Model Building for Community Participating in Rural Tourism and Game Analysis of Core Stakeholders
, *, zhi
1. School of Business Administration, University of Science and Technology Liaoning, Anshan 114051, China; 2. School of Continuing Education, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
1 Introduction
Rural tourism, as an effective means of invigorating rural economy and transforming rural single economic mode, is becoming an essential force for improving rural life and social environment, and has become a new economic growth point of rural areas because of its effective promotion for other industries and entire rural economy. In the process of rural tourism, fair allocation, fair procedure, and fair interaction perceived by residents influence communities participating in rural tourism through influencing sense of community support[1]. Excessive development, unreasonable management, non-cooperative game of stakeholders, institutional vacancy, and management override problems bring about a series of conflicts of economic benefits, rendering this popular tourism to exert a certain negative effect on rural communities. It is necessary to study how to properly balance the relation between stakeholders, build a mechanism integrating tourists, local communities, government and developers, and coordinating economic, social, cultural, and environmental benefits.
2 Connotation and influence of community participation in rural tourism
2.1CommunityparticipationinruraltourismdevelopmentRural tourism refers to the tourism activity that occurs in rural areas, attracts tourists with unique rural culture and landscape (pastoral scenery, agricultural production mode and farmers’ lifestyle), and meets tourists’ demands for sightseeing, leisure, holiday and experience. Most of the visitors it attracts are from urban areas. The essence of rural tourism development is the game process of rights and interests between different stakeholders. In the game process, every stakeholder constantly expands his stock, and brings the game to develop towards the direction favorable for himself. It is necessary to discuss how rural community residents effectively participate in rural tourism activities, so as to promote sustainable development of rural tourism and all-round development of communities. Some scholars believed that interests of residents should enhance environmental protection, improve local economic situation, provide jobs for local communities, and raise community level and grade[2]. At present, community residents fail to participate in rural tourism development mainly because their rights are infringed upon. Therefore, the essence of community participation in rural tourism is the process of community residents safeguarding their lawful rights and interests and common interests. At the same time of promoting tourism development, rural tourism also exerts a series of negative influence on local community residents, which are passively assumed by marginalized community residents, leading to resentment or even boycott of community residents.
2.2InfluenceofcommunityparticipationinruraltourismThe development of rural tourism exerts following 5 levels of influence on communities. Deep level reasons involve different characteristics of stakeholders in rural tourism system[3]. Firstly, the participation in planning and decision making of tourism development is mainly manifested in conducting opinion poll, encouraging farmers to establish long-term and short-term objectives for rural tourism development, and selecting proper opinions of farmers to include into government decisions. According toSustainableDevelopmentofTourism:ALocalAuthorityPerspectiveissued by National Tourism Administration with authorization of World Tourism Organization (WTO) in 1997, community residents participation in the process of tourism planning can be divided into 8 steps, as shown in Fig. 1. Secondly, it is participation in allocation of interests of tourism development. Farmers have right to enjoy economic interests obtained in rural tourism development, provide profitable opportunity for rural residents, including providing opportunity and business opportunity for local residents. Thirdly, communities participate in environmental protection and traditional culture maintenance. A large number of tourism developers put economic benefits in the first place, but neglect ecological environment and local culture protection. Damage to natural resources, excessive development of rural scenic spots, traditional cultural loss, and extensive management mode exert adverse influence on local farmers. Weak force of government is difficult to change current situations, it is necessary to encourage farmers to participate.

Fig.1Generalprocessofcommunityresidentsparticipationintourismplanning
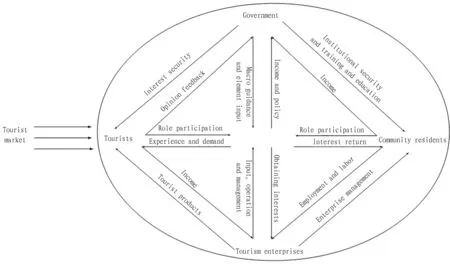
Fig.2Interestrelationmodelforcommunityparticipationinruraltourism
3 Interest relation model for community participation in rural tourism
3.1TypesofstakeholdersofruraltourismThe theory of model building is based on development of stakeholder theory and its application in tourism development practice. People start to realize the essential role of stakeholders in rural tourism development. Some scholars summarized stakeholders as core stakeholders and indirect stakeholders[4]. In accordance with this, stakeholders of rural tourism can be divided into core stakeholders that play an utmost role in development and protection of rural tourism destination (including local government, tourism enterprises, local communities, and rural tourists) and indirect stakeholders that have low influence on rural system (including various non-governmental organizations, industrial associations, tourism planning companies, new media, and workers of tourism enterprises). Core stakeholders are not unchangeable. They will constantly change with development stage at which destination and tourist site remains and also with adjustment of stakeholders, and their role and position will also change accordingly, as shown in Fig. 2. As integrator and coordinator of public resources, government has resource and political rights; tourism enterprises obtain resource rights from government departments by means of capital rights and technological advantages; tourists as purchasers of rural tourist products have rights of product and service selection; community residents form a cooperative or competitive relation with local tourism enterprise through participating in rural tourism development.
3.2InteractionbetweencorestakeholdersIn the model, community residents and tourists are core stakeholders and have two-way interaction in certain sectors of the same rural tourism. Community residents obtain profit from rural tourism, which stimulates community residents to constantly participate in rural tourism. Tourists realize role participation through media of rural tourism and obtain tourist experience and satisfy tourist demands; rural tourism as a certain sector appears covers all elements related to rural tourism. Government and enterprises are security factors of the model and exert influence on two main factors through various forms of expression. Government guides benign development of rural tourism through regulating enterprise management and community participation. Enterprise promote rural tourism development through boosting operation and management. Tourist market beyond the model system mainly plays the role of external promotion. In other words, tourist market constantly creates new demands in the rural tourism development to stimulate generation of new rural tourist products and influence the trend of rural tourism development.
4 Game analysis on conflict of interest between core stakeholders
4.1Interestdemandsandgamebehaviorofcorestakeholders
4.1.1Local government and community residents. Through participating in rural tourism, community residents obtain more job opportunities and increase their income, but local government building tourism infrastructure and undertaking tourism propaganda will reduce income of community residents. Besides, due to increase of local product price, local government and community residents have different opinions as to developing rural tourism. In addition, community residents do not have the right to speak in formulation of rural tourism planning, thus their interest demands are neglected, and there is possibility of game between them.
4.1.2Local government and rural tourism enterprises. Due to difference in role position, local government and rural tourism enterprises have different understanding of rural tourism. Local government pays attention to long-term interests and intends to change existing inherent economic structure to protect and care about rural ecological environment, while tourism enterprises focus on obtaining benefits through extensive operation. As a result, it leads to economic leakage and finally brings about the "tourism enclave" problem. Local government prefers to formulate some management policies to contain shortsighted behavior of tourism enterprises, while tourism enterprises like to take passive measures. As a result, tourism development planning of local government will be influenced, forming the game between them.
4.1.3Community residents and rural tourism enterprises. Imbalance in interest allocation leads to game behavior between community residents and tourism enterprises. Community residents demand higher economic income, but their job participation field is narrow, it is difficult for them to obtain management jobs, and their remuneration is low. With the aid of economic development activities, tourism enterprises take maximizing economic benefits as their goal, and they establish powerful monopoly position with the aid of their capital and technological advantages, which makes family based workshops unable to contend with them and also deteriorates excessive dependence of rural economy on rural tourism enterprises.
4.1.4Community residents and tourists. Community residents influence tourists mainly in their attitude towards tourists, and attitude of community residents is closely related with stage of tourism development[5]. At the early stage, rural economic development level was low. In the process of tourists seeking true tourist products, villagers increased income, improved living conditions, and enriched cultural life. Thus, they widely welcomed tourists, and tourists also obtained excellent tourist experience. At the deepening stage, with collision and influence of consumption behavior and idea of urban and rural residents, tourists started to exert certain negative influence on social, economic and environmental conditions of rural communities and living conditions of community residents, and community residents also had serious psychological imbalance. Then, they started to change attitude towards tourists, or even take illegal operation means to deceive tourists, which brings about game behavior between them.
4.2Gamerevenueanalysisofcorestakeholders
4.2.1Game between community residents and tourists. Villager behavior happens before the strategy, while tourists react after knowing action strategy of villagers. Their game is a dynamic process with action sequence, and the game revenue (payment) results are listed in Table 1. In the Table, R1 denotes faithful operation revenue of community residents; R2 is unlawful operation revenue of community residents; C1 is cost of tourists; C2 is additional cost of tourists due to unlawful operation of community residents; C3 is cost of tourists for complaint; F is fine imposed by government on unlawful behavior; K is compensation obtained by tourists after lodging a complaint. Higher F and K will more effectively prevent occurrence of unlawful operation activities. Orderly and standardized tourism operation market environment relies on constant improvement of government supervision mechanism. Further regulating tourism operation and consumption market can guarantee normal process of market. Information grasping level directly influences revenue (payment) results. Dai Zeguang (2009), through introducing Harsanyi transformation[6], built a uniform probability model to describe processing of participants to incomplete information, transformed incomplete information game into complete but imperfect information game, based on maximizing respective benefits, community residents overcharge tourists at C/( rF+rD+wE), while tourists make complaint at the probability of rF+rB, and discussed the conclusions[7].
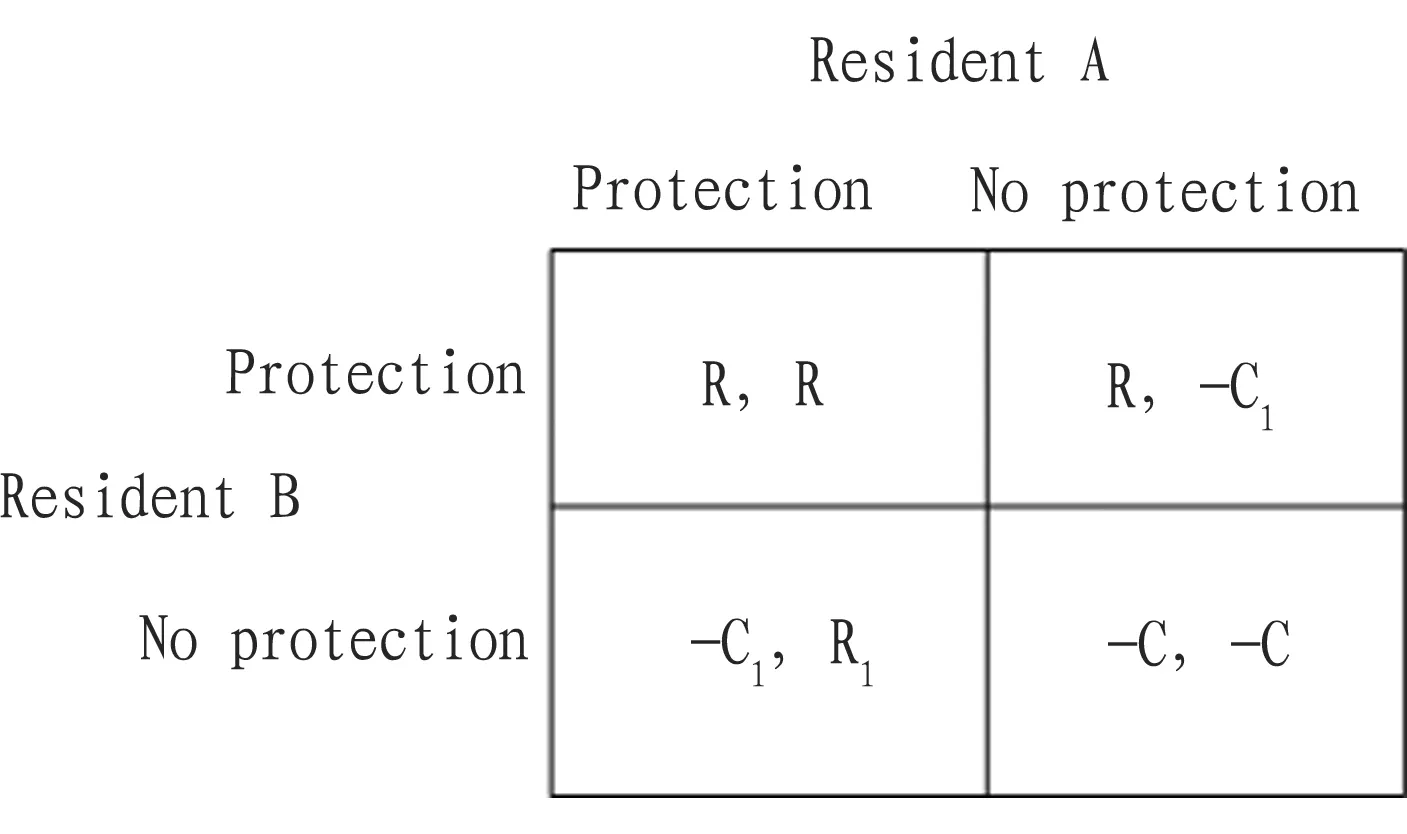
4.2.2Game between community residents. Based on assumption that community residents are rational economic men, due to influence of cultural, economic, and cognition factors, they may pursue maximum profit at the cost of damaging environment, or even scarifying interests of others. Taking A and B as game subjects, if both deteriorate the environment, it will cause loss C; if neither deteriorates the environment, A and B will obtain respective revenue R. Improvement of ecological environment, as public goods with high externality, will be consumed once generated. Thus, no matter one party takes positive or negative attitude, the other party will react with negative attitude. As shown in Fig. 3, if A protects environment actively, he will assume cost for ecological environment, and also assume the losses incurred from noncooperation of B, the loss C1(C Table1Revenueofgamebehaviorbetweencommunityresidentsandtourists ItemTouristsmakingcomplaintNocompensationCompensationRefuseAcceptBehaviorofcommunityresidentsOverchargeR2-K-FS-C1-C2-C3+KComplaintNoncomplaint-R2-KS-C1-C2+KNonoverchargeHonestoperationR1S-C1-F-KS-C3+K-R2S-C1-C2HonestoperationR1S-C1 Fig.3Paymentmatrixforthegamebetweencommunityresidents 5.1ImprovingthesituationofinformationasymmetryThere is information asymmetry in the game between community residents and tourists. Such information asymmetry directly leads to the result that the party with information advantage takes reverse selection in the manner of concealing information, to obtain additional revenue, which will ultimately influence the operation results of the price mechanism and the resource allocation efficiency, and interests of stakeholders will be not optimum. At present, there is serious information asymmetry and incompleteness at China’s tourism market, leading to existence of some non-reasonable or even illegal behavior of developers and tourists. In this situation, government must undertake the responsibility of systematically collecting and promptly issuing information of tourism market, improve the transparency of policies and documents, establish and improve the information network, and raise the market transparency, to overcome the drawback of information asymmetry at the tourism market. 5.2EncouragingcommunityparticipationandinterestsecurityDifferent actions of interests based on different demands of interests will trigger uneven interest distribution and cause conflict, so it is required to comply with the balance principle and establish an effective interest security and allocation mechanism. Besides, it is recommended to specify reasonable revenues and revenue realization approaches for each party, and make clear the coordination methods and solutions once there appears conflict of interest. Some rural tourism largely relies on support of government and financial institutions[8]. It is recommended to establish an effective incentive mechanism from policy preference and fund support, and consider providing certain financial subsidies for those residents not participating in community residents, to realize sustainable development of sharing the interest. If local government or other strong entities increase the control over land resources, it may trigger local residents to fight for the resources, accordingly leading to excessive development and consumption of natural resources[9]. At current stage, government sectors should establish institutional guarantee and effective propaganda and education to raise awareness of community residents for environmental protection and participation in tourism. It is recommended to encourage and guide local community residents to participate in rural tourism resource development, protection and management, to comprehensively participate in and controlling every link of the tourism project planning and implementation, including all processes from policy formulation to development, management and supervision, and from overall participation to investment and interest allocation. Through combining economic benefits of tourism development and overall benefits of local communities, it is expected to realize harmony between development and protection. 5.3BringingintoplayleadingandcoordinationroleofthegovernmentThe key for realizing relative balance of interest is to establish reasonable institutional mechanism and security mechanism, to ensure the rights of community residents to express their opinions and make decisions. According to the theory of stakehold-ers, government sectors should correctly understand their role of managers and supervisors in community participation in rural tourism. At the same time of guiding community residents to participate in tourism development, government should work out corresponding supervision and management measures, impose certain punishment on farmers who overcharge tourists, protect characteristic and typical rural tourism resources, protect historical sites and remains with historical value, avoid artificial destruction to ecological environment and traditional culture, and sternly punish tourists who willfully damage public facilities in tourist areas and those who damage local ecological environment. [1] QING XA, WANG LL, ZHANG GY. Relationships among perceived justice, perceived community support and community participation in tourism development: From the perspective of social exchange theory[J]. Tourism Science,2015(5): 14-26.(in Chinese). [2] ZHANG X, ZHENG YY. On the management of Chinese natural and cultural heritage[M].Beijing:Social Sciences Academic Press(China),2001:184-204.(in Chinese). [3] LANG FP, YANG M. Analysis on the perception of the attitudes of community residents to rural tourism[J]. Chinese Rural Economy,2006(11):68-74. (in Chinese). [4] CHEN HH. Empiricial research on stakeholders’ 3-dimension classification in Chinese enterprises[[J]. Economic Research Journal,2004(4):80-90. (in Chinese). [5] FANG BS. The research of building rural tourism interest coordinating mechanism: Take Wuyishan for example[D].Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,2010:34. (in Chinese). [6] ZHANG WY. Game theory and information economics[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Sanlian Bookstore Press,1996. (in Chinese). [7] DAI ZG, HONG MY. Analysis on game of residents behavior in the rural tourism with community participation[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2009,37(9):261-264. (in Chinese). [8] LIU SR, LI M. Study on the benefits of rural tourism subject in mixed strategy game [J]. Rural Economy and Science-Technology,2011(8):36-38. (in Chinese). [9] BRENDA K, ANNA K, RUTH MD. Collective action, property rights, and devolution of natural resource management[Z]. Policy Brief Number, 2001.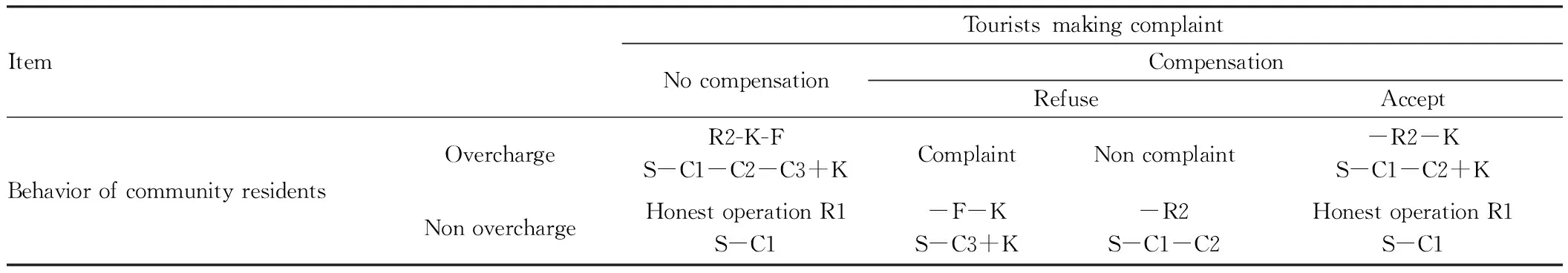
5 Conclusions and recommendations
 Asian Agricultural Research2016年11期
Asian Agricultural Research2016年11期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Feasibility Analysis of Agricultural Product Price Index Insurance Based on Pilot Cases
- Forecast on Price of Agricultural Futures in China Based on ARIMA Model
- Embedded Programmable Single Point Multiple Output Intelligent Data Acquisition and Transmission System
- A Study of the Factors that Affect Farmers’ Willingness to Transfer Land in the Central Regions Based on a Survey of 180 Farmers in Suizhou City
- Comparative Study of Cotton Plant Height Difference in the Arid Areas Based on LandSat8 OLI Data
- How to Enhance the Brand Competitiveness of Ginseng Enterprises?
