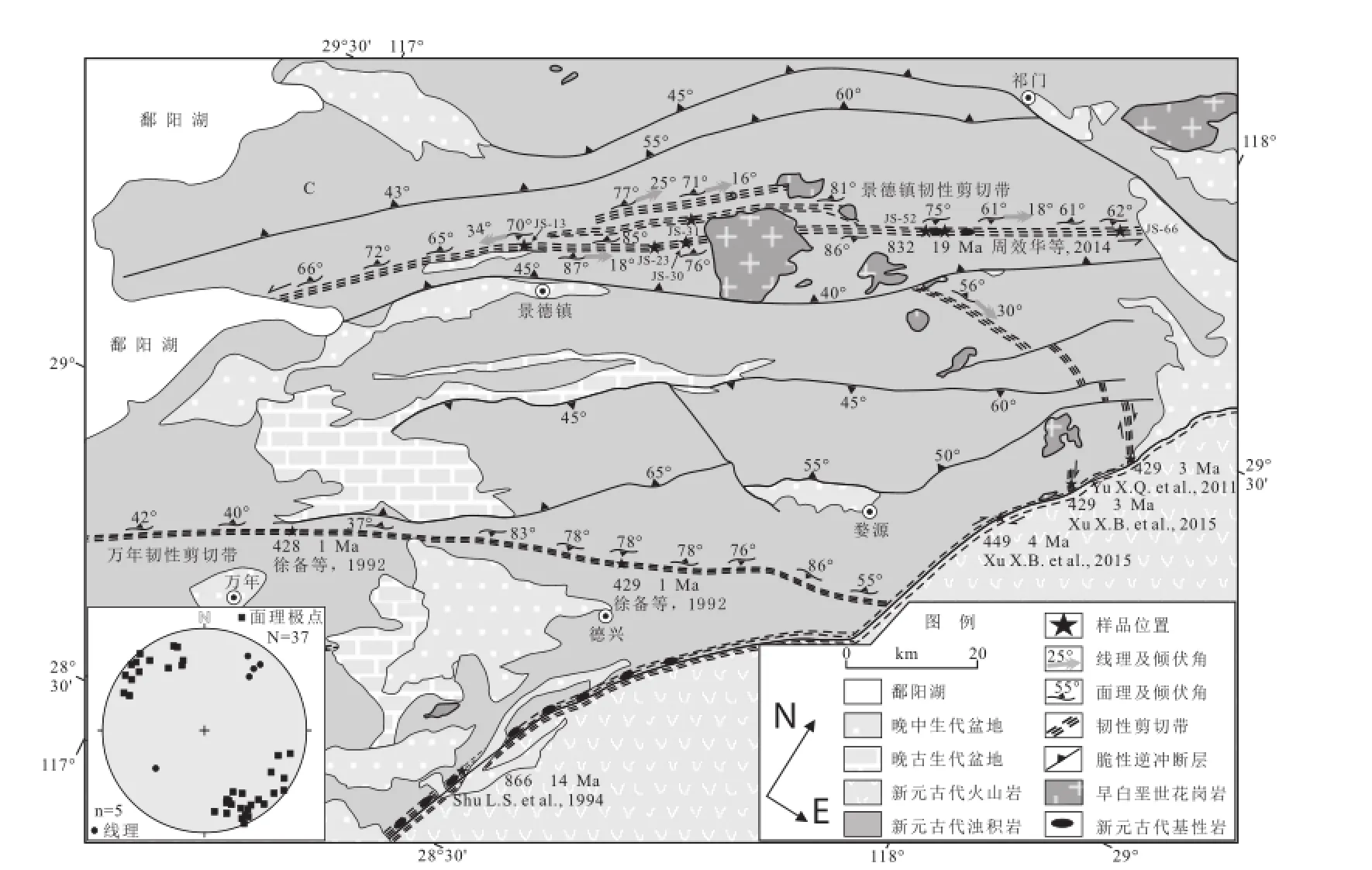
图2 景德镇韧性剪切带地质简图Fig.2 Sketch map of the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone

图3 景德镇韧性剪切带野外照片Fig.3 Field photos of the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone
3 温度和古应力值估算
景德镇剪切带糜棱岩主要石英、黑云母以及少量白云母和长石组成,缺乏合适的温度计进行变形温度估算。前人研究表明,石英和长石矿物变形和重结晶方式可以指示韧性剪切带的形成温度(Gapais,1989;Passchier and Trouw,1996;向必伟等,2007;胡玲等,2009;Xu et al.,2011)。
石英由脆性变形向韧性变形的转换温度为250~300℃(Sibson,1999;Van,1999)。石英的韧性变形方式随着变形温度的升高(300~700℃)依次表现为臌胀重结晶(BLG)、亚颗粒旋转重结晶(SGR)以及颗粒边界迁移重结晶(BGM)(Stipp et al.,2002)。其中,石英BLG形成于300~380℃,在380~420℃表现为BLG和SGR共存;独立的SGR形成于420~480℃,与GBM共存形成于470~530℃;而GBM独立存在的温度为530~630℃。
长石在低于300℃是表现为脆性破裂,在300~400℃表现为显微破裂,波状消光以及双晶纹弯曲,高于400℃开始发生塑性变形和动态重结晶(Tullis and Yund,1987,1991;Pryer,1993)。
依据上述标准,结合表1中石英和长石的变形和重结晶的方式,景德镇韧性剪切带左旋走滑兼逆冲变形形成于420~530℃,而右旋走滑形成于300~420℃。石英动态重结晶颗粒的平均直径可用来估算差应力的大小(Twiss,1977;Post and Tul⁃lis,1999;Stipp and Tullis,2003)。首先选取具有明显指示标志的定向薄片,确定韧性变形的运动学指向。然后确定石英重结晶作用的方式,并测量颗粒的直径。每个样品中至少选择40颗石英动态重结晶颗粒,然后用平均线性法计算颗粒平均直径。最后根据石英重结晶方式和粒径大小进行投图(Passchier and Trouw,1996)。如图5所示,景德镇韧性剪切带左旋走滑兼逆冲作用的差应力为40~300 MPa,而右旋剪切变形的差应力大小为120~350 MPa。
4 讨论
4.1 景德镇韧性剪切带的变形时代
景德镇韧性剪切带发育于新元古代双桥山群和溪口岩群浊积岩和基性岩之中。锆石U-Pb年代学指示卷入变形的浊积岩和基性岩分别形成于840~820 Ma(张彦杰等,2010a;Zhao et al.,2011; Wang et al.,2013b;Yin et al.,2013;Xu et al.,2014)和832±19 Ma(周效华等,2014),指示景德镇韧性剪切带形成于~820 Ma之后。景德镇韧性剪切带还被早白垩世花岗岩(150~120 Ma)所侵位(余明刚等,2010;赵鹏等,2010),指示其形成于~150 Ma之前。区域上,景德镇韧性剪切带被印支-燕山早期脆性逆冲构造所叠加(张彦杰等,2012;王鹏程等,2015),指示韧性变形形成于中生代之前。
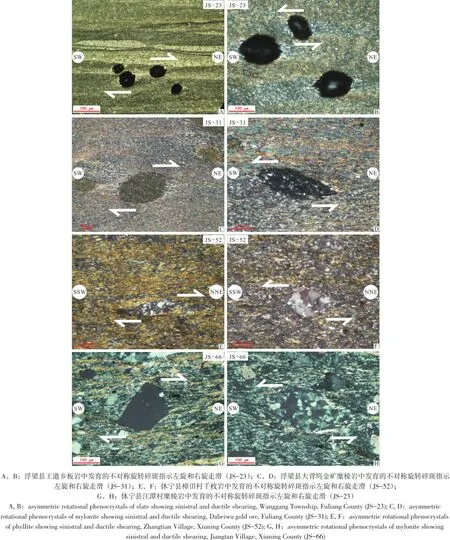
图4 景德镇韧性剪切带左旋和右旋走滑运动学标志Fig.4 Sinistral and dextral shearing markers in the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone
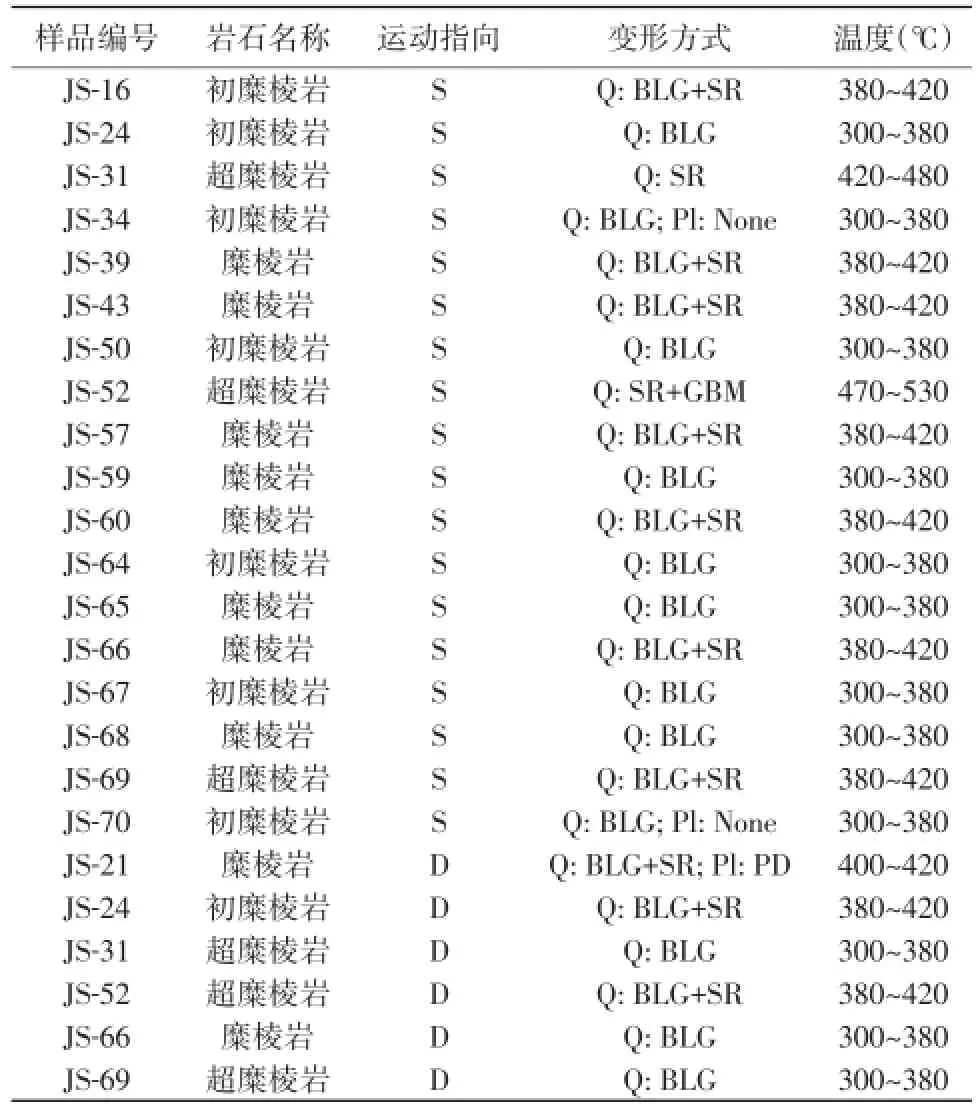
表1 景德镇韧性剪切带变形温度估计表Table 1 Estimated deformation temperature of samples in the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone
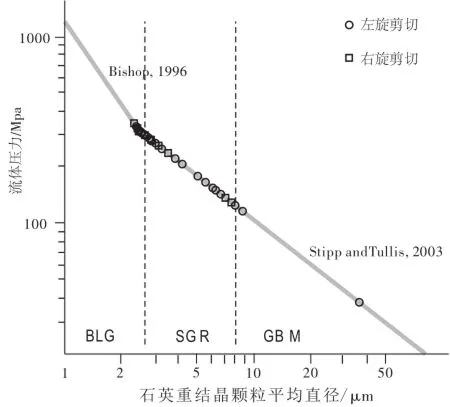
图5 景德镇剪切带差应力估算图Fig.5 Differential stress of the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone (after Passchier and Trouw,1996)
同一构造带如果保存有多期变形特征,其保存的早期变形往往形成温度较高,而晚期变形则形成温度较低,否则晚期高温变形会抹掉早期低温构造变形的记录(许志琴等,2007)。因此,景德镇韧性剪切带早期变形为中温北东向左旋走滑兼逆冲构造,晚期为低温北东向右旋韧性剪切变形。
新元古代-早古生代南昌—万载韧性剪切带面理(150°∠65°)和线理(60°∠20°)产状、运动学指向(左旋)、形成温度(500~600℃)以及差应力(50~190 MPa)与景德镇左旋走滑兼逆冲韧性剪切带基本一致(Shu et al.,1991;舒良树等,1995)。结合南昌—万载韧性剪切带是景德镇韧性剪切带的西延部分(江西省地矿局,1984;张彦杰等,2011,2012;Wang et al.,2013a),景德镇韧性剪切带左旋走滑兼逆冲作用也形成于新元古代-早古生代。最近的云母40Ar/39Ar年代学表明南昌—万载韧性剪切带在早古生代(465~380 Ma)表现为由南向北的韧性逆冲和右旋韧性走滑(Chu and Lin,2014)。另外,江南造山带东段早古生代北北东向韧性剪切带也表现为右旋走滑特征(Xu et al.,2015)。因此,作者推测景德镇韧性剪切带左旋走滑兼逆冲变形发育于新元古代,而右旋韧性走滑形成于早古生代。
4.2 大地构造意义
景德镇韧性剪切带具有超壳断裂特征(江西省地矿局,1984;王鹏程等,2015),指示其可能为地块碰撞拼合边界。剪切带中彰源枕状玄武岩、辉长岩和辉绿岩形成于新元古代(~830 Ma),且具有弧后盆地蛇绿岩地球化学特征,指示景德镇韧性剪切带在~830 Ma为弧后盆地扩张脊(张彦杰等,2011;周效华等,2014)。区域上,皖南歙县伏川蛇绿岩也形成于新元古代(~825 Ma)弧后盆地构造环境(Zhang et al.,2012;2013)。上述二者具有相邻的空间位置、相同的地球化学特征和形成时代,因此歙县断裂带在新元古代为景德镇左旋韧性剪切带的东延部分(张彦杰等,2011;Wang et al.,2013a;周效华等,2014)。结合南昌—万载左旋韧性剪切带在新元古代为景德镇左旋韧性剪切带的西延部分,由上述三条断裂组成的新元古代宜丰—景德镇—歙县剪切带在~830 Ma为统一的弧后盆地扩张脊(江西省地矿局,1984;张彦杰等,2011,2012;Wangetal.,2013a)。
构造要素分析表明宜丰—景德镇韧性剪切带在新元古代表现为左旋走滑兼逆冲作用,与最古老一期逆冲的构造样式不一致(舒良树等,1995),因此笔者推测左旋走滑兼逆冲变形的形成时代晚于逆冲变形。白云母40Ar/39Ar年代学指示伏川蛇绿岩沿歙县断裂带逆冲到歙县岩体之上的时代为768±30 Ma,由逆冲作用导致的德兴西湾钠长花岗岩糜棱岩化的年龄为~799 Ma(胡世玲等,1992)。如果考虑年龄误差的话,新元古代逆冲作用的40Ar/39Ar年龄为~800 Ma。由于云母40Ar/39Ar年龄的封闭温度明显低于锆石U-Pb年龄的封闭温度(Leeetal.,1997;McDougallandHarrison,1999),由逆冲作用形成的~800 Ma40Ar/39Ar年龄应该是华南新元古代(820~810 Ma)扬子与华夏板块碰撞导致~830 Ma弧后盆地关闭(Xu et al.,2014;Zhao,2014;Yao et al.,2015)的冷却年龄。结合区域上东乡—德兴韧性剪切带左旋走滑的形成时代为768±9 Ma(Shu and Charvet,1996),我们推测新元古代江南造山带发育两期韧性变形作用,早期是与扬子与华夏板块碰撞有关的逆冲变形,形成时代为820~810 Ma,其冷却年龄为~800 Ma;晚期是与造山作用调整有关的左旋走滑兼逆冲的压扭变形,其冷却年龄为~770 Ma。区域上,江南造山带造山后伸展和南华裂谷开始于800~760 Ma(Wang and Li,2003;Li et al.,2008;Zheng et al.,2008;Wang et al.,2010,2012)。因此,江南造山带北东—北北东向左旋走滑兼逆的韧性冲变形形成于810~800 Ma。
北东向宜丰—景德镇—歙县剪切带在早古生代表现为右旋韧性走滑特征。另外在江南背斜核部还发育早古生代近东西向和北北东向右旋韧性剪切带(Yu et al.,2011;Chu and Lin,2014;Xu et al.,2015)。区域上江南背斜南部主要表现为北东走向的逆冲作用,而在其北部基本无变形(徐备等,1992;舒良树等,1999,2008;Li et al.,2010;Wang et al.,2013c;Shu et al.,2014),因此其动力来自于沿萍乡—江山—绍兴断裂带发育的陆内俯冲作用(Faure et al.,2009)。云母40Ar/39Ar年代学指示北北东向右旋走滑变形明显早于北东和近东西向右旋走滑,可能与区域上由南北走向主应力向近东西向主应力转变有关(Xu et al.,2015)。
5 结论
(1)景德镇韧性剪切带保存了两期韧性走滑变形,早期变形为左旋走滑兼逆冲作用,形成温度为420~530℃,差应力为40~300 MPa;晚期变形表现为右旋走滑,形成温度为300~420℃,差应力为120~350 MPa。
(2)景德镇剪切带左旋走滑兼逆冲作用形成于新元古代(810~800 Ma),是由同造山挤压到后造山伸展调整的结果;而右旋走滑形成于早古生代,是华南早古生代陆内造山作用的产物。
致谢:感谢三位匿名审稿人对本文提出的意见和建议,使得文章结构和文字组织更为合理,并提高了研究深度。
参考文献(References):
白文吉,甘启高,杨轻绥,等.1986.江南古陆东南缘蛇绿岩完整层序剖面的发现和基本特征[J].岩石矿物学杂志,5(4):289-299.
陈柏林,董法先,沈庭沅.1998.江西大背坞地区浅变质碎屑岩中韧性剪切带变形特征[J].现代地质,12(3):311-317.
董树文,薛怀民,项新葵,等.2010.赣北庐山地区新元古代细碧-角斑岩系枕状熔岩的发现及其地质意义[J].中国地质,37(4):1021-1033.
胡玲,刘俊来,纪沫,等编著.2009.变形显微构造识别手册[M].北京:地质出版社.
胡世玲,邹海波,周新民.1992.江南元古宙碰撞造山带的两个40Ar/39Ar年龄值[J].科学通报,37(3):286-286.
江西省地矿局.1984.江西省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社.
李德威,卢宇.1991.江西大背坞含金剪切带初探[J].江西地质,5(1): 61-68.
楼法生,黄志忠,宋志瑞,等.2003.华南中部中新元古代造山带构造演化探讨[J].地质调查与研究,26(4):200-206.
舒良树,施央申,郭令智.1995.江南中段板块-地体构造与碰撞造山运动学[M].南京:南京大学出版社.
舒良树,卢华复,贾东,等,1999.华南武夷山早古生代构造事件的40Ar/39Ar同位素年龄研究[J].南京大学学报:数学半年刊,(6),668-674.
舒良树,于津海,贾东,等.2008.华南东段早古生代造山带研究[J].地质通报,27(10):1581-1593.
王鹏程,赵淑娟,李三忠,等,2015.长江中下游南部逆冲变形样式及其机制[J].岩石学报,31(1):230-244.
向必伟,朱光,王勇生,等.2007.糜棱岩化过程中矿物变形温度计[J].地球科学进展,22(2):126-135.
徐备,郭令智,施央申.1992.皖浙赣地区元古代地体和多期碰撞造山带[M].北京:地质出版社.
徐先兵,汤帅,李源,等.2015.江南造山带东段新元古代至早中生代多期造山作用特征[J].中国地质,42(1):33-50.
许志琴,戚学祥,杨经绥,等.2007.西昆仑康西瓦韧性走滑剪切带的两类剪切指向,形成时限及其构造意义[J].地质通报,26(10): 1252-1261.
余明刚,邢光福,张彦杰,等.2010.皖赣交界障公山地区燕山期花岗岩年代学和地球化学及成因研究[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报,28卷增刊:128.
张彦杰,廖圣兵,周孝华,等.2010a.江南造山带北缘障公山地区新元古代地层构造变形特征及其动力学机制[J].中国地质,37(4): 978-994.
张彦杰,周效华,廖圣兵,等.2010b.皖赣鄣公山地区新元古代地壳组成及造山过程[J].地质学报,84(10):1401-1427.
张彦杰,周效华,廖圣兵,等.2011.江南造山带北缘鄣源基性岩地质-地球化学特征及成因机制[J].高校地质学报,17(3):393-405.
张彦杰,廖圣兵,周效华,等.2012.江南造山带北缘鄣源构造带主要地质特征[J].地质学报,86(12):1905-1916.
赵鹏,姜耀辉,廖世勇,等.2010.赣东北鹅湖岩体SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄,Sr-Nd-Hf同位素地球化学与岩石成因[J].高校地质学报,16(2):218-225.
钟南昌.1992.江西萍乡—乐平地区推覆构造[J].中国区域地质,19(1): 1-13.
周效华,张彦杰,廖圣兵,等.2012.皖赣相邻地区双桥山群火山岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].高校地质学报,18(4): 609-622.
周效华,高天山,马雪,等.2014.江南造山带东段鄣源枕状玄武岩的年代学与构造属性研究[J].资源调查与环境,35(4):235-244.
周新民,王德滋.1988.皖南低87Sr/86Sr初始比的过铝花岗闪长岩及其成因[J].岩石学报,4(3):37-45.
Bishop R R 1996.Grain boundary migration in experimentally deformed quartz aggregates:the relationship between dynamically recrystallized grain size and steady state flow stress[M].B Sc thesis,Brown University.Charvet J,Shu L S,Shi Y S,et al.1996.The building of south China: collision of Yangzi and Cathaysia blocks,problems and tentative answers[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,13(3-5):223-235.
Chu Y and Lin W.2014.Phanerozoic polyorogenic deformation in southern Jiuling massif,northern South China block:constraints from structural analysis and geochronology[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,86(1): 117-130.
Faure M,Shu L,Wang B,et al.2009.Intracontinental subduction:a possible mechanism for the Early Palaeozoic Orogen of SE China[J].Terra Nova,21(5):360-368.
Gapais D.1989.Shear structures within deformed granites:mechanical and thermal indicators[J].Geology,17(12):1144-1147.
Lee J K,Williams I S,Ellis D J.1997.Pb,U and Th diffusion in natural zircon[J].Nature,390(6656):159-162.
Li X H,Li Z X,Ge W,et al.2003.Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China: crustal melting above a mantle plume at ca.825 Ma?[J].Precambrian Research,122(1):45-83.
Li X H,Li W X,Li Z X,et al.2008.850-790 Ma bimodal volcanic and intrusive rocks in northern Zhejiang,South China:A major episode of continental rift magmatism during the breakup of Rodinia[J].Lithos, 102:341-357.
Li Z X,Li X H,Wartho J A,et al.2010.Magmatic and metamorphic events during the early Paleozoic Wuyi-Yunkai orogeny,southeastern South China:new age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,122:772-793.
Li L M,Lin S,Xing G,et al.2013.Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks from the Shaojiwa Formation and Xingzi Group,Lushan area,SE China:Implications for Neoproterozoic back-arc basin in the Yangtze Block[J].Precambrian Research,238:1-17.
McDougall I and Harrison T M.1999.Geochronology and Thermochronology by the40Ar/39Ar Method[M].Oxford University Press.
Passchier C W and Trouw R A J.1996.Microtectonics[M].Springer verlag Berlin Heidelberg.
Post A and Tullis J.1999.A recrystallized grain size piezometer for experimentally deformed feldspar aggregates[J].Tectonophysics,303 (1):159-173.
Pryer L L.1993.Microstructures in feldspars from a major crustal thrust zone:The Grenville Front,Ontario,Canada[J].Journal of Structural Geology,15:21-36.
Shu L S,Charvet J,Shi Y S,et al.1991.Structural analysis of the Nanchang-Wanzai sinistral ductile shear zone(Jiangnan region,South China)[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,6(l):13-23.
Shu L S,Zhou G Q,Shi Y S,et al.1994.Study of the high-pressure metamorphic blueschist and its Late Proterozoic age in the Eastern Jiangnan belt[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,39:1200-1204.
Shu L S and Charvet J.1996.Kinematics and geochronology of the Proterozoic Dongxiang-Shexian ductile shear zone: with HP metamorphism and ophiolitic mélange(Jiangnan Region,South China)[J].Tectonophysics,267:291-302.
Shu L S,Jahn B M,Charvet J,et al.2014.Early Paleozoic depositional environment and intracontinental orogeny in the Cathaysia Block(South China):implications from stratigraphic,structural,geochemical and geochronologic evidence[J].American Journal of Science,314: 154-186.
Sibson R H.1999.Fault rock distribution and structure within the Alp in fault zone:A preliminary account[J].Bulletin of the Royal Society of New Zealand,18:55-66.
Stipp M,Stünitz H,Heilbronner R,et al.2002.The eastern Tonale fault zone:A natural laboratory’ for crystal p lastic deformation of quartz over a temperature range from 250 to 700℃[J].Journal of Structural Geology,24:1861-1884.
Stipp M and Tullis J.2003.The recrystallized grain size piezometer for quartz[J].Geophysical Research Letters,30(21).Doi:10.1029/ 2003GL018444.
Tullis J and Yund R A.1987.Transition from cataclastic flow to dislocation creep of feldspar:Mechanisms and microstructures[J].Geology,15: 606-609.
Tullis J and Yund R A.1991.Diffusion creep in feldspar aggregates: experimental evidence[J].JournalofStructuralGeology,13(9): 987-1000.
Twiss R J.1977.Theory and applicability of a recrystallized grain size paleopiezometer[M]//Stress in the Earth.Birkhäuser Basel.
Van D.1999.Orientationanalysis of localized shear deformation in quartz fibres at the brittle2ductile transition[J].Tectonophysics,303:83-107.
Wang J and Li Z X.2003.History of Neoproterozoic rift basins in South China:implications for Rodinia break-up[J].Precamb.Research,122: 141-158.
Wang X L,Zhao G C,Zhou J C,et al.2008.Geochronology and Hf isotopes of zircon from volcanic rocks of the Shuangqiaoshan Group,South China:Implications for the Neoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Jiangnan orogeny[J].Gondwana Research,14(3):355-367.
Wang Q,Wyman D A,Li Z X.,et al.2010.Petrology,geochronology and geochemistry of ca 780Ma A-type granites in South China:petrogenesis and implications for crustal growth during the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia[J].Precambrian Research,178(1):185-208.
Wang X L,Shu L S,Xing G F,et al.2012.Post-orogenic extension in the eastern part of the Jiangnan orogen:Evidence from ca 800-760 Ma volcanic rocks[J].Precambrian Research,222-223:404-423.
Wang Y J,Zhang A,Cawood P A,et al.2013a.Geochronological,geochemicaland Nd-Hf-Osisotopicfingerprintingofan early Neoproterozoic arc-back-arc system in South China and its accretionary assembly along the margin of Rodinia[J].Precambrian Research,231: 343-371.
Wang W,Zhou M,Yan D,et al.2013b.Detrital zircon record of Neoproterozoic active-margin sedimentation in the eastern Jiangnan Orogen,South China[J].Precambrian Research,235:1-19.
Wang Y J,Fan W,Zhang G,et al.2013c.Phanerozoic tectonics of the South China Block:key observations and controversies[J].Gondwana Research,23(4):1273-1305.
Wu R X,Zheng Y F,Wu Y B,et al.2006.Reworking of juvenile crust: element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China[J].Precambrian Research,146:179-212.
Xu X B,Zhang Y Q,Shu L S,et al.2011.La-ICPMS U-Pb and40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the sheared metamorphic rocks in the Wuyishan: constraints on the timing of Early Palaeozoic and Early Mesozoic tectonothermal events in SE China[J].Tectonophysics,501:71-86.
Xu X B,Xue D J,Li Y,et al.2014.Neoproterozoic sequences along the Dexing-Huangshan fault zone in the eastern Jiangnan orogen,South China:Geochronological and geochemical constrains[J].Gondwana Research,25(1):368-382.
Xu X B,Li Y,Tang S,et al.2015.Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic polyorogenic deformation in the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block:Constraints from structural analysis and40Ar/39Ar geochronology [J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,98:141-151.
Yao J,Shu L,Santosh M,et al.2015.Neoproterozoic arc-related andesite and orogeny-related unconformity in the eastern Jiangnan orogenic belt: Constraints on the assembly of the Yangtze and Cathaysia blocks in South China[J].Precambrian Research,262:84-100.
Yin C Q,Lin S,Davis D W,et al.2013.Tectonic evolution of the southeastern margin of the Yangtze Block:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb and LA-ICP-MS Hf isotopic studies of zircon from the eastern Jiangnan Orogenic Belt and implications for the tectonic interpretation of South China[J].Precambrian Research,236:145-156.
Yu X Q,Wang D E,Jiang D Z,et al.2011.Deformation stages and Ar-Ar age data of the Wan-Zhe-Gan tectonic zone,southeast China,and their tectonic significance[J].Acta Geological Sinica(English Edition),85(6): 1373-1389.
Zhang S B,Wu R X,Zheng Y F.2012.Neoproterozoic continental accretion in South China:Geochemical evidence from the Fuchuan ophiolite in the Jiangnan orogeny[J].Precambrian Research,220-221:45-64.
Zhang C L,Santosh M,Zou H B,et al.2013.The Fuchuan ophiolite in Jiangnan Orogen:Geochemistry,zircon U-Pb geochronology,Hf isotope and implications for the Neoproterozoic assembly of South China[J].Lithos,179:263-274.
Zhao J H,Zhou M F,Yan D P,et al.2011.Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoicstratain South China:no connection with the Grenvillian orogeny[J].Geology,39(4):299-302.
Zhao G.2014.Jiangnan Orogen in South China:Developing from divergent double subduction[J].Gondwana Research,27(3):1173-1180.
Zheng Y F,Wu R X,Wu Y B,et al.2008.Rift melting of juvenile arc-derived crust:geochemical evidence from Neoproterozoic volcanic and granitic rocksin theJiangnan Orogen,South China[J].Precambrian Research,163:351-383.
中图分类号:P542.3
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1006-7493(2016)02-0308-09
DOI:10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2015090
收稿日期:2015-05-08;修回日期:2015-06-13
基金项目:国家自然科学基金青年基金项目(41402174)
作者简介:徐先兵,男,1983年生,博士;E-mail:xbxu2011@cug.edu.cn;bingge1018@gmail.com
Two kinds of Shear Senses and Tectonic Implication of the Jingdezhen Ductile Shear Zone,Northern Jiangxi Province
XU Xianbing1,TANG Shuai1,Lin Shoufa2
1.School of Earth Sciences,China University of Geosciences,Wuhan 430074,China
2.Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences,University of Waterloo,Ontario N2L 3G1,Canada
Abstract:The Jingdezhen ductile shear zone is located at the core of the Neoproterozoic Jiangnan Orogen.Structural features and geochronology of the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone have a key implication for the Neoproterozoic to Early Paleozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Block.The Jingdezhen ductile shear zone is~180 km long in the NE-striking orientation and~7 km in maximum width.Two-phase ductile strike-slip shearing was identified based on detailed field investigation and observation of oriented thin sections.Moreover,the kinematic indicators and temperature-pressure conditions were studied in this paper.The early sinistral ductile strike-slip with thrusting occurred at 400~500℃and differential stress of 40~300 MPa,whereas the dextral ductile shearing at 300~400℃ and differential stress of 120~300 MPa.Combined with the previous work,the sinistral strike-slip with thrusting of the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone took place at late stage of the Neoproterozoic orogen in the South China Block(810~800 Ma),as a result of transformation from syn-orogeny compression to post-orogeny extension.The dextral shearing of the Jingdezhen ductile shear zone occurred in the Early Paleozoic,triggered by the Early Paleozoic intracontinental orogeny of southeast China.
Key words:kinematic indicator;temperature-pressure condition;Jingdezhen ductile shear zone;Neoproterozoic Jiangnan Orogen;South China Block

