Failure analysis for spindle system of CNC machine tools based on FMECA
Li-tie ZHANG,Li-da ZHU,(Department of Chemical Engineering Mechanics,Jilin Vocational College Of Industry and Technology,Jilin 3003,China)(College of Mechanical Science and Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 300,China)
Failure analysis for spindle system of CNC machine tools based on FMECA
Li-tie ZHANG1,Li-da ZHU1,2
(1Department of Chemical Engineering Mechanics,Jilin Vocational College Of Industry and Technology,Jilin 130013,China)
(2College of Mechanical Science and Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China)
The spindle system is the key subsystem of CNC machine tools,it has lots of failure and has comparison of a single failure phenomenon.Therefore,failure phenomenon often cannot be used to failure diagnosis and troubleshooting.In this paper,FMECA analysis methods was used,to determine the failure mode and causes of the components of the spindle system of CNC machine tools,and further calculate the damage degree of each component.Finally,the damage degree provides the reference for equipment repair strategy.
CNC Machine tools,FMECA,Spindle system
Hydromechatronics Engineering
http://jdy.qks.cqut.edu.cn
E-mail:jdygcyw@126.com
1 Introduction
CNC machine tools is a complex repairable system[1],spindle system is the key subsystems of CNC machine tools.The performance of spindle system directly affects the performance of the machines,and the motion accuracy directly affects machining accuracy.When the spindle system fails,it has lots of failure and has comparison of a single failure phenomenon.The common failure include not turn the spindle,spindle jog,not ATC,servo alarm,PLC alarm,hydraulic system alarm,lack of precision,spindle noise,crashes etc.The failure may be structural design problems,operational problems,programming problems and maintenance problems.The factors causing the failure are complex,and involve many technologies,so the basis of fault diagnostics and troubleshooting can not is the simply Symptom.The characteristics of the spindle system failure are more variety,troubleshooting difficult,thus study failure modes and causes of failure,to determine the extent of damage each component part,which has targeted the establishment of CNC spindle repair strategy is important.
FMECA is Failure Modes,Effects and Criticality A-nalysis,including fault mode and effect analysis(FMEA)and Hazard Analysis(CA).FMECA is a bottom-upsummarizedanalysismethodwhichis classed by the severity of the failure mode and probability of occurrence of the failure[2].The use of FMECA is found the weak link of production that include in production design,product and operate. FMECA can also provide evidence for R(reliability),M(maintainability),S(security),T(testability),S(protection of property).FMECA is an important method in many of engineering that used to reliability design,design optimization and failure analysis.For example,improved FMECA is used to analysis the dangers of the CNC tool post[3-4].
In this paper,studies using quantitative analysis of failure modes occurred actually,the cause and its impact during use of the spindle system of the CNC machine tools,FMECA analysis method is used to determine the extent of damage of the components of the spindle system.Finally,FMECA analysis method provides the evidence for the maintenance strategy of the spindle system.
2 A spindle system failure analysis
In this paper,studies by 17 CNC machine tools,we obtained the relevant maintenance information of the spindle system of CNC machine tool tools based on the collate data of 5 years of maintenance information. The spindle system failure is analyses on the basis of the collate data.
2.1 Fault location analysis
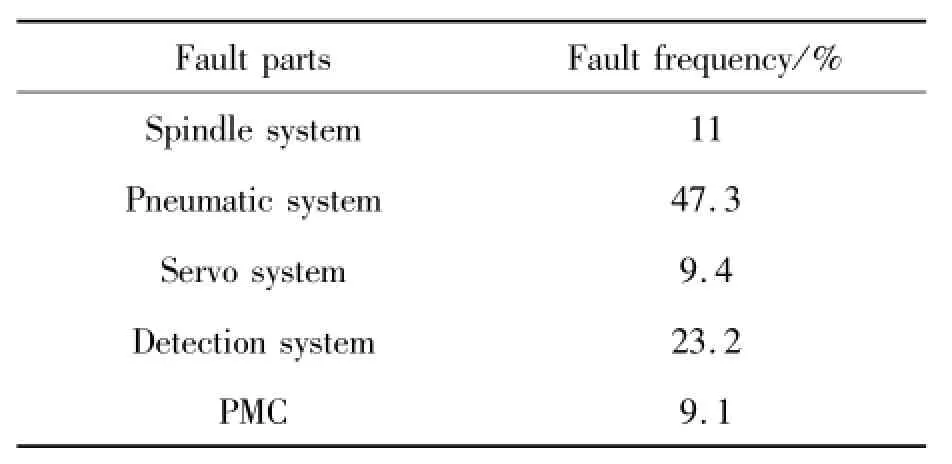
After analysis,fault location and frequency spindle system are shown in Table 1.
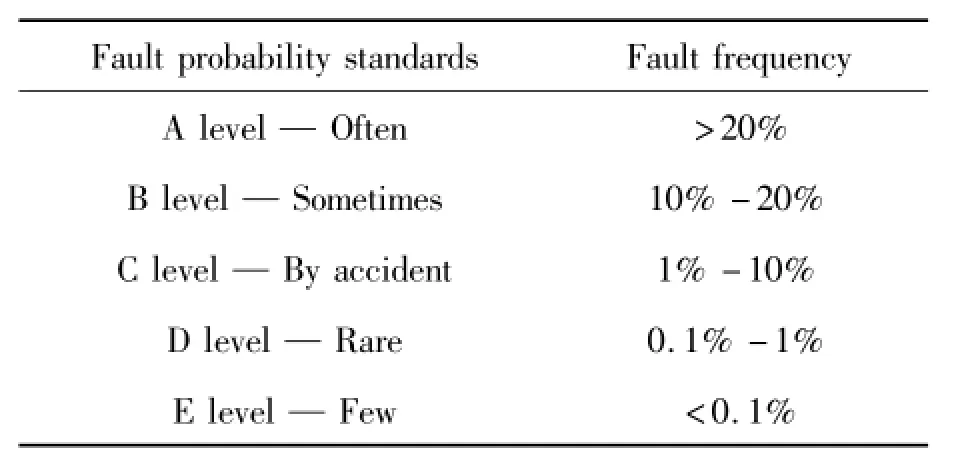
Analysis of the data in Table 1,based on the dividing the standard of the failure probability level(Table 2)can obtains the following conclusions.
TabIe1 FauIt Iocation and frequency of a spindIe system
TabIe2 FauIt probabiIity grading standards
1)The pneumatic system is the most frequent site of failure,its failure as high as 47.3%,and failure level is grade A,the possibility of failure was significantly higher than other four-part,the failure frequency of the detection system came in second place,the proportion of failure is 23.2%,the same as level-A. Therefore,there must be targeted to develop maintenance strategies to ensure the normal operation of the pneumatic system.
2)The proportion of the failure of the spindle mechanical structures were about 11%and the failure level is grade B that sometimes occurs.
3)The proportion of failure of the servo system and the PMC were 9.4%,9.1%,the failure level is grade C that occurs occasionally.
2.2 Failure mode and cause analysis
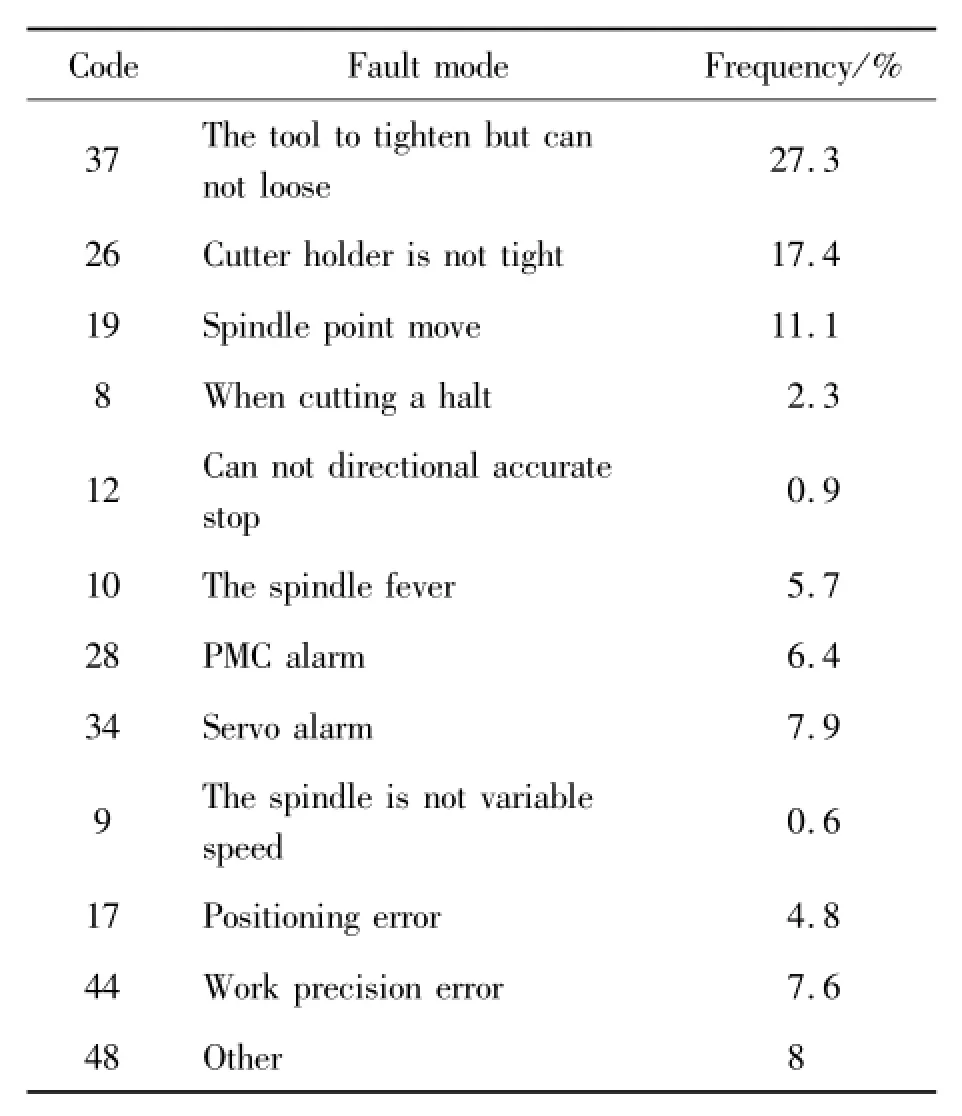
After analysis above maintenance data,failure mode of the spindle system as shown in Table 3.
From the analysis of Table 3,the main three kind of spindle system fault mode is the tool too tighten but can not loose,cutter holder is not tight and Spindle point move.The three fault modes accounted for 55.8%of the total.Of the entire fault mode,the tool to tighten but can not loose occurs most frequently,accounts for about 27.3%of the total fault.
From Table 4,aging,stuck and loose is the main cause of failure,the cause of the three 38.2%of the total.Failures caused by scratch,the gap is too large,the gap is too small are fewer.
TabIe3 SpindIe system fauIt mode and frequency
From the analysis of Table 3,the main three kind of spindle system fault mode is the tool too tighten but can not loose,cutter holder is not tight and Spindle point move.The three fault modes accounted for 55.8%of the total.Of the entire fault mode,the tool to tighten but can not loose occurs most frequently,accounts for about 27.3%of the total fault.
The cause of the fault and frequency are shown in Table 4.

TabIe4 SpindIe system fauIt causes and frequency
Comprehensive analysis of the fault location,failure modes,failure reasons of spindle system,the following conclusions.
1)Pneumatic parts is the highest frequency failure location of spindle system failure,external manifestations is the tool folder is not tight,loose not open to intensify.Secondly,the detection system failure is greater,the external manifestations is alarm,no tool change,spindle jog.
2)The most important failure mode of Spindle system is tools too intensify to loose,the main cause of such failures include:pneumatic accessories aging,stroke cylinder is not in place,the seal component aging,lack of pressure,the detection element loosening.
3)Servo system,PMC and other electrical control system failure is mainly causes by relay malfunction,bad servo signal detection system,interference,brake loose joints shedding,pollution and so on.
4)Failure of the detection system consists of sensors too loose,aging,interference,component damage,moisture short,pollution and other causes.
5)Failure of the mechanical structure included overload,poor lubrication,improper gap adjustment,position limit switch is loose,and parts wear parts,improper operation.
3 Spindle systems hazard analysis
In this paper,the criticality of the failure system components is the basis to formulate maintenance strategy.The spindle system of hazard analysis that is based on the FMEA is the key step for the quantitative treatment of the component failure.Its purpose is research on the harm degree of failure consequence according to the comprehensive influence of severity level or the probability of each failure mode.
According to the analysis required,each part of the spindle system and criticality provides as follows:Spindle mechanical structures(CR1),pneumatic system(CR2),servo system(CR3),the detection system(CR4),PMC(CR5).
The criticality can be formulated components failure modes of failure occurred in a calculation:
CRij=αijβijλi(1)
Thus the part i for the criticality of the spindle system is:
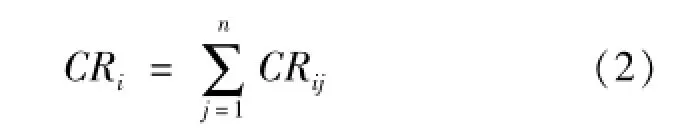
In light of this:

In the equation:n is the parts of i's failure mode number;αijis the parts of n the probability of failure mode with j lead to fault,that is fault probability;βijfor part i to failure mode j when failure occurs the probability of failure at the next higher level,about βijin international draft regulations are shown in Table 5;λiis a basic failure probability of parts i,In this paper,take λimean failure rate data analysis,expressed in λi,values for parts i total number of fault occurring in t time to time t.

TabIe5 The internationaI draft reguIations of βij
All damage to the spindle system is shown in Table 6.
From Table 6,in sorting for the damage are:spindle system CR2(0.005 4)>detection system CR1(0.000 738>PMC CR5(0.000 603)>Servo system CR3(0.000 504).

TabIe6 Each part of the spindIe system’s hazard degree
4 Conclusions
In this paper,we analysis the failure modes,the failure cause of spindle system,and the criticality of the components by using FMECA method.Case study showed that the highest criticality is pneumatic system,and the second criticality is detection system. Thus,it is necessary to routine maintenance.We can take preventive maintenance strategy,the mechanical structure of the spindle must be strengthened the routine maintenance and inspection,servo systems and PMC maintenance strategy can be maintenance afterwards.
[1]SHEN Gui-xiang,SHAO Na,Zhang Ying-zhi,etal.Reliability evaluation of numerically-controlled machine tool based on extenics theory[J].Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition,2011,41(1):106-109.
[2]JIA Xin-zhi,AI Dong-mei,QIU Cheng,etal.CK7815 Nc machine tool fault analysis[J].Manufacturing technology and machine tools,2000(5):57-58.
[3]ZHANG,Ying-zhi ZHENG Shan,SHEN Gui-xiang,etal. Criticality analysis for CNC turret adopting importance and fuzzy reasoning[J].Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition,2012,42(5):1157-1161.
[4]SHEN Gui-xiang,LI Huai-yang,ZHANG Ying-zhi,etal. Failure analysis of turret system of NC lathe[J].MACHINE TOOL&HYDRAULICS,2011,10,39(19):126-129.
基于FMECA的数控机床主轴系统故障分析
张李铁1,朱立达1,2
1.吉林工业职业技术学院化工机械系,吉林 130013
2.吉林大学机械科学与工程学院,吉林长春 130022
数控机床主轴系统是数控机床的关键子系统,其故障较多,而每次故障现象又比较单一,因此,单纯通过故障现象往往不能作为故障诊断和排除的依据。应用FMECA分析方法,分析数控机床主轴系统各组成部分的故障模式及故障原因,并进一步计算各组成部分的危害程度,得到的危害程度为制定设备维修策略提供了参考。
数控机床;FMECA;主轴系统
10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2015.12.024Document code:A
TH17
1 December 2014;revised 12 February 2015;accepted 1 March 2015
*Corresponding author:Li-tie ZHANG,Associate professor,
Postgraduate.E-mail:Zhanglitie1967@163.com
- 机床与液压的其它文章
- Comparative study between the single frequency and synchronous double frequency induction hardening technique for gear
- Finite element simulation of different surface micro-pits textures cutting tool strength based on ANSYS/Workbench
- Design of SMA actuator of stem structure for flower robot
- Research and optimization on the venturi tube dynamic throttling element of new flowmeter
- Study on the defects and improvement of sequential function chart
- Design of quality traceability system for a kind of electromechanical products based on OPC

