井下节流气井的生产动态模拟新方法
安永生曹孟京兰义飞高 月
1.中国石油大学石油工程教育部重点实验室 2.中国石油长庆油田公司勘探开发研究院
井下节流气井的生产动态模拟新方法
安永生1曹孟京1兰义飞2高月1
1.中国石油大学石油工程教育部重点实验室 2.中国石油长庆油田公司勘探开发研究院
安永生等. 井下节流气井的生产动态模拟新方法. 天然气工业, 2016,36(4):55-59.
摘 要为了防止天然气水合物的生成以及井底积液的产生,鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田很多气井在井底都安装了井下节流装置,此类气井的产气量和井底流压均随着生产时间的增长而逐渐下降,没有一个绝对稳定阶段,故如何利用数值模拟的方法来实现对安装井下节流装置气井的动态模拟,是当前亟待解决的问题。为此,从油藏流动模型和井下节流气嘴流动模型出发,以井底为求解节点,通过耦合处理,提出了定气嘴尺寸生产的新理念;建立了气藏渗流、井下节流装置嘴流的计算模型,推导了新的数值模拟源汇项方程,实现了气藏渗流与井下节流装置嘴流的相互耦合。实例计算结果表明:新的数值模拟方法能够更加准确地体现安装井下节流装置气井的生产动态特征,能有效地应用于产能预测和稳产期评价,同时也为类似气井的产能计算提供了技术支撑。
关键词井下节流 天然气水合物 气嘴 生产动态 生产能力 模拟 评价 鄂尔多斯盆地 苏里格气田
鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格气田具有低渗透、低产能的特点,气井在降压生产中井筒和地面节流过程有可能形成天然气水合物(以下简称水合物)。为防止水合物的生成以及井底积液的产生,广泛采用了安装井下节流装置的方式进行生产[1-7]。实践证明此类气井的产量和井底流压均随着生产时间增长而逐渐下降,没有一个绝对稳定阶段,而在常规的数值模拟计算过程中,一般只能采用定产量或者定井底流压的方式对气井的内边界条件进行限制[8-13],这显然与实际生产动态不符。因此,如何利用数值模拟方法实现对安装井下节流装置气井的动态模拟,是当前亟待解决的问题。针对这一问题,笔者通过将油藏流动模型和井下节流气嘴流动模型相结合的方法,首次提出了“定气嘴尺寸生产”的概念,建立了新的安装井下节流装置气井的数值模拟方法,并进行了实例计算分析。
1 安装井下节流气嘴装置气井数学模型
1.1 假设条件
假设气藏为封闭外边界,天然气单相流动,整个流动过程为等温过程且遵守达西定律,井下节流装置安装在气藏中深位置,忽略偏差因子的变化。
天然气从气藏经过渗流流入气井井底,然后通过井下节流气嘴进入采气井筒[14-18],最后通过垂直管流流到地面(图1)。在渗流阶段,天然气流量主要受到生产压差的影响,井底流压越低,流量越大;在嘴流阶段,天然气流量主要受到嘴前压力影响,井底流压越低,流量越小[19-22]。因此,两种流动存在一定的耦合关系,既不是定产量生产,也不是定井底流压生产,而是一种定气嘴尺寸生产,需要对其进行耦合求解。

图1 安装井下节流装置的气井示意图
1.2 气藏流动模型
在气藏数值模拟中,气体单相流动数学模型为:
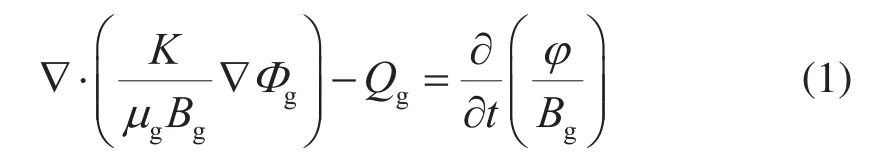
式中K表示气藏绝对渗透率,mD;μg表示气相黏度,mPa·s;Bg表示气相体积系数,m3/m3;Φg表示气相的势,MPa;Qg表示单位时间流出的体积流量,m3/s;φ表示油藏孔隙度;t表示生产时间,s。
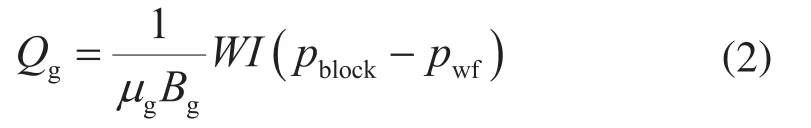
式中WI表示气井井指数;pblock表示气井所在网格的压力,MPa;pwf表示井底流压,MPa。
1.3 井下气嘴流动模型
天然气通过井下节流装置的流动近似为可压缩绝热流动,其流动状态可分为亚临界流与临界流[23-25],笔者以临界流为例介绍其流动模型。即
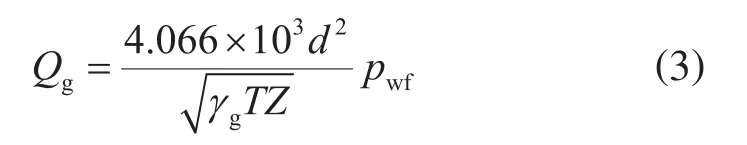
式中d表示节流气嘴直径,mm;γg表示气体相对密度;T表示气藏温度,K;Z表示天然气偏差因子,无因次。
1.4 耦合流动模型
通过联立气藏流动模型中的产量方程(2)与井下节流气嘴流动方程(3),可以得到新的耦合流动模型:

其中
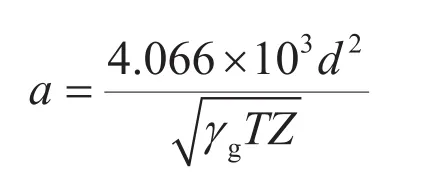
2 数值模拟技术实现
2.1 源汇项修改方法
在数值模拟技术中,对源汇项的处理方法如下:

其中
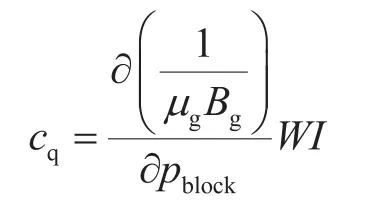
采用新的井下气嘴流动模型后,忽略偏差因子(Z)的变化,系数a在计算过程中可以认为是常数,γg、d和WI均表示常数。μg、Bg、pblock表示压力的函数,因此在数值模拟软件中对源汇项进行重新处理,即

其中
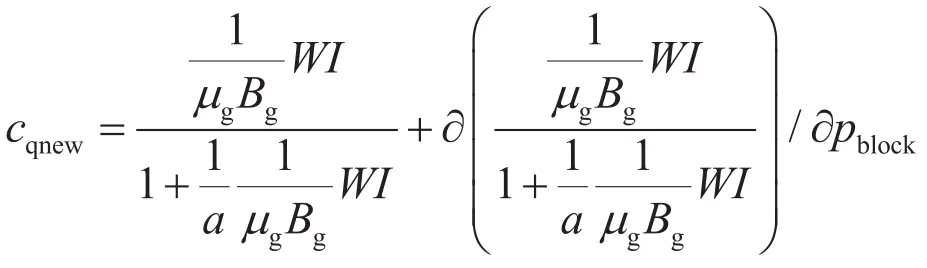
2.2 矩阵修改方法
以1口直井气井为例,位于3×3×3的油藏网格中,在气藏最中心的网格(2,2,2)进行射孔(图2)。
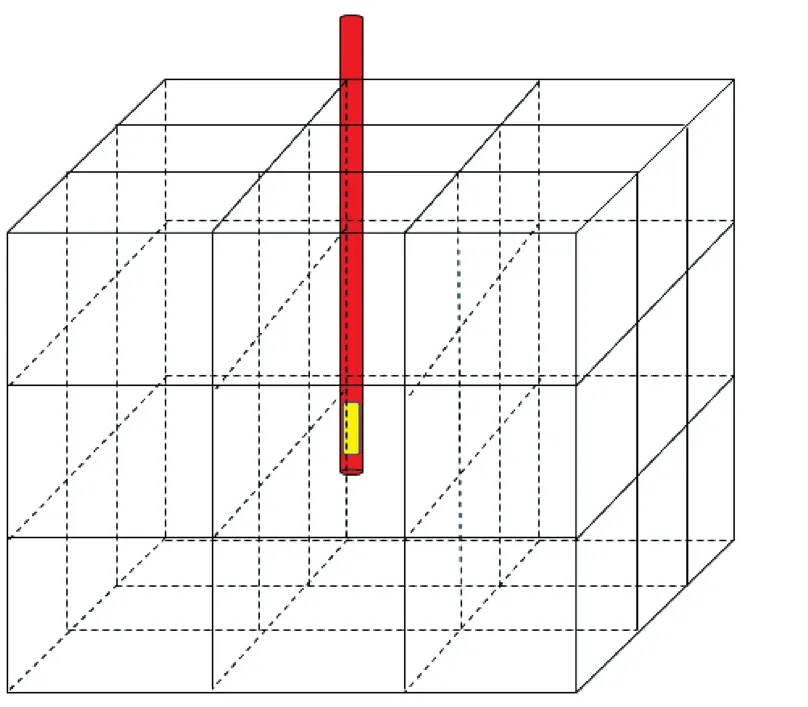
图2 安装井下节流装置气井数值模拟网格划分示意图
在数值模拟中,主矩阵为七对角矩阵(图3),只需要对射孔位置的源汇项系数进行修改,而无需对矩阵结构进行任何变化,就可以实现安装井下节流装置气井的数值模拟。

图3 安装井下节流装置气井数值模拟矩阵示意图
3 实例应用
安装井下节流装置气井数值模拟技术可应用多个领域,以气藏工程中应用较为广泛的气井稳产能力计算为例,可采用如下步骤进行:
1)输入储层物性参数和流体参数建立数值模拟模型。
2)根据历史生产数据和套压数据,计算历史井底流压。
3)生产数据历史拟合。
4)计算不同气嘴尺寸下气井的稳产能力。
5)结果输出与汇总。
以西部某气田1口气井(H1井)的稳产能力计算为例。气井的气藏压力为24.6~29.1 MPa,平均为27.8 MPa,平均压力系数为0.89,地温梯度为3.09 ℃/100 m,储层平均有效孔隙度为9.6%,平均渗透率为0.73 mD,储层平均厚度为8.1 m。
气相物性数据如表1所示。

表1 气藏物性数据表
H1井当前产气量为1.491 8×104m3/d,产水量为1.71 m3/d,套压为16.98 MPa,油压为1.27 MPa,井底流压为21.29 MPa。
采用气嘴直径分别为3 mm(气嘴实际尺寸)、3.2 mm、4.3 mm和5.2 mm 4种情况进行计算。产气量和井底流压随时间变化曲线分别如图4和图5所示。

图4 H1井产气量动态曲线图
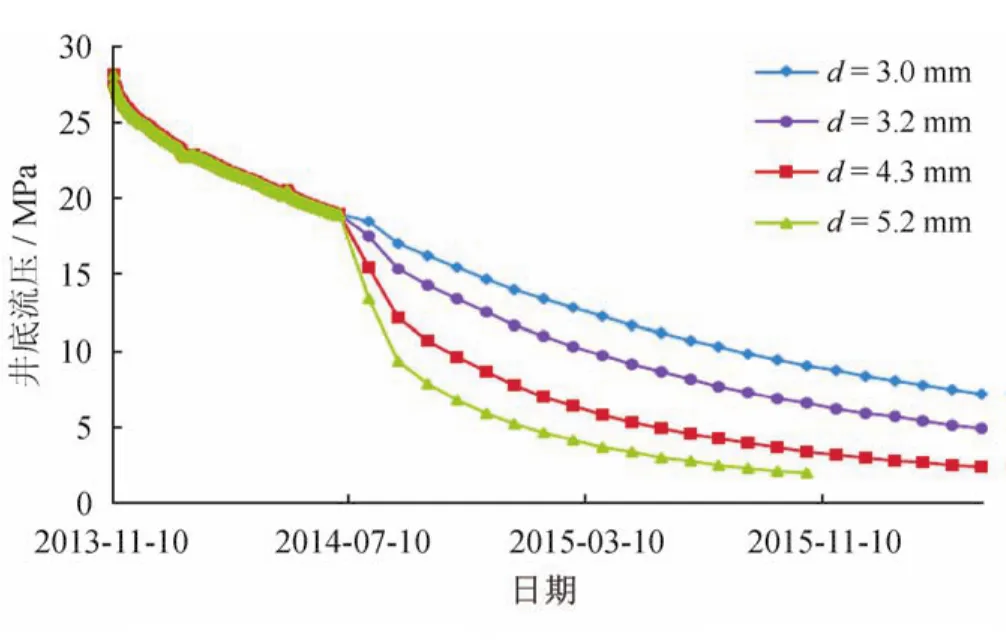
图5 H1井井底流压动态曲线图
通过与生产动态数据对比可以看出,井下节流气井的生产动态模拟新方法的计算结果更加贴近实际,在固定井下节流气嘴直径的情况下,随着生产时间的增长,产量在下降的同时,井底流压也同步在下降。
井下节流气嘴直径越大,初期产量越高,井底流压下降越快,达到废弃压力的时间也就越短。
根据动态曲线进行算术平均,所得到的稳产能力计算结果如表2所示。从表2中可以看出,利用笔者所提出的数值模拟新技术计算结果更加贴近生产实际,预测结果也更加具有可参考性。
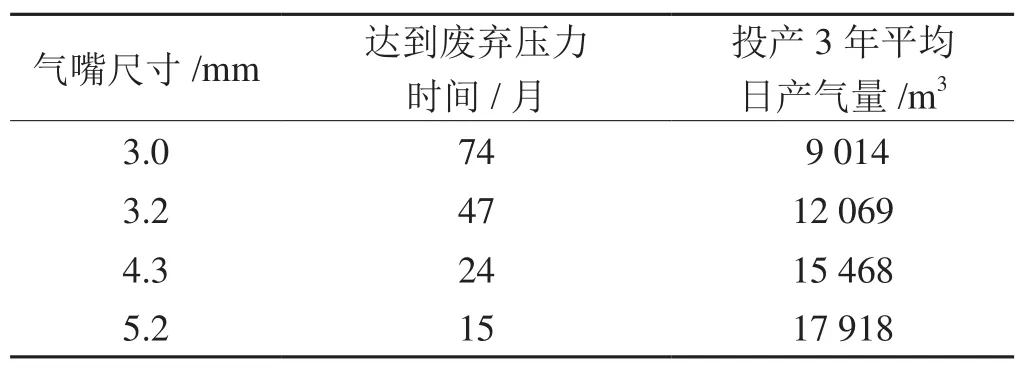
表2 H1井3年稳产能力计算结果表
4 结论
1)分析了气藏渗流、井下节流装置嘴流的特点,首次提出了安装井下节流装置气井属于“定气嘴尺寸生产”的概念。
2)建立了气藏渗流、井下节流装置嘴流的计算模型,推导了新的数值模拟源汇项方程,实现了气藏渗流与井下节流装置嘴流的相互耦合。
3)实例计算结果表明,安装井下节流装置气井数值模拟新模型,计算结果更加贴近生产实际,预测结果也更加具有可参考性。
参 考 文 献
[1] 刘鸿文, 刘德平. 井下油嘴节流机理研究及应用[J]. 天然气工业, 1990, 10(5): 57-62. Liu Hongwen, Liu Deping. Throttling mechanics of downhole choke and its application[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 1990, 10(5): 57-62.
[2] 雷群. 井下节流技术在长庆气田的应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2003, 23(1): 81-83. Lei Qun. Application of downhole choking techniques in Changqing Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2003, 23(1): 81-83.
[3] 韩丹岫, 李相方, 侯光东. 苏里格气田井下节流技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2007, 27(12): 116-118. Han Danxiu, Li Xiangfang, Hou Guangdong. Downhole choke technique applied in Sulige Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(12): 116-118.
[4] 田冷, 何顺利, 舍治成. 苏里格气田井下节流技术现场应用[J].重庆科技学院学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 10(6): 24-26. Tian Leng, He Shunli, She Zhicheng. Analysis and application of the downhole throttle technology in Sulige Gas Field[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology: Natural Sciences Edition, 2008, 10(6): 24-26.
[5] 王荧光, 裴红, 刘文伟, 郭振, 裴巧卉. 苏里格气田井下节流综合预测[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(2): 97-101. Wang Yingguang, Pei Hong, Liu Wenwei, Guo Zhen, Pei Qiaohui. An integrated forecast for downhole throttling at the Sulige Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(2): 97-101.
[6] 牟春国, 胡子见, 王惠, 韩勇. 井下节流技术在苏里格气田的应用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2010, 33(4): 61-65. Mou Chunguo, Hu Zijian, Wang Hui, Han Yong. Application of downhole choke technology to Sulige Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2010, 33(4): 61-65.
[7] 吴革生, 王效明, 韩东, 徐勇. 井下节流技术在长庆气田试验研究及应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2005, 25(4): 65-67. Wu Gesheng, Wang Xiaoming, Han Dong, Xu Yong. Experimental investigation and application of downhole throttle technology in Changqing Gas Field[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2005, 25(4): 65-67.
[8] 杨正明, 张松, 张训华, 黄延章. 气井压后稳态产能公式和压裂数值模拟研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2003, 23( 4): 74-76. Yang Zhengming, Zhang Song, Zhang Xunhua, Huang Yanzhang. The steady-state productivity formula after fracturing for gas wells and fracturing numerical simulation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2003, 25(4): 74-76.
[9] 王宇, 李颖川, 佘朝毅. 气井井下节流动态预测[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(2): 117-119. Wang Yu, Li Yingchuan, She Chaoyi. Prediction of downhole bean performance of gas well[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(2): 117-119.
[10] 蒋代君, 陈次昌, 钟孚勋, 伍超, 唐刚. 天然气井下节流临界状态的判别方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26( 9): 115-117. Jiang Daijun, Chen Cichang, Zhong Fuxun, Wu Chao, Tang Gang. Discriminance of the fow state in downhole choke of natural gas wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(9): 115-117.
[11] 马青印, 李才学, 毕建霞, 苏道敏, 蒋森堡.白庙致密砂岩凝析气藏水平井优化设计[J].西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 36(2): 85-90. Ma Qingyin, Li Caixue, Bi Jianxia, Su Daomin, Jiang Senbao. Optimization design of horizontal wells in tight sandstone reservoir in Baimiao condensate gas[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2014, 36(2): 85-90.
[12] 李志军, 戚志林, 宿亚仙, 李继强, 严文德.基于水侵预警的边水气藏动态预测模型[J].西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 36(3): 87-92. Li Zhijun, Qi Zhilin, Su Yaxian, Li Jiqiang, Yan Wende. Dynamic prediction model of edge-water gas reservoir based on water invasion early warning[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition, 2014, 36(3): 87-92.
[13] 刘占良, 石万里, 孙振, 成育红, 唐婧. 人工神经网络在气井管理及动态预测中的应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(11): 62-65. Liu Zhanliang, Shi Wanli, Sun Zhen, Cheng Yuhong, Tang Jing. Application of artifcial neural network to gas well management and performance prediction[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(11): 62-65.
[14] 蒋代君, 陈次昌, 伍超, 唐刚. 井下节流嘴对天然气井简流场的影响[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2007, 28(4): 595-597. Jiang Daijun, Chen Cichang, Wu Chao, Tang Gang. The infuence of flow field in gas wellbore by downhole-choke[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2007, 28(4): 595-597.
[15] 李莲明, 谭中国, 乔亚斌, 焦廷奎, 龙运辉. 井下节流技术在低温分离工艺中的配套应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(11): 96-98. Li Lianming, Tan Zhongguo, Qiao Yabin, Jiao Tingkui, Long Yunhui. Matching application of downhole throttling technology in low temperature separation process[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(11): 96-98.
[16] 张宗林, 郝玉鸿. 榆林气田井下节流技术研究与应用[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2009, 31(1): 108-112. Zhang Zonglin, Hao Yuhong. Research and application of downhole throttling technology in Yulin Gas Field[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2009, 31(1): 108-112.
[17] 刘永辉, 任桂蓉, 薛承文, 关志全, 胡利平. 凝析气井井筒压力计算[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(9): 64-69. Liu Yonghui, Ren Guirong, Xue Chengwen, Guan Zhiquan, Hu Liping. Calculation of the wellbore pressure of a condensate gas well[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(9): 64-69.
[18] 张培军, 程绪彬, 刘荣和, 杨继辉, 郑可. 土库曼斯坦萨曼杰佩气田气井异常积液与对策[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(4): 62-67. Zhang Peijun, Cheng Xubin, Liu Ronghe, Yang Jihui, Zheng Ke. Abnormal liquid loading in gas-producing wells of the Samandepe Gasfeld in Turkmenistan and countermeasures[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(4): 62-67.
[19] 陈磊, 郭昭学, 万颖, 蒋维, 刘云, 唐一元, 等. 油气井井下节流技术研究与应用[J]. 石油矿场机械, 2010, 39(2): 22-25. Chen Lei, Guo Zhaoxue, Wan Ying, Jiang Wei, Liu Yun, Tang Yiyuan, et al. Development and application of downhole choke technique for oil and gas well[J]. Oil Field Equipment, 2010, 39(2): 22-25.
[20] 宋中华, 张士诚, 王腾飞, 沈建新, 段玉明, 刘兰英. 塔里木油田高压气井井下节流防治水合物技术[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2014, 42(2): 91-96. Song Zhonghua, Zhang Shicheng, Wang Tengfei, Shen Jianxin, Duan Yuming, Liu Lanying. Downhole throttling technology for gas hydrate prevention in deep gas wells of Tarim Oilfeld[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2014, 42(2): 91-96.
[21] 刘永辉, 张中宝, 陈定朝, 唐治平, 胡世强. 高气液比气井井下节流携液分析[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2011, 32(5): 495-497. Liu Yonghui, Zhang Zhongbao, Chen Dingchao, Tang Zhiping, Hu Shiqiang. Analysis of liquid-carrying capacity in high GLR gas wells with downhole choke[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2011, 32(5): 495-497.
[22] 朱红钧, 林元华, 刘辉, 朱达江. 天然气井井下节流后物性参数的变化模拟[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(3): 147-151. Zhu Hongjun, Lin Yuanhua, Liu Hui, Zhu Dajiang. Simulation on physical parameter changes in gas wells after downhole choke[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(3): 147-151.
[23] 曾焱, 陈伟, 段永刚, 唐治平. 井下节流气井的生产动态预测[J]. 西南石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 31(6): 110-112. Zeng Yan, Chen Wei, Duan Yonggang, Tang Zhiping. Production performance prediction of downhole throttling gas well[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University: Science & Technology Edition , 2009, 31(6): 110-112.
[24] 曾文广, 任勇, 马清杰, 姚丽蓉, 劳胜华. 凝析气井井下节流流态变化预测研究及应用[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(12): 153-157. Zeng Wenguang, Ren Yong, Ma Qingjie, Yao Lirong, Lao Shenghua. Prediction of fow variation of downhole throttling in condensate gas wells and its application[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(12): 153-157.
[25] 叶长青, 刘建仪, 吴革生, 胡世强. 气井井下双节流油嘴设计方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2007, 27(10): 73-74. Ye Changqing, Liu Jianyi, Wu Gesheng, Hu Shiqiang. Design of downhole double-throttling choke for gas wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2007, 27(10): 73-74.
(修改回稿日期 2016-01-11 编 辑 韩晓渝)
A new production behavior simulation method for gas wells equipped with a downhole throttling device
An Yongsheng1, Cao Mengjing1, Lan Yifei2, Gao Yue1
(1. MOE Key Laboratory of Petroleum Engineering, China University of Petroleum, Beijing 102249, China; 2. Exploration and Development Research Institute of PetroChina Changqing Oilfield Company, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710018, China)
NATUR. GAS IND. VOLUME 36, ISSUE 4, pp.55-59, 4/25/2016. (ISSN 1000-0976; In Chinese)
Abstract:In the Sulige Gas Field, Ordos Basin, many gas wells are equipped with a downhole throttling device at the bottom holes to prevent the formation of gas hydrate and the accumulation of downhole liquid. And their production rate and bottomhole flowing pressure decrease gradually with the progress of production without an absolute stable stage. At present, the urgent problem lies in the dynamic simulation on gas wells equipped with a downhole throttling device by means of numerical simulation. In this paper, therefore, based on the reservoir flowing model and downhole throttling choke flowing model, a new concept of gas well production with a constant choke size was presented through coupling treatment with the bottom hole as the solution node. Then, the computation model of gas reservoir seepage and downhole throttling choke flow was built. And finally, the source-sink equation of the new numerical simulation was developed. As a result, gas reservoir seepage and downhole throttling choke flow were coupled with each other. It is shown from case computation results that this novel numerical simulation method can describe more accurately the production behavior of gas wells equipped with a downhole throttling device and can perform productivity prediction and stable production evaluation effectively. And furthermore, it provides a technical support for the productivity calculation of similar gas wells.
Keywords:Downhole throttling; Gas hydrate; Choke; Production behavior; Production capacity; Simulation; Evaluation; Ordos Basin; Sulige Gas Field
DOI:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.04.008
基金项目:北京市自然科学青年基金项目“粗糙壁微型水平井筒气液两相流动机理研究”(编号:3154039)、北京市青年英才计划项目“超短半径径向水平井井筒与油藏耦合模型研究”(编号:YETP0673)。
作者简介:安永生,1979年生,助理研究员,博士;主要从事采油采气工程理论与技术方面的教学和研究工作。地址:(102249)北京市昌平区府学路18号。电话:(010)89734339。ORCID:0000-0002-1171-4258。E-mail:an_yongsheng@126.com

