A STABILIZED CRANK-NICOLSON MIXED FINITE VOLUME ELEMENT FORMULATION FOR THE NON-STATIONARY PARABOLIZED NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS∗
Zhendong LUO(罗振东)
School of Mathematics and Physics,North China Electric Power University,Beijing 102206,China
A STABILIZED CRANK-NICOLSON MIXED FINITE VOLUME ELEMENT FORMULATION FOR THE NON-STATIONARY PARABOLIZED NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS∗
Zhendong LUO(罗振东)
School of Mathematics and Physics,North China Electric Power University,Beijing 102206,China
E-mail:zhdluo@163.com;zhdluo@ncepu.edu.cn
A time semi-discrete Crank-Nicolson(CN)formulation with second-order time accuracy for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations is firstly established. And then,a fully discrete stabilized CN mixed finite volume element(SCNMFVE)formulation based on two local Gaussian integrals and parameter-free with the second-order time accuracy is established directly from the time semi-discrete CN formulation so that it could avoid the discussion for semi-discrete SCNMFVE formulation with respect to spatial variables and its theoretical analysis becomes very simple.Finally,the error estimates of SCNMFVE solutions are provided.
non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations;stabilized Crank-Nicolson mixed finite volume element formulation;error estimate
2010 MR Subject Classification 65N12;65M15;65N30
1 Introduction
For the high Reynolds number fluid flow along the x-axis direction,we may omit the second order viscous terms on the x-axis direction,but retain other second order terms and non-viscous nonlinear terms.Thus,we obtain the following non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations(see[20]).
Problem I Find u=(u1,u2)Tand p such that for T∞>0,
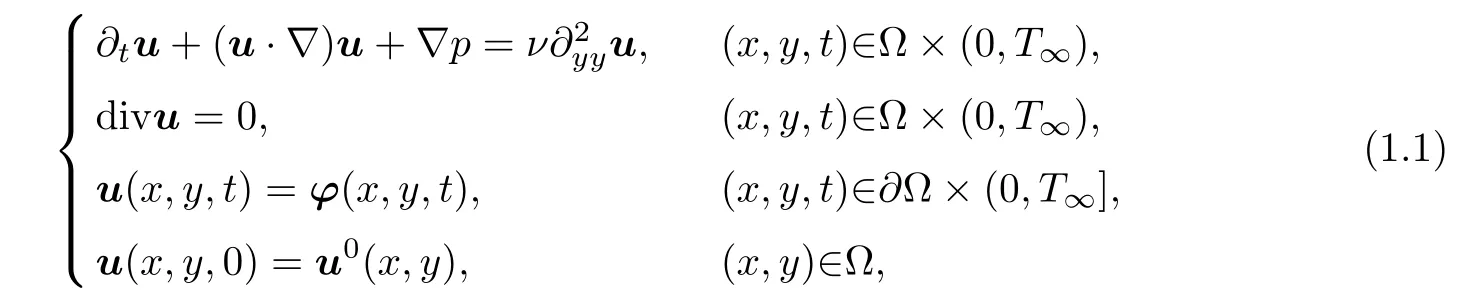
A lot of numerical simulating experiments have shown that,if the computational domain of fluid mainstream direction does not appear on a wide range of separation zone,the numerical simulating results obtained from the parabolized Navier-Stokes equations are very close to those obtained from the full Navier-Stokes equations.Especially,for fluid flow with high Reynolds number,the numerical viscosity for the full Navier-Stokes equations tends to hide some of the real physical viscosity.In other word,for fluid flow problems with high Reynolds number,the numerical solutions obtained from the parabolized Navier-Stokes equations are closer to real physical solutions than those obtained from the full Navier-Stokes equations(see[2,24]). Although,it seems,in principle,unreasonable that the fluid flow of the computational domain appearing separation zone is described by the simplified parabolized Navier-Stokes equations,a lot of calculation examples show that,for the fluid flow including a local small separation zone along the mainstream direction with the high Reynolds number(for example,the front or backward facing step flow,the separation bubble flow,the compression corner flow,the air intake channel flow field),the numerical solutions obtained by the simplified parabolized Navier-Stokes equations are very close to those obtained from the full Navier-Stokes equations(see[8,23,25]).Thus,to study the numerical methods for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations holds important theoretical value and real-life applied meanings.
However,most of existing numerical methods employ the finite difference(FD)scheme to discrete the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations(see,e.g.[7,8,23,25])in addition to using the finite element(FE)method to discrete the linearized stationary parabolized equations in[4]and stabilized Crank-Nicolson mixed finite element(SCNMFE)method to discrete the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations in[19].Compared to FD and FE methods,the finite volume element(FVE)method is considered as most effective discretization approach for PDEs,since it is generally easier to implement and offer flexibility in handling complicated computing domains.More importantly,it can ensure local mass conservation and a highly desirable property in many applications.Thus,in this study,it is chose as the preferred numerical approach to discretize the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations.It is also referred to as the box method(see[14])or the generalized difference method(see[15,17]).But,there exists an important convergence stability condition for the FVE formulations of the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations,which like their FE formulations(see[11]),namely,the combination of finite-dimensional trial function spaces of the velocity and pressure must satisfy the Brezzi-Babuˇska(B-B)inequality.Thus,in this study,we employ Crank-Nicolson(CN)time discretization technique,two local Gaussian integrals,and parameter-free to establish a fully discrete stabilized CN mixed FVE(SCNMFVE)formulation with the second-order time accuracy for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations.A stabilized FVE method for the full non-stationary Navier-Stokes equations was presented in[10],but it has only the first-order time accuracy and employs the stabilisation of the jump operator in pressure so that its degrees of freedom could increase.The fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation here can not only avoid the constraint of Brezzi-Babuˇska(B-B)inequality,but also has the second-order time accuracy and its theory and methods are different from those in[10].Especially,the SCNMFVE method for the simplified parabolized Navier-Stokes equations here is established directly from the time semi-discrete CN formulation so that it could avoid the discussion for semi-discrete SCNMFVE formulation with respect to spatial variables and its theoretical analysis becomes simpler than the existing other methods(see,e.g.,[10]).Though the fully discrete SCNMFE formulation with second-order time accuracy for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations is established in[19],the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation is completely different from and has more advantages than SCNMFE formulation because the FVE method is differing from the FE method and has more virtues than the FE method as mentioned above.This is the improvement and develpment for the existing numerical methods.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows.In Section 2,the time semi-discrete CN formulation with the second-order time accuracy for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations and the error estimates are derived.In Section 3,the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation based on two local Gaussian integrals and parameter-free with the second-order time accuracy is directly established from the time semi-discrete CN formulation.And the existence and uniqueness and the error estimates of the fully discrete SCNMFE solutions are proved.Section 4 provides main conclusions and some discussions.
2 Time Semi-Discrete CN Formulation and Error Estimates
The Sobolev spaces and norms used in this paper are standard(see[1]).LetandThen,the variational formulation for Problem I is read as follows.
Problem IIFind(u(t),p(t)):[0,T∞]→U×M such that

The following properties of trilinear forms a1(·,·,·)are known(see[5,9,10,12,18,22]):

The following properties of bilinear forms a(·,·)are also known(also see[5,9,10,12,18,22]):
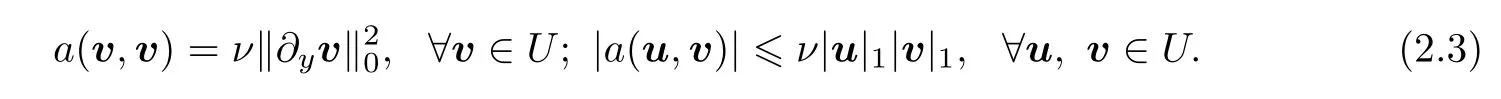
The bilinear form b(·,·)satisfies the following B-B inequality(also see[5,9,10,12,18,22]):
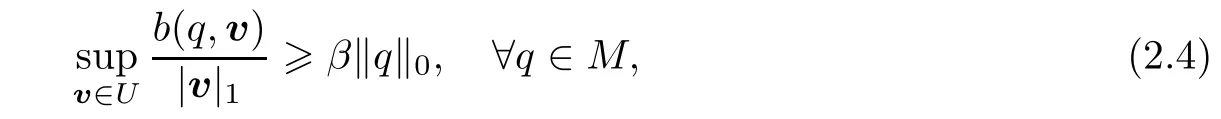
where β is a constant independent of v and q.Put

The following conclusions on the existence and stabilization of the solution to Problem II are provided in[19].
Theorem 1 If u0∈L2(Ω)2and‖ut(x,y,0)‖0is bounded,namely,there exists a constant C0such that‖ut(x,y,0)‖0≤C0,Problem II has a unique solution such that
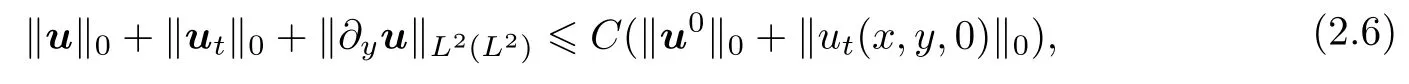
where‖·‖Hm(Hl)are the norm of Hm(0,T∞;Hl(Ω))or Hm(0,T∞;Hl(Ω)2)2(m≥0 and l≥-1)and C is a constant.Further,if‖∇u‖0≤C(‖u0‖0+‖ut(x,y,0)‖0),p is also bounded,namely,

For given positive integer N,let k=T∞/N denote time step,tn=nk,unis the time semi-discrete CN approximation of u at tn=nk(n=0,1,···,N).Let¯∂tun=(un-un-1)/k denote the approximation of ut,¯un=(un+un-1)/2.Then the time semi-discrete CN scheme with the second-order time accuracy for Problem II is read as follows.
Problem IIIFind(un,pn)∈U×M (1≤n≤N)such that
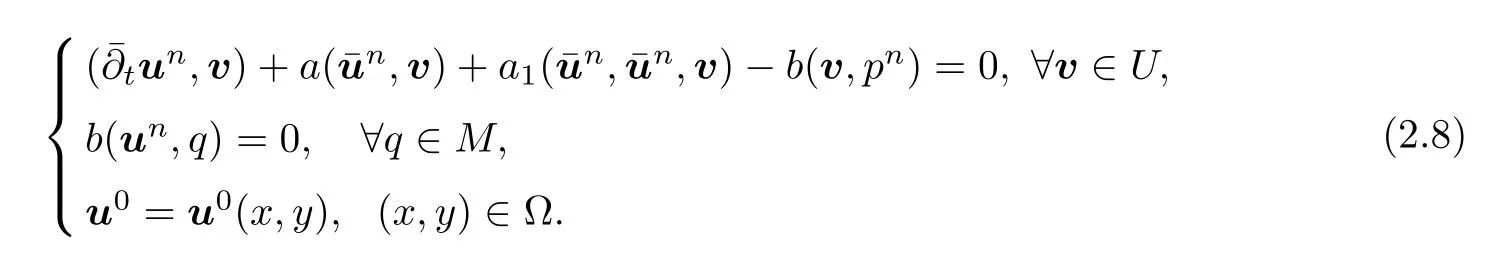
Noting that by Poincar´e inequality,there exists a constant¯C0such that

The following conclusions on the existence and stabilization of the solution to Problem III are provided in[19].
Theorem 2 If u0∈H1(Ω)2,then Problem III has a unique series of solutions(un,pn)∈U×M (n=1,2,···,N)that satisfy the following stability

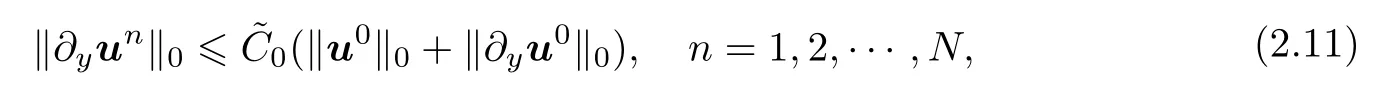


where C(u)is a constant which is possibly different at different occurrences,being independent of k,but dependent on u and ν.
Remark 1 By regularity(see[12,13,22]),it follows u∈H10(Ω)2if f∈H-1(Ω)2.Thus,the assumption for boundness of‖∇un‖0is reasonable.
3 Fully Discrete SCNMFVE Formulation as Well As Existence and Error Estimates of Its Solutions
3.1 Theory of FVE Method
In the following,we start directly from semi-discrete CN formulation with respect to time to establish the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations and to do error analysis.To this end,it is necessary to introduce an FVE approximation for the spatial variables of Problem III,where we cite partly the FVE theory in[15](for more details,see literature[15]).

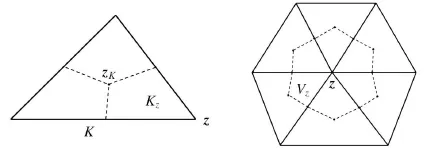
Fig.1 Left chart shows a triangle K partitioned into three sub-regions Kz.Right chart is a sample region with dotted lines indicating the corresponding control volume Vz
We call the partition ℑ∗hregular or quasi-uniform,if there exist two positive constants C1and C2,being independent of the spatial mesh size h and temporal mesh size k,such that

where mes(Vz)denotes the measure of dual element Vz.If the FE triangulation ℑhis quasiuniform,then the dual partition ℑ∗his also quasi-uniform(see[15]or[18]).
The trial function spaces Uhand Mhof the velocity and pressure are respectively defined as follows:

where P1(K)represents the linear function space on K.It is obvious that Uh⊂U=H10(Ω)2.
For u∈U=H10(Ω)2,let Πhu be the interpolating operator of u onto the trial function space Uh.If u∈H2(Ω)2,from the interpolating theorem of Sobolev spaces(see[5,6,15,18]),
we have

where C in this context indicates the positive constant that is possibly different at different occurrences,being independent of the spatial mesh size h and temporal mesh size k.
The test space˜Uhof the velocity is defined as follows:
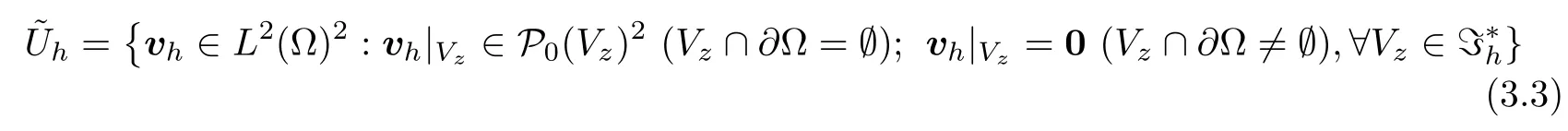
spanned by the following basis functions


Using the interpolating theorem of Sobolev spaces(see[4-6,15]),we obtain the following error estimate

Moreover,we have the following properties for the interpolating operator Π∗h(see[3,16,21]).
Lemma 3 If vh∈Uh,then
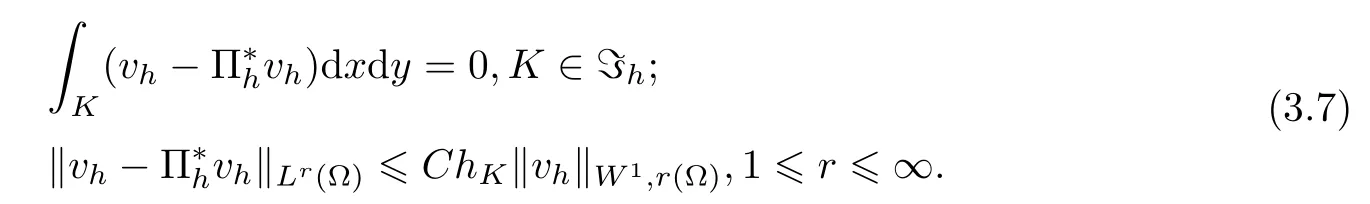
3.2 Fully Discrete SCNMFVE Formulation Based on Two Local Gaussian Integrals and Parameter-Free with the Second-Order Time Accuracy
Though the trial function space Uhsatisfies Uh⊂U,the test space˜Uh/⊂Uh.So the bilinear forms a(u,v)and b(v,p)must be revised accordingly.By Green's formula,we have

where∂Vzdenotes the line integral,with the counter clockwise direction,on the boundary∂Vzof the dual element;n=(n1,n2)Tis the unit outer normal vector to∂Vz.So the bilinear forms a(u,v)and b(v,p)are respectively rewritten as
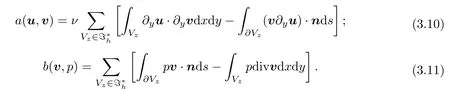

Then,the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation based on two local Gaussian integrals and parameter-free with the second-order time accuracy for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations is read as follows.

where

here ε is a positive real number andK,ig(x,y)dxdy(i=1,2)indicate the appropriate Gaussian integrals over K,which are exact for polynomials of degree i(i=1,2)and g(x,y)=phqhis a polynomial with a degree of no more than i(i=1,2).Thus,for all test functions qh∈Mh,the trial function ph∈Mhmust be piecewise constant when i=1.
Further,we define the L2-projection operator ρh:L2(Ω)→ Whsuch that∀p∈L2(Ω)satisfying
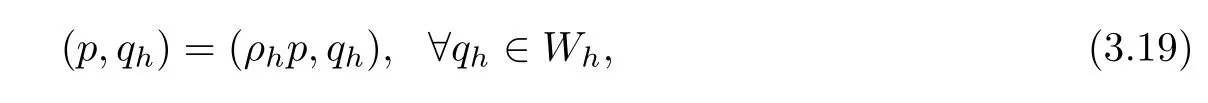
where Wh⊂L2(Ω)denotes the piecewise constant space associated with ℑh.The projection operator ρhhas the following properties(see[5,6,18]):
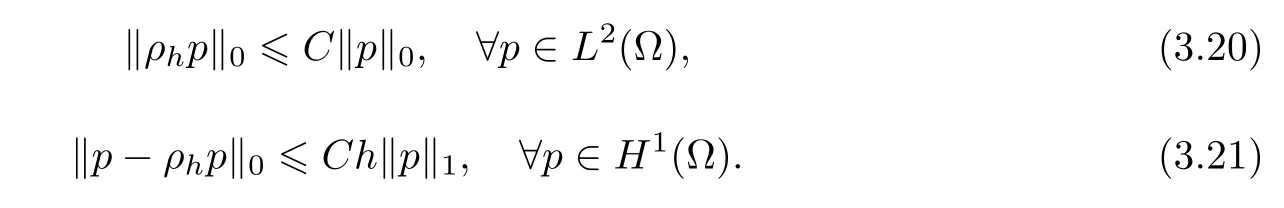
Now,by using the definition of ρh,the bilinear form Dh(·,·)can be rewrite as follows:

3.3 Existence,Uniqueness,and Error Estimates of Fully Discrete SCNMFVE Solutions
In order to discuss the existence,the uniqueness,the stability,and the error estimates of the solutions for fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation with the second-order time accuracy or Problem IV,it is necessary to introduce some preliminary lemmas.
From[3,15,16,21]we have the following two lemmas.
Lemma 4 The following results hold:

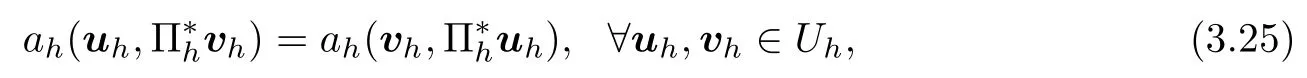
and there exist a positive constants h0≥h>0 such that
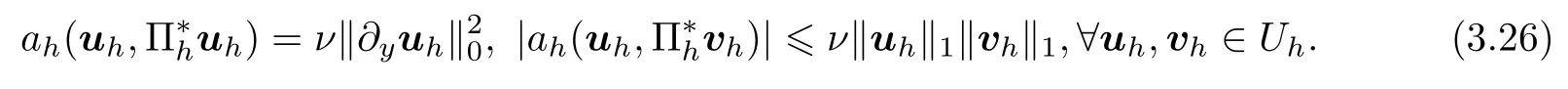
Lemma 5 The following statement holds:

For any u∈Hm(Ω)2(m=0,1)and vh∈Uh,


The following discrete Gronwall lemma(see[9,18])is useful for the proofs of the existence,the uniqueness,the stability,and the error estimates of the solutions for Problem IV.
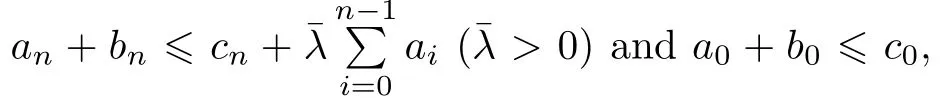
By Lemmas 4 and 5 and using the same approach as the proof of Theorem 4.1 in[3],we can obtain the following inequalities

We have the following results of the existence,the uniqueness,and the stability of the solution to Problem IV.
Theorem 7 Under the hypotheses of Theorems 1 and 2,there exists a unique series of solutionsto the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation with the second-order time accuracy,that is,Problem IV that satisfy

which shows that the series of solutions of Problem IV is stable.
Proof Problem IV has a unique series of solutions(unh,pnh)(n=1,2,···,N)by means of mixed FE methods(see[5,18])due to inequality(3.30).Noting that a1h(¯unh,¯unh,Π∗h¯uh)=0. By taking vh=¯unhin the first equation of Problem IV and qh=pnhin the second equation of Problem IV and by using Lemmas 4 and 5,H¨older inequality,and Cauchy inequality,we obtain

Summing(3.32)from 1 to n,we obtain
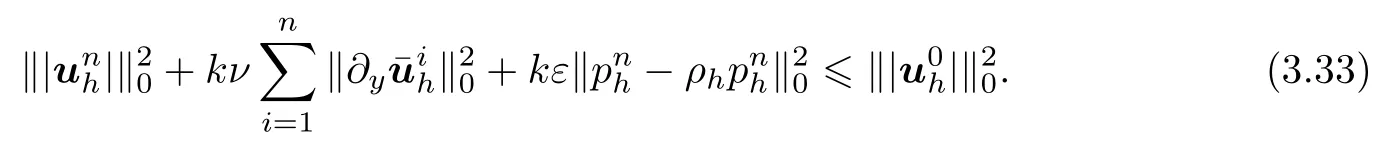

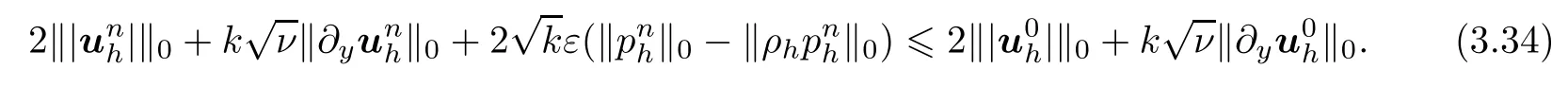
If pnh/=0,then it is easily see that‖pnh‖0>‖ρhpnh‖0from(3.22).Therefore,there exists a constant γ∈(0,1)such that γ‖pnh‖0=‖ρhpnh‖0.Thus,by using inverse estimate(see[5,18])and Lemma 5 and simplifying(3.34),we obtain(3.31).If pnh=0,(3.31)is also correct,which completes the proof of Theorem 7. □
The following Lemma 8 is obtained from the SCNMFE methods(see,e.g.[13,18,19])for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations.
Lemma 8 Let(Shun,Qhpn)be the Navier-Stokes projection of the solutions(un,pn)for Problem III on Uh×Mh,that is,for the solutions(un,pn)∈U×M for Problem III,there exist(Shun,Qhpn)(n=1,2,···,N)such that

where A((Sh¯un,Qhpn);(vh,qh))=a(Sh¯un,vh)+a1(Sh¯un,Sh¯un,vh)-b(vh,Qhpn)+b(Shun,qh)and A((¯un,pn);(vh,qh))=a(¯un,vh)+a1(¯un,¯un,vh)-b(vh,pn)+b(un,qh).Then,there hold
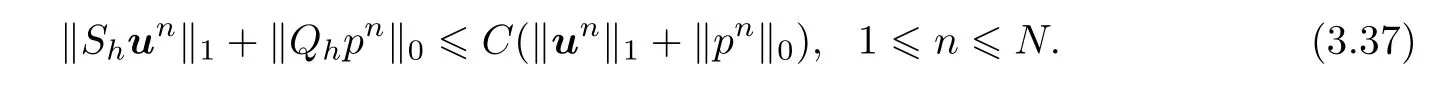
If the solutions(un,pn)∈H2(Ω)2×H1(Ω)(n=1,2,···,N)to Problem III,then we have the following error estimates

Remark 2 In fact,(3.35)and(3.36)are the system of error equations between standard SCNMFE formulation(see[19])and Problem III.Thus,(3.37)and(3.38)are directly obtained from SCNMFE method(see[5,13,18])like the approaches in[19].
Theorem 9 Let(u,p)be the solution to Problem II and(unh,pnh)the solution to Problem IV.Then,under the hypotheses of Theorems 2 and 7,if p0h=p0=0(or p0h=Qhp0),h=O(k),there hold the following error estimates,for n=1,2,···,N,

Proof Subtracting Problem IV from Problem III taking v=vhand q=qh,and using Lemmas 4 and 5,we obtain the following system of error equations,for n=1,2,···,N,
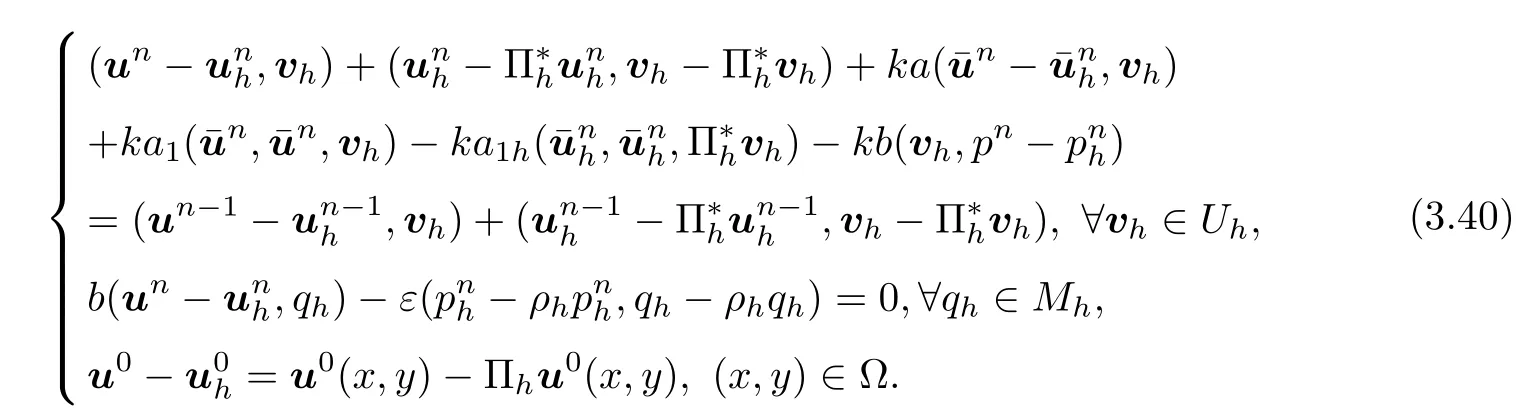

Next,if k=O(h),by using Lemma 4,inverse error estimate,Taylor's formula,H¨older inequality,and Cauchy inequality,we first obtain
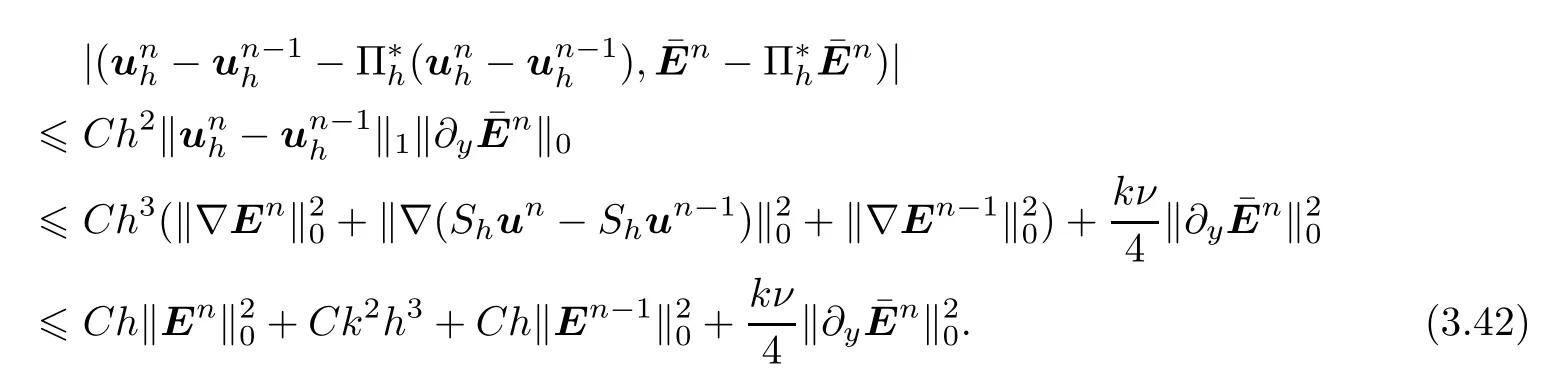
Then,by noting that b(Shun-un,qh)=-kε(Qhpn-ρh(Qhpn),qh-ρhqh),from the properties of operator ρhand the second equation of(3.40),we have


Thus,combining(3.42)-(3.44)with(3.41),we obtain

If h is sufficiently small such that Ch≤1/2 in(3.45)and p0h=p0=0(or p0h=Qhp0),noting that‖Shu0-u0h‖0≤‖Shu0-u0‖0+‖u0-u0h‖0≤Ch2and summing(3.45)from 1 to n,we obtain
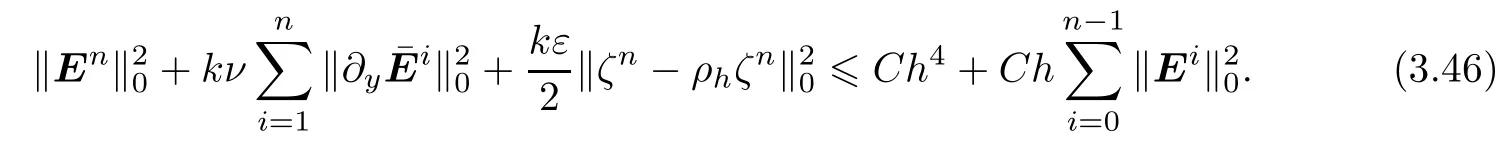
Applying Gronwall Lemma 6 to(3.46),we obtain

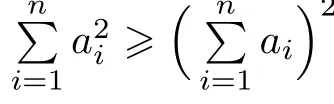
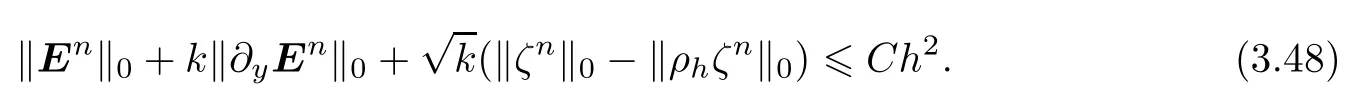
If ζn/=0,then‖ζn‖0> ‖ρhζn‖0.Therefore,there exists a constant δ∈(0,1)such that δ‖ζn‖0=‖ρhζn‖0.Thus,by simplifying(3.48),we have

If ζn=0,then(3.49)is also correct.By using(3.38),Theorem 2,and triangle inequality,we obtain(3.39). □
Remark 3 It is known from Theorem 7 and its proof that¯C1ν-1‖∇¯unh‖0≤1/4(n= 1,2,···,N)hold if‖u0‖1is sufficiently small.
4 Conclusions and Discussions
In this study,we have employed the CN technique to establish the time semi-discrete CN formulation with the second-order time accuracy for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations and to derive the error estimates of its solutions firstly.And then,the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation based on two local Gaussian integrals and parameter-free with the second-order time accuracy has been directly established from the time semi-discrete CN formulation so that it could avoid the discussion for semi-discrete SCNMFVE formulation with respect to spatial variables and its theoretical analysis becomes very simple.Finally,the existence and uniqueness and the error estimates of the fully discrete SCNMFVE solutions are proved.
Though the FE method for the linearized stationary parabolized equations was presented in[4]and the fully discrete SCNMFE formulation with second-order time accuracy for the nonstationary parabolized Navier-Stokesequations in[19],the fully discrete SCNMFVE formulation dose not only include all advantages of FVE method,but also holds the second-order timeaccuracy and its theory and methods all are the improvement and develpment for the existing numerical methods.
[1]Adams R A.Sobolev Spaces.New York:Academic Press,1975
[2]Alekseev A K,Navon I M,Steward J L.Comparison of advanced large-scale minimization algorithms for the solution of inverse ill-posed problems.Optimization Methods&Software,2009,24(1):63-87
[3]An J,Sun P,Luo Z D,Huang X M.A stabilized fully discrete finite volume element formulation for non-stationary Stokes equations.Math Numer Sin,2011,33(2):213-224
[4]Bourgault Y,Caussignac P,Renggli L.Finite element methods for parabolized Navier-Stokes equations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng,1994,111(3/4):265-282
[5]Brezzi F,Fortin M.Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods.New York:Springer-Verlag,1991
[6]Ciarlet P G.The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems.Amsterdam:North-Holland,1978
[7]D'Ambrosio D,Marsilio R.A numerical method for solving the three-dimensional parabolized Navier-Stokes equations.Computers&Fluids,1997,26(6):587-611
[8]Gao Z.Significance and use of basic equation system governing high Reynolds number flows and diffusionparabolized Navier-Stokes equations.Adv Mech,2005,35(3):427-438
[9]Girault V,Raviart P A.Finite Element Methods for Navier-Stokes Equations:Theory and Algorithms. Berlin Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag,1986
[10]He G L,He Y N,Feng X L.Finite volume method based on stabilized finite elements for the non-stationary Navier-Stokes problem.Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations,2007,23(5):1167-1191
[11]He Y,Lin Y,Sun W.Stabilized finite element method for the non-stationary Navier-Stokes problem.Disc Cont Dyn Syst B,2006,6(1):41-68
[12]Heywood J G,Rannacher R.Finite element approximation of the non-stationary Navier-Stokes problem,I.Regularity of solutions and second order estimates for spatial discretization.SIAM J Num Anal,1982,19(2):275-311
[13]Heywood J G,Rannacher R.Finite element approximation of the non-stationary Navier-Stokes problem part IV:error analysis for second-order time discretization.SIAM J Num Anal,1990,27(2):353-384
[14]Jones W P,Menziest K R.Analysis of the cell-centred finite volume method for the diffusion equation.J Comput Phys,2000,165(1):45-68
[15]Li R H,Chen Z Y,Wu W.Generalized Difference Methods for Differential Equations-Numerical Analysis of Finite Volume Methods.Monographs and Textbooks in Pure and Applied Mathematics 226.New York: Marcel Dekker Inc,2000
[16]Li J,Chen Z X.A new stabilized finite volume method for the stationary Stokes equations.Adv Comput Math,2009,30:141-152
[17]Li H R,Luo Z D,Li Q.Generalized difference methods for two-dimensional viscoelastic problems.Chinese J Numer Math Appl,2007,29(3):251-262
[18]Luo Z D.The Foundations and Applications of Mixed Finite Element Methods.Beijing:Science Press,2006(in Chinese)
[19]Luo Z D.A stabilized Crank-Nicolson mixed finite element method for the non-stationary parabolized Navier-Stokes equations.Acta Mathematica Applicatae Sinica,in press(Accepted for publication)
[20]Pratap V S,Spalding D B.Fluid flow and heat transfer in three-dimensional duct flows.Int J Heat Mass Transfer,1976,19:1183-1188
[21]Shen L H,Li J,Chen Z X.Analysis of a stabilized finite volume method for the transient stationary Stokes equations.Int J Numer Anal Model,2009,6:505-519
[22]Temam R.Navier-Stokes Equations.3rd ed.New York:North-Holland,Amsterdam,1984
[23]Wang R,Shen Y.Numerical solutions of the diffusion parabolized Navier-Stokes Equations.Adv Mech,2005,35(4):481-497
[24]Zhang H,Guo C,Zong W.Problems about gird and high order schemes.Chinese J Theoretical Appl Mech,1999,31(4):398-405
[25]Zhang H,Yu Z,Lu L,Ma Z.Numerical solutions of supersonic and hypersonic laminar separated flow. Chinese J Theoretical Appl Mech,1981,13(4):333-345
∗Received February 26,2014;revised October 18,2014.Research of this work was mainly supported by National Science Foundation of China(11271127)and Science Research Project of Guizhou Province Education Department(QJHKYZ[2013]207).
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2015年5期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2015年5期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- ALL MEROMORPHIC SOLUTIONS OF AN AUXILIARY ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION AND ITS APPLICATIONS∗
- APPROXIMATION OF COMMON FIXED POINT OF FAMILIES OF NONLINEAR MAPPINGS WITH APPLICATIONS∗
- SOME COMPLETELY MONOTONIC FUNCTIONS ASSOCIATED WITH THE q-GAMMA AND THE q-POLYGAMMA FUNCTIONS∗
- SUB-ADDITIVE PRESSURE ON A BOREL SET∗
- AN APPLICABLE APPROXIMATION METHOD AND ITS APPLICATION∗
- ORBITAL INSTABILITY OF STANDING WAVES FOR THE GENERALIZED 3D NONLOCAL NONLINEAR SCHR¨ODINGER EQUATIONS∗
