Roux-en-Y胃旁路术对血管内皮细胞P-选择素表达的影响
柴 芳,齐凤杰,赵树鹏,王 月,王 俊,李 强
·论著·
Roux-en-Y胃旁路术对血管内皮细胞P-选择素表达的影响
柴 芳,齐凤杰,赵树鹏,王 月,王 俊,李 强
121001 辽宁省锦州市,辽宁医学院附属第一医院普外科(柴芳,赵树鹏,王俊,李强),病理科(齐凤杰,王月)
【摘要】目的通过建立2型糖尿病(T2DM)大鼠模型,观察Roux-en-Y胃旁路术(RYGB)对血管内皮细胞P-选择素表达的影响,探讨其对血管内皮细胞的保护机制。方法2014年10月—2015年4月,采用随机数字表法将60只SD大鼠分为正常对照组(NC组)、T2DM组和RYGB组,各20只。T2DM组和RYGB组予以高脂饮食3周,腹腔注入链脲佐菌素(STZ)30 mg/kg建立T2DM模型;NC组喂养普通饲料,腹腔注入相同浓度的柠檬酸盐缓冲液。RYGB组行RYGB,NC组及T2DM组行假手术。记录大鼠一般情况,包括术前、术后21 d体质量。采用ELISA法检测术前、术后21 d肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、脂联素水平,HE染色法测定术后21 d血管内膜厚度,免疫组化SABC法检测术后21 d P-选择素表达情况。结果术后RYGB组2只大鼠因吻合口梗阻死亡。T2DM组、RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于NC组(P<0.05);RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于T2DM组(P<0.05)。NC组大鼠术后体质量高于术前(P<0.05);RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于术前(P<0.05)。T2DM组术前、术后TNF-α水平均高于NC组,术前、术后脂联素水平均低于NC组(P<0.05);RYGB组术前TNF-α水平高于NC组,术前脂联素水平低于NC组(P<0.05);RYGB组术后TNF-α水平低于T2DM组,术后脂联素水平高于T2DM组(P<0.05)。RYGB组术后TNF-α水平低于术前,术后脂联素水平高于术前(P<0.05)。3组大鼠血管内膜厚度比较,差异无统计学意义(F=1.337,P=0.271)。NC组、RYGB组P-选择素表达阳性率低于T2DM组(P<0.05)。结论RYGB可能通过脂联素/TNF-α通路减少P-选择素表达,进而减轻血管内皮细胞损伤程度。
【关键词】糖尿病,2型;胃旁路术;P选择素;脂联素
柴芳,齐凤杰,赵树鹏,等.Roux-en-Y胃旁路术对血管内皮细胞P-选择素表达的影响[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(15):1792-1795.[www.chinagp.net]
Chai F,Qi FJ,Zhao SP,et al.Effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on the expression of P-selectin in vascular endothelial cells[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(15):1792-1795.
微血管病变是2型糖尿病(T2DM)的重要病理改变。研究表明,Roux-en-Y胃旁路术(RYGB)在有效降低血糖的同时,可以减少心脑血管事件的发生,明显改善血管功能[1]。血管内皮细胞P-选择素是炎性反应中白细胞黏附、锚定的关键步骤,与糖尿病微血管病变密切相关[2]。本研究通过建立T2DM大鼠模型,观察RYGB对血管内皮细胞P-选择素表达的影响,探讨其对血管内皮细胞的保护机制。
1材料与方法
1.1动物来源60只SPF级雄性SD大鼠由辽宁医学院动物实验中心提供,7~8周龄,体质量210~243 g,饲养环境温度(22±2)℃,相对湿度45%。
1.2主要材料链脲佐菌素(STZ,美国Sigma公司);大鼠脂联素试剂盒(Phoenix,美国);肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)试剂盒、兔抗鼠P-选择素一抗、羊抗兔二抗、即用型SABC免疫组化染色试剂盒(武汉博士德生物工程有限公司)。
1.3研究方法
1.3.1造模及分组2014年10月—2015年4月,采用随机数字表法将60只SD大鼠分为正常对照组(NC组)、T2DM组和RYGB组,各20只。NC组喂养普通饲料3周;T2DM组和RYGB组予以高脂饮食(22.19 kJ/g,蛋白质占35%,碳水化合物占5%,脂类占60%)3周。第13天时清晨空腹12 h后,T2DM组和RYGB组腹腔注入STZ 30 mg/kg(0.1 mol/L柠檬酸盐缓冲液配制),NC组腹腔注入相同浓度的柠檬酸盐缓冲液。72 h后测定空腹血糖(≥7.8 mmol/L)或餐后随机血糖(≥11.1 mmol/L),提示造模成功。
1.3.2手术方法禁食12 h但不禁水,腹腔注入10%水合氯醛(3 ml/100 g)麻醉。RYGB组行RYGB,经上腹正中切口入腹,经胃大小弯间切断胃体,贲门附近保留20%胃体,距Treizs韧带10 cm离断空肠,远端空肠与残胃吻合,距吻合口10 cm行空肠端侧吻合,缝合切口,术毕。NC组及T2DM组行假手术,胃前壁切开7 mm后原位缝合。
1.4指标检测
1.4.1一般情况记录大鼠一般情况,包括周龄、术前及术后21 d体质量。
1.4.2ELISA法检测TNF-α、脂联素水平术前及术后21 d时经鼠尾静脉采血,1 500 r/min离心10 min(离心半径15 cm),收集血清,按TNF-α试剂盒、大鼠脂联素试剂盒说明书操作,测定OD值,计算TNF-α、脂联素水平。
1.4.3HE染色法测定血管内膜厚度术后21 d时经腹腔注射10%水合氯醛麻醉,取部分胸主动脉经4%多聚甲醛固定,常规经脱水、二甲苯透明、包埋,制作石蜡切片,切片厚度为4 μm,常规HE染色,采用HPLAS-1000型图像分析系统测定血管内膜厚度。
1.4.4免疫组化SABC法检测P-选择素表达情况术后21 d时取部分胸主动脉经4%多聚甲醛固定,常规制作石蜡切片,采用免疫组化SABC法检测P-选择素表达情况。兔抗鼠P-选择素一抗为1∶200稀释,羊抗兔二抗为1∶100稀释,按即用型SABC免疫组化染色试剂盒说明书操作,DAB显色,苏木素复染,脱水,透明,封片。所有切片经3名病理医师采用双盲法进行阅片,细胞呈棕黄色为阳性表达,随机读取5个高倍视野(×400)计数阳性细胞率,结果采用半定量法分析。阳性细胞率≤25%为0分,26%~50%为1分,51%~75%为2分,>75%为3分;染色强度定义为:无显色为0分,浅棕黄色为1分,棕黄色为2分,棕褐色为3分。将上述两项得分相加,0分判为“-”,1~2分判为“+”,3~4分判为“++”,5~6分判为“+++”。“-”和“+”定义为阴性表达,“++”和“+++”定义为阳性表达。

2结果
2.1一般情况术后RYGB组2只大鼠因吻合口梗阻死亡。3组大鼠周龄、术前体质量比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);3组大鼠术后体质量比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。T2DM组、RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于NC组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于T2DM组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。NC组大鼠术后体质量高于术前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);T2DM组大鼠术前、术后体质量比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于术前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表1)。
2.2TNF-α、脂联素水平比较3组大鼠术前、术后TNF-α、脂联素水平比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。T2DM组术前、术后TNF-α水平均高于NC组,术前、术后脂联素水平均低于NC组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);RYGB组术前TNF-α水平高于NC组,术前脂联素水平低于NC组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);RYGB组术后TNF-α水平低于T2DM组,术后脂联素水平高于T2DM组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。RYGB组术后TNF-α水平低于术前,术后脂联素水平高于术前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表2)。
2.3血管内膜厚度比较NC组血管内膜厚度为(10.0±1.8)μm,T2DM组血管内膜厚度为(11.6±2.5)μm,RYGB组血管内膜厚度为(10.8±2.0)μm。3组大鼠血管内膜厚度比较,差异无统计学意义(F=1.337,P=0.271)。
2.4P-选择素表达情况比较NC组P-选择素表达阳性4只(20.0%),T2DM组P-选择素表达阳性15只(75.0%),RYGB组P-选择素表达阳性3只(16.7%)。3组大鼠P-选择素表达阳性率比较,差异有统计学意义(χ2=18.027,P<0.001);NC组、RYGB组P-选择素表达阳性率低于T2DM组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01,见图1,本文图1彩图见本刊官网www.chinagp.net电子期刊相应文章附件)。
3讨论
P-选择素是黏附分子家族中的重要成员之一,其表达水平与肥胖、高血压、高脂血症、糖化血红蛋白水平呈正相关[3]。P-选择素储存于内皮细胞的怀布尔-帕拉德小体(Weibel-Palade小体),活化时表达于细胞膜,与白细胞表面的P-选择素1配体结合,使白细胞黏附,促进动脉硬化的形成,并可通过促进血小板聚集及血栓形成引起血管内皮细胞损伤[4-5]。研究表明,P-选择素水平与外周动脉硬化性病变的病程进展程度呈正相关[6]。P-选择素/基质金属蛋白酶1(MMP1)可通过抑制一氧化氮合酶从小窝蛋白解离而损伤血管内皮细胞[7]。而手术减重可以持久有效地缓解T2DM患者的高血糖,并可减少心脑血管事件的发生,对动脉硬化有缓解作用[1,8-9]。本研究结果显示,NC组、RYGB组P-选择素表达阳性率低于T2DM组,提示P-选择素在T2DM血管慢性损伤中发挥重要作用,RYGB可能通过降低P-选择素水平来减轻血管内皮细胞损伤程度。
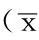
表1 3组大鼠一般资料比较±s)
注:NC=正常对照,T2DM=2型糖尿病,RYGB=Roux-en-Y胃旁路术;与NC组比较,aP<0.05;与T2DM组比较,bP<0.05;与术前比较,cP<0.05
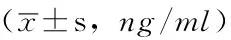
Table2ComparisonofthelevelsofTNF-αandadiponectinconcentrationamongthethreegroups

组别只数TNF-α术前 术后脂联素术前 术后NC组201.3±0.31.3±0.55.6±1.35.6±1.4T2DM组204.0±0.7a4.1±0.7a1.2±0.9a1.5±0.7aRYGB组184.2±1.0a1.7±0.4bc1.4±0.8a5.2±0.9bcF值82.870147.75457.87743.206P值<0.001<0.001<0.001<0.001
注:TNF-α=肿瘤坏死因子α;与NC组比较,aP<0.05;与T2DM组比较,bP<0.05;与术前比较,cP<0.05
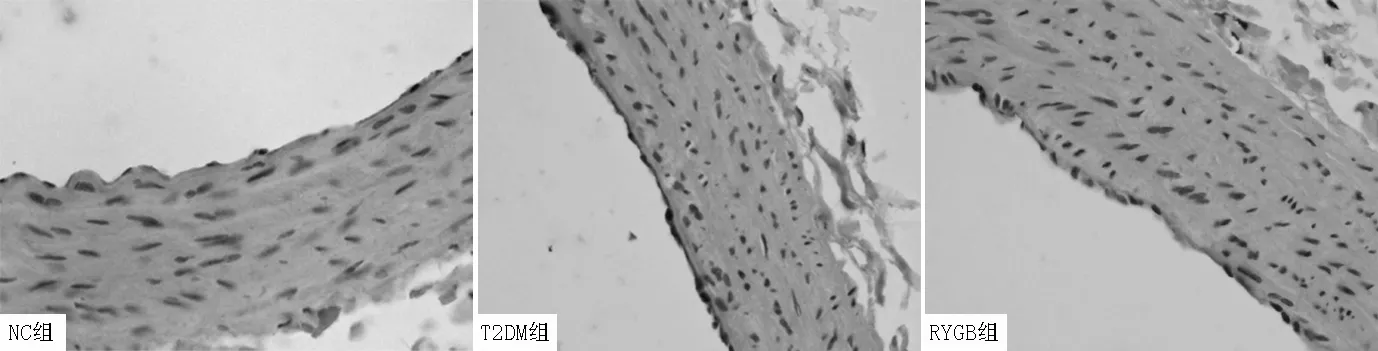
注:NC=正常对照,T2DM=2型糖尿病,RYGB=Roux-en-Y胃旁路术
图1免疫组化SABC法检测P-选择素表达情况(×400)
Figure 1Expression of P-selectin detected by immunohistochemical SABC method
本研究结果显示,RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于NC组、T2DM组,RYGB组大鼠术后体质量低于术前,考虑可能与大鼠RYGB后进食量减少及体内激素变化有关。T2DM组大鼠术后体质量与术前无差异,但低于NC组、高于RYGB组,考虑可能与自身患有T2DM影响生长有关。NC组大鼠术后体质量高于术前,考虑与正常生长发育有关。
脂联素由脂肪细胞分泌,具有减轻胰岛素抵抗、减少心脑血管疾病等多种生物学作用,脂联素水平降低对高脂血症诱导的血管损伤的保护作用减弱[10]。临床研究显示,RYGB后心脑血管事件发生减少与脂联素/TNF-α通路相关[11]。脂联素可以减少T2DM小鼠主动脉TNF-α表达水平[12]。研究表明,TNF-α具有增加血管内皮细胞P-选择素表达的作用[13]。本研究结果显示,T2DM组术前、术后TNF-α水平均高于NC组,术前、术后脂联素水平均低于NC组;RYGB组术前TNF-α水平高于NC组,术前脂联素水平低于NC组;RYGB组术后TNF-α水平低于T2DM组,术后脂联素水平高于T2DM组;RYGB组术后TNF-α水平低于术前,术后脂联素水平高于术前。考虑脂联素水平降低及TNF-α水平升高与T2DM血管病变密切相关,提示RYGB作为一种手术减重的方法能够上调脂联素水平,并可能通过降低TNF-α水平来减少P-选择素表达,进而影响糖尿病血管病变的早期事件。这一机制考虑与RYGB治疗后体质量减轻、体内能量平衡改变、脂肪组织释放的生物活性因子改变有关。本研究结果显示,3组大鼠血管内膜厚度无差异,与既往研究不一致[14],考虑可能与本实验造模时间短、动物血管病理损伤相对轻有关。
总之,RYGB可能通过脂联素/TNF-α通路减少P-选择素表达,进而减轻血管内皮细胞损伤程度,TNF-α、脂联素、P-选择素等分子为T2DM血管病变的治疗提供了新靶点,但其具体分子机制有待进一步证实。
作者贡献:柴芳进行实验设计与实施、资料收集整理、撰写论文、成文并对文章负责;齐凤杰、王月、王俊、李强进行实验实施、评估、资料收集;赵树鹏进行质量控制及审校。
本文无利益冲突。
参考文献
[1]Boido A,Ceriani V,Cetta F,et al.Bariatric surgery and prevention of cardiovascular events and mortality in morbid obesity:mechanisms of action and choice of surgery[J].Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis,2015,25(5):437-443.
[2]Penman A,Hoadley S,Wilson JG,et al.P-selectin plasma levels and genetic variant associated with diabetic retinopathy in African Americans[J].Am J Ophthalmol,2015,159(6):1152-1160.e2.
[3]Bielinski SJ,Berardi C,Decker PA,et al.P-selectin and subclinical and clinical atherosclerosis:the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis(MESA)[J].Atherosclerosis,2015,240(1):3-9.
[4]Abou-Saleh H,Hachem A,Yacoub D,et al.Endothelial progenitor cells inhibit platelet function in a P-selectin-dependent manner[J].J Transl Med,2015,13:142.
[5]Xu T,Liu W,Yang C,et al.Lipid raft-associated β-adducin is required for PSGL-1-mediated neutrophil rolling on P-selectin[J].J Leukoc Biol,2015,97(2):297-306.
[6]Wassel CL,Berardi C,Pankow JS,et al.Soluble P-selectin predicts lower extremity peripheral artery disease incidence and change in the ankle brachial index:the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis(MESA)[J].Atherosclerosis,2015,239(2):405-411.
[7]Carrizzo A,Lenzi P,Procaccini C,et al.Pentraxin 3 induces vascular endothelial dysfunction through a P-selectin/matrix metalloproteinase-1 pathway[J].Circulation,2015,131(17):1495-505;discussion 1505.
[8]Yang J,Wang C,Cao G,et al.Long-term effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy versus roux-en-Y gastric bypass for the treatment of Chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with body mass index 28-35 kg/m(2)[J].BMC Surg,2015,15:88.
[9]Valenta I,Dilsizian V,Quercioli A,et al.Impact of obesity and bariatric surgery on metabolism and coronary circulatory function[J].Curr Cardiol Rep,2014,16(1):433.
[10]Li R,Xu M,Wang X,et al.Reduced vascular responsiveness to adiponectin in hyperlipidemic rats—mechanisms and significance[J].J Mol Cell Cardiol,2010,49(3):508-515.
[11]Appachi S,Kelly KR,Schauer PR,et al.Reduced cardiovascular risk following bariatric surgeries is related to a partial recovery from "adiposopathy"[J].Obes Surg,2011,21(12):1928-1236.
[12]Lee S,Zhang H,Chen J,et al.Adiponectin abates diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction by suppressing oxidative stress,adhesion molecules,and inflammation in type 2 diabetic mice[J].Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol,2012,303(1):H106-115.
[13]Weller A,Isenmann S,Vestweber D.Cloning of the mouse endothelial selectins.Expression of both E- and P-selectin is inducible by tumor necrosis factor alpha[J].J Biol Chem,1992,267(21):15176-15183.
[14]Lundby-Christensen L,Tarnow L,Hansen DL,et al.Carotid intima-media thickness is reduced 12 months after gastric bypass surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance[J].J Diabetes Complications,2014,28(4):517-522.
(本文编辑:崔丽红)
Effect of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on the Expression of P-selectin in Vascular Endothelial Cells
CHAIFang,QIFeng-jie,ZHAOShu-peng,etal.
DepartmentofGeneralSurgery,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofLiaoningMedicalUniversity,Jinzhou121001,China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo observe the influence of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass(RYGB) on the expression of P-selectin by establishing T2DM rat models and to investigate its protection mechanism for vascular endothelial cells.MethodsFrom October 2014 to April 2015,we divided sixty SD rats into three groups:normal control group(NC group),T2DM group and RYGB group,with 20 rats in each group.T2DM group and RYGB group were administrated with high fat diet for three weeks and were given 30 mg/kg streptozotocin(STZ) by intraperitoneal injection to build T2DM models,and NC group was fed with normal fodder and was given citric acid buffer solution of the same concentration.RYGB was undertaken in RYGB group,and sham operation was undertaken in NC group and T2DM group.The general data of the rats were recorded,including body weight before surgery and 21 days after surgery.The levels of TNF-α and adiponectin concentration were detected by ELISA before surgery and 21 days after surgery;vessel intima thickness was determined by HE staining method 21 days after surgery,and the expression of P-selectin was detected by immunohistochemistry SABC method 21 days after surgery.ResultsTwo rats in RYGB group died from anastomotic obstruction after surgery.T2DM group and RYGB group were lower than NC group in postoperative body weight(P<0.05);RYGB group was lower than T2DM group in body weight after surgery(P<0.05).NC group had higher body weight after surgery than that before surgery(P<0.05);RYGB group had lower body weight after surgery than that before surgery(P<0.05).T2DM group was higher in TNF-α level and lower in adiponectin concentration than NC group before and after surgery(P<0.05).RYGB group was higher in TNF-α level and lower in adiponectin concentration than NC group before surgery(P<0.05);RYGB group was lower in TNF-α level and higher in adiponectin concentration than T2DM group after surgery(P<0.05).RYGB group had lower TNF-α level and higher adiponectin concentration after surgery than those before surgery(P<0.05).The three groups were not significantly different in vessel intima thickness(F=1.337,P=0.271).NC group and RYGB group were lower than T2DM group in the positive rate of P-selectin expression(P<0.05).ConclusionRYGB possibly reduces P-selectin expression by adiponectin/TNF-α signaling pathways,and then reduces the damage of vascular endothelial cells.
【Key words】Diabetes mellitus,type 2;Gastric bypass;P-selectin;Adiponectin
基金项目:辽宁省自然科学基金资助项目(2013022044);辽宁医学院博士科研启动基金项目(Y2012B017);辽宁医学院附属第一医院科技启动基金项目(Fyk201211)
通信作者:赵树鹏,121001 辽宁省锦州市,辽宁医学院附属第一医院普外科;E-mail:lyfsdyyy@163.com
【中图分类号】R 587.1
【文献标识码】A
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.15.011
(收稿日期:2015-09-23;修回日期:2016-03-07)

