当归多糖与川芎嗪不同配比对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤神经可塑性的影响
刘洛同,明扬,陈礼刚Δ,周杰,彭里磊,孙霞
(1.泸州医学院附属医院 神经外科,四川 泸州 646000;2.山东大学 分子药理学系,山东 济南 250100)
当归多糖与川芎嗪不同配比对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤神经可塑性的影响
刘洛同1,明扬1,陈礼刚1Δ,周杰1,彭里磊1,孙霞2
(1.泸州医学院附属医院 神经外科,四川 泸州 646000;2.山东大学 分子药理学系,山东 济南 250100)
目的 研究低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪(LMW-ASP)不同配比对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后神经可塑性的影响。方法 将42只实验大鼠随机分为对照组(N)、假手术组(S)、模型组(M)、50:10组(mg/kg:mg/kg)(E1)、25:10组(E2)、50:20组(E3)、25:20组(E4)。N组不进行任何手术处理,S组除不插线栓外,余同模型组,M、E1、E2、E3、E4组大鼠建立MCAO再灌注模型,其中N、S、M组不给药治疗,腹腔注射相同剂量的生理盐水,E1-E4分别腹腔注射相应比例的低分子量当归多糖和川芎嗪,于再灌注即刻开始注药,1次/日,共7次。分别在再灌注后4 h、24 h、3 d、7 d进行大鼠神经功能缺损评分,并于第7 d多聚甲醛固定后断头取脑进行免疫组织化学方法检测脑梗死周围皮质MAP-2、SYP的表达。结果 免疫组织化学方法检测脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2、SYP表达显示,在第7d,建立脑缺血再灌注损伤模型的各组MAP-2、SYP的免疫活性较N组、S组强,药物干预组MAP-2、SYP的免疫活性高于M组,且差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05);低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪不同配比组间MAP-2的免疫活性差异有统计学意义,其活性分别为E3>E1>E4>E2;低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪不同配比组间SYP的免疫活性差异均有统计学意义,其活性分别为E3>E1>E4>E2。其比例为50 mg/kg:20 mg/kg时最适宜。结论 大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后神经功能部分可自行恢复,低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪配伍干预后可促进大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2、SYP的表达,恢复效果更显著。
当归多糖;川芎嗪;大脑缺血再灌注模型
缺血性脑卒中是脑血管疾病发病率最高的一类疾病,其致残率也居首位[1-3]。本课题以线栓法大脑中动脉阻塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion, MCAO)再灌注大鼠为实验对象,通过观察MCAO再灌注大鼠脑缺血后神经功能损伤行为学变化、缺血脑组织周围MAP-2和SYP的表达,探讨低分子量当归多糖与川芎嗪不同配比对脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经可塑性的影响,寻找2者最佳配比。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物及术前准备 成年健康雄性Sprague-Dawley大鼠,SPF级,体质量(220 ± 20)g,由上海大学动物实验中心提供,合格证号4200500164。饲养于上海大学生物安全三级动物实验室(animalBiosafety Level 3 Laboratory, ABSL-3),饲养环境保持室温22 ℃,湿度72%,12 h昼夜交替。术前大鼠环境适应性喂养1周,自由进食、饮水。术前禁食12 h,不禁水。本实验遵循《实验动物保护条例》。线栓总长度40 mm,线头直径(0.32±0.02)mm,线身直径0.24 mm,术前用肝素钠溶液浸润备用。
1.2 实验方法 将42只实验大鼠随机分为对照组(N)、假手术组(S)、模型组(M)、50:10组(mg/kg:mg/kg)(E1)、25:10组(E2)、50:20组(E3)、25:20组(E4)。N组不进行任何手术处理,S组除不插线栓外,余同模型组,M、E1、E2、E3、E4组大鼠建立MCAO再灌注模型,其中N、S、M组不给药治疗,腹腔注射相同剂量的生理盐水,E1-E4分别腹腔注射相应比例的低分子量当归多糖和川芎嗪,于再灌注即刻开始注药,1次/天,共7次。分别在再灌注后4 h、24 h、3 d、7 d进行大鼠神经功能缺损评分,并于第7 d多聚甲醛固定后断头取脑进行免疫组织化学方法检测脑梗死周围皮质MAP-2、SYP的表达。
2 结果
2.1 大脑中动脉缺血再灌注模型的大鼠的基本状况 纳入实验的SD大鼠共42只,制作MCAO再灌注模型的大鼠30只,整个实验中制作MCAO再灌注模型实际使用的SD 大鼠42 只,总体造模成功率71.4%,具体情况如下:M:9只,1只在手术后24 h内死亡,1只第2 天死亡,1只在第4 天死亡;E1:8只,1只苏醒神经功能评分为0 分而剔除实验,1只在术后24 h内死亡;E2:8只,1只在术中死亡,1只在第2天死亡;E3:9只,1只苏醒后神经功能评分为4 分剔除实验,1 只在术后24 h内死亡,1只第7天死亡;E4:8只,1只术后拔线栓时大出血而死亡,1只术后24 h内死亡;对照组,假手术组未出现发生死亡。
2.2 免疫组化测定脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2 表达 采用免疫组化SP 法检测梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2表达。在大鼠脑缺血再灌注后第7 d,脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2表达的灰度值明显低于正常组(N)和假手术组(S),即MAP-2免疫活性较正常组和假手术组强,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);实验组E1-E4 MAP-2 表达的灰度值低于模型组M(209.54±1.62),差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪不同配比干预组中,实验组E3(200.64 ± 0.95)灰度值最低,MAP-2 的免疫活性最强,实验组E2(206.49±1.23)灰度值最高,MAP-2免疫活性最弱,MAP-2免疫活性强弱为E3(200.64±0.95)>E1(202.43±1.66)>E4(204.67±1.44)>E2(206.49±1.23),见图1。

图1 各组大鼠在脑缺血再灌注后第7 d脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2的表达(×400)Fig.1 Expression of MAP-2 in cerebral infarction around rats cortex at 7th after cerebral ischemia reperfusion(×400)
2.3 免疫组化测定脑梗死灶周围皮质SYP 的表达 在大鼠脑缺血再灌注后第7d,建立MCAO 再灌注模型的大鼠脑梗死灶周围皮质SYP 表达的灰度值明显低于正常组(N)和假手术组(S),差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);实验组E1-E4 SYP 表达的灰度值低于模型组M(208.41±1.77),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);低分子量当归多糖与川芎嗪不同配比干预组中,实验组E3(197.07±0.63)灰度值最低,SYP 的免疫活性最强,两者成反比关系,实验组E2(206.29±0.98)灰度值最高,SYP 免疫活性最弱,在药物干预组中SYP 免疫活性强弱为E3(197.07±0.63)>E1(199.12±1.31)>E4(203.93±1.74)>E2(206.29±0.98),见图2。
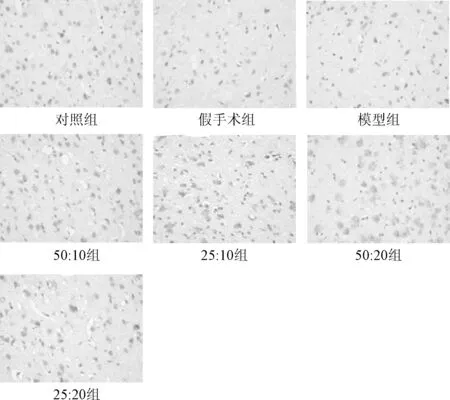
图2 各组大鼠在脑缺血再灌注后第7d 脑梗死灶周围皮质SYP 的表达(×400)Fig.2 Expression of SYP in cerebral infarction around rats cortex at 7th after cerebral ischemia reperfusion(×400)
3 讨论
本实验通过制备低分子量当归多糖和研究低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪不同配比对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤神经功能和脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2、SYP 表达水平的影响,可得到如下结论:
大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后神经功能可自行恢复[4-8],中药低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪配伍干预后恢复效果更显著。低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪不同配比可上调大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤脑梗死灶周围皮质MAP-2、SYP 的表达[9],促进神经的可塑性,比例为50 mg/kg:20 mg/kg 时效果最显著。
本次研究对于进一步探索低分子量当归多糖-川芎嗪配伍对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的神经保护作用的最佳比例具有重要意义。
[1] Hardie K,Hankey GJ,Jamrozik K,et al.Ten-year risk of first recurrent stroke and disability after first-ever stroke in the Perth Community Stroke Study[J].Stroke,2004,3(3):731-735.
[2] Roger VL,Go AS,Lloyd-Jones DM,et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics-2012 update a report from the American Heart Association[J].Circulation,2012,125(1):e2-e220.
[3] Heidenreich PA,Trogdon JG,Khavjou OA,et al.Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States:a policy statement from the American Heart Association[J].Circulation.2011,123(19):933-944.
[4] Mehta SL,Manhas N,Raghubir R.Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics[J].Brain Res Rev,2007,54(1):34-66.
[5] Oh MS,Yu KH,Chu MK,et al.Long-term prognosis of symptomatic isolated middle cerebral artery disease in Korean stroke patients[J].BMC Neurol,2011,11:138.
[6] Matesric DF,Lin RC.An early indicator of ischemia-induced neurodegeneration in the gerbil forebrain[J].J Neurochem,1994,63(3):1012-1020.
[7] Wiedenmann B,Franke WW.Identification and localization of synaptophysin,an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles[J].Cell,1985,41(3):1017-1028.
[8] Valtorta F,Pennuto M,Bonanomi D,et al.Synaptophysin:leading actor or walk-on role in synaptic vesicle exocytosis?[J].Bioessays,2004,26(4):445-453.
[9] Liu C,Li JQ,Meng FY,et al.Polysaccharides from the root of Angelica sinensis promotes hematopoiesis and thrombopoiesis through the PI3K/AKT pathway[J].BMC Complementary Altern Med,2010,10:79.
(编校:谭 玲)
Neuroplasticity effects of compatibility of angelica sinensis polysaccharide and tetramethylpyrazine on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
LIU Luo-tong1,MING Yang1,CHEN Li-gang1Δ,ZHOU Jie1,PENG Li-lei1,SUN Xia2
(1.Department of Neurosurgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Luzhou Medical College, Luzhou 646000, China; 2.Department of Molecular Pharmacology, Shandong University, Ji’nan 250100,China)
ObjectiveTo construct a middle cerebral artery occlusion(MCAO)/reperfusion rat model and study the effect of the different compatibility ratios of LMW-ASP and tetramethylpyrazine on the effects of neuroplasticity, and explore the best compatibility ratio between LMW-ASP and tetramethylpyrazine.MethodsIn the study, 42 experimental rats were divided into seven groups, they were normal group(N), sham operation group(S), model group(M),50:10 group(E1),25:10 group(E2),50:20 group(E3) and 25:20 group(E4).N group would not be carried out any operation, while S group was performed in the same way with M group but without inserting the intraluminal suture.MCAO reperfusion models were established in rats of the M,E1,E2,E3,E4 groups.The corresponding compatibility ratios of LMW-ASP and tetramethylpyrazine were injected to the E1-E4 groups by intraperitoneal injection in reperfusion instantly,once a day,a total of seven times.Neurological severity scores in rats were done in 4 h,24 h,3 d,7 d after reperfusion.In 7 d, The rats brains were removed after fixed using paraformaldehyde and then the immunohistochemistry method was used to detect the expression of MAP-2 and SYP in the cortex around cerebral infarction.ResultsIn 7 d, using the immunohistochemical methods detected the expression of MAP-2 and SYP in the cortex around cerebral infarction.The immune activity of MAP-2 and SYP in groups of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury model was stronger than the N group, S group and the difference was significant(P<0.05), and the immune activity of MAP-2 and SYP in the cortex around cerebral infarction in drug intervention groups were stronger than the M group and they had a significant difference(P<0.05); the immune activity of MAP-2 between the different compatibility ratios groups of LMW-ASP and tetramethylpyrazine was statistical difference(P<0.05), and the activity was E3>E1>E4>E2;the immune activity of SYP between the different compatibility ratios groups of LMW-ASP and tetramethylpyrazine was statistical difference(P<0.05), and the activity was E3>E1>E4>E2, and the compatibility ratio of 50 mg/kg:20 mg/kg was best effect. ConclusionsIn this study, we found that neurological function after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury can be partially self-recovery and the recovery effect after the drug intervention of the different compatibility ratios between the LMW-ASP and Tetramethylpyrazine is more pronounced.The compatibility of LMW-ASP and tetramethylpyrazine can promote the expression of MAP-2 and SYP in the cortex around cerebral infarction.
angelica sinensis polysaccharide; tetramethylpyrazine; middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion
山东省医药卫生科技发展计划项目(2009QW003)
刘洛同,男,硕士,副主任医师,研究方向:神经外科,E-mail:qch18214600123@163.com;陈礼刚,通讯作者,男,博士,副主任医师,研究方向:神经外科,E-mail:qch18214600124@163.com。
R285.5
A
1005-1678(2015)03-0036-03

