芳酰腙和麦芽酚混合配体钒(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、表征、晶体结构及其类胰岛素活性
贺淼 焦庆祝*, 陈相飞 李健 陈杰 盛桂华 由忠录*,
(1辽宁师范大学化学化工学院,大连116029) (2山东理工大学生命科学学院,淄博255049)
芳酰腙和麦芽酚混合配体钒(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、表征、晶体结构及其类胰岛素活性
贺淼1焦庆祝*,1陈相飞2李健2陈杰2盛桂华2由忠录*,1
(1辽宁师范大学化学化工学院,大连116029) (2山东理工大学生命科学学院,淄博255049)
制备了2个钒配合物[VOLL1](1)和[VOLL2](2),其中L为N′-(3,5-二溴-2-羟基苯甲基)-3-甲基苯甲酰肼,L1为甲基麦芽酚,L2为乙基麦芽酚。通过物理化学方法和单晶X-射线衍射对配合物的结构进行了表征。在每个配合物中,钒原子都是由来自配体L中的3个配位原子,来自L1或L2中的2个配位原子,以及1个氧基配体进行配位的,形成八面体配位构型。将配合物通过灌胃对正常的大鼠和四氧嘧啶糖尿病大鼠给药2周时间,结果表明这2个配合物在剂量为10.0和20.0 mgV·kg-1时可以显著降低四氧嘧啶糖尿病大鼠的血糖值,而正常大鼠的血糖值却没有改变。
钒配合物;芳酰腙;晶体结构;类胰岛素活性
Since1980s,inorganicvanadiumsaltsand vanadium complexes with various ligands have been reported to possess potent pharmacological effects of insulin-mimetic activity[1-4].Studiesindicated that vanadium compounds improve not only hyperglycemia in human subjects and animal models of typeⅠdiabetes but also glucose homeostasis in typeⅡdiabetes[5-6].However,the inorganic vanadium salts are considered as less active and more toxic.In order to reduce the side effects of inorganic vanadium salts, vanadium complexes have received particular attention and demonstrated to be effective[7-9].Schiff bases play important role in the development of coordination chemistry related to their biological properties.Several vanadium complexes derived from Schiff bases have shown to normalize blood glucose level with high efficiency and low toxicity,even at low concentration[10-11].Schiff bases with hydrazone type are particular interesting due to their biological properties[12-16]. In addition,vanadium complexes with maltol ligands such as bis(maltolato)oxovanadium(Ⅱ)(BMOV)and bis (ethylmaltolato)oxovanadium(Ⅱ)(BEOV)have been proved to possess effective insulin enhancing activity[17-19].In order to explore novel material with effective insulin-likeactivity,inthepresentwork, aroylhydrazone and maltol ligands were combined together by coordinating to V atom.Two vanadium complexes,[VOLL1](1)and[VOLL2](2),where L is the dianionic form ofN′-(3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3-methylbenzohydrazide,and L1and L2are the monoanionic form of methylmaltol(HL1)and ethylmaltol(HL2),respectively(Scheme 1),have been prepared and studied on their insulin-like activity to both normal and alloxan-diabetic mices.

Scheme 1
1Experimental
1.1 Materials and measurements
Starting materials,reagents and solvents were purchased from commercial suppliers with AR grade, and used without purification.HL1and HL2were purchased from Haiqu Chemical Company(Shanghai). Elemental analyses were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 240C elemental analyzer.IR spectra were recorded on a Jasco FT/IR-4000 spectrometer as KBr pellets in the 4 000~400 cm-1region.UV-Vis spectra were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer Lambda 900 spectrometer.1H NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker spectrometer at 300 MHz.
1.2 Synthesis of H2L
3,5-Dibromosalicylaldehyde(2.80 g,0.01 mol) and 3-methylbenzohydrazide(1.50 g,0.01 mol)were reacted in 50 mL methanol.The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 h to give a clear colorless solution.The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to give colorless solid,which was recrystallized from ethanol to give crystalline product of H2L.Yield 83%. Anal.Calcd.for C15H12Br2N2O2(%):C,43.7;H,2.9;N, 6.8.Found(%):C,43.5;H,3.1;N,6.7.IR data(cm-1): 3 376(m),3 212(w),1 653(vs),1 600(s),1 541(s), 1 435(s),1 340(m),1 281(s),1 217(m),1 159(m), 1 021(m),951(m),861(w),808(m),739(w),679 (m),633(w),558(w).UV(λ/nm,ε/(L·mol-1·cm-1)): 293,2.08×104;302,1.90×104;338,8.73×103.1H NMR(300 MHz,DMSO-d6):δ 12.76(s,1H,OH), 12.50(s,1H,NH),8.53(s,1H,CH=N),7.84~7.74 (m,4H,ArH),7.45(d,2H,ArH),2.41(s,3H,CH3).
1.3 Synthesis of the complexes
Complexes 1 and 2 were prepared by the same method as described here.A methanolic solution(30 mL)of VO(acac)2(0.27 g,1.0 mmol)was added to a methanolic solution(20 mL)of H2L(0.41 g,1.0 mmol) and methylmaltol(0.13 g,1.0 mmol)for 1 or ethylmaltol(0.14 g,1.0 mmol)for 2,with stirring.The mixtures were stirred at room temperature for 30 min to give deep brown solution.The resulting solution was allowed to stand in air for a few days until three quarters of the solvent was evaporated.Brown blockshaped single crystals of the complexes,suitable for X-ray single crystal diffraction were formed at the bottom of the vessel.The crystals were isolated by filtration,washed three times with cold methanol and dried in air.Yields:61%(1)and 73%(2).
1:Anal.Calcd.for C21H15Br2N2O6V(%):C,41.9; H,2.5;N,4.7.Found(%):C,42.1;H,2.6;N,4.6.IR data(cm-1):1 609(s),1 595(s),1 529(s),1 430(m), 1 354(m),1 264(m),1 196(s),1 039(w),976(s),928(w),860(w),825(w),728(s),650(m),595(w), 479(m),437(w).UV(λ/nm,ε/(L·mol-1·cm-1)): 280,2.05×104;345,8.06×103;456,4.77×103.
2:Anal.Calcd.for C22H17Br2N2O6V(%):C,42.9; H,2.8;N,4.5.Found(%):C,42.8;H,2.7;N,4.7.IR data(cm-1):1 608(s),1 595(s),1 529(s),1 433(m), 1 354(m),1 264(m),1 198(s),1 027(w),976(s), 925(w),863(w),825(w),771(w),725(s),652(m), 587(w),556(w),475(m),446(w).UV(λ/nm,ε/ (L·mol-1·cm-1)):280,2.31×104;337,6.78×103;456, 5.23×103.
1.4 X-ray crystallography
Diffraction intensities for complexes 1 and 2 were collected at 298(2)K using a Bruker SMART 1000 CCD area-detector diffractometer with Mo Kα radiation(λ=0.071 073 nm)and Cu Kα radiation(λ= 0.154 178 nm),respectively.The collected data were reduced with SAINT[20],and multi-scan absorption correction was performed using SADABS[21].Structures of the compounds were solved by direct methods and refined against F2by full-matrix least-squares method using SHELXTL[22].All of the non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically.All hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms.Crystallographic data for the complexes are summarized in Table1 .Selected bond lengths and angles are given in Table2 .
CCDC:1059791,1;1059793,2.

Table1 Crystal data and structure refinement of complexes 1 and 2

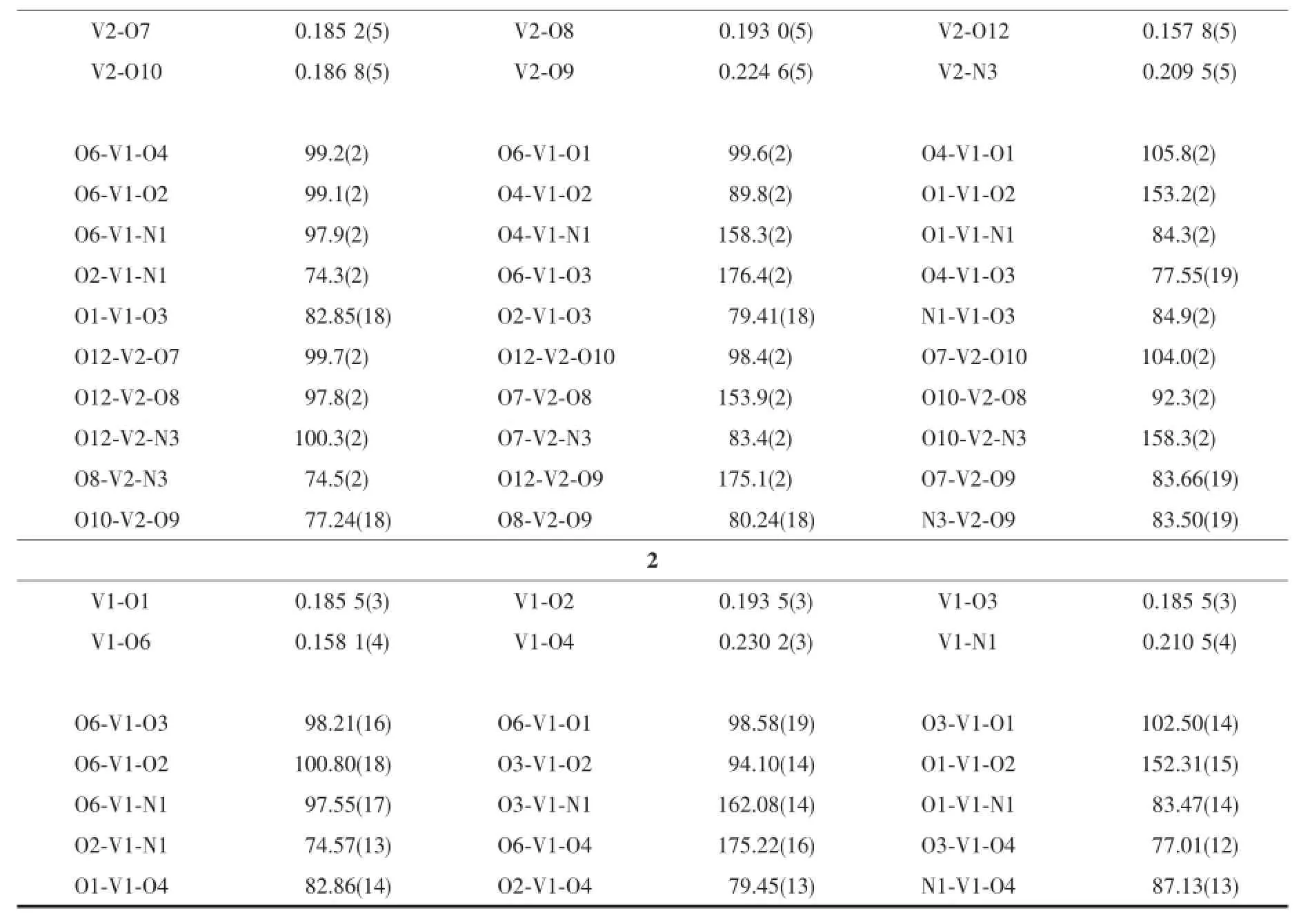
Table2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)for the complexes
Continued Table1
1.5 Glucose-lowering assay
The animal study was carried out according to the guidelines of Animals Ethics Committee.Male Kunming mices,weighing about 25~32 g,were obtained from Experimental Animal Center,Shandong LukangPharmaceuticalCo.,LtdofChina,and maintained on a light/dark cycle.All animals were allowed free access to food and water.Temperature and relative humidity were maintained at 24℃and 50%.Mices were acclimatized for seven days prior to induction of diabetes.All care and handling of animalswereperformedwiththeapprovalof Institutional Authority for Laboratory Animal Care. Diabetes was induced by a single intra-peritoneal injection of freshly prepared alloxan(200 mg·kg-1body weight)in 0.9%saline.The control mices were injected with an equal volume of vehicle.After seven days,blood was collected from the tail vein and serum samples were analyzed for blood glucose.Animals showing fasting(12 h)blood glucose higher than 11.1 mmol·L-1were considered to be diabetic and used for the study.
The experimental animals were randomly divided into six groups with six mices each according to the blood glucose.Group 1,normal control group:normal mices treated with 0.5%carboxymethylcellulose (CMC).Group 2~4,treated normal group:normal mices treated with 20 mgV·kg-1vanadium complexes. Group 5,diabetic control group:alloxan diabetic mices treated with 0.5%CMC.Group 6~11,treated diabetic group:alloxan diabetic mices treated with vanadium complexes at dose of 10 and 20 mgV·kg-1by intragastrical administration.The complexes were administered as suspensions in 0.5%CMC.The substances were administered intragastrically once a day at the volume of 10 mL·kg-1for two weeks.
Throughout the experimental period,the body weight of mices was monitored daily.Blood samples were obtained from the tail vein of the mices and blood glucose levels were determined with an Accu-Chek blood glucose monitor(Roche Diagnostics GmbH,Mannheim,Germany).
2Results and discussion
The aroylhydrazone compoundN′-(3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3-methylbenzohydrazidewas readily prepared by condensation reaction of 3,5-dibromosalicylaldehyde with 3-methylbenzohydrazide in methanol.The complexes were prepared by reaction of equimolar quantities of the aroylhydrazone,VO (acac)2and maltol ligands in methanol.Crystals of the complexes are stable in open air at room temperature. Elemental analyses are in good agreement with the chemical formula proposed for the compounds.
2.1 Structure description of the complexes
Fig.1 and 2 give perspective view of complexes 1 and 2 together with the atomic labeling system.The asymdium complex molecules.Structures of the complexes are very similar except for the slight difference of the maltol ligands,viz.methylmaltol for 1 and ethylmaltol for 2.The V atoms in the complexes are in octahedral coordination,with the phenolate O, imino N,and enolate O atoms of L,and the hydroxy O atom of the maltol ligand defining the equatorial plane,and with one oxo O and the carbonyl O atom of the maltol ligand locating at the axial positions.The V atoms deviate from the least-squares planes defined by the equatorial atoms by 0.030 1(1)nm for 1 and 0.029 2(1)nm for 2.The coordinate bond lengths in both complexes are similar to each other,and also comparable to those observed in vanadium complexes witharoylhydrazone ligands[23-25].Distortion of the octahedral coordination can be observed from the coordinate bond angles,ranging from74.3(2)°to 105.8(2)°for 1,and from 74.6(1)°to 102.5(1)°for 2, for the perpendicular angles,and from 153.2(2)°to 176.4(2)°for 1,and from 152.3(2)°to 175.2(2)°for 2, for the diagonal angles.The dihedral angles between the benzene rings of the aroylhydrazone ligands are 16.1(3)°for the V1 molecule and 4.7(3)°for the V2 molecule for 1,and 8.1(4)°for 2.

Fig.1 Molecular structure of 1 showing the atomnumbering scheme

Fig.2 Molecular structure of 2,showing the atomnumbering scheme
2.2 IR and UV-Vis spectra
The medium and broad absorption centered at 3 376 cm-1in the spectrum of H2L substantiates the presence of phenol group,which is absent in the complex.The sharp band indicative of the N-H vibration is located at 3 212 cm-1,and the intense band indicative of the C=O vibration is located at 1 653 cm-1in the spectrum of H2L,which are absence in the complexes,indicating the enolisation of the amide functionality and subsequent proton replacement by the V atoms.The strong absorption bands at 1 600 cm-1for H2L and 1 609 cm-1for the complexes are assigned to the azomethine ν(C=N)[26].The typical absorption at 976 cm-1can be assigned to the V=O vibration[23].
Electronic spectra of H2L and the complexeswere recorded in 10-5mol·L-1in methanol and acetonitrile,respectively,in the range of 200~600 nm. In the UV-Vis region the complexes show bands at approximately 340 nm and weak bands at about 456 nm.The weak bands are attributed to intramolecular charge transfer transitions from the pπ orbital on the nitrogen and oxygen to the empty d orbitals of the metal[27].The intense bands observed at about 280 nm for the complexes and 293 nm for H2L are assigned to intraligand π-π*transitions[27].
2.3 Effects of complex on blood glucose in both normal and alloxan-diabetic mices
The complexes were administered intragastrically to both normal and alloxan-diabetic mices for two weeks.The results(Table3 )showed that both complexes had blood glucose-lowering effect at doses of 10.0 and 20.0 mgV·kg-1,could significantly decrease the blood glucose level in alloxan-diabetic mices,but the blood glucose level in the treated normal mices (20.0 mgV·kg-1by intragastrical admini-stration for two weeks)was not altered as compared with the untreated normal mices(P〉0.05).After two-week administration with the complexes,the blood glucose level was decreased compared with the diabetic control group (P〈0.05).During the experiment,themeanbody weight in alloxan-diabetic mices was lower than normalmices.Two-weekadministrationofthe complexes had no effect on the body weight in the diabetic group,compared with the diabetic control group(Table4 ).
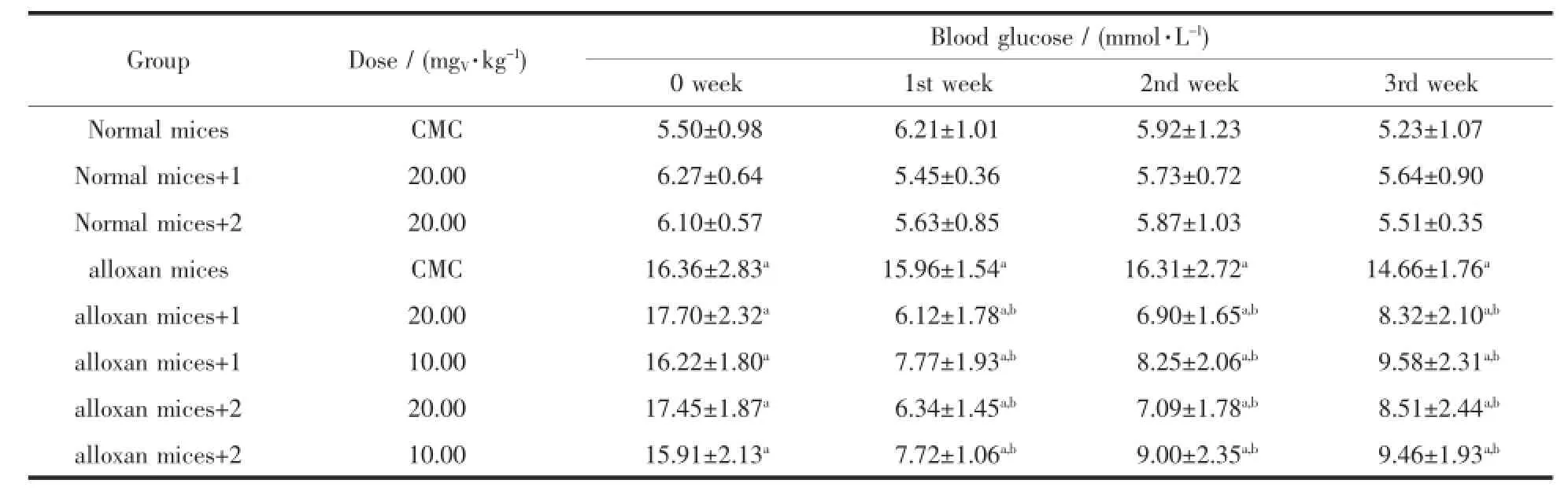
Table3 Effects of the vanadium complexes on blood glucose levels in both normal and diabetic mices*

Table4 Effects of the complexes on body weight of both normal and diabetic mices*
3Conclusions
The present study reports synthesis,characterization and crystal structures of two vanadium(Ⅱ)complexes withN′-(3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene) -3-methylbenzohydrazide and maltol mixed ligands.Methylmaltol and ethylmaltol as co-ligands are readily coordinate to the V atoms through the carbonyl and deprotonated phenol groups.The complexes have effectiveinsulin-likeactivityonalloxan-diabetic mices.Methylmaltol and ethylmaltol as coligands in the complexes have not obvious difference for the antidiabetic effect on alloxan-diabetic mices.
[1]Pillai S I,Subramanian S P,Kandaswamy M.Eur.J.Med. Chem.,2013,63:109-117
[2]Smee J J,Epps J A,Ooms K,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem.,2009, 103:575-584
[3]Sanna D,Micera G,Garribba E.Inorg.Chem.,2013,52:11975 -11985
[4]He L,Wang X S,Zhao C,et al.Metallomics,2014,6:1087-1095
[5]Crans D C,Trujillo A M,Pharazyn P S,et al.Coord.Chem. Rev.,2011,255:2178-2192
[6]Sheela A,Roopan S M,Vijayaraghavan R.Eur.J.Med. Chem.,2008,43:2206-2210
[7]Zhang Y,Yang X D,Wang K,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem.,2006, 100:80-87
[8]Dornyei A,Marcao S,Pessoa J C,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem., 2006,18:3614-3621
[9]Haratake M,Fukunaga M,Ono M,et al.J.Biol.Inorg.Chem., 2005,10:250-258
[10]Nejo A A,Kolawole G A,Opoku A R,et al.J.Coord.Chem., 2009,62:3411-3424
[11]Xie M J,Yang X D,Liu W P,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem., 2010,104:851-857
[12]Mendes I C,Botion L M,Ferreira,A V M,et al.Inorg.Chim. Acta,2009,362:414-420
[13]Rajitha G,Prasad K V S R G,Umamaheswari A,et al.Med. Chem.Res.,2014,23:5204-5211
[14]El-Sayed M A A,Abdel-Aziz N I,Abdel-Aziz A A M,et al. Bioorg.Med.Chem.,2011,19:3416-3424
[15]Horiuchi T,Chiba J,Uoto K,et al.Bioorg.Med.Chem.Lett., 2009,19:305-308
[16]Zhang M,Xian D-M,Li H-H,et al.Aust.J.Chem.,2012, 65:343-350
[17]Liboiron B D,Thompson K H,Hanson G R,et al.J.Am. Chem.Soc.,2005,127:5104-5115
[18]Thompson K H,Orvig C.J.Inorg.Biochem.,2006,100:1925 -1935
[19]Thompson K H,Lichter J,LeBel,C,et al.J.Inorg.Biochem., 2009,103:554-558
[20]Bruker,SMART and SAINT,Bruker AXS Inc.,Madison, 2002.
[21]Sheldrick G M.SADABS,University of Göttingen,Germany, 1996.
[22]Sheldrick G M.Acta Crystallogr.,2008,A64:112-122
[23]Sangeetha N R,Kavita V,Wocadlo S.J.Coord.Chem., 2000,51:55-66
[24]REN Jin-Qi(任晋琦),JIAO Qing-Zhu(焦庆祝),WANG Yi-Nuo(王艺诺),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2014,30(3):640-648
[25]ZHAO Yue(赵月),HAN Xiao(韩笑),ZHOU Xiao-Xia(周晓霞),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(无机化学学报),2013,29 (4):867-874
[26]You Z L,Xian D M,Zhang M.CrystEngComm,2012,14: 7133-7136
[27]Asgedom G,Sreedhara A,Kivikoski J,et al.J.Chem.Soc., Dalton Trans.,1996,1:93-97
Syntheses,Characterization,Crystal Structures and Insulin-Like Activity of Vanadium(Ⅱ)Complexes with Aroylhydrazone and Maltol Mixed-Ligands
HE Miao1JIAO Qing-Zhu*,1CHEN Xiang-Fei2LI Jian2CHEN Jie2SHENG Gui-Hua2YOU Zhong-Lu*,1
(1Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Liaoning Normal University,Dalian,Liaoning 116029,China)
(2School of Life Sciences,Shandong University of Technology,Zibo,Shandong 255049,China)
Two vanadium(Ⅱ)complexes,[VOLL1](1)and[VOLL2](2)(L=N′-(3,5-dibromo-2-hydroxybenzylidene)-3-methylbenzohydrazide,L1=methylmaltol,L2=ethylmaltol),have been prepared.The complexes have been characte-rized by physico-chemical methods and single crystal X-ray determination.The V atom in each complex is coordinated by three donor atoms of L,two donor atoms of L1or L2,and one oxo group,forming octahedral coordination.The complexes were administered intragastrically to both normal and alloxan-diabetic mices for two weeks.The biological activity results show that the complexes at doses of 10.0 and 20.0 mgV·kg-1,can significantly decrease the blood glucose level in alloxan-diabetic mices,but the blood glucose level in the treated normal mices was not altered.CCDC:1059791,1;1059793,2.
vanadium complex;aroylhydrazone;crystal structure;insulin-like activity
O614.51+1
A
1001-4861(2015)08-1590-07
10.11862/CJIC.2015.174
2015-04-16。收修改稿日期:2015-04-23。
辽宁省高校优秀青年人才支持计划(No.LR2014032)资助项目。*

