带有未知参数和通讯时延的多智能体蜂拥控制
张青, 李萍, 杨正全, 陈增强,2
(1.中国民航大学 理学院, 天津300300;2.南开大学 计算机与控制工程学院,天津300071)
带有未知参数和通讯时延的多智能体蜂拥控制
张青1, 李萍1, 杨正全1, 陈增强1,2
(1.中国民航大学 理学院, 天津300300;2.南开大学 计算机与控制工程学院,天津300071)
摘要:模拟自然界蜂拥现象的蜂拥控制是多智能体协同控制中的一个重要问题。针对带有未知参数的复杂多智能体系统研究其蜂拥控制策略,并且考虑了蜂拥过程中存在通讯时变时延的情况。采用参数自适应控制方法,给出了带有未知参数和通讯时延的多智能体系统分布式自适应控制器;依据代数图知识和Lyapunov 定理,对建立的多智能体分布式控制系统进行了稳定性分析。理论分析结果表明,在分布式自适应控制作用下,带有未知参数和通讯时延的多智能体系统能够很好地达到蜂拥状态;数值仿真结果也验证了该蜂拥控制算法的有效性。
关键词:多智能体系统; 蜂拥控制; 时变时延; 未知参数; 分布式自适应控制
网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1390.U.20160411.0845.012.html
自然界生物的群体行为引起国内外学者的广泛关注。如鸟类排成一定的队形飞翔与迁徙,鱼群的聚集,蚂蚁成群觅食等[1-3]。受到生物群体运动的启发,许多学者研究生物群体运动的内在规律与机理,将多智能体系统看作是对生物种群样本的模拟,通过学习种群个体间的信息交流机制、组织与决策能力,并引入群体个体间的协调合作思想,为多智能体系统的蜂拥问题提出了系统的理论、模型设计方法和控制算法,并将蜂拥思想应用于智能控制领域[4-5]。1987年,Reynolds 提出了一个在三维空间上用计算机来模拟群体行为的模型,这个模型要求一群智能体的群体行为满足3条基本规则:分离、聚合和速度匹配[6]。Tanner等在此基础上提出了一种简单的编队控制律并分析了系统的稳定性[7]。Saber 等将动态理论引入障碍物环境下的分布式编队系统[8]。与此同时,许多学者对蜂拥问题也进行了进一步研究,其中包括不同拓扑结构下的蜂拥运动策略、基于一致性协议的运动方案设计与调整、虚拟领导者在蜂拥运动中的作用及稳定性影响,以及基于人工势场法的多种蜂拥运动算法等[9-11]。由于在实际问题中移动多智能体之间的信息交流存在通讯时延, 并且往往时延是时变的,因此讨论带有时变时延的智能体蜂拥控制算法更具有实际意义[12]。在实际系统运行过程中存在内部结构和参数的变化等不确定性因素,不确定性的存在可能会严重影响控制系统性能。因此,需要开展对参数不确定多智能体系统控制方法的研究。为此,需要设计一种控制器,它能够自动地补偿在模型阶次和参数方面非预知的变化,即实现系统自适应控制[13-16]。
本文的主要工作是:1)目前研究的多智能体系统,每个智能体个体动力学多为线性系统,本文研究中的智能体是二阶非线性动力学系统,并且包含有未确定的参数,同时考虑多智能体之间的信息交互时延是时变函数,因此整个系统更为复杂,对其进行控制设计和分析具有更大难度,但是获得的方法具有更强的适用性。2)针对上述带有未知参数和时变时延的非线性多智能体系统,设计了分布式自适应控制器,辨识未知的不确定参数,实现多智能体系统的蜂拥控制,并从理论上严格证明了控制系统的收敛性和稳定性。
1问题描述
假设N(N≥2) 个智能体在n维欧几里得空间移动,其动态方程表示如下:
(1)
(2)

(3)
定义误差向量
(4)
由ei的定义,可以得到下面的等式:
(5)
(6)

(7)
定义1多智能体的蜂拥[10]:当N个智能体速度达到一致,位置保持相同的距离,并且在运动过程中避免碰撞,称这N个智能体达到了蜂拥。


图1 动态图的切换过程Fig.1 The Switch process for Dynamic Graph

定义3连通图[10]:若图G(t)中任意顶点i和顶点j之间都有至少一条路径存在,则称图G(t)是连通图。否则为非连通图。
定义4基于动态图的多智能体的蜂拥[10]:N(N≥2) 个智能体所构成的系统由定义2的动态图G(t)描述,G(t)的N个顶点就表示N个智能体。如果智能体i与智能体j之间在t时刻有信息的交流就表示图G(t)中顶点i和顶点j之间在t时刻有连边。CN是具有N个顶点的连通图的集合,如果G(t0)∈CN,设计控制器ui(t) ,使得对所有的t≥t0都有G(t)∈CN成立,并且能达到所有的智能体最终速度保持一致,位置保持相同的距离,并且在运动过程中避免碰撞,称这N个智能体达到了蜂拥。
2分布式自适应控制器设计
对于任意动态图G(t)=(V,E(t)),定义控制输入:
(8)

(9)
其中,xij=xi-xj,当‖xij‖→R-时,Vij趋于无穷,当‖xij‖→0时,Vij趋于无穷。
根据Vij的定义,可以得到下面的等式
(10)
式中:i,j=1,2,…,N。
(11)
由等式(1)、(2)和(11)可以得到误差的微分方程
(12)

3主要结果


证明:构造Lyapunov函数
(13)

(14)
由等式(4)和(10), 可以得到
由等式(8)、(12)和不等式(3),可以化简等式(14)的前两部分
(15)
因此可以得到:
其中,
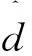
推论1在设计的控制输入(8) 的作用下,系统(1)、(2)时间切换的次数是有限的。
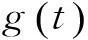
(16)
则‖xi-xj‖=mij(mij为常数,且与时间t无关,所以多智能体之间趋于稳定的距离,且由定理1可知mij为非零常数,所以智能体之间无碰撞。
4数值仿真
本节采用数值仿真来验证所设计的控制方法的有效性。利用R3空间中的20个智能体和Chen混沌系统来进行仿真。Chen系统可以表示如下:


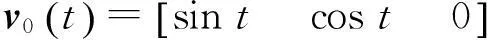

图2 20 个智能体最初的状态Fig.2 The initial states for the 20 agents

图3 20 个智能体最终达到的蜂拥状态Fig.3 The final flocking states for the 20 agents
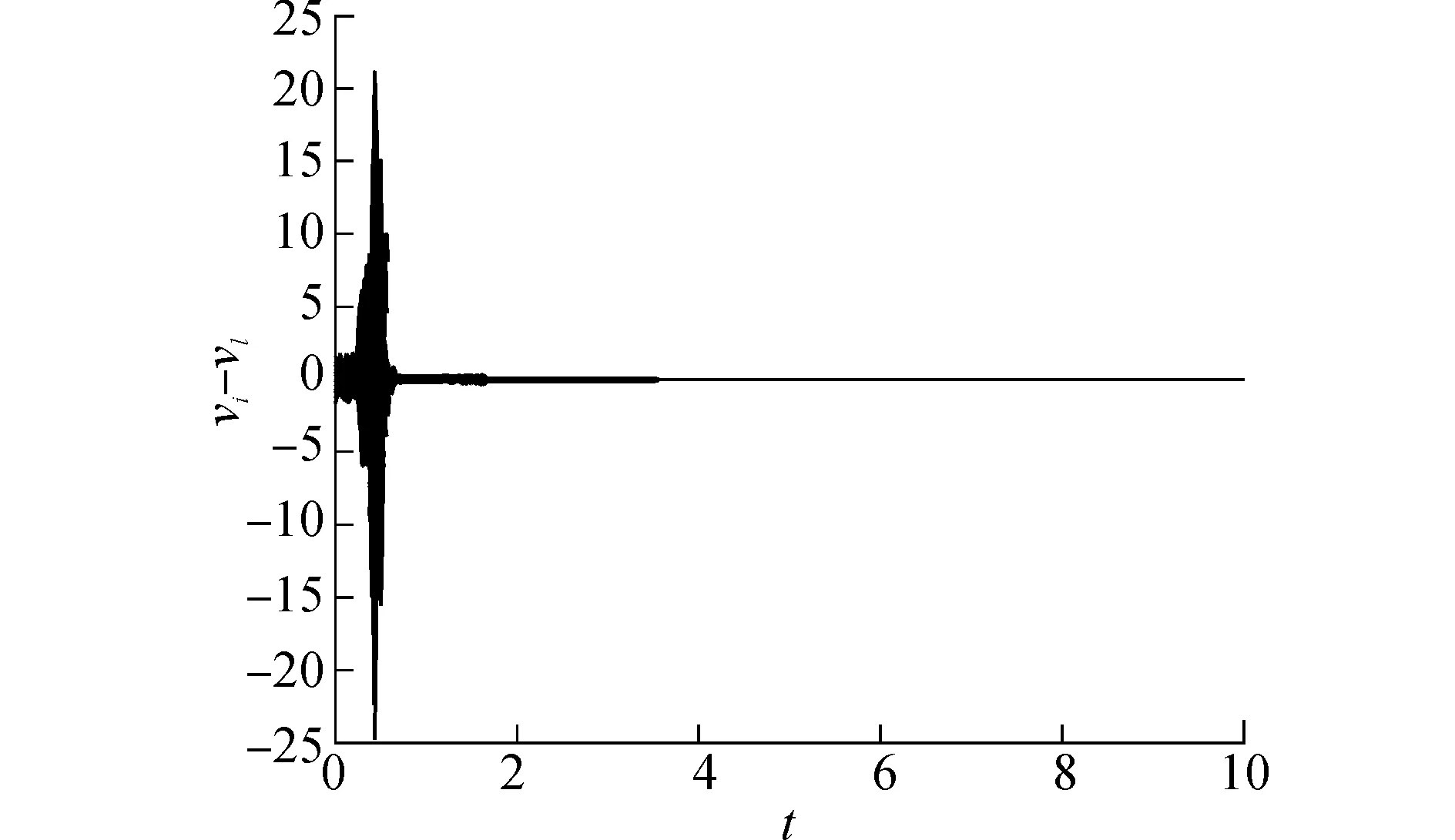
图4 20个智能体速度变化曲线Fig.4 The speed varying curves for the 20 agents

图5 未知参数估计值的变化曲线Fig.5 The varying curves for the estimated parameter
5结论
本文研究带有未知参数和通讯时延的非线性多智能体系统蜂拥控制问题,设计了分布式自适应控制器,包括分布式控制律和分布式参数估计算法两部分。
基于Lyapunov稳定性定理和拉萨尔不变集原理分析了所建立的多智能体自适应蜂拥控制的性能,证明了在分布式自适应控制作用下,带有未知参数和通讯时延的多智能体系统能够很好地达到蜂拥状态,即所有的智能体的速度趋于一致,相互位置趋于固定的距离,并且在运动过程中避免发生碰撞。
数值仿真结果也验证了理论分析结果,表明该自适应控制算法通过参数辨识和分布式反馈控制,使多智能体系统能够最终达到稳定的蜂拥状态。
今后进一步研究方向包括带有非线性内部耦合函数的多智能体系统自适应蜂拥问题、以及异质多智能体自适应蜂拥控制问题等。
参考文献:
[1]PARRISH J K, EDELSTEIN-KESHET L. Complexity, pat-
tern, and evolutionary trade-offs in animal aggregation[J]. Science, 1999, 284(5411): 99-101.
[2]PARTRIDGE B L. Internal dynamics and the interrelations of fish in schools[J]. Journal of comparative physiology, 1981, 144(3): 313-325.
[3]DO K D. Flocking for multiple elliptical agents with limited communication ranges[J]. IEEE transactions on robotics, 2011, 27(5): 931-942.
[5]JADBABAIE A, LIN Jie, MORSE A S. Coordination of groups of mobile autonomous agents using nearest neighbor rules[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2003, 48(6): 988-1001.
[6]REYNOLDS C W. Flocks, herds and schools: a distributed behavioral model[J]. ACM SIGGRAPH computer graphics, 1987, 21(4): 25-34.
[7]TANNER H G, JADBABAIE A, PAPPAS G J. Flocking in fixed and switching networks[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2007, 52(5): 863-868.
[8]OLFATI-SABER R. Flocking for multi-agent dynamic systems: algorithms and theory[J]. IEEE transactions on automatic control, 2006, 51(3): 401-420.
[9]TANNER H G, JADBABAIE A G, PAPPAS J. Stable flocking of mobile agents, part I: fixed topology[C]//Proceedings of the 42nd IEEE conference on Decision and Control. Maui, Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2003, 2: 2010-2015.
[10]ZAVLANOS M M, JADBABAIE A, PAPPAS G J. Flocking while preserving network connectivity[C]//Proceedings of the 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. New Orleans, LA: IEEE, 2007: 2919-2924.
[11]FERRARA A, VECCHIO C. Collision avoidance strategies and coordinated control of passenger vehicles[J]. Nonlinear dynamics, 2007, 49(4): 475-492.
[12]YANG Zhenquan, ZHANG Qing, JIANG Zuolian, et al. Flocking of multi-agents with time delay[J]. International journal of systems science, 2012, 43(11): 2125-2134.
[13]ZHANG Qing, LI Ping, YANG Zhengquan, et al. Adaptive flocking of multi-agents with nonlinear inner-coupling function[J]. ICIC express letters, part b: applications, 2014, 5(5): 1445-1452.
[14]SU Housheng, ZHANG Ningzi, CHEN M Z Q, et al. Adaptive flocking with a virtual leader of multiple agents governed by locally Lipschitz nonlinearity[J]. Nonlinear analysis: real world applications, 2013, 14(1): 798-806.
[15]HU Jiangping, ZHENG Weixing. Adaptive tracking control of leader-follower systems with unknown dynamics and partial measurements[J]. Automatica, 2014, 50(5): 1416-1423.
[16]WANG Li, SUN Shiwen, XIA Chengyi. Finite-time stability of multi-agent system in disturbed environment[J]. Nonlinear dynamics, 2012, 67(3): 2009-2016.
本文引用格式:
张青, 李萍, 杨正全,等. 带有未知参数和通讯时延的多智能体蜂拥控制[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2016, 37(5): 696-700.
ZHANG Qing,LI Ping,YANG Zhengquan, et al. Flocking control of a multi-agent system with unknown parameters and communication delays[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2016, 37(5): 696-700.
Flocking control of a multi-agent system with unknown parameters and communication delays
ZHANG Qing1,LI Ping1,YANG Zhengquan1,CHEN Zengqiang1,2
(1. College of Science, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300,China; 2. College of Computer and Control Engineering, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071,China)
Abstract:Flocking control, which simulates the flocking phenomenon in the natural world, is an important research topic in the multi-agent system coordinate control. Flocking control strategies were studied that investigated the complex multi-agent systems including unknown parameters and communication delays during the flocking process. By utilizing parameter estimation in an adaptive control method, a distributed adaptive controller was proposed for the multi-agent system with unknown parameters and communication delays. Based on algebraic graph knowledge and the Lyapunov theorem, the stability analysis was given for the multi-agent distributed control system. The theoretical analysis results show that the flocking states were obtained for the multi-agent system with unknown parameters and communication delays. Finally, the numerical simulation results also verified the effectiveness of the proposed flocking control scheme.
Keywords:multi-agent system; flocking control; time-varying delay; unknown parameter; distributed adaptive control
收稿日期:2015-02-27.
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(61573199 );天津市自然科学基金资助项目(14JCYBJC18700);中央高校基本业务费基金资助项目(3122015C025).
作者简介:张青(1965-), 女, 教授. 通信作者:张青,E-mail:qz120168@hotmail.com.
DOI:10.11990/jheu.201502024
中图分类号:TP 272
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1006-7043(2016)05-0696-05
网络出版时间:2016-04-11.

