随机恒速运动目标的搜索方程及持续探测概率
陈建勇,张 驰
(海军航空工程学院a.电子信息工程系;b.研究生管理大队,山东烟台264001)
随机恒速运动目标的搜索方程及持续探测概率
陈建勇a,张驰b
(海军航空工程学院a.电子信息工程系;b.研究生管理大队,山东烟台264001)
根据目标位置的初始分布和速度分布,给出了随机恒速运动目标在任意时刻位置和速度分布密度函数。定义了探测函数、目标存在和探测不成功的联合概率密度函数和目标存活概率函数,建立了基于目标速度分布的搜索方程并给出了其特征迹线解。在目标初始分布和速度分布均为圆正态分布条件下,分析了搜索方程特征迹线的基本特征和持续探测发现概率积分域的形态。给出了一个以直升机吊放声纳探测潜艇为背景的持续探测发现概率的算例,算例表明,对随机恒速运动目标持续探测的发现概率,与对静止目标进行持续探测的发现概率相似,服从时间的指数规律。
搜索方程;运动目标;探测概率;最优搜索
文献[1]针对二维空间的随机恒速运动目标的离散时间有限区域搜索问题,提出了基于已知目标初始位置分布密度和速度分布密度的最优搜索算法。以该算法为基础,文献[2-4]应用没有时间变量的空间探测函数概率模型,分析了持续探测概率的时间收益问题和发现概率的时间最优性问题。因为空间探测函数中没有时间变量,以此为基础对概率的时间变化关系进行的分析和计算,受到比较严格的限制,并且误差较大。本文以定义时间和空间变量的探测函数为基础,根据Hellman提出的运动目标搜索的建模和求解方法[5-13],运用特征迹线法,给出了基于目标速度分布函数的恒速随机运动目标区域持续探测发现概率的积分表达式。以目标速度分布和初始位置分布均为圆正态分布为条件,讨论了时变的发现概率积分域的变化特征,并给出了一个算例。
1 随机恒速运动目标
设时间t∈[t0,∞)。搜索和目标空间X=[x,y]∈ℝ2,速度空间v=[vx,vy]∈ℝ2。已知目标的初始分布密度函数ρ(X,t0),速度分布密度函数为w(v,t0)。对随机恒速运动目标有X(t)=X(t0)+v·(t-t0)。令g[X(t0),v·(t-t0)]为关于X(t0),v·(t-t0)的联合概率密度函数。因为X(t0),v·(t-t0)相互独立,所以:
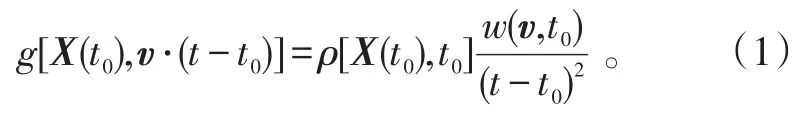
对于任意给定的t>t0,

设tm>t时刻的空间变量为X(tm)。
由X(tm)=X(t0)+v·(tm-t0)=X(t)+v(x)·(tm-t),得:
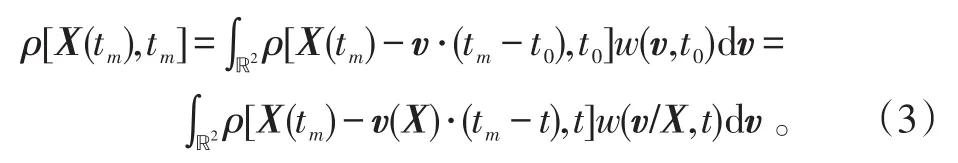
对于恒速目标,任意速度空间V∈ℝ2,都有:
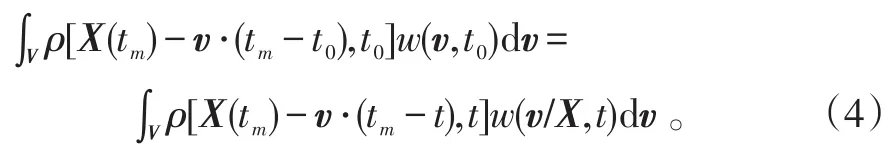

对于连续的联合分布密度函数g(X,v),有:根据式(6)可以得出随机运动目标在t时刻速度的空间条件分布w(v/X,t)的表示式:

2 基于目标速度分布的搜索方程及其特征迹线解
定义探测率函数b(X,t,a):
b(X,t,a)Δt=
Prob{在a点探测,
于τ∈[t,t+Δt]发现目标/目标在X}+O(Δt)。假设单连通域Ω={X:b(X,t,a)>0}为凸集,称探测域。a定义为探测器(或称搜索者)的定点探测位置。
定义联合概率密度函数 f(X,t,a):
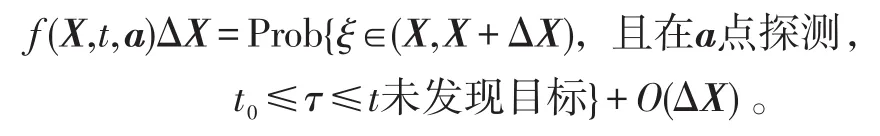
定义存活概率u(X,t,T,a):
u(X,t,T,a)=Prob{在a点探测,t≤τ≤T,搜索未发现目标/t时刻目标处于X}。
设t+Δt时刻的空间为X,t时刻的空间则为X-vΔt。根据独立性假设,
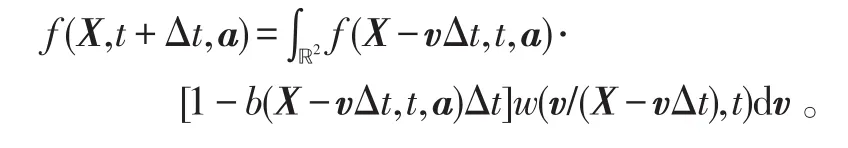
作泰勒级数展开,令Δt→0,得到搜索方程:
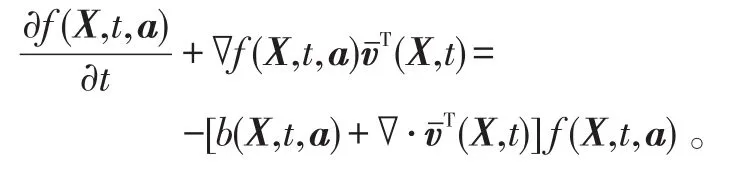
空间的特征线族。
在特征线上重写搜索方程,得:
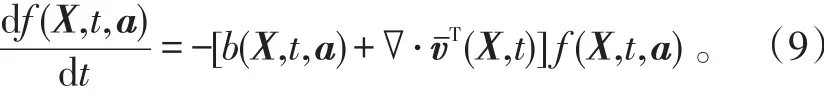
已知初始条件 f(X,t0,a)=ρ[X(t0),t0]。给出任一点(X0,t0),可解得在该点所在的特征线上:
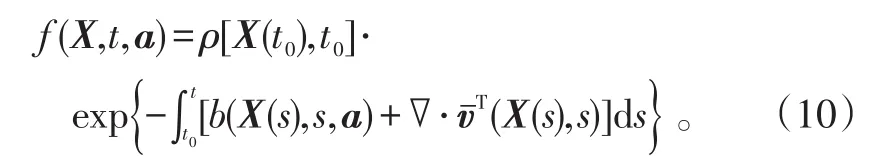
当b[X(t),t,a]≡0,即无探测时,

所以,联合概率密度函数又可以表示为:


类似地,可获得关于生存概率的搜索方程及在特征线上的解:

将t、T分别置换为t0、t,得t0时到目标处于X(t0)的条件下,在搜索到t时刻该目标的生存概率为:

根据对联合概率密度函数和生存概率的定义可得,在a点持续探测到t时刻,发现目标的概率:
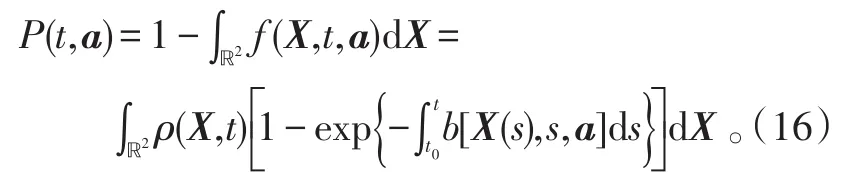
同样有:
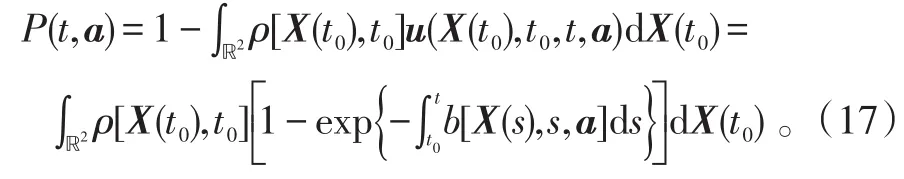
3 圆正态分布的单点持续探测概率
初始位置分布和速度分布均为圆正态分布,即:
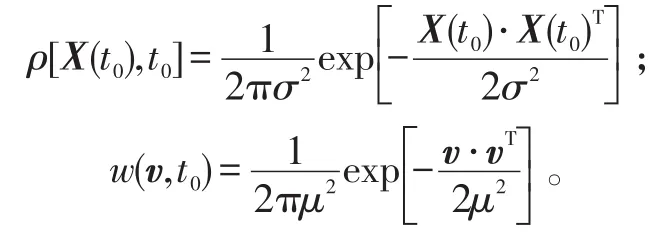
目标空间分布的表达式为:
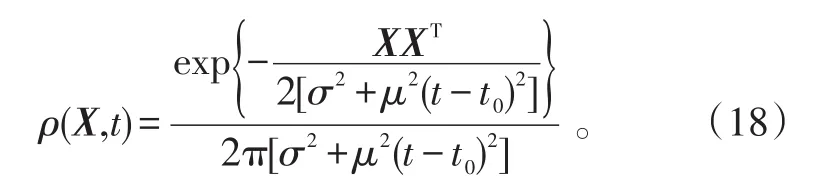
速度的空间条件分布密度为:

空间条件的目标速度期望值及其散度为:
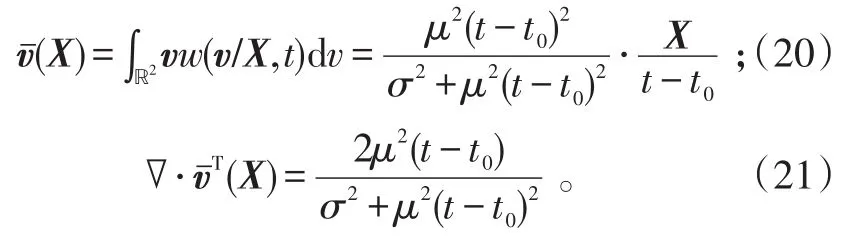
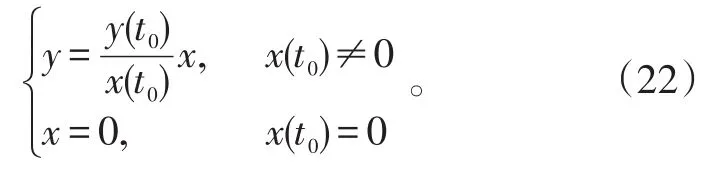
显然,特征迹线为通过坐标原点和X(t0)的直线。特征线族的方程
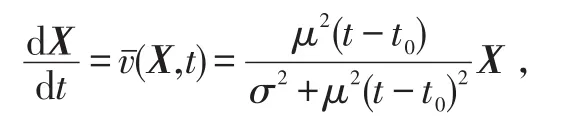
解得X(t0)点所在的特征线方程为:
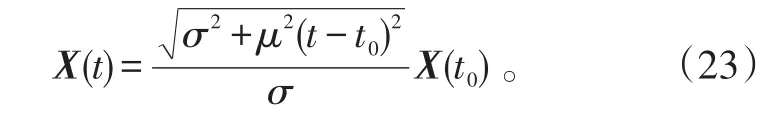
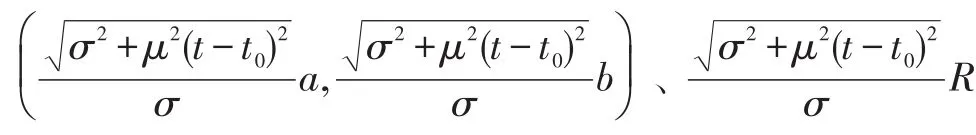
图1为B(阴影区域),在t2>t1>t0时刻映射的空间集的示意图。
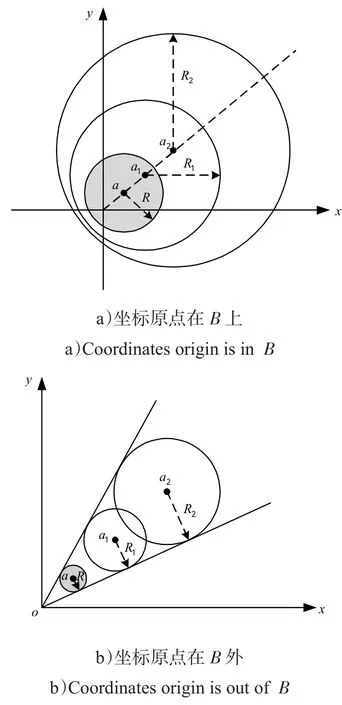
图1 空间集映射示意图Fig.1 Diagram of space map
根据式(16)、(17),在a点持续探测到t时刻,发现目标的概率:



图2 坐标原点在Ω上的积分域ωfFig.2 Integral domainωfof the coordinates onΩ

图3 坐标原点在Ω外的积分域ωfFig.3 Integral domainωfof the coordinates out ofΩ
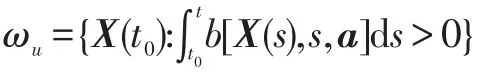
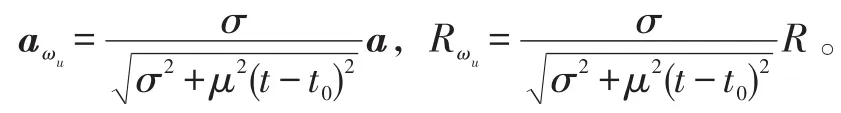
可以证明,对于圆正态分布,任意t>t0,ωu的内圆、Ω的边界圆和ωf的外圆都是在同一个扇面内的内切圆。
图4 坐标原点在Ω外的积分域ωuFig.4 Integral domainωuof the coordinates out ofΩ

图5给出探测点在a=(0,0)nm和a=(5,5)nm时,0≤t≤30 s,单点探测的发现概率随时间的连续变化关系。

图5 定点持续探测的发现概率Fig.5 Single point continuous detection
4 结语
本文在随机恒速运动目标的假设条件下,建立了搜索方程,并给出了搜索方程特征线解得表达式。在目标初始位置分布和速度分布均为圆正态分布情况下,分析了搜索方程特征迹线解的基本特征,单点持续探测发现概率的2种积分形式和非零积分域的形态及时变规律。本文基于搜索方程特征迹线解的单点持续探测发现概率算法,为研究多点探测中发现概率的时间最优性问题和概率的时间收益问题奠定了基础。文中以直升机吊放声纳单点探测为背景,给出一个数值算例。从算例结果可以看到,对随机恒速运动目标单点持续探测的发现概率,仍然是时间的指数规律,其可能达到的极限值,由分布参数和探测点与分布中心的距离决定。
[1]陈建勇,王健,单志超.离散时间探测随机恒速目标的最优搜索算法[J].系统工程与电子技术,2013,35(8):1627-1630. CHEN JIANYONG,WANG JIAN,SHAN ZHICHAO. Optimal search algorithm for a random invariant speed target detecting in discrete time[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics,2013,35(8):1627-1630.(in Chinese)
[2]陈建勇,曲晓慧,王健.随机运动目标有限区域探测的概率时间收益[J].系统工程与电子技术,2014,36(6):1039-1043. CHEN JIANYONG,QU XIAOHUI,WANG JIAN.Probability increment with detection duration in a limited space for random moving target[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics,2014,36(6):1039-1043.(in Chinese)
[3]陈建勇,单志超,王健.随机运动目标区域持续探测的概率最优性[J].火力与指挥控制,2014,39(6):9-12. CHEN JIANYONG,SHAN ZHICHAO,WANG JIAN. The probability optimality of area persistence detection for a random moving target[J].Fire Control and Command Control,2014,39(6):9-12.(in Chinese)
[4]陈建勇,单志超,张驰.随机运动目标区域持续探测概率的近似模型[J].海军航空工程学院学报,2015,30(3):201-205. CHEN JIANYONG,SHAN ZHICHAO,ZHANG CHI. Approximate probability model of area persistence detection for a random moving target[J].Journal of Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University,2015,30(3):201-205.(in Chinese)
[5]HELLMAN O.On the effect of a search upon the probability distribution of a target whose motion is a diffusionprocess[J].Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1970,41:1717-1724.
[6]HELLMAN O.Optimal search for a randomly moving object in a special cases[J].Journal of Applied Probability,1971,8:606-611.
[7]HELLMAN O.On the optimal search for a randomly moving target[J].SIAM Journal of Applied Mathematics,1972,22(4):545-552.
[8]LUKKA M.On the optimal searching tracks for a moving target[J].SIAM Journal ofApplied Mathematics,1977,32(1):126-132.
[9]MANGEL M.Search for a randomly moving object[J]. SIAM Journal ofApplied Mathematics,1981,40(2):327-338.
[10]MANGEL M.Probability of success in the search for a moving target[J].Operations Research,1982,30(1):216-222.
[11]OHSUMI A.Stochastic control with searching a randomly moving target[C]//Proceedings of American Control Conference.San Diego:IEEE Press.1984:500-504.
[12]FORAKER III J C.Optimal search for moving targets in continuous time and space using consistent approximations[D].Monterey California:Naval Postgraduate School,2011.
[13]杨艳芹,齐美彬,王倩,等.基于运动检测与运动搜索的多目标跟踪[J].计算机工程,2008,34(19):222-224. YANG YANQIN,QI MEIBIN,WANG QIAN,et al.Multiobject tracking based on motion delection and motion search[J].Computer Engineering,2008,34(19):222-224.(in Chinese)
Search Equation of Moving Target with Random Constant Velocity and the Probability of Persistence Detecting
CHEN Jianyonga,ZHANG Chib
(Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University a.Department of Electronic and Information Engineering;b.Graduate Students’Brigade,Yantai Shandong 264001,China)
According to the target distribution density functions of initial location and velocity,the distribution density function of moving target with a random constant velocity at any time was given.Defined the detection function,the joint probability density function of target existence and unsuccessful detection,and the survival probability function,the search equation based on the velocity distribution density function was established,then its trace solution was obtained. Under the condition of target distribution of initial location and velocity were both circular normal distribution,the basic characteristics of the trace of search equation and the integral domains of the probability with persistence detecting was an⁃alysed.A computing example of persistence detecting probability based on detect a submarine with helicopter dipping so⁃nar was given.The simulation results showed that the discovery probability detecting a random moving target,similarly with a stationary target,was an index function of time.
search equation;moving target;detection probability;optimal search
E926.38;O229
A
1673-1522(2015)06-0521-05DOI:10.7682/j.issn.1673-1522.2015.06.005
2015-09-08;
2015-10-08
国家自然科学基金资助项目(61271444)
陈建勇(1962-),男,教授,博士。

