菵草对3种ACCase抑制剂抗性的琼脂快速检测方法建立
邹红梅, 李香菊, 崔海兰, 何 林
(1.中国农业科学院植物保护研究所,北京 100193;2.西南大学植物保护学院,重庆 400715)
菵草对3种ACCase抑制剂抗性的琼脂快速检测方法建立
邹红梅1,2, 李香菊1, 崔海兰1, 何林2
(1.中国农业科学院植物保护研究所,北京 100193;2.西南大学植物保护学院,重庆 400715)
摘要:以菵草的1个敏感种群和2个抗药性种群为试材,在用整株测定法明确其对精唑禾草灵、高效氟吡甲禾灵、炔草酯3种ACCase抑制剂抗性水平的基础上,采用琼脂法,以新根率为指标筛选出3种药剂对抗性菵草的检测浓度。结果表明,整株测定法和琼脂法具有很好的相关性,通过琼脂法能够检测菵草对3种ACCase抑制剂的抗性,精唑禾草灵检测浓度为 0.4 μmol/L,高效氟吡甲禾灵检测浓度为0.2 μmol/L,炔草酯检测浓度为0.4 μmol/L,3种除草剂的最快检测时间为4 d。
关键词:菵草;ACCase抑制剂;抗性;快速检测


1材料与方法
1.1材料
供试菵草种群的采集地点及相关信息见表1。

表1 不同菵草种群的采集信息
1.2方法
1.2.1菵草不同种群对3种除草剂抗性水平的整株测定菵草幼苗的准备:将壤土与有机肥料按 3 ∶1 混合均匀,装于直径为9 cm的塑料盆钵内备用。用0.1%GA3浸泡菵草种子12~24 h,打破休眠,用清水反复清洗后均匀播种在事先准备好的盆钵中,均匀覆土,置于温室条件下培养,白天温度20~27 ℃,夜间温度12~17 ℃,培养期间按需浇水。待菵草生长至2~3叶期,间苗,每盆保留生长一致的植株10株。药剂处理:根据预试验,设计每种药剂的浓度梯度,每处理重复3次,详见表2。喷雾压力0.275 MPa,喷液量367.5 kg/hm2。

表2 不同药剂的剂量设计
数据调查与分析:施药21 d后,将菵草地上部分剪下,80 ℃烘干并称其干质量,计算干质量抑制率,将干质量抑制率和药剂剂量进行转换,拟合回归方程:
Y=b+kX。
式中:Y为概率值(将地上部分干质量抑制率转换成概率值);b为截距;k为斜率;X为lg(药剂剂量)。
根据上面的公式计算各种群的GR50值(GR50值表示在药剂作用下,植物干质量降低 50%时,所需要的药剂剂量),并根据下面公式计算抗药性指数(resistance index,RI)
RI=抗性种群GR50/敏感种群GR50。

新根率=生长新根株数/接种总株数×100%。
2结果与分析
2.1菵草不同种群对3种除草剂抗性水平的整株测定

表3 菵草不同种群对3种除草剂的抗性水平
2.2菵草对3种除草剂抗性的琼脂法检测
3个菵草种群在不含除草剂的琼脂培养基中的新根率随时间的变化情况见图1。WC4#、WC5#、WC8#的对照组从培养2 d开始就能够观察到新根发生,培养4 d新根率分别为26.67%、56.67%和6.67%,培养4~7 d新根率直线上升,培养7~11 d陆续达到最高,培养11 d新根率分别达到93.33%、100%和100%,培养12 d新根率不再增加,从地上部分已能观测到没有生长新根的植株死亡。

3结论与讨论

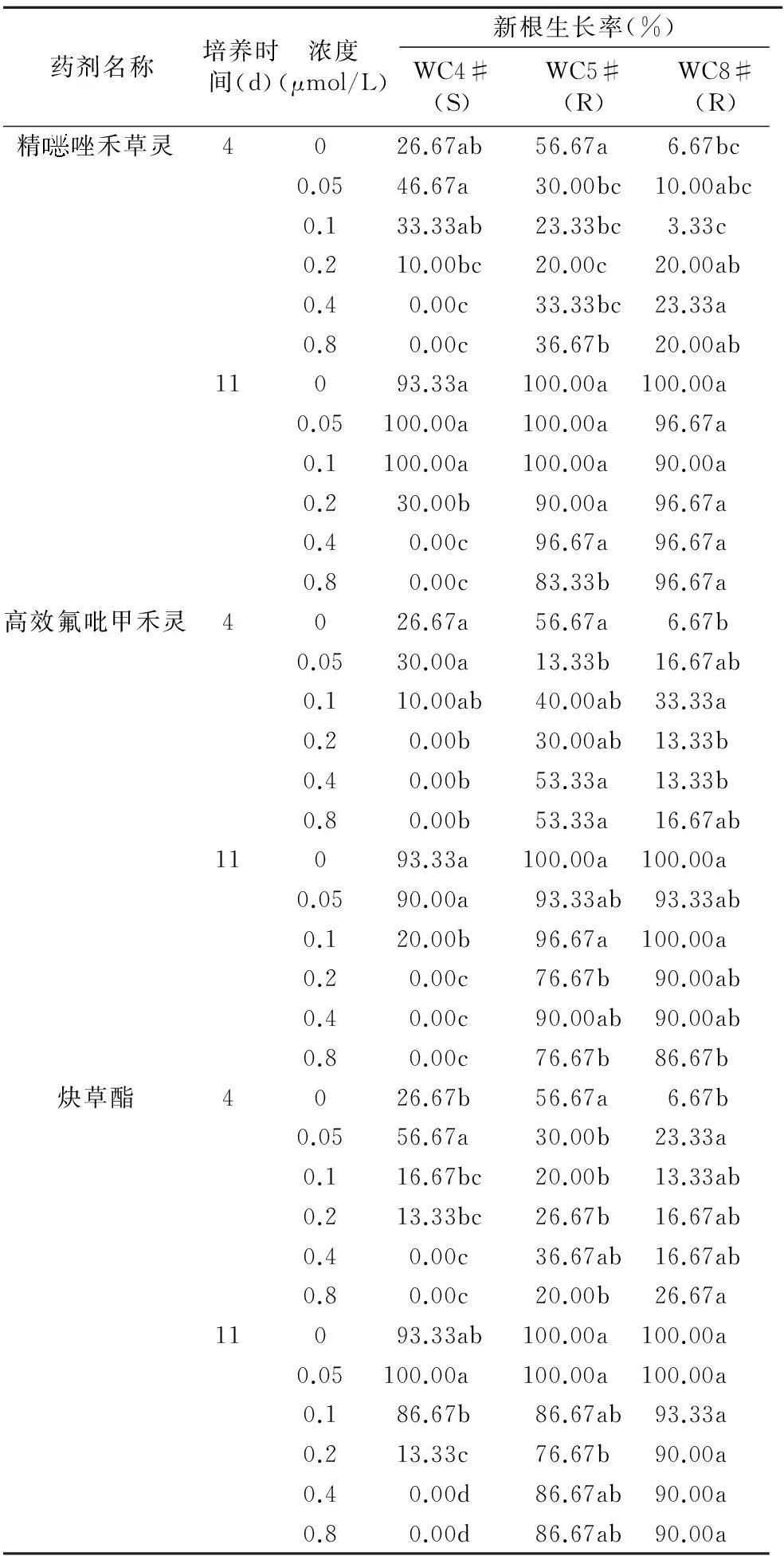
表4 各药剂检测浓度筛选
注:表中同列数字后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。
参考文献:
[1]Rao N,Dong L Y,Li J,et al. Influence of environmental factors on seed germination and seedling emergence of American sloughgrass (Beckmanniasyzigachne)[J]. Weed Science,2008,56(4):529-533.
[2]吉林,张亚明,金水明,等. 太湖地区麦田菵草迅速蔓延的原因及防除对策[J]. 江苏农业科学,1999(5):37-39.
[3]王爽,张荣全,叶非. 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶抑制剂的研究进展[J]. 农药科学与管理,2003,24(10):26-32.
[4]Li L,Du L,Liu W,et al. Target-site mechanism of ACCase-inhibitors resistance in American sloughgrass (BeckmanniasyzigachneSteud.) from China[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,2014,110:57-62.
[5]Li L X,Bi Y L,Liu W T,et al. Molecular basis for resistance to fenoxaprop-p-ethyl in American sloughgrass (BeckmanniasyzigachneSteud.)[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,2013,105(2):118-121.
[7]Beckie H J,Heap I M,Smeda R J,et al. Screening for herbicide resistance in weeds[J]. Weed Technology,2000,14(2):428-445.
[8]Tal A,Kotoula-Syka E,Rubin B. Seed-bioassay to detect grass weeds resistant to acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase inhibiting herbicides[J]. Crop Protection,2000,19(7):467-472.
[9]Letouzé,Gasquez. A pollen test to detect ACCase target-site resistance with in Alopecurus myosuroides populations[J]. Weed Research,2000,40(2):151-162.
[10]Kaundun S S,Hutchings S J,Dale R P,et al. Syngenta‘RISQ’test:a novel in-season method for detecting resistance to post-emergence ACCase and ALS inhibitor herbicides in grass weeds[J]. Weed Research,2011,51(3):284-293.
[11]黄世霞,王庆亚,董立尧,等. 乙酰辅酶A羧化酶抑制剂类除草剂与杂草的抗药性[J]. 杂草科学,2003(2):2-6.
[12]马晓渊. 农田杂草抗药性的发生为害、原因与治理[J]. 杂草科学,2002(1):5-9.
[14]Yang C H,Dong L Y,Li J,et al. Identification of Japanese foxtail(Aalopecurusjaponicus)resistant to haloxyfop using three different assay techniques[J]. Weed Science,2007,55(6):537-540.
[15]胡茂龙,孔令娜,龙卫华,等. 油菜乙酰羟基酸合酶基因BnAHAS1的克隆及其重组蛋白质的原核表达[J]. 江苏农业学报,2014,30(5):986-991.
[16]Délye C,Matéjicek A,Gasquez J. PCR-based detection of resistance to acetyl-CoA carboxylase-inhibiting herbicides in black-grass (AlopecurusmyosuroidesHuds) and ryegrass (Loliumrigidumgaud)[J]. Pest Management Science,2002,58(5):474-478.
[17]Kaundun S S,Windass J D. Derived cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence,a simple method to detect a key point mutation conferring acetyl CoA carboxylase inhibitor herbicide resistance in grass weeds[J]. Weed Research,2006,46(1):34-39.
张纪利,吴尚,李保同,等. 江西省稻田稗草对丁草胺和二氯喹啉酸的抗药性测定[J]. 杂草科学,2015,33(3):29-33.
Novel in-Season Agar Method for Detecting Resistance ofBeckmannia
syzigachneto Three Post-Emergence ACCase Inhibitor Herbicides
ZOU Hong-mei1,2, LI Xiang-ju1, CUI Hai-lan1, He Lin2
(1.Institute of Plant Protection,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Beijing 100193,China;
2.College of Plant Protection,Southwest University,Chongqing 400715,China)
Abstract:The response to three ACCase inhibitors (fenoxaprop-P-ethyl,haloxyfop-R-methyl and clodinafop-propargyl) of a susceptible and two resistant populations of Beckmannia syzigachne were determined by conventional whole-plant pot bioassays. Resistance eas further assessed in an agar bioassay using the new root growth rate as the diagnostic variable. There was very good agreement between the whole-plant pot and the agar bioassays that clearly detected the resistant levels of B. syzigachne to the three ACCase inhibitors. The detectable concentrations of fenoxaprop-P-ethyl haloxyfop-R-methyl and clodinafop-propargyl by the agar test were 0.4,0.2,and 0.4 mmol/L,respectively. The quickest detection time of these herbicides was four days after treatment.
Key words:Beckmannia syzigachne;ACCase inhibitor;resistance;quick detection
通信作者:崔海兰,博士,副研究员,从事杂草抗药性研究,E-mail:cuihailan413@163.com;何林,博士,教授,从事杂草抗药性研究,E-mail:helinok@vip.tom.com。
作者简介:邹红梅(1990—),女,重庆人,硕士研究生,从事杂草抗药性研究。E-mail:zhmei99@yeah.net。
基金项目:国家自然科学基金面上项目(编号:31371952);公益性行业(农业)科研专项(编号:201303031)。
收稿日期:2015-04-22
中图分类号:S451
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1003-935X(2015)03-0024-05

