青藏高原东南部寒武纪花岗岩类:岩石学和锆石Hf 同位素研究*
董昕 张泽明
大陆构造与动力学国家重点实验室,中国地质科学院地质研究所,北京 100037
1 引言
位于青藏高原南部的拉萨地体不仅经历了强烈的中生代新特提斯洋北向拉萨地体之下俯冲的安第斯型造山作用,还经历了新生代印度与欧亚大陆碰撞、俯冲导致的喜马拉雅型造山作用(许志琴等,2006,2011)。从北到南,拉萨地体被狮泉河-纳木措蛇绿混杂岩带和洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带分为北拉萨地体、中拉萨地体和南拉萨地体(Zhu et al.,2009a)。北部拉萨地体目前为止还没有中生代以前的岩浆和变质事件报道,中生代岩浆岩的全岩Nd 同位素和岩石中的锆石Hf同位素组成表明北拉萨地体大部分地区为新生地壳(Zhao et al.,2008;Zhu et al.,2011,2013)。中部拉萨地体不仅具有中、新元古代的岩浆作用(胡道功等,2005;Xu et al.,2013),而且经历了新元古代的变质作用(Dong et al.,2011a;Zhang et al.,2012a),说明其确实存在前寒武纪的变质基底,Zhu et al.(2009b,2011,2013)认为中部拉萨地体为一个微陆块。南部拉萨地体中大量中-新生代岩浆岩以高且正的锆石εHf(t)值和小于1.0Ga 的地壳模式年龄为主,显示新生地壳的特征(Chung et al.,2009;Ji et al.,2009;Zhu et al.,2011;张立雪等,2013),Chu et al.(2011)认为南拉萨地体是一个年轻的洋内岛弧地体。而最近的研究表明,南拉萨地体存在寒武纪和晚泥盆世-早石碳世的岩浆作用(Ji et al.,2012;Dong et al.,2010,2014)。Lin et al.(2013)在东构造结的拉萨地体中获得了中元古代的岩浆和新元古代的变质作用年龄,但是由于中-新生代造山过程中的强烈构造运动,该年龄所代表的构造域(归属于中拉萨地体/南拉萨地体)还有待商榷。因此,南部拉萨地体是否存在古老的基底还存在争论。
松多晚古生代(~260Ma)高压变质带和邻区近同期的变质、变形和岩浆作用的报道(李才等,2003;张宏飞等,2007;Li et al.,2009;Yang et al.,2009;Zhu et al.,2009b,2010;Dong et al.,2011b),证实拉萨地体存在晚古生代-早中生代造山作用。Yang et al.(2009)认为该造山作用与南、北(上述中拉萨地体)拉萨地体的拼合有关;而Zhu et al.(2009b)认为拉萨地体(中拉萨地体)曾经是古特提斯洋中的一个微地块,晚古生代的造山作用是其与澳大利亚大陆北缘的碰撞造山作用有关。如果南拉萨地体为中-新生代形成的岛弧,那么晚古生代南、北拉萨地体拼合的观点既不成立。因此,南拉萨地体是否存在古老基底关系到松多高压变质岩的成因,以及晚古生代-早中生代造山作用等重要问题。
笔者之前首次报道了南拉萨地体寒武纪花岗岩的形成时间(样品TM08-41-1,496Ma;Dong et al.,2010),但对其岩石成因未做深入探讨。本文在已有研究基础上,对南拉萨地体眼球状的寒武纪花岗岩进行了岩石学、锆石U-Pb 定年和Hf 同位素的研究。为了对比,本文对Zhang et al.(2012b)报道的邻区高喜马拉雅岩系中近同期的花岗质片麻岩(503~490Ma,样品6-10-1、6-14-1、6-17-1)进行了锆石Hf 同位素的补充,对青藏高原东南部寒武纪花岗岩的成因和构造意义进行了探讨,为青藏高原的起源提供了重要限定。
2 地质背景和样品
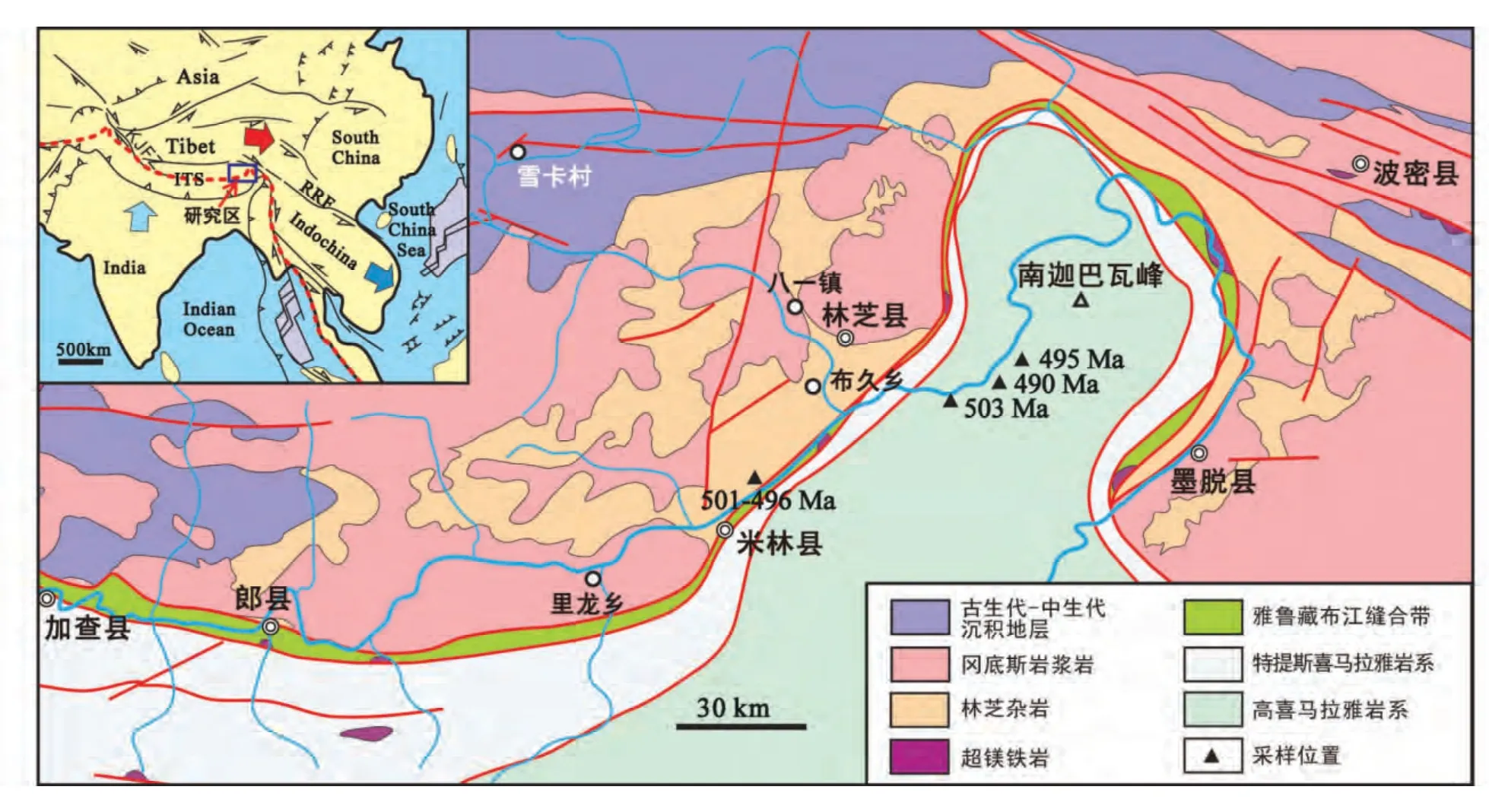
图1 青藏高原东南部地质简图(据张泽明等,2007 修改)Fig.1 Geological map of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau (after Zhang et al.,2007)
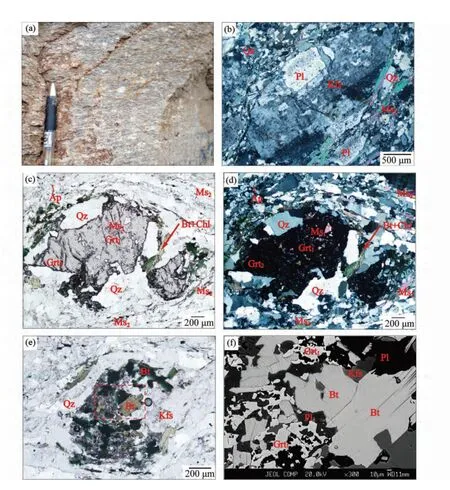
图2 米林地区眼球状花岗岩的野外和显微照片以及背散射图像(a)眼球状花岗岩的野外照片;(b)花岗岩的糜棱结构和钾长石斑晶;(c、d)花岗岩的石榴石变斑晶;(e)石榴石变斑晶被黑云母和长石交代的残余;(f)图2e 中红色虚线框部分的背散射图像.矿物缩写据Whitney and Evans,2010Fig.2 Field views,photomicrographs and back-scattered-electron image of the Milin augen granites
青藏高原从北到南主要由四个大陆地块或地体组成,依次为松潘-甘孜地体、羌塘地体、拉萨地体和喜马拉雅带(Yin and Harrison,2000;许志琴等,2006)。研究区位于青藏高原东南部,主要由3 个构造单元组成:拉萨地体、高喜马拉雅带和特提斯喜马拉雅带。雅鲁藏布江蛇绿岩混杂岩带呈马蹄状分布于北部的拉萨地块和南部的高喜马拉雅带和特提斯喜马拉雅带中(图1)。
拉萨地体主要由古生代-中生代沉积岩、中、新生代冈底斯岩浆岩和峰期角闪岩相至麻粒岩相的林芝杂岩组成。过去的研究认为,这套中、高级的变质岩——林芝杂岩,是拉萨地体的前寒武纪变质基底,曾被命名为念青唐古拉片麻岩系/岩群、冈底斯岩群和林芝岩群(李璞,1955;甘肃省地质矿产局区域地质调查队,1995①甘肃省地质矿产局区域地质调查队.1995.1∶20 万通麦-波密幅区域地质调查报告;云南省地质调查院,2003②云南省地质调查院.2003.1∶25 万林芝幅区域地质调查报告)。而最新的研究表明,这些变质岩系的原岩主要由形成在晚古生代的沉积岩、中生代-新生代的岩浆岩和少量的古生代岩浆岩组成,其角闪岩相-麻粒岩相的变质作用发生在新特提斯洋北向拉萨地体之下俯冲导致的安第斯型造山作用和印度-欧亚大陆碰撞引起的喜马拉雅型造山作用过程中,是中、新生代的复合变质带(王金丽等,2009;董昕等,2012;Dong et al.,2010,2014;Zhang et al.,2010a,2013,2014;Guo et al.,2012)。本文样品采自南拉萨地体米林县北北东方向,属于林芝杂岩的一部分(图1)。野外调查表明,寒武纪岩石靠近雅江缝合带,经历了强烈的变形作用,具有眼球状或条带状构造,花岗岩中的长石颗粒被压扁拉长呈椭圆形(图2a)。
高喜马拉雅带中的岩石,被称为南迦巴瓦杂岩,由高级变质的片麻岩、角闪岩、片岩、大理岩、麻粒岩和混合岩组成,原岩可能为元古代岩石(Liu and Zhong,1997;Burg et al.,1998;Ding and Zhong,1999;Geng et al.,2006)。最近的研究显示,南迦巴瓦杂岩由古元古代晚期(1759~1594Ma)和古生代早期(约500Ma)的岩浆岩,和元古代至古生代早期的沉积岩组成(郭亮等,2008;Zhang et al.,2012b)。多数岩石经历了麻粒岩相变质作用,变质和混合岩化时间持续较长,约从40 至7Ma(Burg et al.,1998;Ding et al.,2001;Booth et al.,2004,2009;Liu et al.,2007;Xu et al.,2010;Zhang et al.,2010b,2012b;Su et al.,2012)。本文对比的同期寒武纪岩石,即为南迦巴瓦杂岩中原岩为503~490Ma的花岗质片麻岩(图1;Zhang et al.,2012b)。
3 分析方法
3.1 全岩化学成分
全岩主量和微量元素化学成分分析在国家地质实验测试中心完成。主量元素采用XRF(X-ray fluorescence)方法进行测定,分析精度优于5%。微量元素采用等离子质谱仪ICP-MS(Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry)方法进行测定,含量大于10 ×10-6的元素测试精度为5%,而小于10 ×10-6的元素测试精度为10%。CIPW 计算采用Geokit(路远发,2004)软件完成。
3.2 矿物化学成分
矿物化学成分电子探针分析在中国地质科学院地质研究所国土资源部大陆动力学实验室完成,所用仪器为日本电子JEOL 公司生产的电子探针显微分析仪(Electron Probe MicroAnylyzer),仪器型号:JXA-8100。实验条件为加速电压15kV,束流2 ×10-8A,束斑直径5μm,摄谱时间10sec,ZAF校正。SPI 标准矿物校正。
3.3 锆石U-Pb 定年
锆石阴极发光成像在中国地质科学院地质研究所北京离子探针中心完成。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 和微量元素分析在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成。所使用的ICP-MS 仪器型号为Elan6100DRC,激光剥蚀系统为德国Lamda Physik 公司的Geolas200M 深紫外(DUV)193nm ArF 准分子(excimer)激光剥蚀系统,激光束斑直径采用32μm。实验中采用He 作为剥蚀物质的载气,哈佛大学标准锆石91500 作为外标,29Si 作为内标。采用ICPMSDataCal(V3.7)软件对同位素比值数据进行处理,详细的仪器操作条件和数据处理方法见Liu et al.(2008,2010)。ISOPLOT 程序(Ludwig,2003)进行锆石加权平均年龄计算及谐和图的绘制。
3.4 锆石Lu-Hf 同位素分析
锆石Hf 同位素测试在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室Neptune 多接收等离子质谱和Newwave UP213 紫外激光剥蚀系统(LA-MCICP-MS)上进行的,实验过程中采用He 作为剥蚀物质载气,剥蚀直径采用55μm,测定时使用锆石国际标样GJ1 作为参考物质。相关仪器运行条件及详细分析流程见侯可军等(2007)。分析过程中锆石标准GJ1 的176Hf/177Hf 测试加权平均值为0.282038 ±4(2σ,n =33)。计算初始176Hf/177Hf 时,Lu 的衰变常数采用1.865 ×10-11a-1(Scherer et al.,2001),εHf(t)值的计算时采用球粒陨石Hf 同位素值176Lu/177Hf =0.0336,176Hf/177Hf=0.282785(Bouvier et al.,2008)。在Hf的地幔模式年龄计算中,亏损地幔176Hf/177Hf 现在值采用0.28325,176Lu/177Hf 采用0.0384(Griffin et al.,2000),地壳模式年龄计算时采用平均地壳的176Lu/177Hf =0.015(Griffin et al.,2002)。
4 岩石学
4.1 岩相学
米林地区的眼球状花岗岩经历了变形和弱的变质作用,具有斑状变晶结构或糜棱结构,主要由斜长石、钾长石和石英组成,含有少量石榴石、白云母、黑云母矿物和磷灰石等副矿物(图2b-f)。碎斑/变斑晶主要为钾长石和石榴石(图2bd)。石榴石变斑晶他形,核部(Grt1)含有不同于基质中的他形片状白云母(Ms1),边部(Grt2)被黑云母和石英替代(图2c,d);部分石榴石(Grt1)已被黑云母和他形斜长石全部替代,仅剩少量残余(图2e,f)。基质由细粒和重结晶条带状的石英、他形的斜长石和钾长石,以及条带状的白云母组成(图2b-d)。条带状的石英和白云母(Ms2)定向排列构成线理(图2b-d)。
南迦巴瓦地区的寒武纪花岗质片麻岩具有片麻状构造,主要由斜长石、条纹长石、石英和黑云母组成,含有少量石榴石、角闪石和褐帘石,矿物共生组合说明岩石经历了角闪岩相的变质作用(见Zhang et al.,2012b,在此不赘述)。
4.2 矿物化学
米林地区眼球状花岗岩中石榴石和白云母的代表性化学成分见表1、表2,典型特征描述如下。
由于岩石变质程度低,原生的岩浆成因石榴石得以保存。原生岩浆成因的石榴石以石榴石变斑晶核部和他形残余形式出现(Grt1;图2c-f),主要由铁铝榴石(42.3%~62.5%)和钙铝榴石(14.3%~44.4%)组成;因为含有高的MnO 含量(5.58%~9.69%),锰铝榴石端元组分相对较高(13.0%~23.1%)(表1)。石榴石变斑晶的边部(Grt2;图2c,d)经历变质作用,相比岩浆成因的石榴石具有低的MnO(2.54%和2.78%)含量,端元组分分别为铁铝榴石51.3%和52.1%,钙铝榴石42.0%和42.4%,以及锰铝榴石5.7%和6.2%(表1)。

表1 米林眼球状花岗岩中代表性石榴石成分(wt%)Table 1 The compositions of representative garnet from the Milin augen granites (wt%)
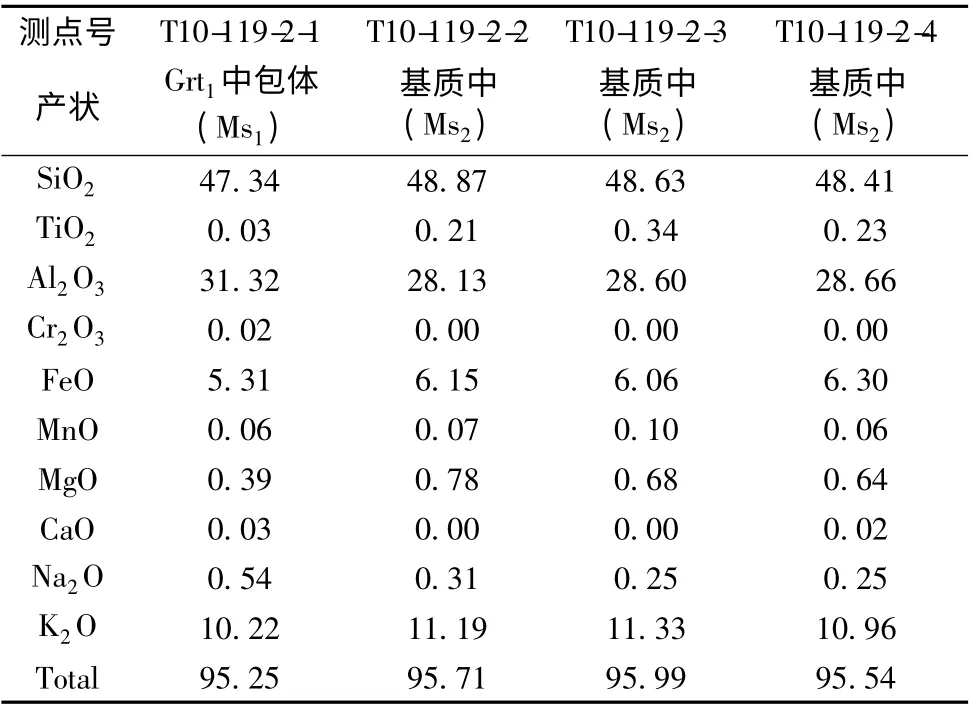
表2 米林眼球状花岗岩中代表性白云母成分(wt%)Table 2 The compositions of representative muscovite from the Milin augen granites (wt%)
原生岩浆成因的白云母以包体形式产出在岩浆成因的石榴石核部,数量较少,他形(Ms1);变质成因的白云母全部产出在基质中,为长的条带状(Ms2)(图2b-d)。岩浆成因的白云母较变质成因的白云母具有略低的SiO2(47.34%)含量,低的MgO(0.39%)和TiO2(0.03%)以及高的Na2O(0.54%)含量(表2)。变质成因的白云母上述成分分别:SiO2为48.41%~48.87%,MgO 为0.64%~0.78%,TiO2为0.21%~0.34%和Na2O 为0.25%~0.31%(表2)。

表3 寒武纪花岗质岩石的全岩化学成分(主量元素:wt%;微量元素:×10 -6)Table 3 Whole-rock chemical compositions from the Cambrian granitoids (major elements:wt%;trace elements:×10 -6)

图3 青藏高原东南部寒武纪花岗岩类的全岩地球化学分类图解(a)侵入岩的TAS 图解;(b)A/CNK-A/NK 图解.图4、图9 图例同此图Fig.3 Whole-rock geochemical classification diagrams of the Cambrian granitoids form the southeastern Tibetan Plateau

图4 青藏高原东南部寒武纪花岗岩类的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough,1989)Fig.4 Normalized trace elements diagrams of the Cambrian granitoids form the southeastern Tibetan Plateau (normalization values after Sun and McDonough,1989)
4.3 全岩主、微量地球化学
青藏高原东南部寒武纪花岗质岩石的全岩主量和微量元素成分见表3。
米林地区眼球状花岗岩具有相似的主量元素成分:SiO2为76.0%~77.5%、Al2O3为12.4%~13.5%、CaO 为0.51%~1.73%、Na2O 为2.58%~4.84% 和K2O 为1.36%~5.35%,为钙碱性花岗岩。在侵入岩的 TAS 图解中(Middlemost,1994),全部落入花岗岩区域(图3a)。铝饱和指数(A/CNK)为1.07~1.16,为准铝质到过铝质(图3b),刚玉分子数较高(均大于1,表3)。球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素图解中(图4a),轻、重稀土元素分异不明显,轻稀土元素含量略高于重稀土元素((La/Yb)N=2.09~2.68),具有明显的Eu 负异常(δEu=0.04~0.21);原始地幔标准化的多元素图解中,显示明显的Ba、Nb、Sr、P 和Ti 的负异常(图4b)。
南迦巴瓦地区花岗质片麻岩较米林眼球状花岗岩具有低的SiO2含量(62.5%~72.9%),高的CaO(1.80%~4.88%)含量,和相似的全碱含量,为钙碱性。在TAS 图解中,落入闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和花岗岩区域(图3a)。铝饱和指数(A/CNK)均小于1.1,为准铝质(图3b),刚玉分子数略低(表3)。具有明显分异的稀土元素特征(图4a),富集轻稀土元素、亏损重稀土元素((La/Yb)N=5.26~12.01),弱的Eu 负异常(δEu=0.32~0.72);原始地幔标准化的多元素图解中,同样具有Ba、Nb、Sr、P 和Ti 的负异常(图4b)。
5 锆石U-Pb 定年
本文对米林地区眼球状花岗岩的2 个样品(T10-119-2和T10-119-6)进行了LA-ICP-MS 锆石U-Pb 定年。锆石定年和微量元素分析结果见表4 和表5。
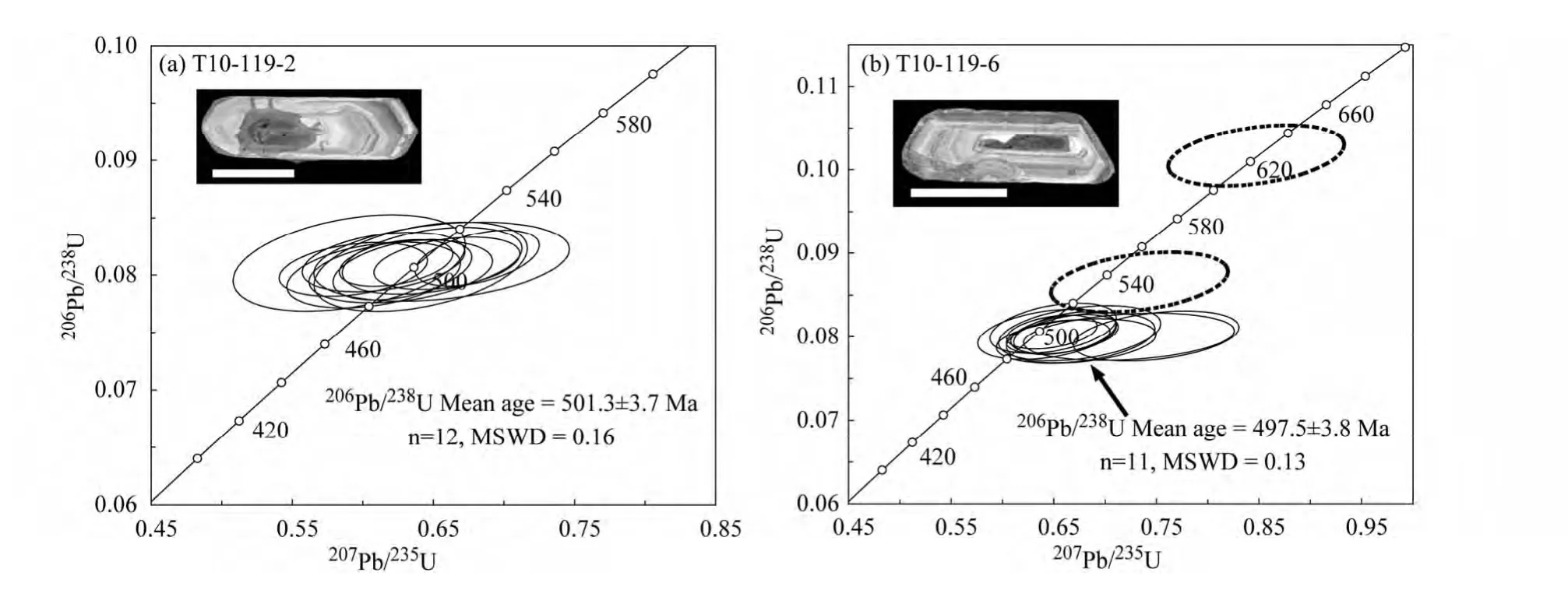
图5 米林眼球状花岗岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄谐和图和代表性锆石的阴极发光图像阴极发光图像中比例尺为100μmFig.5 Zircon U-Pb age concordia diagrams and cathodoluminescence images of representative zircon from the Milin augen granites,with a scale bar of 100μm
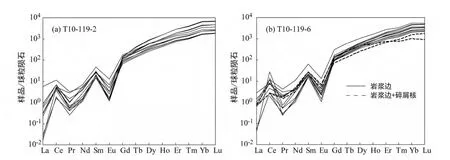
图6 米林眼球状花岗岩中锆石的稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解Fig.6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of zircon from the Milin augen granites
样品中的锆石半自形-自形长柱状,无色至浅褐色,颗粒长径约为200~300μm。阴极发光图像表明,大多数锆石具核-边结构,核部为形状不规则的具不清晰环带的继承性碎屑锆石,边部较宽,具岩浆锆石典型的振荡环带(图5)。样品T10-119-2 边部获得12 个谐和的测试点,206Pb/238U 年龄范围为505~496Ma 之间,加权平均值为501.3 ± 3.7Ma(MSWD=0.16,图5a)。样品T10-119-6 边部获得13 个谐和的测试点,206Pb/238U 年龄范围为624~493Ma 之间,剔除2个核-边混合较老的年龄,11 个点的加权平均值为497.5 ±3.8Ma(MSWD=0.13,图5b)。分析的岩浆锆石的稀土元素配分模式图表现为LREE 亏损,HREE 富集,具明显的Ce 正异常和Eu 负异常(图6),锆石稀土元素总量较高范围为745×10-6~2800 ×10-6(表5),Th/U 比值均大于0.1(表4),为典型岩浆成因锆石特征(例如Rubatto,2002;Geisler et al.,2007)。因此,结合之前报道的数据(496Ma,Dong et al.,2010),米林地区眼球状花岗岩的结晶年龄为寒武纪的501~496Ma。
6 锆石Hf 同位素
本文对米林地区眼球状花岗岩的3 个样品(T10-119-2、T10-119-6 和TM08-41-1)和南迦巴瓦地区片麻状花岗岩3 个样品(6-10-1、6-14-1 和6-17-1)进行了锆石Hf 同位素测试。锆石Hf 同位素组成见表6。
锆石Hf 同位素分析结果表明,米林3 个样品中的岩浆锆石的初始176Hf/177Hf 比值非常相似,范围为0.282297~0.282481(表6),相应的εHf(t)值分别为- 5.4~- 2.2、-5.5~-2.8 和-6.2~0.3(表6、图7a),地壳Hf 模式年龄变化范围为1.85~1.43Ga(表6、图7b)、南迦巴瓦3 个样品中的岩浆锆石的初始176Hf/177Hf 比值有一定变化,范围分别为0.282111~0.282302、0.282241~0.282449 和0.282205~0.282310(表6),相应的εHf(t)值分别为-12.9~-6.2、-8.2~-0.9 和-9.3~-5.6(表6、图7a),地壳Hf 模式年龄变化范围分别为2.26~1.84、1.97~1.51 和2.05~1.81Ga(表6、图7b)。

表4 米林眼球状花岗岩中锆石的U-Pb定年结果Table4 The U-Pb dating results of zircon from the Milin augen geanites
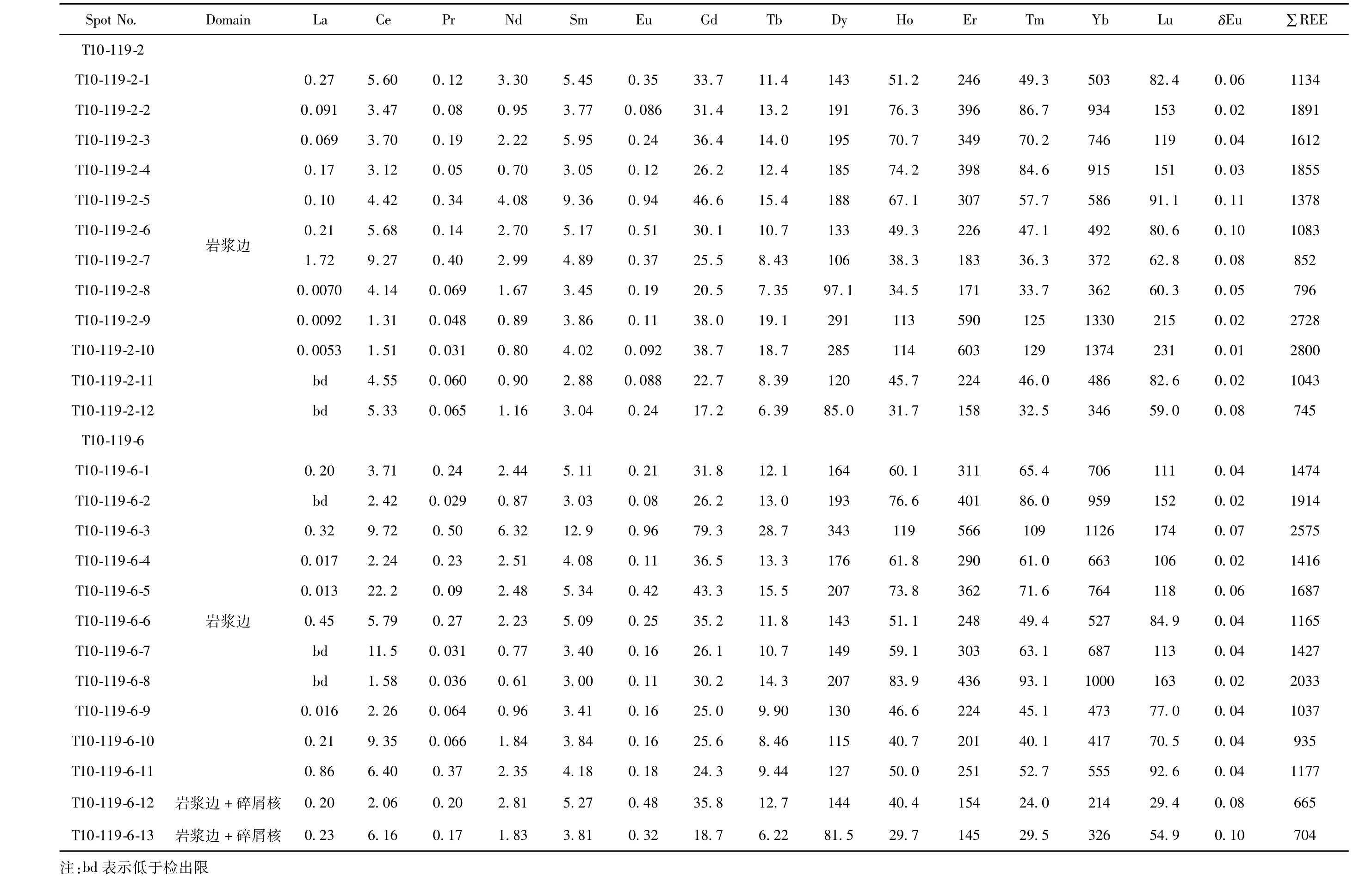
表5 米林眼球状花岗岩中锆石的稀土元素含量 ( ×10-6)Table5 Therare-earth element contents of zircon from the Milin augen granites( ×10 -6)
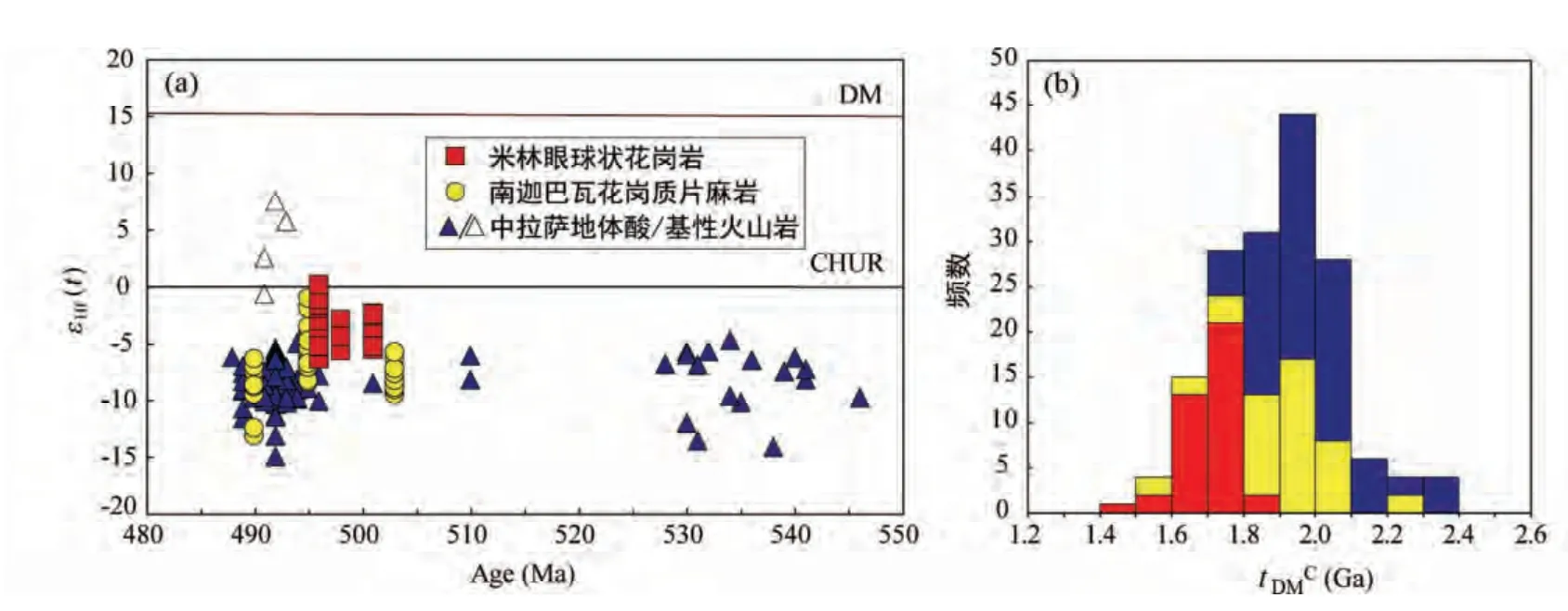
图7 锆石的U-Pb 年龄-εHf(t)值图解(a)和地壳Hf 模式年龄直方图(b)中拉萨地体寒武纪火山岩中锆石的Hf 同位素数据引自Zhu et al.,2012Fig.7 Diagram of U-Pb ages vs.εHf(t)values (a)and crustal-model ages (tDMC)histogram (b)of zircon

图8 米林寒武纪花岗岩中锆石的微量元素双变量图解(a)Pb-Th 图解;(b)δEu-(Nb/Pb)N图解,I 型和S 型花岗岩中锆石微量元素分区据Wang et al.(2012)Fig.8 Bivariate diagrams of zircon trace elements from the Milin Cambrian granites
7 讨论
7.1 拉萨地体寒武纪S 型花岗岩类
锆石U-Pb 年代学表明本文所研究的花岗岩类的结晶年龄为寒武纪的501~496Ma。由于靠近雅鲁藏布江缝合带,米林地区的寒武纪花岗岩遭受了变形和低级的变质作用,呈眼球状或条带状构造,对其花岗岩源岩类型的恢复有一定难度。本次的研究表明,该期岩浆岩均为花岗质岩石(图3a),全岩主量元素特征表明岩石具有较高的SiO2含量,为钙碱性花岗岩、偏铝质至弱过铝质,尽管CIPW 计算结果表明岩石具有类似S 型花岗岩的较高刚玉分子数(表3),但还不能确定岩石的类型。岩相学的观察表明,岩石经历了低级变质作用,原生岩浆成因矿物较难判别,但通过矿物化学分析,仍鉴别出了原生岩浆成因的过铝质矿物。原生岩浆成因的石榴石较变质作用的石榴石具有较高的MnO 含量(Miller and Stoddard,1981;Villaros et al.,2009;Zhang et al.,2013),以石榴石核部和他形残留体的形式存在(图2c-f),邻区林芝杂岩S 型花岗岩中的石榴石同样以高的锰铝榴石端元组分为特征(Zhang et al.,2013);原生岩浆成因的白云母以包体形式保存于岩浆成因的石榴石核部(图2c,d),较基质中变质成因的条带状白云母具有较低的SiO2和MgO 含量(表2)。同时,花岗岩中锆石核部保存了继承的碎屑锆石;岩浆成因的锆石边部具有较高的Pb 含量、低的(Nb/Pb)N比值和显著的Eu 负异常(表4、表5 和图8),这些都是S 型花岗岩中锆石的典型特征(Wang et al.,2012)。因此,上述证据表明米林眼球状花岗岩应为S 型的花岗岩。
由于采集的样品数目过少,限制了岩石成因的讨论。但是从仅有的米林花岗岩的稀土元素特征中,我们可以看出,岩石具有明显且一致的Eu、Ba 和Sr 的负异常(图4),说明岩浆经历了斜长石的分离结晶作用;而岩石轻稀土元素的低含量和P 的负异常(图4)可能与褐帘石和磷灰石,或者是独居石的分离结晶有关。独居石发生分离结晶作用时,Th 和LREE的含量会降低(Vidal et al.,1982;Cuney et al.,1984;Guillot and Le Fort,1995),图9 中可见二者随SiO2含量的增高,成正相关性降低(同期南迦巴瓦花岗质片麻岩即不具这种特征),因此,本文认为米林花岗岩的上诉特征是由于独居石的分离结晶所致,这一现象在喜马拉雅带新生代的S 型花岗岩中也广泛存在(张宏飞等,2005;Guo and Wilson,2012;Zeng et al.,2012)。
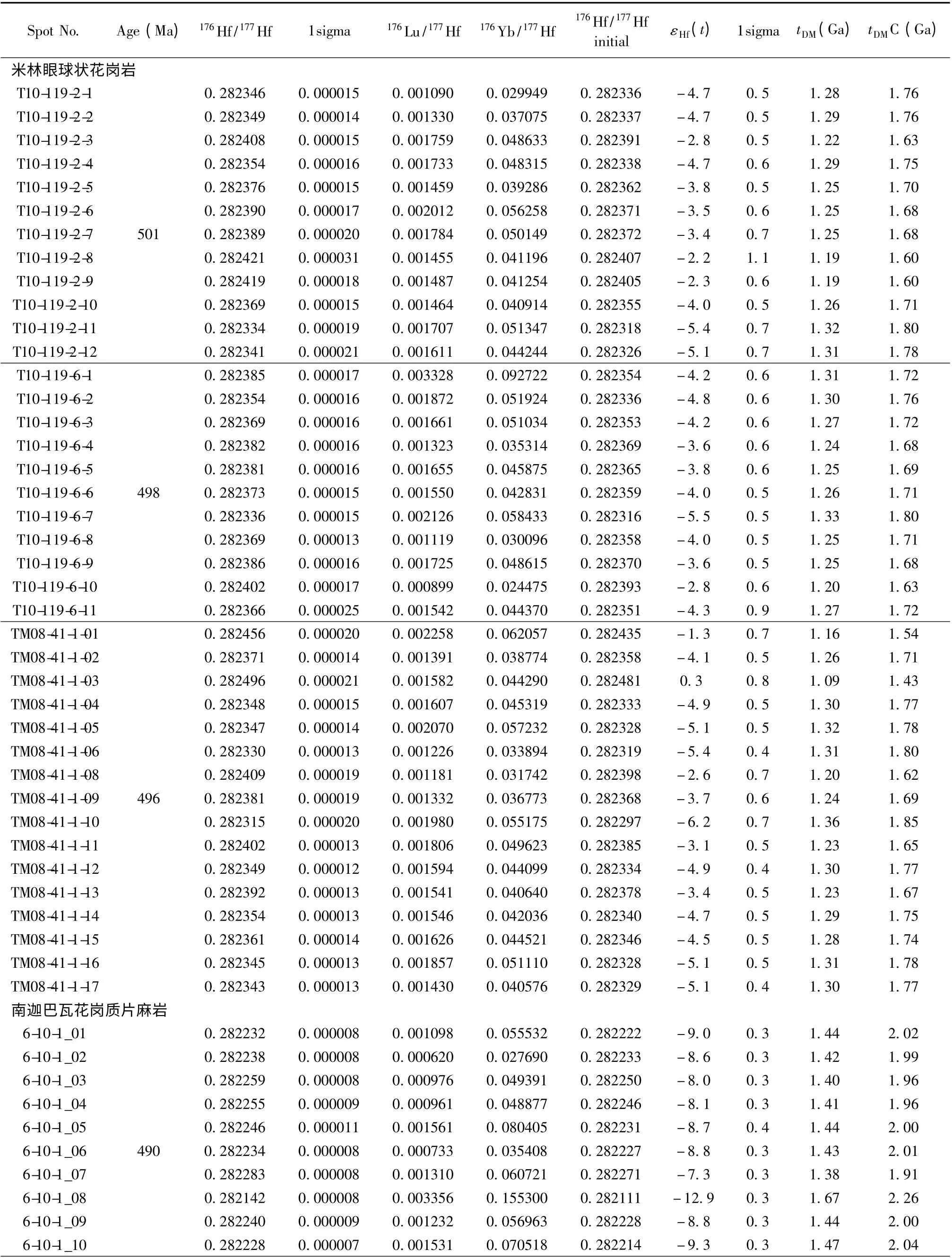
表6 寒武纪花岗质岩石中锆石的Hf 同位素组成Table 6 The Hf isotope components of zircon from the Cambrian granitoids
续表6Continued Table 6
7.2 拉萨地体的结晶基底
相对于拉萨地体广泛分布的与中、新生代造山作用相关的巨型冈底斯岩浆岩(Chung et al.,2003,2005;Hou et al.,2004;Nomade et al.,2004;莫宣学等,2005,2007,2009;许志琴等,2006;Chu et al.,2006;Mo et al.,2007,2008;侯增谦等,2008;朱弟成等,2008a,b;Wen et al.,2008a,b;Zhu et al.,2008,2009a,b,2011;Ji et al.,2009;Zhao et al.,2009;Zhang et al.,2010;Xu et al.,2012),古生代以及之前的岩浆作用寥寥可数。至今,北拉萨地体还没有中生代以前的岩浆事件相关报道。中拉萨地体目前已报道的最古老的结晶基底是东构造结墨脱地区的~1.3Ga 中元古代花岗岩类,锆石Hf 模式年龄集中在2.0~1.6Ga,并具有正的εHf(t)值(Xu et al.,2013),中部申扎地区出露了525~490Ma 的火山岩(计文化等,2009;Zhu et al.,2012;Hu et al.,2013;Ding et al.,2014)和510Ma 的花岗岩(Gehrels et al.,2011)。申扎地区寒武纪酸性火山岩中的锆石具有极负的εHf(t)值,范围为-14.8~-4.6,古老的地壳模式年龄(2.4~1.8Ga)(图7;Zhu et al.,2012)。此外,Dong et al.(2011a)和Zhang et al.(2012a)的研究证明在纳木措西存在新元古代的高压-中压变质岩。以上证据均表明,中拉萨地体存在中元古代甚至更老的结晶基底。
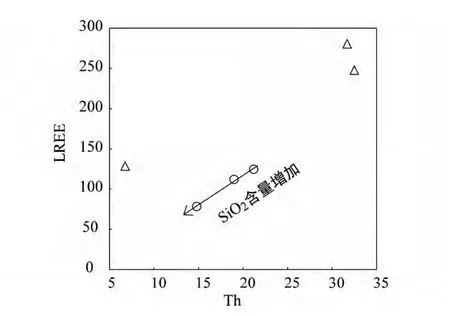
图9 米林寒武纪花岗岩的Th-LREE 图解Fig.9 Diagram of Th vs.LREE from the Milin Cambrian granites
最新的研究表明,在南拉萨地体东南部的朗县和加查县附近存在晚泥盆世-早石炭世(371~346Ma)的岩浆作用,酸性岩中锆石的地壳Hf 模式年龄范围为1.9~1.4Ga;基性岩中锆石的地幔Hf 模式年龄为1.3~1.1Ga(Ji et al.,2012;Dong et al.,2014)。而本文报道的寒武纪花岗岩类位于其东侧的米林地区,锆石U-Pb 年代学证明其结晶年龄为501~496Ma,Hf 同位素具有近一致的负εHf(t)值(表6),地壳Hf模式年龄年龄范围为1.9~1.4Ga,集中在1.8~1.6Ga(图7b),说明该寒武纪花岗岩可能来源于中-新元古代物质的部分熔融。同时,笔者未发表数据表明南拉萨地体存在约600Ma 的岩浆岩,因此,本文认为南拉萨地体存在前寒武纪的结晶基底,而并不是一个年轻的岛弧地体(Chu et al.,2011)。
7.3 构造意义
通常认为,随着分割东、西冈瓦纳大陆的Mozambique 洋的闭合和东非造山作用(570~520Ma),南方大陆冈瓦纳大陆最终拼合起来(McWilliams,1981;Stern,1994)。但是,最近的研究表明,冈瓦纳大陆的拼合涉及到其内部一系列的造山作 用(Fitzsimons,2000a,b;Collins et al.,2003a,b;Meert,2003;Boger and Miller,2004;Johnson and Oliver,2004;Collins and Pisarevsky,2005;Fitzsimons and Hulscher,2005)。其中,东冈瓦纳大陆的拼合过程包括:Kalahari、Mawson 和India 地块之间的Kuunga 造山带(560~530Ma),Australia-Mawson 和India 地块之间的Pinjarra 造山带(560~520Ma)。随着冈瓦纳大陆拼合的结束,其周缘又开始形成新的俯冲带和增生造山作用,冈瓦纳大陆周缘转变为活动陆缘,南部大陆边缘由于原太平洋的俯冲,形成从Australia 东部、New Zealand、Antarctica、South Africa 持续到American 西南海岸的Terra-Australis 造山带(530~490Ma)。北部由于原特提斯洋的俯冲,在印度地块北部形成北印度造山带(又名Bhimphedian 造山带,530~470Ma)(Cawood et al.,2007)。
Ji et al.(2012)研究表明中、南拉萨地体在晚古生代之前为一个块体。他们和高喜马拉雅带共同位于东冈瓦纳大陆的北缘(Cawood et al.,2007)。高喜马拉雅带南迦巴瓦杂岩中的正变质岩主要由古元古代晚期(1759~1594Ma)和古生代早期(约500Ma)的岩浆岩组成(郭亮等,2008;Zhang et al.,2012b)。其中,寒武纪花岗质片麻岩具有低的铝饱和指数和刚玉分子数,样品中的锆石核部均为岩浆成因,岩浆核获得了正片麻岩的原岩年龄为503~490Ma(Zhang et al.,2012b)。锆石具有负的εHf(t)值(表6、图7a),地壳Hf 模式年龄范围为元古代的2.3~1.5Ga(图7b)。因此,本文推测其可能为元古代的地壳物质部分熔融产生的I 型花岗岩。同时,南迦巴瓦杂岩还经历了538Ma 的变质作用(Zhang et al.,2012b)。上述岩浆和变质作用与南拉萨地体米林地区S 型花岗岩和中拉萨地体申扎地区双峰式火山岩近同期。这种I 型和S 型花岗岩同时产生的现象在典型的安第斯型造山过程中,例如澳大利亚的Delamerian、Lachlan 和New England 造山带广泛存在(Chappell and White,1992;Kemp et al.,2009)。这一安第斯型的造山作用在印度北部喜马拉雅带、中拉萨地体申扎和滇西地区还造成早古生代地层的不整合(Funakawa,2001;Miller et al.,2001;Gehrels et al.,2003,2006,2011;李才等,2010;黄勇等,2012;蔡志慧等,2013)。因此,本文报道的青藏高原东南部的寒武纪花岗质岩石为古生代早期原特提斯洋俯冲导致的安第斯型造山作用的产物。
8 结论
(1)青藏高原东南部寒武纪花岗质岩石位于南拉萨地体的米林地区和高喜马拉雅带的南迦巴瓦地区,原岩类型包括闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和花岗岩。米林地区眼球状花岗岩中保存了原生岩浆成因的过铝质矿物石榴石和白云母。结合全岩化学成分、锆石结构及微量元素成分特征,本文推测其为S型花岗岩类,岩浆演化过程中发生了斜长石和独居石的分离结晶作用。
(2)锆石U-Pb 年代学和Hf 同位素研究表明,南拉萨地体眼球状花岗岩的结晶年龄为501~496Ma,锆石具有近一致负的εHf(t)值,地壳Hf 模式年龄主要集中在1.8~1.6Ga,说明其可能来源于中-新元古代物质的部分熔融,南拉萨地体并不是一个年轻的岛弧地体。高喜马拉雅带寒武纪花岗质片麻岩具有负的εHf(t)值,地壳Hf 模式年龄范围为元古代的2.3~1.5Ga。
(3)青藏高原东南部S 型和I 型的花岗岩类共同记录了原特提斯洋俯冲过程中安第斯型造山作用。
致谢 感谢中国地质大学(北京)赵志丹和朱弟成教授在文章发表过程中的指导,中国地质科学院地质研究所戚学祥研究员和于胜尧副研究员在评审过程中提出的宝贵意见,以及中国地质科学院地质研究所蔡志慧、田作林博士在文章撰写中和中国地质科学院矿产研究所郭春丽副研究员在实验中的帮助!
Boger SD and Miller JM.2004.Terminal suturing of Gondwana and the onset of the Ross-Delamerian Orogeny:The cause and effect of an Early Cambrian reconfiguration of plate motions.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,219 (1-2):35-48
Booth A,Zeitler P,Kidd W,Wooden J,Liu Y,Idleman B,Hren M and Chamberlain P.2004.U-Pb zircon constraints on the tectonic evolution of southeastern Tibet,Namche Barwa area.American Journal of Science,304(10):889-929
Booth AL,Chamberlain CP,Kidd WSF and Zeitler PK.2009.Constraints on the metamorphic evolution of the eastern Himalayan Syntaxis from geochronologic and petrologic studies of Namche Barwa.Geological Society of America Bulletin,121(3-4):385-407
Bouvier A,Vervoort JD and Patchett PJ.2008.The Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic composition of CHUR:Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,273(1-2):48-57 Burg JP,Nievergelt P,Oberli F,Seward D,Davy P,Maurin JC,Diao ZZ and Meier M.1998.The Namche Barwa syntaxis:Evidence for exhumation related to compressional crustal folding.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,16(2-3):239-252
Cai ZH,Xu ZQ,Duan XD,Li HQ,Cao H and Huang XM.2013.Early stage of Early Paleozoic orogenic event in western Yunman Province,southeastern margin of Tibet Plateau.Acta Petrologica Sinica,29(6):2013-2140 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cawood PA,Johnson MRW and Nemchin AA.2007.Early Palaeozoic orogenesis along the Indian margin of Gondwana:Tectonic response to Gondwana assembly.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,255(1-2):70-84
Chappell BW and White AJR.1992.I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt.Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh,83(1-2):1-26
Chu MF,Chung SL,Liu DY,O’Reilly SY,Pearson NJ,Ji JQ and Wen DJ.2006.Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on the Mesozoic tectonics and crustal evolution of southern Tibet.Geological Society of America,34(9):745-748
Chu MF,Chung SL,O’Reilly SY,Pearson NJ,Wu FY,Li XH,Liu DY,Ji JQ,Chu CH and Lee HY.2011.India’s hidden inputs to Tibetan orogeny revealed by Hf isotopes of Transhimalayan zircons and host rocks.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,307(3-4):479-486
Chung SL,Liu DY,Ji WQ,Chu MF,Lee HY,Wen DJ,Lo CH,Lee TY,Qing Q and Zhang Q.2003.Adakites from continental collision zones:Melting of thickened lower crust beneath southern Tibet.Geology,31(11):1021-1024
Chung SL,Chu MF,Zhang Y,Lo CH,Lee TY,Lan CY,Li X,Zhang Q and Wang Y.2005.Tibetan tectonic evolution inferred from spatial and temporal variations in post-collisional magmatism.Earth Science Reviews,68(3-4):173-196
Chung SL,Chu MF,Ji JQ,O’Reilly SY,Pearson NJ,Liu DY,Lee TY and Lo CH.2009.The nature and timing of crustal thickening in Southern Tibet:Geochemical and zircon Hf isotopic constraints from postcollisional adakites.Tectonophysics,477(1-2):36-48
Collins AS,Fitzsimons ICW,Hulscher B and Razakamanana T.2003a.Structure of the eastern margin of the East African Orogen in central Madagascar.Precambrian Research,123(2-4):111-133
Collins AS,Kröner A,Fitzsimons ICW and Razakamanana T.2003b.Detrital footprint of the Mozambique ocean:U-Pb SHRIMP and Pb evaporation zircon geochronology of metasedimentary gneisses in eastern Madagascar.Tectonophysics,375(1-4):77-99
Collins AS and Pisarevsky S.2005.Amalgamating eastern Gondwana:The evolution of the circum-Indian orogens.Earth-Science Reviews,71(3-4):229-270
Cuney M,Le Fort P and Wang ZX.1984.Uranium and thorium geochemistry and mineralogy in the Manaslu leucogranite (Nepal,Himalaya).In:Xu KQ and Tu GC (eds.).Proceedings of the Sympoium on “Geology of Granites and Their Metallogenic Relations”Nanjing Univ.,China 1982.Beijing:Science Press,853-873
Ding HX,Zhang ZM,Dong X,Yan Y,Lin YH and Jiang HY.2014.Cambrian ultrapotassic rhyolites from the Lhasa terrane,South Tibet:Evidence for Andean-type magmatism along the northern active margin of Gondwana.Gondwana Research,27(4):1616-1629
Ding L and Zhong DL.1999.Metamorphic characteristics and geotectonic implications of the high-pressure granulites from Namjag Barwa,eastern Tibet.Science in China (Series D),42(5):491-505
Ding L,Zhong DL,Yin A,Kapp P and Harrison TM.2001.Cenozoic structural and metamorphic evolution of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis(Namche Barwa).Earth and Planetary Science Letters,192(3):423-438
Dong X,Zhang ZM and Santosh M.2010.Zircon U-Pb chronology of the Nyingtri Group, Southern Lhasa Terrane, Tibetan Plateau:Implications for Grenvillian and Pan-African Provenance and Mesozoic-Cenozoic metamorphism.The Journal of Geology,118(6):677-690
Dong X,Zhang ZM,Santosh M,Wang W,Yu F and Liu F.2011a.Late Neoproterozoic thermal events in the northern Lhasa terrane,South Tibet:Zircon chronology and tectonic implications.Journal of Geodynamics,52(5):389-405
Dong X,Zhang ZM,Liu F,Wang W,Yu F and Shen K.2011b.Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Nyainqentanglha Group from the Lhasa terrane:New constraints on the Triassic orogeny of the South Tibet.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,42(4):732-739
Dong X,Zhang ZM,Liu F,Wang W,Yu F,Lin YH,Jiang HY and He ZY.2012.Genesis of the metamorphic rock from southeastern Lhasa terrane and the Mesozoic-Cenozoic orogenesis.Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(6):1765-1784 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Dong X,Zhang ZM,Liu F,He ZY and Lin YH.2014.Late Paleozoic intrusive rocks from the southeastern Lhasa terrane,Tibetan Plateau,and their Late Mesozoic metamorphism and tectonic implications.Lithos,198-199:249-262
Fitzsimons ICW.2000a.Grenville-age basement provinces in East Antarctica:Evidence for three separate collisional orogens.Geology,28(10):879-882
Fitzsimons ICW.2000b.A review of tectonic events in the East Antarctic Shield and their implications for Gondwana and earlier supercontinents.Journal of African Earth Sciences,31(1):3-23
Fitzsimons ICW and Hulscher B.2005.Out of Africa:Detrital zircon provenance of central Madagascar and Neoproterozoic terrane transfer across the Mozambique Ocean.Terra Nova,17(3):224-235
Funakawa S.2001.Lower Palaeozoic Tethys sediment from the Kathmandu nappe,Phulchauki area,central Nepal.Journal of Nepal Geological Society,25:123-134
Gehrels G,Decelles PG,Martin A,Ojha TP,Pinhassi G and Upreti BN.2003.Initiation of the Himalayan Orogen as an Early Paleozoic thinskinned thrust belt.GSA Today,13(9):4-9
Gehrels G,Decelles PG,Ojha TP and Upreti BN.2006.Geologic and UTh-Pb geochronologic evidence for Early Paleozoic tectonism in the Kathmandu thurst sheet,central Nepal Himalaya.Geological Society of America Bulletin,118(1-2):185-195
Gehrels G,Kapp P,Decelles P,Pullen A,Blakey R,Weislogel A,Ding L,Guynn J,Martin A,McQuarrie N and Yin A.2011.Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan Himalayan orogen.Tectonics,30(5):TC5016,doi:10.1029/2011TC002868
Geisler T,Schaltegger U and Tomaschek F.2007.Re-equilibration of zircon in aqueous fluids and melts.Elements,3(1):43-50
Geng QR,Pan GT,Zheng LL,Chen ZL,Fisher RD,Sun ZM,Ou CS,Dong H.Wang XW,Li S,Lou XY and Fu H.2006.The eastern Himalayan syntaxis:Major tectonic domains,ophiolitic mélanges and geologic evolution.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,27(3):265-285
Griffin WL,Pearson NJ,Belousova E,Jackson SE,van Achterbergh E,O’Reilly SY and Shee SR.2000.The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,64(1):133-147
Griffin WL,Wang X,Jackson SE,Pearson NJ,O’Reilly SY,Xu XS and Zhou XM.2002.Zircon chemistry and magma mixing,SE China:In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes,Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes.Lithos,61(3-4):237-269
Guillot S and Le Fort P.1995.Geochemical constraints on the bimodal origin of High Himalayan leucogranites.Lithos,35(3-4):221-234
Guo L,Zhang HF and Xu WC.2008.U-Pb zircon ages of migmatite and granitic gneiss from Duoxiongla in eastern Himalayan syntaxis and their geological implications.Acta Petrologica Sinica,24(3):421-429 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo L,Zhang HF,Harris N,Parrish R,Xu WC and Shi ZL.2012.Paleogene crustal anatexis and metamorphism in Lhasa terrane,eastern Himalayan syntaxis:Evidence from U-Pb zircon ages and Hf isotopic compositions of the Nyingchi Complex.Gondwana Research,21(1):100-111
Guo ZF and Wilson M.2012.The Himalayan leucogranites:Constraints on the nature of their crustal source region and geodynamic setting.Gondwana Research,22(2):360-376
Hou KJ,Li YH,Zou TR,Qu XM,Shi YR and Xie GQ.2007.Laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS technique for Hf isotope microanalysis of zircon and its geological applications.Acta Petrologica Sinica,23(10):2595-2604 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hou ZQ,Gao YF,Qu XM,Rui ZY and Mo XX.2004.Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during Mid-Miocene east-west extension in southern Tibet.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,220(1-2):139-155
Hou ZQ,Wang EQ,Mo XX,Ding L,Pan GT and Zhang ZJ.2008.Collision Orogeny and Mineralization of Tibetan Plateau.Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
Hu DG,Wu ZH,Jiang W,Shi YR,Ye PS and Liu QS.2005.SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and Nd isotope research of Nyainqentanglha Group,Tibet.Science in China (Series D),35(1):29-37 (in Chinese)
Hu PY,Li C,Wang M,Xie CM and Wu YW.2013.Cambrian volcanism in the Lhasa terrane,southern Tibet:Record of an Early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc along the Gondwana proto-Tethyan margin.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,77:91-107
Huang Y,Hao JX,Bai L,Deng GB,Zhang GX and Huang WJ.2012.Stratigraphic and petrologic response to Late Pan-African Movement in Shidian area,western Yunnan Province.Geological Bulletin of China,31(2-3):306-313 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ji WH,Chen SJ,Zhao ZM,Li RS,He SP and Wang C.2009.Discovery of the Cambrian volcanic rocks in the Xainza area,Gangdese orogenic belt, Tibet, China and its significance.Geological Bulletin of China,28(9):1350-1354 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ji WQ,Wu FY,Chung SL,Li JX and Liu CZ.2009.Zircon U-Pb chronology and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Gangdese batholiths,southern Tibet.Chemical Geology,262(3-4):229-245
Ji WQ,Wu FY,Liu CZ and Chung SL.2012.Identification of Early Carboniferous granitoids from southern Tibet and implications for terrane assembly related to the Paleo-Tethyan evolution.The Journal of Geology,120(5):531-541
Johnson SP and Oliver GJH.2004.Tectonothermal history of the Kaouren arc,northern Zimbabwe:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Irumide and Zambezi Belts of south central Africa.Precambrian Research,130(1-4):71-97
Kemp AIS,Hawkesworth CJ,Collins WJ,Gray CM,Blevin PL and EIMF.2009.Isotopic evidence for rapid continental growth in an extensional accretionary orogen:The Tasmanides,eastern Australia.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,284(3-4):455-466
Li C,Wang TW,Li HM and Zeng QG.2003.Discovery of Indosinian megaporphyritic granodiorite in the Gangdise area:Evidence for the existence of Paleo-Gangdise.Geological Bulletin of China,22(5):364-366 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li C,Wu YW,Wang M and Yang HT.2010.Significant progress on Pan-African and Early Paleozoic orogenic events in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Discovery of Pan-African orogenic unconformity and Cambrian System in the Gangdise area,Tibet,China.Geological Bulletin of China,29(12):1733-1736 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li HQ,Xu ZQ,Yang JS,Cai ZH,Chen SY and Tang ZM.2009.Records of Indosinian orogenesis in Lhasa terrane,Tibet.Journal of Earth Science,20(2):348-363
Li P.1955.Primary understanding of geology,Eastern Tibet.Chinese Science Bulletin,(7):62-71 (in Chinese)
Lin YH,Zhang ZM,Dong X,Shen K and Lu X.2013.Precambrian evolution of the Lhasa terrane,Tibet:Constraint from the zircon UPb geochronology of the gneisses.Precambrian Research,237:64-77
Liu Y and Zhong D.1997.Petrology of high-pressure granulites from the eastern Himalayan syntaxis.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,15(4):451-466
Liu Y,Yang ZQ and Wang M.2007.History of zircon growth in a highpressure granulite within the eastern Himalayan Syntaxis and tectonic implications.International Geology Review,49(9):861-872
Liu YS,Hu ZC,Gao S,Günthe D,Xu J,Gao CG and Chen HH.2008.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard.Chemical Geology,257(1-2):34-43
Liu YS,Gao S,Hu ZC,Gao CG,Zong KQ and Wang DB.2010.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating,Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths.Journal of Petrology,51(1-2):537-571
Lu YF.2004.GeoKit:A geochemical toolkit for Microsoft Excel.Geochemistry,33 (5):459- 464 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ludwig KR.2003.ISOPLOT 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel.Berkeley,CA:Berkeley Geochronology Center
McWilliams MO.1981.Palaeomagnetism and Precambrian tectonic evolution of Gondwana.In:Kröner A (ed.).Precambrian Plate Tectonics.Amsterdam:Elsevier,649-687
Meert JG.2003.A synopsis of events related to the assembly of eastern Gondwana.Tectonophysics,362(1-4):1-40
Middlemost EAK.1994.Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system.Earth Science Reviews,37(3-4):215-224
Miller C,Thöni M,Frank W,Grasemann B,Klötzli U,Guntli P and Draganits E.2001.The Early Palaeozoic magmatic event in the Northwest Himalaya,India:Source,tectonic setting and age of emplacement.Geological Magazine,138(3):237-251
Miller CF and Stoddard EF.1981.The role of manganese in the paragenesis of magmatic garnet:An example from the Old Woman-Piute Range,California.The Journal of Geology,89(2):233-246 Mo XX,Dong GC,Zhao ZD,Zhou S,Wang LL,Qiu RZ and Zhang FQ.2005.Spatial and temporal distribution and characteristics of granitoids in the Gangdese,Tibet and implication for crustal growth and evolution.Geological Journal of China Universities,11(3):281-290 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mo XX,Hou ZQ,Niu YL,Dong GC,Qu XM,Zhao ZD and Yang ZM.2007.Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision:Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet.Lithos,96(1-2):225-242
Mo XX,Zhao ZD,Zhou S,Dong GC and Liao ZL.2007.On the timing of India-Asia continental collision.Geological Bulletin of China,26(10):1240-1244 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mo XX,Niu YL,Dong GC,Zhao ZD,Hou ZQ,Zhou S and Ke S.2008.Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism to continental crust growth:A case study of the Paleogene Linzizong volcanic succession in southern Tibet.Chemical Geology,250(1-4):46-67
Mo XX,Zhao ZD,Yu XH,Dong GC,Li YG,Zhou S,Liao ZL and Zhu DC.2009.Cenozoic Collisional-postcollisional Igneous Rocks in the Tibetan Plateau.Beijing:Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
Nomade S,Renne PR,Mo XX,Zhao ZD and Zhou S.2004.Miocene volcanism in the Lhasa block,Tibet:Spatial trends and geodynamic implications.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,221(1-4):227-243
Rubatto D.2002.Zircon trace element geochemistry:Partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism.Chemical Geology,184(1-2):123-138
Scherer E,Munker C and Mezger K.2001.Calibration of the Lutetium-Hafnium clock.Science,293(5530):683-687
Stern RJ.1994.Arc assembly and continental collision in the Neoproterozoic East African Orogen: Implications for the consolidation of Gondwanaland.Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,22(1):319-351
Su W,Zhang M,Liu XH,Lin JF,Ye K and Liu X.2012.Exact timing of granulite metamorphism in the Namche-Barwa,eastern Himalayan syntaxis:New constrains from SIMS U-Pb zircon age.International Journal of Earth Sciences,101(1):239-252
Sun SS and McDonough WF.1989.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes.In:Sanders AD and Norry MJ (eds.).Magmatism in Ocean Basins.Geological Society,London,Special Publication,42(1):313-345
Vidal P,Cocherie A and Le Fort P.1982.Geochemical investigations of the origin of the Manaslu leucogranite (Himalaya, Nepal).Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,46(11):2279-2292
Villaros A,Stevens G and Buick IS.2009.Tracking S-type granite from source to emplacement:Clues from garnet in the Cape Granite Suite.Lithos,112(3-4):217-235
Wang JL,Zhang ZM,Dong X,Liu F,Yu F,Wang W,Xu FJ and Shen K.2009.Discovery of Late Cretaceous garnet two-pyroxene granulite in the southern Lhasa terrane,Tibet and its tectonic significances.Acta Petrologica Sinica,25(7):1695- 1706 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang Q,Zhu DC,Zhao ZD,Guan Q,Zhang XQ,Sui QL,Hu ZC and Mo XX.2012.Magmatic zircons from I-,S-and A-type granitoids in Tibet:Trace element characteristics and their application to detrital zircon provenance study.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,53:59-66
Wen DR,Chung SL,Song B,Iizuka Y,Yang HJ,Ji JQ,Liu DY and Gallet S.2008a.Late Cretaceous Gangdese intrusions of adakitic geochemical characteristics,SE Tibet:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications.Lithos,105(1-2):1-11
Wen DR,Liu DY,Chung SL,Chu MF,Ji JQ,Zhang Q,Song B,Lee TY,Yeh MW and Lo CH.2008b.Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages of the Gangdese Batholith and implications for Neotethyan subduction in southern Tibet.Chemical Geology,252(3-4):191-201
Whitney DL and Evans BW.2010.Abbreviations for names of rockforming minerals.American Mineralogist,95(1):185-187
Xu WC,Zhang HF,Parrish R,Harris N,Guo L and Yuan HL.2010.Timing of granulite-facies metamorphism in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and its tectonic implications.Tectonophysics,485(1-4):231-244
Xu WC,Zhang HF,Harris N,Guo L,Pan FB and Wang S.2013.Geochronology and geochemistry of Mesoproterozoic granitoids inthe Lhasa terrane,south Tibet:Implications for the early evolution of Lhasa terrane.Precambrian Research,236:46-58
Xu ZQ,Li HB and Yang JS.2006.An orogenic plateau:The orogenic collage and orogenic types of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Earth Science Frontiers,13 (4):1- 17 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu ZQ,Yang JS,Li HB,Ji SC,Zhang ZM and Liu Y.2011.On the tectonics of the India-Asja collision.Acta Geologica Sinica,85(1):1-33 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu ZQ,Ji SC,Cai ZH,Zeng LS,Geng QR and Cao H.2012.Kinematics and dynamics of the Namche Barwa Syntaxis,eastern Himalaya:Constraints from deformation,fabrics and geochronology.Gondwana Research,21(1):19-36
Yang JS,Xu ZQ,Li ZL,Xu XZ,Li TF,Ren YF,Li HQ,Chen SY and Robinson PT.2009.Discovery of an eclogite belt in the Lhasa block,Tibet:A new border for Paleo-Tethys?Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,34(1):76-89
Yin A and Harrison TM.2000.Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen.Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science Letters,28(1):211-280
Zeng LS,Gao LE,Dong CY and Tang SH.2012.High-pressure melting of metapelite and the formation of Ca-rich granitic melts in the Namche Barwa Massif,southern Tibet.Gondwana Research,21(1):138-151
Zhang HF,Harris N,Parrish R,Zhang L,Zhao ZD and Li DW.2005.Geochemistry of North Himalayan leucogranites: Regional comparison,petrogenesis and tectonic implications.Earth Science,30(3):275-288 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang HF,Xu WC,Guo JQ,Zong KQ,Cai HM and Yuan HL.2007.Indosinian orogenesis of the Gangdise terrane:Evidences from zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of granitoids.Earth Science,32(2):155-166 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang HF,Harris N,Guo L and Xu WC.2010.The significance of Cenozoic magmatism from the western margin of the eastern syntaxis,southeast Tibet.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,160(1):83-98
Zhang LX,Wang Q,Zhu DC,Jia LL,Wu XY,Liu SA,Hu ZC and Zhao TP.2013.Mapping the Lhasa terrane through zircon Hf isotopes:Constraints on the nature of the crust and metallogenic potential.Acta Petrologica Sinica,29 (11):3681- 3688 (in Chinese with English abstract)Zhang ZM,Zheng LL,Wang JL,Zhao XD and Shi C.2007.Garnet pyroxenite in the Namjagbarwa Group-complex in the eastern Himalayan tectonic syntaxis,Tibet,China:Evidence for subduction of the Indian continent beneath the Eurasian plate at 80~100km depth.Geological Bulletin of China,26(1):1-12 (in Chinese with English abstract)Zhang ZM,Zhao GC,Santosh M,Wang JL,Dong X and Shen K.2010a.Late Cretaceous charnockite with adakitic affinities from the Gangdese batholith,southeastern Tibet:Evidence for Neo-Tethyan mid-ocean ridge subduction?Gondwana Research,17 (4):615-631 Zhang ZM,Zhao GC,Wang JL,Dong X and Liou JG.2010b.Two stages of granulite facies metamorphism in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, South Tibet: Petrology, zircon geochronology and implications for the subduction of Neo-Tethys and the Indian continent beneath Asia.Journal of Metamorphic Geology,28(7):719-733
Zhang ZM,Dong X,Liu F,Lin YH,Yan R,He ZY and Santosh M.2012a.The making of Gondwana:Discovery of 650Ma HP granulites from the North Lhasa,Tibet.Precambrian Research,212- 213:107-116
Zhang ZM,Dong X,Santosh M,Liu F,Wang W,Yiu F,He ZY and Shen K.2012b.Petrology and geochronology of the Namche Barwa Complex in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis,Tibet:Constraints on the origin and evolution of the north-eastern margin of the Indian Craton.Gondwana Research,21(1):123-137
Zhang ZM,Dong X,Xiang H,Liou JG and Santosh M.2013.Building of the deep Gangdese arc,South Tibet:Paleocene plutonism and granulite-facies metamorphism.Journal of Petrology,54(12):2547-2580
Zhang ZM,Dong X,Santosh M and Zhao GC.2014.Metamorphism and tectonic evolution of the Lhasa terrane,Central Tibet.Gondwana Research,25(1):170-189
Zhao TP,Zhou MF,Zhao JH,Zhang KJ and Chen W.2008.Geochronology and geochemistry of the ca.80Ma Rutog granitic pluton,northwestern Tibet:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the Lhasa Terrane.Geological Magazine,145(6):845-857
Zhao ZD,Mo XX,Dilek Y,Niu YL,Depaolo DJ,Robinson P,Zhu DC,Sun CG,Dong GC,Zhou S,Luo ZH and Hou ZQ.2009.Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-O isotopic compositions of the postcollisional ultrapotassic magmatism in SW Tibet:Petrogenesis and implications for India intra-continental subduction beneath southern Tibet.Lithos,113(1-2):190-212
Zhu DC,Pan GT,Chung SL,Liao ZL,Wang LQ and Li GM.2008.SHRIMP zircon age and geochemical constraints on the origin of Lower Jurassic volcanic rocks from the Yeba Formation,southern Gangdese,South Tibet.International Geology Review,50(5):442-471
Zhu DC,Pan GT,Wang LQ,Mo XX,Zhao ZD,Zhou CY,Liao ZL,Dong GC and Yuan SH.2008a.Spatial-temporal distribution and tectonic setting of Jurassic magmatism in the Gangdise belt,Tibet,China.Geological Bulletin of China,27(4):458-468 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu DC,Pan GT,Wang LQ,Mo XX,Zhao ZD,Zhou CY,Liao ZL,Dong GC and Yuan SH.2008b.Tempo-spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Gangdise belt,Tibet,China,with a discussion of geodynamic setting-related issues.Geological Bulletin of China,27(9):1535-1550 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu DC,Mo XX,Niu YL,Zhao ZD,Wang LQ,Liu YS and Wu FY.2009a.Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa Terrane,Tibet.Chemical Geology,268(3-4):298-312
Zhu DC,Mo XX,Niu YL,Zhao ZD,Wang LQ,Pan GT and Wu FY.2009b.Zircon U-Pb dating and in-situ Hf isotopic analysis of Permian peraluminous granite in the Lhasa terrane,southern Tibet:Implications for Permian collisional orogeny and paleogeography.Tectonophysics,469(1-4):48-60
Zhu DC,Mo XX,Zhao ZD,Niu YL,Wang LQ,Chu QH,Pan GT,Xu JF and Zhou CY.2010.Presence of Permian extension-and arc-type magmatism in southern Tibet: Paleogeographic implications.Geological Society of America Bulletin,122(7-8):979-993
Zhu DC,Zhao ZD,Niu YL,Mo XX,Chung SL,Hou ZQ,Wang LQ and Wu FY.2011.The Lhasa Terrane:Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,301(1-2):241-255
Zhu DC,Zhao ZD,Niu YL,Dilek Y,Wang Q,Ji WH,Dong GC,Sui QL,Liu YS,Yuan HL and Mo XX.2012.Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa Terrane,southern Tibet:Record of an early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc in the Australian proto-Tethyan margin.Chemical Geology,328:290-308 Zhu DC,Zhao ZD,Niu YL,Dilek Y,Hou ZQ and Mo XX.2013.The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau.Gondwana Research,23(4):1429-1454
附中文参考文献
蔡志慧,许志琴,段向东,李化启,曹汇,黄学猛.2013.青藏高原东南缘滇西早古生代早期造山事件.岩石学报,29(6):2123-2140
董昕,张泽明,刘峰,王伟,于飞,林彦蒿,姜洪颖,贺振宇.2012.拉萨地体东南部变质岩的成因与中-新生代造山作用.岩石学报,28(6):1765-1784
郭亮,张宏飞,徐旺春.2008.东喜马拉雅构造结多雄拉混合岩和花岗片麻岩锆石U-Pb 年龄及其地质意义.岩石学报,24(3):421-429
侯可军,李延河,邹天人,曲晓明,石玉若,谢桂青.2007.LA-MCICP-MS 锆石Hf 同位素的分析方法及地质应用.岩石学报,23(10):2595-2604
侯增谦,王二七,莫宣学,丁林,潘桂棠,张中杰.2008.青藏高原碰撞造山与成矿作用.北京:地质出版社
胡道功,吴珍汉,江万,石玉若,叶培盛,刘琦胜.2005.西藏念青唐古拉岩群SHRIMP 锆石U-Pb 年龄和Nd 同位素研究.中国科学(D 辑),35(1):29-37
黄勇,郝家栩,白龙,邓贵标,张国祥,黄文俊.2012.滇西施甸地区晚泛非运动的地层学和岩石学响应.地质通报,31(2-3):306-313
计文化,陈守建,赵振明,李荣社,何世平,王超.2009.西藏冈底斯构造带申扎一带寒武系火山岩的发现及其地质意义.地质通报,28(9):1350-1354
李才,王天武,李慧民,曾庆高.2003.冈底斯地区发现印支期巨斑花岗闪长岩:古冈底斯造山的存在证据.地质通报,22(5):364-366
李才,吴彦旺,王明,杨韩涛.2010.青藏高原泛非-早古生代造山事件研究重大进展——冈底斯地区寒武系和泛非造山不整合的发现.地质通报,29(12):1733-1736
李璞.1955.西藏东部地质的初步认识.科学通报,(7):62-71
路远发.2004.GeoKit:一个用VBA 构建的地球化学工具软件包.地球化学,33(5):459-464
莫宣学,董国臣,赵志丹,周肃,王亮亮,邱瑞照,张风琴.2005.西藏冈底斯带花岗岩的时空分布特征及地壳生长演化信息.高校地质学报,11(3):281-290
莫宣学,赵志丹,周肃,董国臣,廖忠礼.2007.印度-亚洲大陆碰撞的时限.地质通报,26(10):1240-1244
莫宣学,赵志丹,喻学惠,董国臣,李佑国,周肃,廖忠礼,朱弟成.2009.青藏高原新生代碰撞-后碰撞火成岩.北京:地质出版社
王金丽,张泽明,董昕,刘峰,于飞,王伟,徐方建,沈昆.2009.西藏拉萨地体南部晚白垩纪石榴石二辉麻粒岩的发现及其构造意义.岩石学报,25(7):1695-1706
许志琴,李海兵,杨经绥.2006.造山的高原——青藏高原巨型造山拼贴体和造山类型.地学前缘,13(4):1-17
许志琴,杨经绥,李海兵,嵇少丞,张泽明,刘焰.2011.印度-亚洲碰撞大地构造.地质学报,85(1):1-33
张宏飞,Harris N,Parrish R,张利,赵志丹,李德威.2005.北喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩地球化学:区域对比、岩石成因及其构造意义.地球科学,30(3):275-288
张宏飞,徐旺春,郭建秋,宗克清,蔡宏明,袁洪林.2007.冈底斯印支期造山事件:花岗岩类锆石U-Pb 年代学和岩石成因证据.地球科学,32(2):155-166
张立雪,王青,朱弟成,贾黎黎,吴兴源,刘盛遨,胡兆初,赵天培.2013.拉萨地体锆石Hf 同位素填图:对地壳性质和成矿潜力的约束.岩石学报,29(11):3681-3688
张泽明,郑来林,王金丽,赵旭东,石超.2007.东喜马拉雅构造结南迦巴瓦岩群中的石榴辉石岩——印度大陆向欧亚板块之下俯冲至80~100km 深度的证据.地质通报,26(1):1-12
朱弟成,潘桂棠,王立全,莫宣学,赵志丹,周长勇,廖忠礼,董国臣,袁四化.2008a.西藏冈底斯带侏罗纪岩浆作用的时空分布及构造环境.地质通报,27(4):458-468
朱弟成,潘桂棠,王立全,莫宣学,赵志丹,周长勇,廖忠礼,董国臣,袁四化.2008b.西藏冈底斯带中生代岩浆岩的时空分布和相关问题的讨论.地质通报,27(9):1535-1550

