Three New Records of Rhizocarponfrom China
WANG Weicheng,ZHAO Zuntian
(College of Life Science,Shandong Normal University,Ji’nan 250014,China)
RhizocarponRamond ex DC.(Rhizocarpaceae)is agenus of about 200species worldwide,and 36species have been found in China[1-3].It is usually characterized by areolate or rimose thallus,black lecideine apothecia between areoles,Rhizocarpon-type asci,1-septate to muriform ascospores with halo,brown hypothecium,anastomosing and branched paraphyses[4].
In this paper,three new records ofRhizocarponfrom China are reported.R.atrovirellumandR.furaxare both collected from Xinjiang Mt.Tianshan No.1Glacier in 2011and 2012,whereasR.simillimumis collected from Xinjiang Changji City August First Forest Farm in 2012.
1 Materials and methods
The examined specimens were collected from Xinjiang,China and preserved in SDNU (the Lichen Section of Plant Herbarium,Shandong Normal University).Their morphological and anatomical characters were examined under a stereo-microscope(Olympus SZ)and a polarizing microscope(Olympus CX21).Color reactions (spot tests)were made using standard methods[5].The chemical constituents were identified using thin layer chromatography(TLC).Photos were taken under Olympus SZX16and BX61with DP72.
2 Results
2.1 Rhizocarpon atrovirellum (Nyl.)Zahlbr.,Cat.Lich.Univers.4:347(1926).PlateⅠ,Fig.1-4
Thallus parasitic onAspicilia;areolate,usually small,only a few millimeters in diameter,sometimes up to 1.5cm diam.;medulla I-;prothallus absent;areoles bright-yellow,angular,up to 0.8 mm diam.,flat to slightly convex.Apothecia usually developed in the areoles,which surround them like a collar,up to 0.7mm diam.,slightly convex,margin indistinct.Epihymenium and exciple brownblack,K+red;hymenium colorless,up to 75μm diam.;hypothecium browm,K-.Ascospores 8per ascus,2 to 6-celled,ellipsoid,dark-brown,halonate,(15-20)×(7.5-10)μm.
Chemistry:Medulla K-,C-,P-.Chemical constituent:rhizocarpic acid.
Habitat:On siliceous rocks.
Notes:Rhizocarponviridiatrumis similar toR.atrovirellumbut differs in having muriform ascospores with six to ten cells,roundish and highly convex areoles and larger thallus(up to 2cm diam.).R.atrovirellumwas reported from central Europe[6]and is new to China.
Specimens examined:Xinjiang,Tianshan Mountain,No.1 Glacier,alt.3 750 m,on rocks,27 Aug.2011,Lulu Zhang 20125920;alt.3 800 m,on rock,27 Aug.2011,Lin Li 20126159.
2.2 Rhizocarpon furax Poelt & V.Wirth,Mitt.bot.StSamml.,Münch.8:94(1970).PlateⅠ,Fig.5-8
Thallus parasitic onLecidea,small,up to 4 mm diam.;medulla I+violet;prothallus absent;areoles bright-yellow,angular-roundish,up to 0.8 mm diam.,dull,slightly convex.Apothecia black,immersed,up to 0.5 mm diam.,more or less surrounded by an areole collar,flat.Epihymenium and exciple red-brown,K+red;hymenium colorless,up to 125μm diam.;hypothecium browm,K-.Ascospores 8per ascus,mostly with 3transverse septa,fusiform,blue-green,halonate,(20-25)×7.5μm.
Chemistry:Medulla K-,C-,P-.Chemical constituent:rhizocarpic acid.
Habitat:On siliceous rocks.
Notes:Rhizocarponfuraxis close toR.intermediellumbut the latter has smaller ascospores[(12-21)×(6-10)μm],distinctly marginate apothecia,angular areoles and non-parasitic thallus(or parasitic only when young)[7].
Specimens examined: Xinjiang, Tianshan Mountain,No.1 Glacier,alt.3700 m,on rocks,17 Aug.2012,Xin Zhao 20129094,20129069.
2.3 Rhizocarpon simillimum (Anzi.)Lettau,
Hedwigia 52:156(1912).PlateⅠ,Fig.9~13
Thallus areolate,3cm in diam.;medulla I+violet;prothallus distinct,black;areoles up to 0.5 mm diam.,dull,contiguous,angular,slightly convex.Apothecia up to 0.7mm diam.,black,epruinose,angular,flat,margin present.Epihymenium and exciple brown-black,K+red;hymenium colorless to pale brown;hypothecium dark brown;paraphyses branched and anastomosing.Ascospores 8 per ascus,1-septate,olive-green or brown,ellipsoid,halonate,(12.5-16)×6.5μm.
Chemistry:Medulla K-,C-,P-.No lichen substances detected by TLC.
Habitat:On siliceous rocks.
Notes:R.simillimumhas been reported from Europe,North and South America[8],it is recognized by its amyloid medulla,1-septate small brown and halonate ascospores and dark brown,well developed thallus.R.disporumlooks likeR.simillimumbut has muriform ascospores.
Specimens examined:Xinjiang,Changji,August First Forest Farm,alt.2 100 m,on rock,10 Aug.2012,Xin Zhao 20128966,20128972,20128973,20128980.
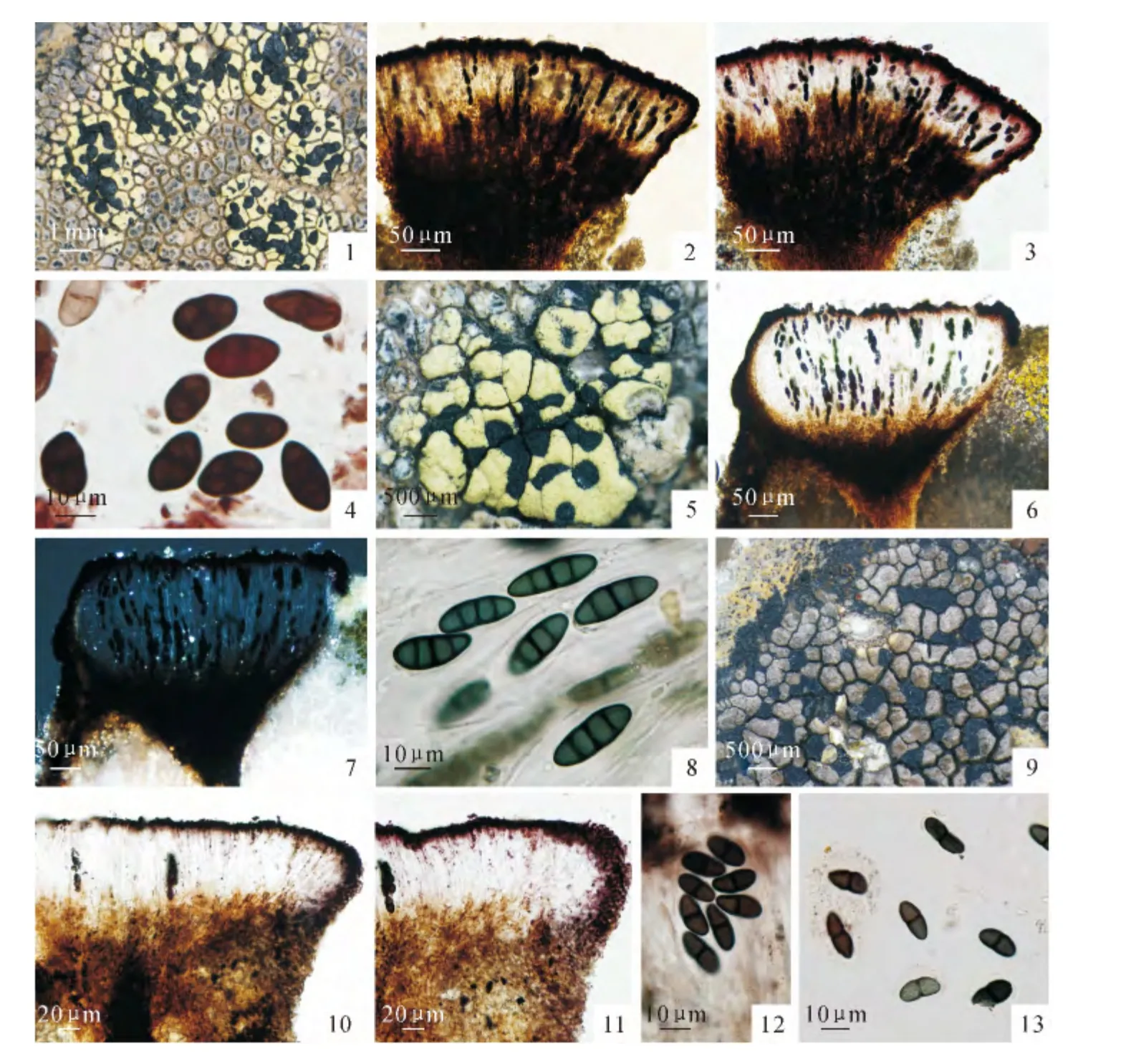
PlateⅠ Morphological and anatomical structures of the newly reported taxa.
[1] MCCARTHY P M,ELIX J A.The lichen genusRhizocarponin mainland Australia[J].Telopea,2014,16:195-211.
[2] MAHIRE H(玛伊热·努尔艾合麦提),TURSUNGUL R(吐尔逊古丽·热哈提),ABDULLA A(阿不都拉·阿巴斯),etal.A prelimilary study on the lichen genusRhizocarponRamond ex DC.in Xinjiang,China[J].ActaBotanicaBoreali-OccidentaliaSinica(西北植物学报),2015,35(2):422-426(in Chinese).
[3] ZHAO Z T(赵遵田),LI C(李 超),ZHAO X(赵 欣),etal.New records ofRhizocarponfrom China[J].Mycotaxon,2013,125:217-226.
[4] FLETCHER A,GILBERT O L,CLAYDEN S,Fryday A M.Rhizocarpon[M]//CW Smithetal.The lichens of Great Britain and Ireland.London:British Lichen Society,2009:792-808.
[5] ORANGE A,JAMES P W,WHITE F J.Microchemical Methods for the Identification of Lichens[M].London:British Lichen Society,2001:1-101.
[6] POELT J.RhizocarponRam.em.Th.Fr.subgen.Rhizocarponin Europe[J].ArcticandAlpineResearch,1988,20(3):292-298.
[7] POELT J.Mitteleuropaische Flechten IX.[J].Mitteil.Bot.StaatssammlungMünchen,1970,8:191-210.
[8] FEUERER T,TIMDAL E.Rhizocaron[M]//TH Nash III.Lichen Flora of the Greater Sonoran Desert Region(Vol.2).Tempe:Lichens Unlimited,Arizona State University,2004:456-466.

