Research on polycondensation process of poly(aryl imino amide)s
JIAO Ya,ZHANG Lin,LIN Runxiong(1.Research Center of Laser Fusion,China Academy of Engineering Physics,Mianyang 61900,Sichuan,China;.Engineering Research Center of High Performance Polymer and Molding Technology of Ministry of Education,Qingdao University of Science and Technology,Qingdao 6604,Shandong,China)
Polyaramide(PARA),consisting of amide groups and aromatic rings,is a significant high performance polymer material.The rigidity framework and intensive intermolecular hydrogen-bond interaction of the polymer make it possess superior thermal stability and mechanical property[1-4].At the same time,the structural features of PARA make it hard to dissolve in common organic solvents.Its softening and melting temperature are extremely high,which make it very difficult to be processed[5-6].We have synthesized two novel heat-resistant polymers-poly(aryl imino-amide)s viapalladium-catalyzed C-N crosscoupling reaction of p-phenylenediamine,4,4′-diaminodiphenylether and 1,4-bis-(4′-bromobenzoyl)benzene.The introduction of N-H bond in the polymer chain makes it possible to form the same hydrogen-bond as the traditional PARA.But the density of the hydrogen-bond is slightly weakened and the flexibility of the polymer chain is strengthened,which keep the excellent thermal stability of the polymer when im-proving the polymer’s solubility in organic solvent[7-9].
Based on the synthesis and characterization of poly(aryl imino amide)s above,further researches of poly(aryl imino amide)s are carried out in this paper.Additionally,the optimal conditions of palladium-catalyzed C-N cross-coupling polycondensation reaction for obtaining poly(aryl imino amide)s are obtained.
1 Experimental section
1.1 Materials
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)-dipalladium(0)(Pd2(dba)3)and BINAP were purchased from Aldrich Chemical Company.p-Phenylenediamine,4-halobenzoyl chloride and sodium tert-butoxide were purchased from Acros Organics.The rest materials and reagents were obtained from different commercial sources and used without further purification.N,N′-bis(4-fluorobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine,N,N′-bis(4-chlorobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine,N,N′-bis(4-bro-mobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine and N,N′-bis(4-iodobenzoyl)-pphenylenediamine were synthetized prophase.
1.2 Synthesis of poly(aryl imino amide)s
A 100mL over-dried three-necked flask equipped with magnetic stirrer,a nitrogen outlet and inlet,and water-cooled condenser was charged with a mixture of N,N′-bis(4-halobenzoyl)-p-diphenylenediamine(10mmol),aromatic diamines(10mmol),tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0)(0.1mmol),2,2′-bis-(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl(0.30mmol),sodiumtert-butoxide(24mmol)and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone.The reaction mixture was flushed with high purity nitrogen.The flask was immersed in a 130℃ oil bath for 10-12 h.As the viscosity of the solution obviously going up,the resulting polymer solution was slowly cold to room temperature,then filtered,washed with methanol and water several times,and at last dried at 100℃ under vacuum.Taking N,N′-bis(4-bromobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine as an example,the synthetic route is shown as below(Fig.1).
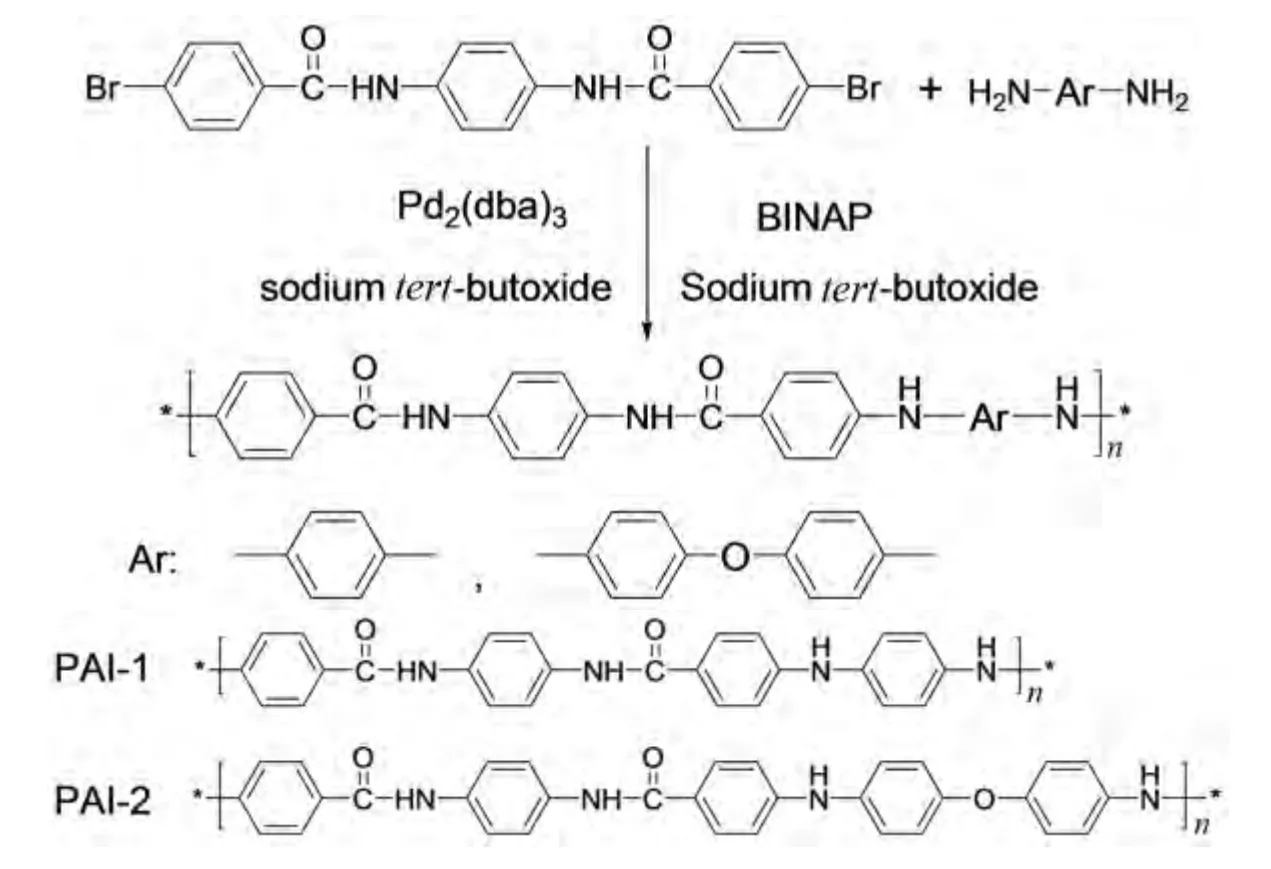
Fig.1 The synthesis of poly(aryl imino amide)s via Pd-catalyzed aryl amination
2 Results and disscussion
2.1 Effect of the species of halogen
Taking PAI-1as an example,we made Pd-catalyzed polycondensation of N,N′-bis(4-fluorobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine,N,N′-bis(4-chlorobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine,N,N′-bis(4-bromobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine and N,N′-bis(4-iodobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine with p-phenylenediamine.Four kinds of polymers were obtained.Comparison of their relative molecular weight is shown in Table 1.
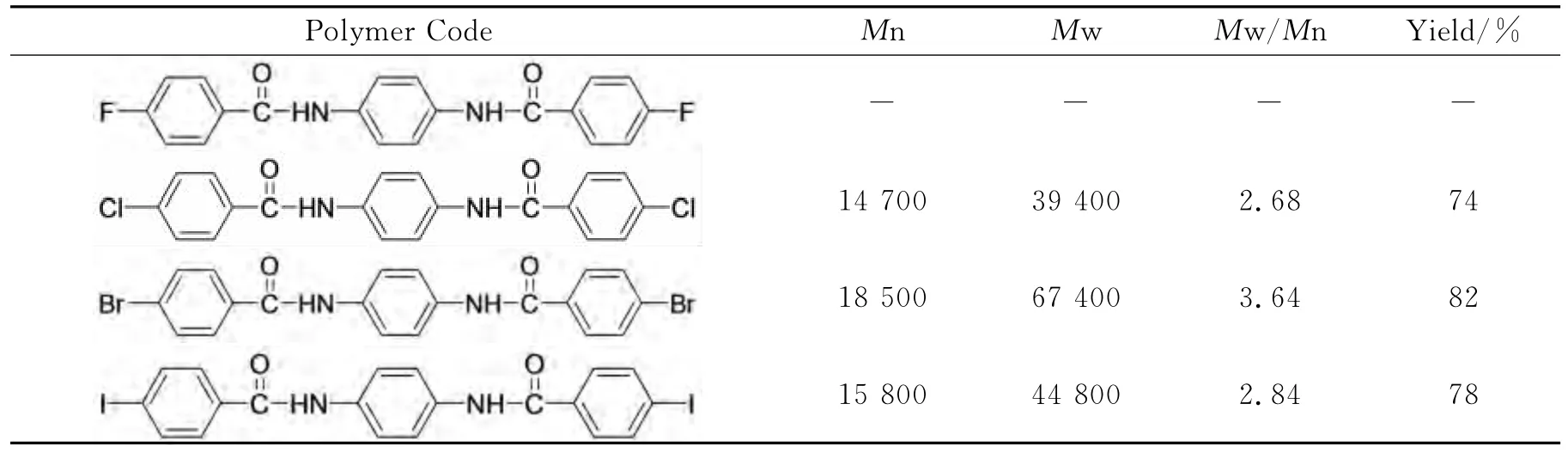
Table 1 The polymer weight and polydiapersity index(PDI)of poly(aryl imino amide)s
According to the measurement result,the polymer which uses N,N′-bis(4-bromobenzoyl)-pphenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine as monomers shows the largest relative molecular weight and yield the most.The relative molecular weights of polymers which are synthetized with N,N′-bis(4-chlorobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine,N,N′-bis(4-iodobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine are almost the same.But N,N′-bis(4-fluorobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine rarely reacts with p-phenylenediamine,though fluorine atom is easier to leave;with the advance of halogen atoms′electronegativity,the amination weakens.Moreover,the oxidation is restricted.So we choose N,N′-bis(4-bromobenzoyl)-p-phenylenediamine as the optimal monomer to react with aromatic diamines to obtain different kinds of poly(aryl imino amide)s.
2.2 Effect of solvent and concentration of the monomer
PAIs were obtained by solution polymerization.So the category of solvent we used would influence the relative molecular weight of the polymers.The solvent should be droped out of the reaction.And,both monomers and polymers should be well dissolved in the solvent.Taking PAI-1as an example,we did polycondensation in different solvents.As a result,the N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone is the optimal solvent for obtaining ideal relative molecular weight polymer.Moreover,concentration of the monomer is also an important factor which influences the relative molecular weight and distribution.The solubility of PAIs and dibromo monomer will decrease when the concentration of monomer is too thick.Thus,the relative molecular weight and distribution will be influenced;when the concentration of monomer is too thin,the reaction time will increase and the relative molecular weight will lower than that of the thick one.Still taking PAI-1for instance,we did polycondensation with different concentration of monomer under the same temperature and time.The results are shown in Fig.2.With the increase of the monomer concentration,relative molecular weight distribution of PAI-1gradually broadens,and relative molecular weight of PAI-1increases and then decreases after the first.Under condition of lower monomer concentration,the collision probability between the reactant functional groups is relatively smaller,which leads to relatively slower reaction rate,lower relative molecular weight and wider relative molecular weight distribution.On contrary,under condition of high monomer concentration,we got high reaction rate,large relative molecular weight and narrow distribution.Considering all above,we choose NMP as reaction solvent,and the optimal monomer concentration is 0.5 mol/L as preparing poly(aryl imino amide)s.
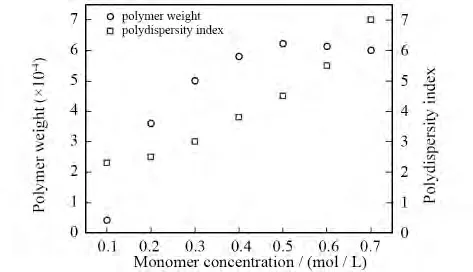
Fig.2 Effect of monomer concentration on polymer weight and PDI of PAI
2.3 Effect of temperature
The mechanism of palladium-catalyzed C-N cross coupling reaction of dibromo monomer and aromatic diamine is step-reaction.Generally,the heat generated by polycondensation is low.But its activation energy is relatively high.The polycondensation reaction temperature should be relatively high to enhance the reaction rate.But higher temperature may cause monomer volatilizing,thermolysis loss and oxidation of aromatic diamine.All above mentioned will lead to inequality of molar weight of the two functional groups.Then the two functional groups will bechance end-capping polymerization,so higher relative molecular weight compounds cannot be obtained.
In addition,the C-N cross coupling reaction of dibromo monomer and aromatic diamines is a balance reaction.We can check the change rate of equilibrium constant K to temperature,the value of ΔH and its gradient are negative.That is to say,the equilibrium constant decreases while the temperature increases.

So,when the reaction temperature is too low,the reaction rate will be very low or without reaction.But the equilibrium constant falls or comes into side reaction when the temperature is too high.For the optimal temperature of this reaction,taking PAI-1 for an example,we do a series of experiments under the same conditions except for temperature(Fig.3).Then we can see that the relative molecular weight distribution of the polymer broadens while the temperature increases,and the maximum value of relative molecular weight is derived under 130℃.
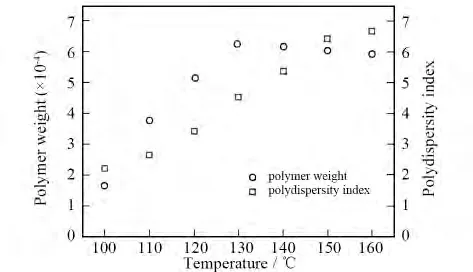
Fig.3 Effect of temperature on polymer weight and PD of PAI
2.4 Effect of the catalysis system
The reactivity of dibromo monomer and aromatic diamine is not good.So catalyst is needed to obtain polymer.Palladium-catalysis system which consists of catalyst and ligand is used in this reaction.There are different catalytic effects when different palladium catalysis systems are used.Two palladium catalyst,(Pd2(dba)3and Pd(OAc)2),and five kinds of ligand are investigated;taking PAI-1for instance,the molecular weight and distribution of PAI-1when we use different kinds of catalysis systems are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 shows that when using the organism combination of ligand(a)(BINAP)and Pd2(dba)3as catalysis system,the relative molecular weight of PAI-1is the biggest,while its relative molecular weight distribution is narrow relatively.Therefore,it is the most effective catalysis system to obtain poly(aryl imino amide)s.
The additive amount of palladium catalyst influences the relative molecular weight and distribution of PAIs directly.When the system lacks catalyst,the reaction of monomers can′t finish,and the relative molecular weight distribution broadens.The palladium catalyst is very expensive,which leads to the increase of both the cost of obtaining PAIs and the difficulty of separating the polymer and catalyst.Taking PAI-1as an example,we only change the amount of palladium catalyst with reaction condition remain unchanged,and the relative molecular weight and distribution of PAIs are as below(Fig.4).
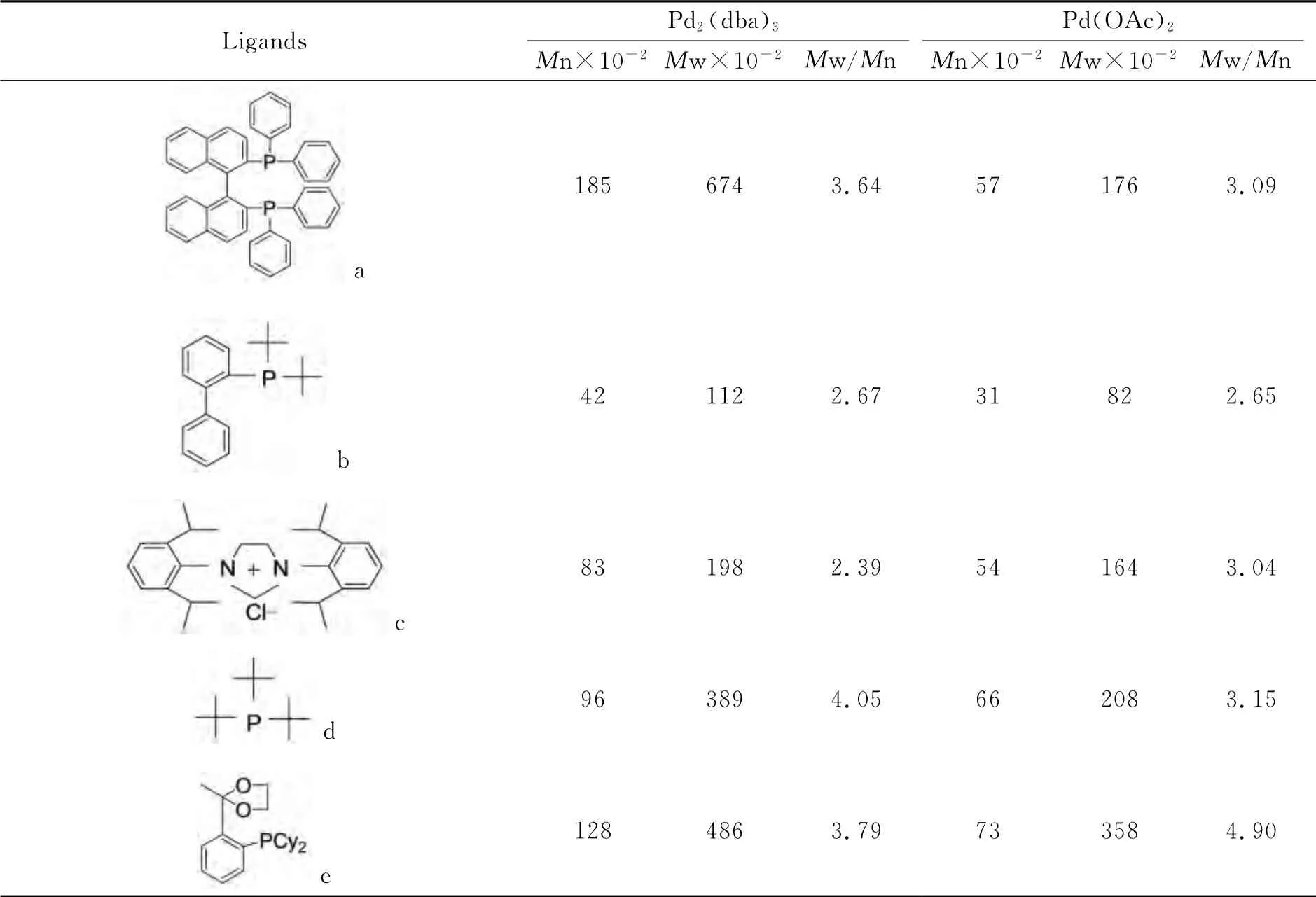
Table 2 The effect of catalyst system on polymer weight and PD of PAIs
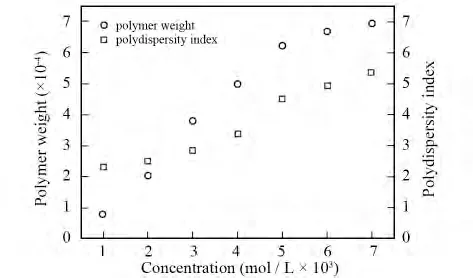
Fig.4 Effect of catalyst content on polymer weight and PD of PAI
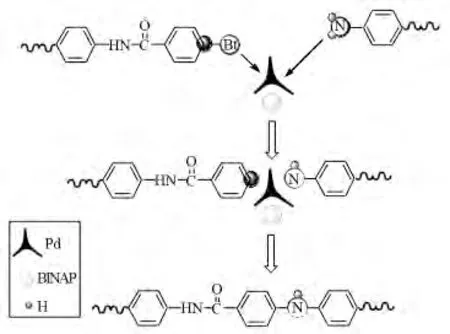
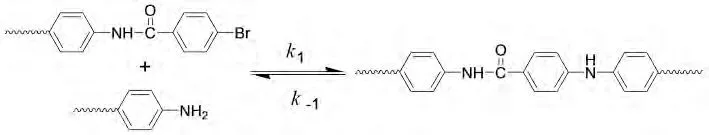
Fig.5 Palladium catalyst acts as an intermediary between the dibromides and diamines
According to Fig.4,both the relative molecular weight and the distribution of PAI-1go up with the increase of catalyst amount.Palladium catalysis system runs a C-N coupling function in the polymerization progress.As shown in Fig.5,it acts as a‘medium’.So the probability of the two functional groups(-Br and-NH2)combining with each other increases while the‘medium’amount increases.In macroscopic,the relative molecular weight increases.The additive amount of palladium catalyst can influence the Mw a little when it goes up to 0.05mmol.Otherwise,palladium catalyst is very expensive.Generally speaking,0.05 mmol palladium catalyst,that is to say the moleratio of catalyst and monomer is 1∶100,is best for the polycondensation reaction.
For getting the optimum volume ratio of palladium and ligand to obtain high relative molecular weight polymer,it needs to consider starting from the mechanism of palladium-catalyzed C-N crosscoupling reaction.We use 1,4-bis-(4′-bromobenzoyl)benzene and aromatic diamine as monomer,palladium as catalyst to synthetize the target product PAIs;this reaction belongs to a kind of catalytic amination reaction of arylene halides,and oxidation progress of 1,4-bis-(4′-bromobenzoyl)benzene to palladium catalyst is a part of the reaction mechanism.Otherwise,inducement makes for the para bromine substitution reaction of 1,4-bis-(4′-bromobenzoyl)benzene and electron donor(aromatic diamine).Firstly,BINAP and Pd2(dba)3form(BINAP)Pd(dba);Secondly,(dba)separates from(BINAP)Pd.Because of the oxidation of the dibromide compounds,(BINAP)Pd(dba)and bromide form a complex of palladium and bromide,the complex then form an amido complex with aromatic diamine in alkaline condition.Finally we obtained the target polymer by deacidize and expunction,and the palladium catalyst was regenerated at the same time.Fig.6 shows the particular reaction progress.
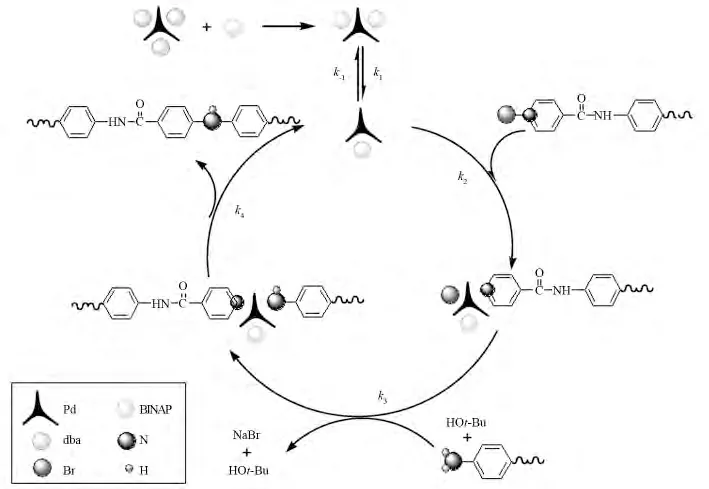
Fig.6 Pd/BINAP-catalytic cycle of amination of aryl bromides with diamines
By the palladium-catalyzed C-N cross-coupling reaction theory above,the catalyst which participates in the reaction cycle process is(BINAP)Pd.So the theoretical mole ratio of catalyst and ligand should be 1∶2if they would match each other one by one.But,due to the reversible reaction between(BINAP)2Pd and(BINAP)Pd,the two complexes coexist in the system.So,the practical mole ratio of Pd2(dba)3and ligand(BINAP)should be 1∶4 to 1∶2.To get the optimum mole ratio of them,taking synthesized PAI-1as an example,we did a series of contrast experiments by changing the additive amount of ligands while the additive amount of palladium(0.05 mmol)remains unchanged.Fig.7 shows the result.
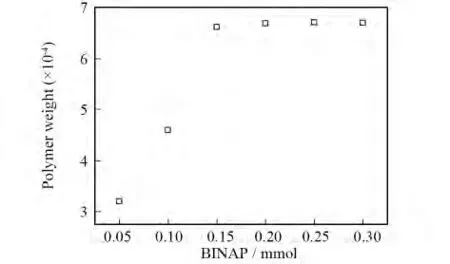
Fig.7 Effect of BINAP content on polymer weight of PAI
From Fig.7 we can see that when the amounts of ligand increase to 0.15 mmol,the relative molecular weight of PAI-1stop increasing.That is to say,when BINAP increases to 0.15 mmol,the redundant BINAP no longer participates in the polycondensation progress.Therefore,the optimal mole ratio of Pd2(dba)3and ligand(BINAP)is 1∶3 when obtaining PAIs.
3 Conclusions
In the condition of using palladium catalysis system Pd2(dba)3/BINAP as catalyst,1,4-bis-(4′-bromobenzoyl)benzene reacted with both p-phenylenediamine and 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl ether.Then two PAIs with different structures were obtained.Effect of the process conditions such as species of halogen monomer,solvent,concentration of the monomer,reaction temperature,the quantity and species of catalyst on PAIs′relative molecular weight and distribution were discussed.Then the experiments results show the polymer which uses 1,4-bis-(4′-bromobenzoyl)benzene and p-phenylenediamine as monomer has the biggest relative molecular weight and relatively higher productivity.In NMP solvent,the optimal concentration of the monomer is 0.5mol/L.The relative molecular weight could come to maximum value when the reaction temperature is 130℃.The optimal catalysis condition is the organism combination of palladium catalyst and ligand BINAP as catalyst system and their mole ratio is 1∶3.
[1]CHANG G J,YANG L,YANG J X,et al.Facile synthesis of soluble aromatic poly(amide amine)s via C-N coupling reaction:characterization,thermal,and optical properties[J].J Polym Sci Pol Chem,2013,51(22):4845-4852.
[2]ARUN A,DULLAERT K,GAYMANS R J.Structure and properties of mono-,di-,tri-and multiblock segmented copolymers with diamide hard segments[J].Macromol Chem Phys,2009,210(1):48-59.
[3]GARCIA J M,GARCIA F C,SERNA F,et al.Highperformance aromatic polyamides[J].Prog Polym Sci,2010,35:623-686.
[4]FINK J K.High performance polymers[M].William Andrew:NewYork,2008.
[5]LIOU G S,CHANG C W.Highly stable anodic electrochromic aromatic polyamides containing N,N,N′,N′-tetraphenyl-p-phenylenediamine moieties:synthesis,electrochemical,and electrochromic properties[J].Macromolecules,2008,41:1667-1674.
[6]LAURATI M,SOTTA P,LONG D R,et al.Dynamics of water absorbed in polyamides[J].Macromolecules,2012,45:1676-1687.
[7]SHENG S R,PEI X L,HUANG Z Z,et al.Novel soluble fluorinated aromatic polyamides derived from 2-(4-trifluoromethylphenoxy)terephthaloyl chloride with various aromatic diamines[J].Eur Polym J,2009,45:230-236.
[8]SHOCKRAVI A,ABOUZARI-LOTF E,TAHERI S,et al.Synthesis and properties of novel fluorinated polyamides based on noncoplanar sulfoxide containing aromatic bis(ether amine)[J].Polym J,2009,41:174-180.
[9]HUANG G S,ZHANG S X,LI D S,et al.Facile synthesis of processable aromatic polyamides containing thioether units[J].Polym Int,2013,62:411-418.
