含区间参数的结构-声耦合系统摄动分析方法
第一作者牛明涛男,硕士,工程师,1986年8月生
含区间参数的结构-声耦合系统摄动分析方法
牛明涛,李昌盛,陈利源(中国石化石油工程技术研究院,北京100101)
摘要:针对实际工程中普遍存在的结构-声耦合系统,充分考虑系统本身及外载荷不确定性,基于摄动理论建立一阶及高阶参数摄动两种区间分析方法。从耦合系统有限元平衡方程出发,引入区间变量对系统不确定参数进行定量化描述。据传统的一阶Taylor展式及摄动理论,可快速估算系统响应区间上下界。高阶区间参数摄动分析方法除采用改进的Taylor展式对区间矩阵、向量近似估算外,亦保留Neumann级数中部分高阶项,可有效提高响应范围的计算精度。以长方体密闭舱室为研究对象,将计算结果与传统蒙特卡洛方法对比,充分验证所提数值计算方法求解含区间参数结构-声耦合问题的可行性、有效性。
关键词:结构-声耦合系统;区间不确定性;区间参数摄动方法;Neumann级数
基金项目:中国石化“十二五”重点信息化项目 (G11-MM-2011-080);中国石化重点科技攻关项目(P13093)
收稿日期:2014-03-26修改稿收到日期:2014-05-16
中图分类号:O328;O422.6文献标志码:A
Perturbation methods for structural-acoustic coupled systems with interval parameters
NIUMing-tao,LIChang-sheng,CHENLi-yuan(Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Engineering, Beijing 100101, China)
Abstract:Based on the perturbation theory, two interval analysis methods named first-order interval parameter perturbation method (FIPPM) and high-order interval parameter perturbation method (HIPPM) were proposed for the structural-acoustic coupled system response prediction with interval uncertainties in both system parameters and external loads. The structural-acoustic discrete equilibrium equations were established based on the finite element method. Interval variables were used to quantitatively describe the uncertain parameters with limited information. According to the first-order Taylor series and the first-order perturbation theory, the system response interval could be quickly estimated with FIPPM. HIPPM introduced the modified Taylor series to approximately estimate the non-linear interval matrix and vector. Part of higher order terms of Neumann expansion were retained to calculate the interval matrix inverse. A 3D cuboid model was taken as a study object, its computing results using the propose methods were compared with those using the traditional Monte Carlo method. It was shown that the proposed methods are feasible and effective to predit the sound pressure ranges of structural-acoustic coupled systems.
Key words:structural-acoustic coupled system; interval uncertainty; interval parameter perturbation method; Neumann series
工程设计通常希望降低有害振动及噪声幅值以提升系统的安全性、舒适性。而柔性结构振动与充满流体介质封闭声场之间的耦合问题较多见,其声场内部噪声由结构振动引起。若考虑内部声压对结构的反作用,该系统称结构-声耦合系统,在汽车、航空、船舶等工业领域普遍存在[1]。对此类系统中、低频响应的数值分析主要用有限元[2]、边界元[3]两种方法对声场进行离散。工程中,材料物理参数与边界条件会受多种不确定性因素影响,由此引起结构振动声辐射呈一定程度不确定性。处理此类不确定声学问题的常用方法主要源于概率理论,James等[4]通过将不确定参数定量化,研究确定声场概率密度函数的计算方法。Finette[5]提出随机响应面方法预测海洋不确定环境下声场的传播规律。Liu等[6]给出基于有限-边界元方法、虚拟激励原理的随机结构振动声辐射灵敏度问题解决方法。
建立概率模型需预知不确定量的概率密度函数,而足够的信息往往预先难以获得。相比之下,区间方法仅需用少量信息确定不确定参数的上下界,具有较好的方便性、经济性[7]。与处理区间问题常用的蒙特卡洛方法[8]、顶点法[9]相比,摄动方法[10]凭借其独特的计算效率颇受关注[11]。随不确定性定量精细化发展趋势,传统摄动方法因忽略高阶项所致计算精度问题日益严重。鉴于此,本文以含区间参数的结构-声耦合系统为研究对象,提出改进的高阶区间参数摄动方法,可保留Neumann级数中部分高阶项。通过数值算例验证该方法有效性,且能满足工程对计算效率、精度需求。
1结构-声耦合系统有限元方程
针对图1结构-声耦合系统,在频域分析下,内部声场压强p可由Helmholtz方程表示,即
(1)
据变分原理,得具有弹性边界声场的有限元方程为
(Ka+jωCa-ω2Ma)P=ρω2SUs
(2)
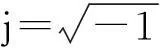

图1 结构-声耦合系统模型 Fig.1 Model of the coupled structural-acoustic system
充分考虑内部声压对结构的反作用,在频域下结构有限元运动方程为
(KsjωCs-ω2Ms)Us=Fs+STP
(3)
式中:Ks,Ms,Cs分别为结构刚度、质量、阻尼矩阵;Fs为施加于结构的外力。
联合式(2)、式(3),得结构-声耦合系统有限元方程为
(-ω2M+jωC+K)U=F
(4)
式中:
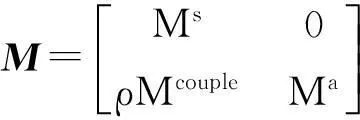
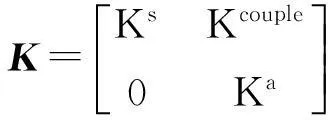
Mcouple=S;Kcouple=-ST
为表示方便,将式(4)记为
AU=F
(5)
式中:
A=-ω2M+jωC+K
(6)
实际问题中,由于工艺限制及环境变化等因素,结构-声耦合系统存在大量不确定性。本文引入如区间向量表示所有不确定参数,即
(7)
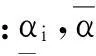
显然,式(4)中系数矩阵及右端向量均与此区间向量相关联。因此,耦合有限元方程(5)可改写为
A(αI)U(αI)=F(αI)
(8)
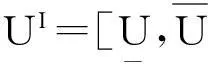
A(αI)UI=F(αI)
(9)
2一阶区间参数摄动分析方法
将式(9)中系数矩阵及右端向量在区间参数中值处进行一阶Taylor展开,得
(10)
(11)
用中心区间表示方法将系统响应记为UI=Uc+ΔUI,将式(10)、(11)代入式(9),得
(Ac+ΔAI)(Uc+ΔUI)=Fc+ΔFI
(12)
忽略二阶及以上高阶小量,利用摄动理论得
(13)
考虑矩阵Ac总可逆,故有
Uc=(Ac)-1Fc
(14)
ΔUI=(Ac)-1(ΔFI-ΔAI(Ac)-1Fc)
(15)
将式(10)、(11)代入式(15),得
ΔUI=
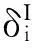
ΔU=
因此,利用一阶区间参数摄动分析方法获得结构-声耦合系统区间响应上、下界分别为
(18)
3高阶区间参数摄动分析方法
区间不确定参数变化范围较大或数量较多时,忽略高阶项的一阶参数摄动方法所致区间扩张问题有时较严重。为此,基于改进的Taylor展式、Neumann级数,提出高阶区间参数摄动分析方法。通过空间近似曲面导轨生成方式[12]获得(9)系数矩阵的近似表示
A(αI)=A(α1,α2,…,αm)=
(19)
式中:
(20)
(21)
式中:
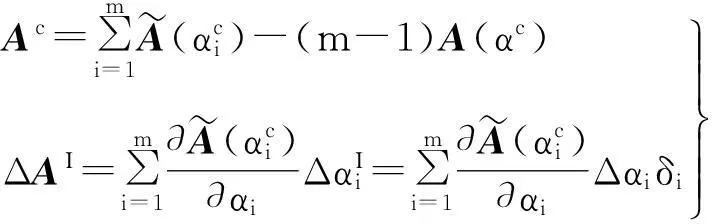
(22)
用相同处理方式,区间参数向量F(αI)可表示为
(23)
式中:
(24)
将式(21)、(23)代入式(9),两边左乘(Ac+ΔAI)-1得
Uc+ΔUI=(Ac+ΔAI)-1(Fc+ΔFI)
(25)
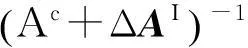
(Ac+ΔAI)-1=(Ac)-1+
(26)
借助式(22)得
(27)
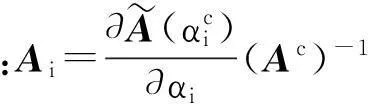
针对不同r值,上式可表示为
(28)
将式(27)、(28)代入式(26),得
(29)
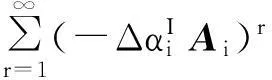
(30)

(31)
(32)
将式(30)代入式(25),利用摄动理论,忽略高阶交叉向量,得
(33)
(34)
利用式(24),将式(34)改写为
(35)
(36)
利用高阶区间参数摄动分析方法所得结构-声耦合系统区间响应上、下界分别为
(37)
4数值算例
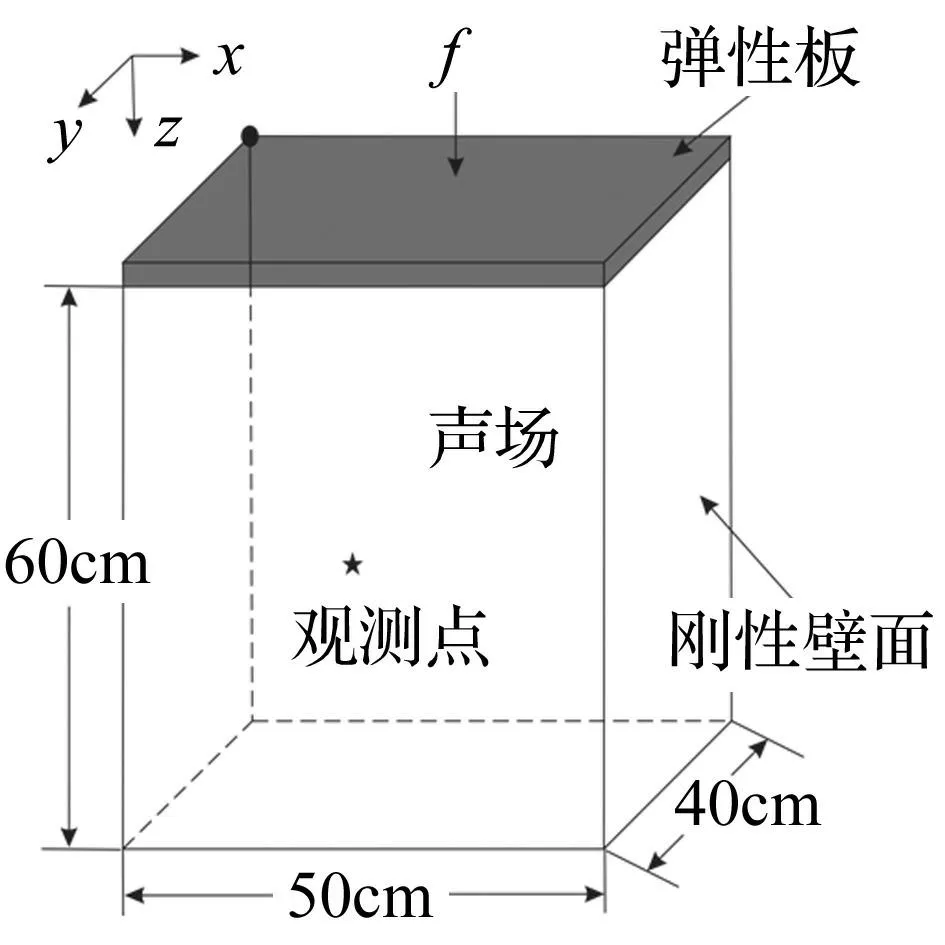
图2 长方体密闭舱室模型 Fig.2 Model of acuboid airtight cabin
考虑图2的长50 cm、宽40 cm、高60 cm长方体舱室模型,四周由同一种铝合金材料围成封闭空间,内部充满空气介质,构成结构-声耦合系统。其中舱室顶部为2 mm厚弹性铝板,其余为刚性壁面。由于材料的初始缺陷,铝合金密度、弹性模量分别在2 565~2 835 kg/m3及67.5~74.5 GPa范围变化。因周围温度环境变化,空气密度、声速被认为区间不确定参数,其变化区间分别为[1.164,1.286] kg/m3,[323,357]m/s。有一简谐激励作用于顶部铝板中心处,激励幅值为[0.95,1.05] N,计算0~300 Hz频域范围声腔观测点的声压值。
由传统蒙特卡洛方法(MCM)的概率收敛特征知,随样本的不断增加,由随机抽样计算所得响应区间逐渐收敛于真实解。故本算例中经105随机抽样所得声压响应区间作为参考解,验证区间参数摄动方法精度。利用本文一阶区间参数摄动分析方法(FIPPM)及高阶区间参数摄动分析方法(HIPPM)求解含不确定参数的结构-声耦合有限元方程,观测点声压范围上界(UB)、下界(LB) 及相对误差见表1。由表1看出,高阶摄动方法相对误差远小于一阶摄动方法,表明在求矩阵逆过程中,通过保留Neumann展式的部分高阶项可有效提高参数摄动方法计算精度;对计算耗时而言,高阶摄动方法程序运行时间稍高于一阶摄动方法,复杂问题会更明显。考虑高阶摄动方法对计算精度的有效改善,运行时间稍长完全可接受。
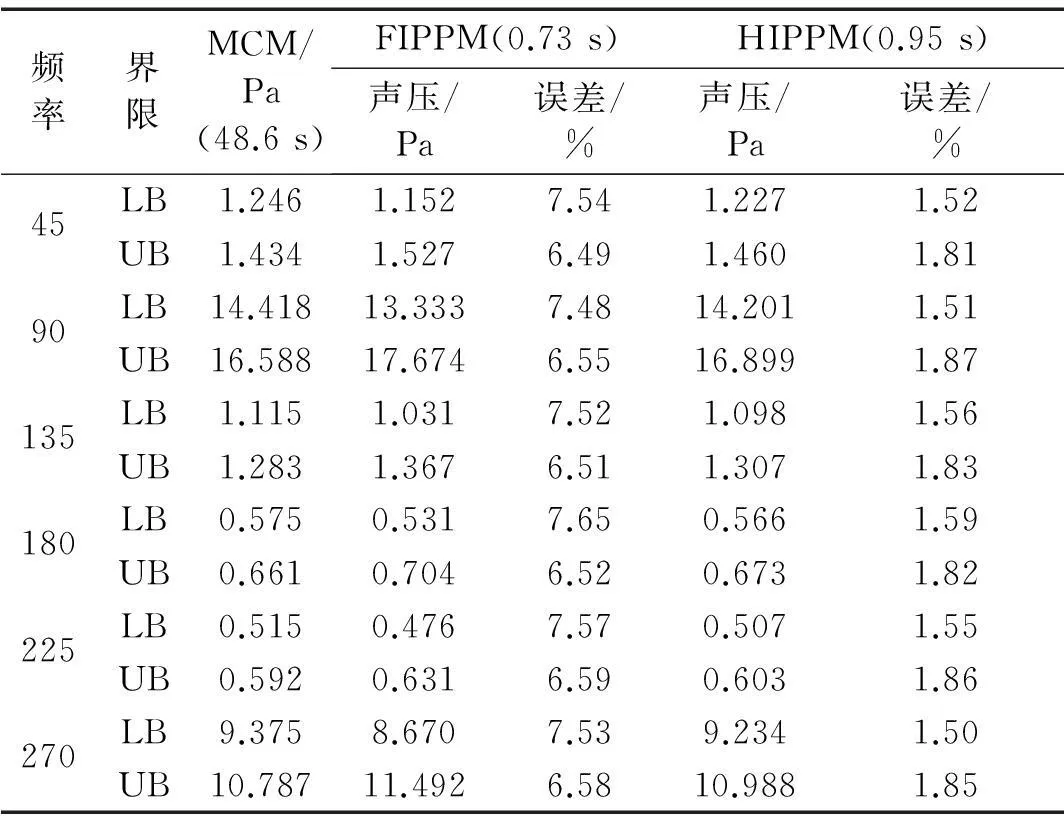
表1 声压幅值区间界限及相对误差
在0~300 Hz内,由三种方法计算所得声压幅值区间见图3。与一阶摄动方法结果相比,高阶摄动方法在整个频域范围内的频响区间均较小。与蒙特卡洛模拟所得参考值相比,高阶摄动方法仍存在一定区间扩张,但差别较小。精度要求不太高时,高阶摄动方法所得结果完全可信,且可有效减少大量随机抽样所致计算耗费,从而有效提高计算效率。
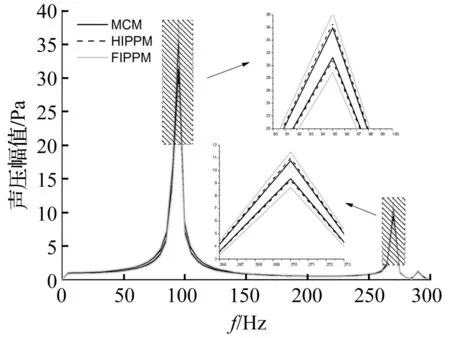
图3 0~300 Hz频域内声压幅值范围 Fig.3 Bounds of the sound pressure amplitude in the frequency band 0~300 Hz
5结论
(1)兼顾系统自身参数及外载荷非概率不确定性,利用区间变量对不确定参数定量化,充分考虑弹性结构及内部声场的耦合作用,建立含区间参数的结构-声耦合系统动力学平衡方程;
(2)将区间摄动理论与有限元计算方法相结合,提出快速求解系统响应范围的区间参数摄动分析方法。通过采用改进的Taylor展式及保留Neumann级数中的部分高阶项,可有效提高计算精度;
(3)长方体密闭舱室模型计算结果表明,由于在系数矩阵求逆过程保留了Neumann级数的部分高阶项,本文所建高阶摄动方法所得较传统一阶摄动方法精度更高的声压范围,可有效减少蒙特卡洛模拟带来的计算耗费;
(4)本文研究的不确定数值计算方法不仅适用于声场预测,亦为不确定结构静/动力学响应分析提供新思路。
参考文献
[1]陈馨蕊, 郝志勇, 杨陈, 等. 结构-声耦合法在汽车仪表板隔声性能仿真分析中的应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2009, 28(8): 154-157.
CHEN Xin-rui, HAO Zhi-yong, YANG Chen, et al. Simulation on sound insulation performance analysis of automotive dash by using structural-sound interaction method [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2009, 28(8): 154-157.
[2]Li S. A state-space coupling method for fluid-structure interaction analysis of plates [J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 118(2): 800-805.
[3]Raveendra S T. An efficient indirect boundary element technique for multi-frequency acoustic analysis [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1999, 44(1): 59-76.
[4]James K R, Dowling D R. A probability the density function method for acoustic fielduncertainty analysis [J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 118(5): 2802-2810.
[5]Finette S. A stochastic response surface formulation of acoustic propagation through anuncertain ocean waveguide environment [J]. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2009, 126(5): 2242-2247.
[6]Liu B S, Zhao G Z. PEM based sensitivity analysis for acoustic radiation problems of random responses [J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2010,132(2): 0210121-02101211.
[7]王冲, 邱志平, 吴迪, 等. 结构-声场耦合系统区间鲁棒优化设计[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(17): 8-13.
WANG Chong, QIU Zhi-ping, WU Di, et al. Interval robust optimization of a coupled structural-acoustic system [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(17): 8-13.冲, 邱志平, 吴迪, 等. 结构-声场耦合系统区间鲁棒优化设计[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(17): 8-13.
WANG Chong, QIU Zhi-ping, WU Di, et al. Interval robust optimization of a coupled structural-acoustic system [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(17): 8-13.
[8]Edgecombe S, Linse P. Monte carlo simulation of two interpenetrating polymer networks: structure, swelling and mechanical properties [J]. Polymer, 2008, 49(7):1981-1992.
[9]Qiu Z P, Xia Y Y, Yang J. The static displacement and the stress analysis of structures with bounded uncertainties using the vertex solution theorem [J]. Computer Method in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 196: 4965-4984.
[10]Qiu Z P, Chen S H, Elishakoff I. Bounds of eigenvalues for structures with an interval description of uncertain-but-non-random parameters [J]. Chaos Solitons & Fractals, 1996, 7(3): 425-434.
[11]Xia B Z, Yu D J, Liu J. Interval and subinterval perturbation methods for a structural-acoustic system with interval parameters [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2013, 38: 146-163.
[12]Chen S H, Ma L, Meng G W, et al. An efficient method for evaluating the natural frequency of structures with uncertain-but-bounded parameters [J]. Computers and Structures, 2009, 87(9/10):582-590.


