难治性炎症性肠病患者英夫利西血药浓度的检测及疗效评价
范如英,盛剑秋,王晓伟,杨欣艳,王继恒,李恕军,李世荣
北京军区总医院消化内科,北京 100700
难治性炎症性肠病患者英夫利西血药浓度的检测及疗效评价
范如英,盛剑秋,王晓伟,杨欣艳,王继恒,李恕军,李世荣
北京军区总医院消化内科,北京 100700
目的 探讨炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)患者英夫利西(infliximab,IFX)血药浓度与疗效的关系,了解抗IFX抗体产生情况。方法 选取2013年5月-2014年8月应用IFX治疗的14例难治性IBD住院患者,每例患者于应用IFX前空腹抽取血样1~4份,共获得血液样品31份,采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)测量全部31份血清中IFX血药浓度及其中的26份血清中抗IFX抗体产生情况,同时每个采血点对溃疡性结肠炎患者进行Mayo评分,克罗恩病患者进行CDAI评分从而进行疗效评价。结果 31次抽血时有17次患者有效,有效率为54.8%,IFX有效浓度为2.16~41.83 μg/ml,平均(15.79±13.87)μg/ml;14次抽血无效时IFX浓度为0.69~23.67 μg/ml,平均(6.36±6.09)μg/ml,两组间比较差异有统计学意义(t=2.359,P=0.025)。26份血清样品检测了抗IFX抗体,结果显示1份3.8%(1/26)为阳性,其余25份均为阴性。结论 IFX疗效与其血药浓度呈正相关;抗IFX抗体产生率较低。
炎症性肠病;英夫利西;血药浓度;抗英夫利西抗体;疗效
我国人群炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)的发病率逐年增加[1],逐渐成为消化系常见疾病,一些IBD患者对传统治疗效果差,严重影响患者的生存质量,甚至危及生命。生物制剂英夫利西单抗(infliximab,IFX)的出现为患者带来了希望,如何进行个体化治疗及提高IFX的临床疗效,成为目前临床面临的问题,而IFX及其抗体的检测是近年来研究的热点,本文对IBD患者IFX血药浓度与疗效的关系进行初步探讨 。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2013年5月-2014年8月住院的IBD患者14例,其中包括激素治疗无效或依赖的难治性中-重度溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis,UC)患者9例(中度3例,重度6例),中-重度克罗恩病(crohn’s disease,CD)患者5例(中度3例,重度2例)。男11例,女3例,年龄11~64岁,平均年龄(39.2±16.07)岁。
1.2 纳入及排除标准 纳入的IBD患者的诊断、严重程度分级及疗效评判均符合中华医学会消化病学分会制定的炎症性肠病诊断治疗规范[2]。纳入标准为难治性中-重度CD及中-重度UC患者。排除标准为IFX单抗禁忌的人群,包括活动性感染(结核、病毒性肝炎及其他潜在感染)、神经脱髓鞘疾病、恶性肿瘤、充血性心力衰竭、对鼠源蛋白成分过敏者、妊娠或哺乳期妇女。
1.3 疗效判定 UC疗效判定[2]:UC有效:Mayo评分相对于基线值的降幅≥30%及≥3分,且便血的分项评分降幅≥1分或该评分为0分或1分。CD疗效判定[2]:CDAI下降≥70分或CDAI≤150分为有效,否则判定为无效。
1.4 IFX及其抗体检测 入组的14例患者应用IFX单抗2~12次,13例患者每次应用IFX为5 mg/kg,1例UC患者给予10 mg/kg,在应用IFX前为预防不良反应发生均给予地塞米松5 mg 静脉滴注。2例UC患者及1例CD患者应用IFX的同时,口服硫唑嘌呤50~100 mg/d。每例患者于应用IFX前空腹抽取血样1~4份,共采取血液31份,每份抽血2 ml,置入非抗凝管,1 500 r/min离心5 min,分离血清-80 ℃保存备用。每份血样取50 μl血清检测IFX血药浓度,同时取50 μl血清检测抗IFX抗体(5份样本因血清量不足无法完成抗IFX抗体的测量)。IFX及其抗体检测均采用酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA),酶标仪为iMark168-1130。
每次抽血时均对UC患者进行Mayo评分,CD患者进行CDAI评分,对疗效进行评判。
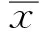
2 结果
2.1 IFX血药浓度与疗效 31次抽血有17次有效,有效率为54.8%,IFX有效血药浓度为2.16~41.83 μg/ml,平均(15.79±13.87)μg/ml,14次无效时IFX浓度为0.69~23.67 μg/ml,平均(6.36±6.09)μg/ml,两组间比较,差异有统计学意义(t=2.359,P=0.025)。IFX单抗对IBD的疗效与其血药浓度呈正相关(见图1)。
2.2 IFX抗体检测结果 26份样品中抗IFX抗体1份阳性,其余25份均阴性,抗IFX抗体产生率为3.8%,1例抗IFX抗体阳性的患者IFX治疗无效。
3 讨论
IBD为慢性、反复发作的非特异性炎症性疾病,包括UC及CD,其病因尚不明确,部分患者对传统治疗效果不满意,IFX、阿达木单抗等生物制剂的应用明显破解了难治性IBD患者的治疗难题,其不但提高了疗效[3],一些患者还可减少住院次数及避免手术[4]。

图1 IFX血药浓度与疗效关系
Fig 1 The relationship between IFX serum concentration and clinical effect
IFX为抗肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)的人鼠嵌合体单克隆抗体,TNF-α为关键的促炎因子[5],IFX通过拮抗TNF-α达到治疗IBD的目的。尽管IFX的应用为IBD患者带来了希望,但并非所有患者均有满意疗效,Hanauer等[6]进行的多中心随机对照研究表明58%的CD患者对IFX首次治疗有效。随着疗程的延长,对IFX的应答率逐渐降低。 Gisbert等[7]研究表明IFX约40%初始有效的CD患者在随后的治疗过程中逐渐对IFX失去应答反应。其原因与IFX代谢有关,IFX代谢动力学在不同个体间存在较大差异,影响其代谢动力学进而影响疗效的因素复杂多样,包括全身炎症反应程度、血清白蛋白水平、IBD类型(CD或UC)、体质量指数、是否应用免疫抑制剂、是否产生抗IFX抗体等重要因素,全身炎症反应加重、低蛋白血症、抗IFX抗体、高体质量指数均与临床疗效呈负相关,免疫抑制剂可减少IFX的清除,提高疗效;在治疗过程中,UC患者清除IFX单抗的速度快于CD患者,其原因除了与UC患者全身炎症反应程度较重、易发生低蛋白血症有关外,还与IFX的肠道丢失有关[8]。在所有影响IFX疗效的诸多因素中,原始TNF-α水平、IFX血药浓度及其抗体最为重要,对其检测进行个体化治疗具有重要的指导作用。多项研究[9-12]证实IFX对IBD患者的疗效与IFX血清浓度呈正相关,与抗IFX抗体呈负相关,随着血清中IFX浓度升高,IBD疗效提高,而抗IFX抗体与IFX结合形成免疫复合物,降低了IFX生物活性,从而降低了IFX的疗效。本研究结果与上述结果一致,IFX平均血药浓度在有效组显著高于无效组,两组间差异有统计学意义,但抗IFX抗体产生阳性率3.8%(1/26)低于国外报道[11],可能与我们在应用IFX 前常规静脉给予激素及应用硫唑嘌呤有关,应用免疫抑制剂能够降低抗IFX抗体的产生,提高IFX 的疗效[13]。 在IFX治疗过程中对其血药浓度检测有利于治疗方案的选择,对于IFX治疗无效的患者,临床常通过采用增加剂量或缩短疗程来提高疗效。本研究中1例患者开始时采用5 mg/kg,3次治疗无效后增加剂量到10 mg/kg,得到了临床缓解,但该方法存在一定的局限性。目前推荐更科学的方法,即通过治疗药物监测选择治疗方案,对IFX无效的患者,如果IFX血药浓度低于有效阈值,且抗IFX抗体阴性的患者可增加IFX剂量,如果抗IFX抗体阳性可转换为其他TNF-α拮抗剂如阿达木单抗。如果IFX 血药浓度高于有效阈值,但临床仍无治疗效果,表明患者存在TNF-α外炎症激活机制,无论是否存在抗IFX抗体,均主张转为TNF-α拮抗剂以外的制剂进行治疗[8]。一项随机、对照研究[14]表明对基于IFX血药浓度及其抗体监测结果选择治疗方案有利于优化患者治疗方案,并可提高IFX的效价比,为患者节省费用。
关于IFX有效阈浓度值不同的检测方法有较大的差异[8],国外多采用ELISAs方法,文献报告有效阈浓度值差异较大,多为1.0~7.19 μg/ml[10,15-17],目前尚缺乏我国人群的相关报道,本研究为小样本初步探讨,有待扩大样本量计算出我国人群的IFX有效药物阈值。
[1]Yun J,Xu CT,Pan BR. Epidemiology and gene markers of ulcerative colitis in the Chinese [J]. World J Gastroenterol,2009,15(7): 788-803.
[2]Digestive Disease Branch of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Study Group,the Chinese Medical Association. The consensus of diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (2012 Guangzhou) [J]. Chin J Intern Med,2012,51(10): 818-831. 中华医学会消化病学分会炎症性肠病学组. 炎症性肠病诊断与治疗的共识意见(2012·广州)[J]. 中华内科杂志,2012,51(10): 818-831.
[3]Fan RY,Sheng JQ,Lu XJ,et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab on inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2013,22(9): 898-900. 范如英,盛剑秋,陆晓娟,等. 英夫利单抗对炎症性肠病的疗效及安全性分析[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2013,22(9): 898-900.
[4]Costa J,Magro F,Caldeira D,et al. Infliximab reduces hospitalizations and surgery interventions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis,2013,19(10): 2098-2110.
[5]Nielsen OH,Gionchetti P,Ainsworth M,et al. Rectal dialysate and fecal concentration of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin,interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in ulcerative colitis [J]. Am J Gastroenterol,1999,94(10): 2923-2928.
[6]Hanauer SB,Feagan BG,Lichtenstein GR,et al. ACCENT Ⅰ Study Group. Maintenance infliximab for Crohn’s disease: the ACCENT Ⅰrandomised trial [J]. Lancet,2002,359(9317): 1541-1549.
[7]Gisbert JP,Panés J. Loss of response and requirement of infliximab dose intensification in Crohn’s disease: a review [J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2009,104(3): 760-767.
[8]Khanna R,Feagan BG. Current and future status of therapeutic drug monitoring in the treatment of IBD [J]. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol,2014,12(1): 76-89.
[9]Nanda KS,Cheifetz AS,Moss AC. Impact of antibodies to infliximab on clinical outcomes and serum infliximab levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): a meta-analysis [J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2013,108(1): 40-47.
[10]Bortlik M,Duricova D,Malickova K,et al. Infliximab trough levels may predict sustained response to infliximab in patients with Crohn’s disease [J]. J Crohns Colitis,2013,7(9): 736-743.
[11]Warman A,Straathof JW,Derijks LJ. Therapeutic drug monitoring of infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease patients in a teaching hospital setting: results of a prospective cohort study [J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2015,27(3): 242-248.
[12]Yanai H,Lichtenstein L,Assa A,et al. Levels of drug and antidrug antibodies are associated with outcome of interventions after loss of response toinfliximab or adalimumab [J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol,2015,13(3): 522-530.
[13]van Schaik T,Maljaars JP,Roopram RK,ea al. Influence of combination therapy with immune modulators on anti-TNF trough levels and antibodies in patients with IBD [J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis,2014,20(12): 2292-2298.
[14]Steenholdt C,Brynskov J,Thomsen O,et al. Individualised therapy is more cost-effective than dose intensification in patients with Crohn’s disease who lose response to anti-TNF treatment: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Gut,2014,63(6): 919-927.
[15]Cornillie F,Hanauer S,Diamond R. Early serum infliximab trough level,clinical disease activity and CRP as markers of sustained benefit of infliximab treatment in Crohn’s disease: a post-hoc analysis of the ACCENT 1 trial [J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2011,106: S462-S463.
[16]Arias MT,Van de Casteele N,Drobne D,et al. Importance of trough levels and antibodies on the long-term efficacy of infliximab therapy in ulcerative colitis [J]. J Crohns Colitis,2012,6: S5.
[17]Hibi T,Sakuraba A,Watanabe M,et al. Decrease in serum infliximab level precedes loss of clinical response and can be easily detected by the elevation of C-reactive protein in Crohn’s disease [J]. Gastroenterology,2012,1: S388.
(责任编辑:陈香宇)
Clinical effect and detection of Infliximab serum levels in patients with refractory inflammatory bowel disease
FAN Ruying,SHENG Jianqiu,WANG Xiaowei,YANG Xinyan,WANG Jiheng,LI Shujun,LI Shirong
Department of Gastroenterology,Beijing Military General Hospital,Beijing 100700,China
Objective To investigate the relationship between serum concentration of Infliximab (IFX) and clinical effect and to explore the situation of antibodies to IFX. Methods Fourteen inpatients with refractory inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (5 moderate and severe Crohn’s disease cases and 9 ulcerative colitis cases) were selected from May. 2013 to Aug. 2014. Thirty-one of blood sample were drawn from the 14 patients (each patient was drawn blood from 1 to 4 times) for the determination of IFX trough levels and 26 blood sample for the determination of antibodies to IFX (ATI) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Disease activity indices [Crohn’s disease activity index (CDAI) and Mayo scores for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis,respectively] were obtained at every drawn blood point to assess efficacy of IFX. Results The response rates to IFX was 54.8%. The IFX serum trough level in effective group was higher compared with non-responders group [2.16-41.83 μg/ml; mean: (15.79±13.87) μg/ml versus 0.69-23.67 μg/ml; mean: (6.36±6.09) μg/ml,P=0.025]. Positive rate of antibodies to IFX was 3.8% (1/26). Conclusion There is a significant association between remission of patients with IBD and IFX trough levels. Positive rate of antibodies to IFX is low.
Inflammatory bowel disease; Infliximab; Serum concentration; Antibodies to infliximab; Clinical effect
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2016.02.023
范如英,博士,副教授,研究方向:IBD诊治。E-mail: fanri@163.com
李世荣,教授,研究方向:大肠癌及IBD诊治。E-mail: lishirong@aliyun.com
R574
A
1006-5709(2016)02-0202-03
2015-05-30

