促进工业节水的水价调控战略研究
李太龙,沈满洪
(1. 浙江理工大学经济管理学院,浙江杭州 310018; 2. 宁波大学商学院,浙江宁波 315211)
促进工业节水的水价调控战略研究
李太龙1,沈满洪2
(1. 浙江理工大学经济管理学院,浙江杭州 310018; 2. 宁波大学商学院,浙江宁波 315211)
我国工业水价既存在价格缺失的问题,又存在价格扭曲的问题。优化工业水价具有直接价格效应、结构调整效应、循环用水效应、技术进步效应这四大效应。工业水价应由水利供水工程成本、制水企业成本、制水企业利润、污水治理成本、水生态保护成本和水资源所有者收益等部分构成。促进工业节水的水价调控战略应体现水资源稀缺程度、水资源外部性内部化、制水企业的产业管制要求、各种供水的价格统筹和因地制宜地确定水价等原则。
工业用水;工业节水;水价调控
我国是缺水国家。实施最严格的水资源管理制度刻不容缓。虽然工业结构调整和技术升级使得我国单位工业增加值的工业用水量不断下降[1],但是工业用水总量仍随工业增加值的快速增长而不断上升,从2002年的1142.4亿m3递增到2011年的1461.6亿m3。我国工业用水效率的提高和节水建设尚未实现工业用水总量的下降。贾绍凤[2]研究表明,发达国家工业化初期的用水量呈现快速增长的趋势,而后达到零增长甚至负增长,工业节水可以实现工业用水总量的下降。贾绍凤[3]、李眺[4]对中国工业企业的经验研究发现,企业对水价敏感。这意味着价格杠杆对工业节水有效。深化工业水价改革,有助于促进工业节水、提高用水效率。
一、工业水价影响工业节水的机理分析
价格杠杆的基本原理是通过提高水价来降低用水需求。虽然学术界关于工业用水和水价关系的研究较少,但既有研究大多证实工业用水的需求价格弹性为负,即价格杠杆起作用。尽管有国外研究者提出,弹性数值较大时,应降低水价,以增加工业用水,提高工业产出。但这一论断的出发点是当地水资源充足,例如加拿大、法国以及美国五大湖地区,并不适合水资源紧缺地区。大多数学者认为,在提升水价减少工业用水的过程中,应先减少水资源利用率低的行业和企业的用水量,以促使工业企业投入更多资金来提高水资源利用效率,这样不仅不会妨碍工业经济的发展,反而会通过工业节水大大提高全社会的用水福利。
1.工业用水的需求价格弹性回顾
发达国家的工业化时间较早,其工业用水需求与水价关系的研究主要出现在20世纪七八十年代。DeRooy[5]在研究美国新泽西州30个大型化工企业的工业用水需求时,以平均成本方式核定企业自供水价格,将水价、劳动投入、技术水平和产出等指标体系作为用水需求方程的解释变量,经验结果表明新泽西州化工行业的用水需求受水价影响显著。Ziegler等[6]使用截面数据研究美国阿肯色州23个用水最多的造纸和化工企业的工业用水需求,将边际成本和平均成本定价引入工业用水需求方程,研究证实水价对造纸和化工行业的用水需求有显著影响。Renzetti[7]依据工业用水的原水取水、预处理、循环用水和排污四个环节建立联立方程模型研究加拿大卑斯省制造业的工业用水需求,使用包含372个观测值的企业层面截面数据测算得出石油化工业、重工业、林木业和轻工业等四个行业的原水取水的价格弹性依次为-0.119、-0.249、-0.506和-0.537,原水取水和循环用水的交叉价格弹性分别为0.146、0.253、0.156和0.209。这些弹性测算结果表明,提高原水取水的价格会促使各行业企业减少原水使用,增加循环用水。
随着我国水资源危机的加剧,国内外学者开始关注中国工业用水的效率和需求问题。由于水价政策主要由地方政府制定和实施,所以国内学者研究水价和工业用水问题多从省市层面着眼。毛春梅[8]估算江苏省棉纺织业用水的需求价格弹性为-0.157,建议改革现有水价制度以提高工业用水效率。刘昕等[9]利用咸阳市1991—2005年的工业用水数据估计咸阳工业用水的需求价格弹性为-0.711,认为工业水价杠杆作用明显且存在较大的提价空间。张宁等[10]分析浙江省各地市工业用水的资源配置效率后认为,浙江的工业节水潜力较大,可以通过提高水价的方式促进节水。
相对而言,国际学者更注重研究中国省际和行业层面的工业用水问题。Wang等[11]利用包含两千多个观测值的大中型制造业企业截面数据分析中国工业生产的边际生产力模型,发现1993年全部16个行业的工业用水边际产出值广泛分布在从0.05元/吨至26.83元/t的区间,平均为2.45元/t,而当年全国各地的水价介于0.70元/t至1.20元/t之间,因此工业水价存在较大的提价空间。在假定工业用水成本按照边际产出值定价后,他们进一步测算各行业用水的需求价格弹性介于-0.57至-1.2之间,平均为-1.03。这表明提升水价能有效促进工业节水效果。Fujii等[12]采用有向距离函数方法测算中国工业用水的效率和影子价格,估计1996至2007年的省际和行业面板数据得到结果表明,中国工业用水的省际差异和行业特征突出,工业用水效率在水资源短缺的北方省份更高,除石油冶炼外其他行业的工业用水效率逐年提高,六大耗水行业中纺织和石油冶炼行业用水的影子价格较高,而造纸和电力行业较低。
尽管受地区水资源禀赋差异和工业行业布局特点的影响,学术界测算工业用水需求的价格弹性有一定差别,但普遍认为价格杠杆对降低工业用水需求作用明显,在水资源紧缺背景下,应提高水价促进工业节水。
2.工业水价的公共供水或自供水选择效应
按照价格杠杆的一般规律,以居民生活用水为代表,水价越高,用水量越低。但是工业用水并不必然如此,因为许多工业企业的用水不是来自公共供水系统。事实上,用水量大的工业企业通常建有自供水系统,它们引用地表水或抽取地下水加以净化处理后使用。其中,在使用地表水还是地下水的选择上,自供水企业不仅要考虑地理位置和降水情况、水源条件、取水设施和原水净化处理成本等因素,也要考虑地表水和地下水的水资源价格差别。因此,公共供水和自供水之间、地表水和地下水之间都存在一定的替代性,只提高公共供水定价未必会降低工业用水量,反而可能导致更多企业选择自供水,即工业用水的水价政策具有公共供水或自供水选择效应,见图1。
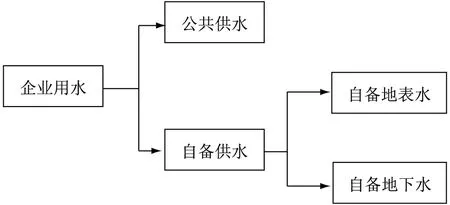
图1 企业用水的替代与选择
如果自供水成本小于公共供水成本,在公共供水价格提升的情况下,工业企业的理性选择是尽量减少来自公共供水系统的用水,并且始终会做出这样的选择。工业企业在取用自供水时,到底用地表水还是地下水,取决于水质相当的情况下取水成本的高低,哪个水源的取水成本低就取用哪个水源。在水质不同的情况下,取决于取用不同水源的性价比,哪个性价比高就选用哪个。工业节水价格调控的目的是减少区域社会的取水总量,偿还部分生态用水。如果公共供水的价格上升,反而导致全社会取水量增加,那就起到适得其反的效果。另外,与居民生活用水不同,除了食品和饮料行业外,工业用水对水质的要求相对较低,而且不同企业的要求也不一致,所以公共供水的定价在用水量大的企业看来非常不经济。
3.工业水价对工业节水的传递机理
价格机制是市场机制的核心。在水资源需求具有弹性的情况下,需求法则必然发挥作用。
(1)工业水价促进节水的直接价格效应
长期以来我国一直实行福利水价,水资源价格远远低于供求均衡价格。这既造成我国水资源的短缺又造成严重的水资源浪费。如图2所示,P2所示的福利水价加剧了水资源供需的矛盾,导致水资源的过量需求比均衡数量超出(Q2-Q1)。此时水价不能反映水资源的全部经济价值,理性个体也会从自身的利益出发,过度消耗水资源。这种福利水价政策将会造成社会总福利的下降。
过低的水价不仅会造成水资源的掠夺性开发,而且会阻碍用水效率的提高以及节水技术的推广。比如,在水价偏低的情况下,节约用水并不能给企业带来太大的经济效益,反而会增加运行成本,因此企业缺乏节水的积极性和动力。相反,如果把工业水价提高到均衡水平P1,Q1的供水量就能够保持供求均衡。相对于Q2的过度用水需要,实现了(Q2-Q1)的节水效果,这就是市场机制的威力。正因为如此,要让市场机制在水资源配置中发挥决定性作用。
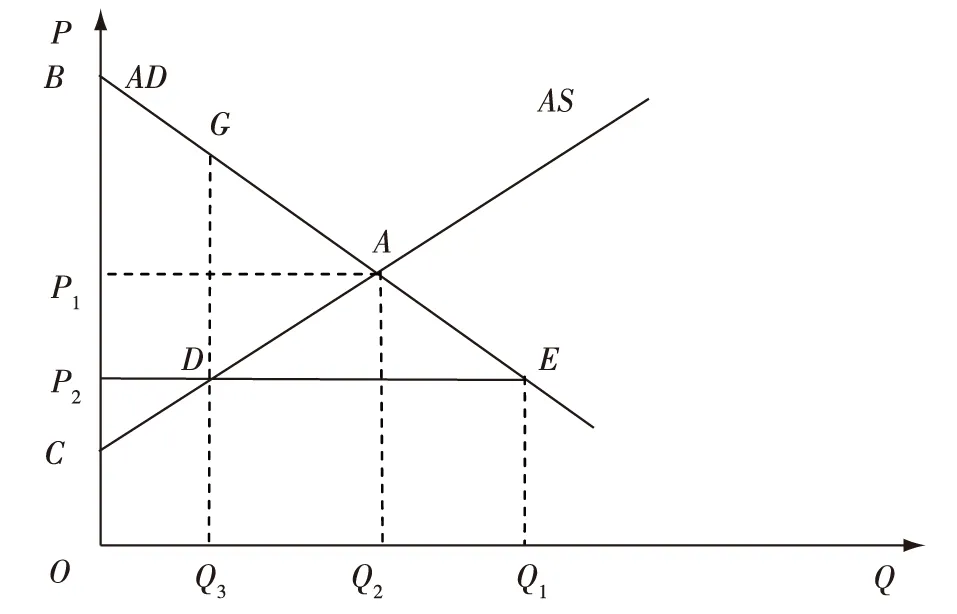
图2 福利水价的福利损失
(2)工业水价促进节水的结构调整效应
在工业水价较低的背景下,由于要素成本没有反映要素稀缺性,即使是高耗水的粗放型工业企业也可能在市场中获得利润甚至超额利润。在工业水价达到均衡水价的情况下,工业企业就要权衡:继续从事高耗水产业的生产还是转向低耗水产业的生产?只要在均衡水价下低耗水行业的利润率高于高耗水行业的利润率,工业企业必然转产。这就是工业水价可能带来的结构调整效应。
(3)工业水价促进节水的循环用水效应
循环用水是工业节水中既要发挥价格杠杆作用又不能影响工业经济发展的决定性因素。工业用水可以分为两类:一类是没有使用过的新鲜水,也称作自然水;另一类是已经使用过的废水或污水经净化处理而得的再生水。从广义上看,循环用水即是使用再生水。狭义上看,循环用水需要工业企业、车间或工段的给水排水系统组成一个闭路循环的用水系统,将系统内产生的废水经适当处理后重复使用。这一过程中,不补充或少补充新鲜水,不排放或少排放废水。
循环用水从两个方面促进工业节水:一方面,企业采用循环用水代替新鲜水,直接具有减量用水的节水效应。另一方面,企业增加循环用水意味着废水处理更彻底,直接减少废水排放,间接减轻水环境的生态修复压力,相当于减少生态用水和增加生产生活用水,因而具有“固本培元”的节水效应。
如果工业用新鲜水来自自供水系统,用水成本主要是水资源费、原水处理成本和排污费;如果来自公共供水系统,用水成本主要是工业水价,包含水资源费、商品水价和排污费。循环用水的成本主要是再生水成本,即污水或废水净化处理并再生的成本。工业废水在排放前,企业仍需自行处理达到排放标准,这也需要一定的处理成本。按照长期均衡的观点,当新鲜水使用成本与废水处理成本之和大于再生水成本时,企业就会采用或增加循环用水替代新鲜水。这是价格杠杆推动循环用水效应起到节水作用的内在机理。
工业部门中用水量最大的是石油、化工、煤炭、电力、钢铁、冶金、造纸、食品和饮料等行业。尽管不同行业企业对水量、水质和水温有不同要求,但工业用水的主要用途仍可分为两大类:一是原料用水,这是直接作为原料的生产用水,是消耗性用水,占工业用水总量的0.5%~10%,主要用于食品和饮料行业,对水质要求高;二是产品处理用水、锅炉用水、冷却用水和清洁用水等非消耗性用水,它们主要用于石油、化工、煤炭、电力、钢铁、冶金、造纸等行业,其中冷却用水占工业用水总量的60%~70%左右。工业用水总量虽大,但实际消耗并不多,非消耗用水对水质的要求也不高,90%以上的非消耗用水在净化降温处理后都可循环使用。这为发挥水价调节作用推动循环用水奠定了基础,也为工业节水提供了空间。
但是,采用再生水技术以及循环供水系统都需要工业企业进行固定成本投入。如何让企业对有关的节水项目进行投资成为需要攻克的难关。从短期均衡的观点看,只有新鲜水使用成本与废水处理成本之和超过再生水成本,才能使循环用水真正发挥“循环且经济”的效应。而且,水价提升幅度越大,企业采用循环用水的积极性越高,工业节水效果越明显。
(4)工业水价促进节水的技术进步效应
当水价调节机制起作用时,工业企业还有多种办法节约用水,例如采用先进的节水生产技术和工艺。这会带动有关科研单位和工业企业合作,为改进涉水技术工艺和研发节水治污设备进行智力投入和资金投入。科技创新投入和技术知识存量具有累积效应和溢出效应,会持续推动节水技术进步,因此,借助价格杠杆可以撬动节水技术市场,形成节水技术进步效应。
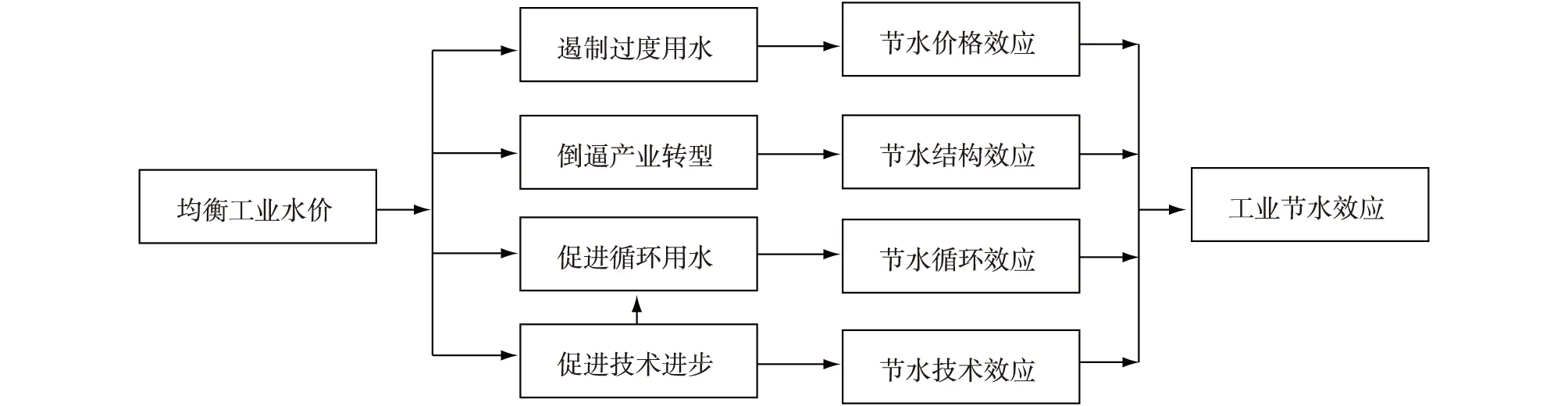
图3 工业水价的节水效应传递机理
总之,工业水价从低于均衡价格到均衡价格的调整,可以实现四大节水效应:一是遏制过度用水,获取节水价格效应;二是倒逼产业转型,获取节水结构效应;三是促进循环用水,获取节水循环效应;四是促进技术进步,获取节水技术效应。其中,价格效应还可以激励工业企业之间开展水权交易,把水资源配置到能够带来最高效益的企业;技术进步对促进循环用水和推动产业转型都可以发挥作用。因此,工业水价调控可以获得综合性的节水效果。
二、促进工业节水的水资源定价内涵与方式
长期以来,学术界主要从水资源的公共品属性和供水企业的公用事业性质着手研究生活用水定价,尤为关注居民生活用水的需求价格弹性[13]、成本收益均等的供水定价方式和低收入群体的生活用水保障等问题[14],但对工业用水的研究不多。为了适应水资源日益紧缺的变化趋势并满足经济社会的发展需要,水资源定价研究开始转变视角,从以资源配置效率为目标转为兼顾经济效率、社会公平和环境保护等多重目标。
1.水资源定价内涵与方式回顾
学术界一般认为水价应包含三部分:体现水资源所有权的水资源费(或水资源税)、水作为商品的价格和为治理水污染及保护水生态所支付的环境水价(或水环境税)。沈满洪等[15]对水价的内涵进行细致梳理后给出如下定义:“水价是由政府相关部门根据水资源产权状况、水资源供需状况、供水成本以及用水户承受能力等因素制定的反映水资源稀缺性程度的杠杆,是用水户获得每单位水资源时,应向供水企业支付的货币金额。”
在可以不断增加供水量来满足用水需求的情况下,按照供水企业制水的边际成本定价是水资源有效配置的最优定价方式,但供水企业制水的固定成本远高于可变成本,所以平均成本定价或两部制定价是能够保证供水企业收回成本的次优定价方式[16]。两部制定价包含两个部分:一部分是与使用量无关的、定期支付的基本费或容量水价,另一部分是按使用量支付的从量费或计量水价。作为公共品的水资源定价应遵循服务费用原则或自融资原则:用水户应为所享受的服务支付足够的费用,但不应超出供水企业在提供这一服务时所产生的支出。在水量丰裕的季节、用水较少的时段或距离水源地较近的地段,供水成本较低,按照服务费用原则,水价应较低。因此,即便在同一地区,水价也可随用水季节、时段和地段做出调整。
为应对水资源日益紧缺和水污染依然严峻的现实,学术界日益关注水的生态价值、用水的负外部性和水的稀缺价值,因此,水资源定价开始包含生态水价、污染水价和资源水价等部分。除了供水企业的生产成本以外,引入基于水循环和水环境自净化过程的水资源生态价值共同构成供水的总成本,根据成本收益分析的均衡条件可得式(1):
(1)
式(1)中:p表示水价;Q表示供水量;C(Q)表示供水企业的生产成本;v表示水在生态环境中的影子价格。影子价格反映的是为满足用水需要所抽取的水资源在生态环境中的边际价值。当水资源紧缺或者取水对生态环境造成负担时,水的生态价值显著为正,其影子价格也为正。从水价等于社会供水和生态环境供水总边际成本的角度看,这是一种最优定价方式。换一个视角,把v视为治理水污染的边际成本,并按照污染者和使用者付费原则根据污染程度向污水排放者收取相应的污染水价,这就“内部化”了用水的负外部性,此时它是一种次优定价方式。生态水价和污染水价都是环境水价的组成部分,它们分别衡量用水环节的上端和下端——原水抽取和污水排放——对水资源生态环境的负面影响,这种负面影响越大,相应的水价越高。
还可以将v视为体现水资源稀缺价值的资源水价。按照需求侧管理原则,当水资源紧缺时,水价应提高至供水能力容许范围之内的价格水平上,通过水价杠杆降低用水需求达到控制用水总量并实现供需平衡的目的。即是说,按照制水的边际成本定价仅在供水企业的生产能力和可用水资源充足时有效,当供水能力不足或水资源紧缺时,根据稀缺程度加价才能提高水资源的配置效率并实现供需平衡。其中,递增的阶梯定价是降低用水需求的主要加价方式,这是因为随着用水量的增加,水资源的稀缺价值越来越高。水资源稀缺不仅意味着生产和生活用水稀缺,也一定意味着生态用水稀缺,所以资源水价应包含生态水价。
无论环境水价(包括生态水价和污染水价)还是资源水价(包含生态水价)都表明,水资源定价政策已经不仅是水资源管理的重要方式,而且是水生态和水环境社会化综合治理的重要手段。水资源日益紧缺的现实使得不同经济部门、不同地区、不同产业和行业甚至生态环境都竞争性地利用水资源。不恰当的水资源定价政策会带来经济、社会和环境的多重损失。无效的水价政策一方面使供水或用水的“跑冒滴漏”现象严重,导致原水抽取过度和利用效率低下,无法准确反映水资源的稀缺价值;另一方面还使污水排放过量,导致水环境恶化并加剧水资源短缺,不能有效内部化污水排放的负外部性。所以,无效的水价政策会带来全社会用水的福利损失。
2.促进工业节水的水资源定价内涵
从水资源价格的组成来看,水资源费、商品水价和环境水价对工业用水的影响相互交织又各自独立。
首先,由于工业水价政策具有供水系统选择效应,所以工业节水的水资源定价内涵重在水资源费和环境水价(包括生态水价和污染水价),它们应对选择公共供水或选择自供水的工业企业同等有效。由于商品水价主要衡量公共供水企业的制水成本,而工业企业可以通过选择自供水系统降低并内化这部分制水成本,所以商品水价对工业节水的影响有限。
其次,水资源费是水资源使用者为了获得水资源使用权而向水资源所有者(包括国家和集体)支付的费用,它是水资源所有权在经济上实现的重要形式。因此,在工业用水中,无论公共供水企业抽取原水还是自供水企业抽取原水,都应缴纳等同费率的水资源费。
再者,生态水价是社会生产和生活同生态环境竞争使用水资源的价值体现,是水资源使用者向水生态环境或水生态保护者支付的补偿费用。污染治理水价是水资源使用者用水后直接向环境排放污水或向城市污水集中处理设施排放污水需要缴纳的费用。在使用者和污染者付费原则下,生态水价和污染水价是内部化原水抽取和污水排放负外部性的重要经济手段。
由于原水抽取对生态环境的负外部性是由原水取用数量决定——即取水只有数量效应,所以无论选择公共供水的企业还是选择自供水的企业,无论工业用水用途为何的企业,都应按照同样的费率结构支付生态水价。在这一意义下,生态水价和水资源费一致。
污染水价的含义有所不同。不同企业的废水类型、浓度和数量不同,废水处理成本和污染危害有差别——即废水既有质量效应又有数量效应,所以原则上用水企业应按照与其废水种类相应的费率支付污染水价。当前,依照环境保护法律法规规定,企业需在工业废水处理达标后再予排放。这样,污染水价主要由用水企业承担,以实现负外部性的内部化。但是,工业企业仍应按照废水处理后的排放标准支付相应费率的污染水价,无论其用水来自公共供水系统还是自供水系统。在这一意义下,污染水价的定价费率相对不同工业产业、行业和企业具有可变性。不过,需要注意的是,污染水价的制定应依据污染者和使用者付费原则,并不直接以节水为目的。
3.促进工业节水的水资源定价组成
理论上讲,水价是由不同的部分组成的。如果用p表示水价,p1表示水利供水和制水工程成本,p2表示制水企业利润,p3表示污水治理成本,p4表示水生态保护补偿成本,p5表示水资源所有者收益,那么,水价的理论构成为:
p=p1+p2+p3+p4+p5
(2)
在相当长的一段时间中,在劳动价值论的指导下,我国的水价仅仅体现供水和制水工程成本p1和制水企业利润p2。随着水环境污染问题的加剧,水价中增加了污水治理成本p3。至今,总体上还较少考虑水生态保护(补偿)成本p4和水资源所有者收益p5。
供水和制水工程成本p1是同水资源禀赋和制水工艺与技术相关的,这个部分不能成为调控工业水价的变量,但是要加强制水企业的内部管理,不断提高管理效率和企业效益。
制水企业利润p2一般按照成本加成法确定,但是需要政府价格管理部门的管控。从目前自然垄断行业职工收入普遍偏高的角度看,这个部分总体上被高估。从维护工业企业利益的角度,这个部分应该是能降则降。
污水治理成本p3已经被纳入绝大多数地方的工业水价之中,也就是说部分实现了外部性内部化。但是,污水治理成本被严重低估,导致污水治理不充分,达不到环境功能要求,尚未做到充分的外部性内部化。这个部分可以成为工业水价调控的重要指标,其极限是达到污水治理的完全成本。
水生态保护补偿成本p4是指给定的水资源是由于其他地区或其他主体生态保护的结果,由于他们保护了水生态,放弃了经济发展的机会,因此,需要用水户对其进行补偿。目前,在工业水价中这个因素考虑极少。这也是一个外部性内部化的问题,补偿的极限是水生态及其保护者的机会成本。
工业用水的水资源基本上属于国家所有,但是,目前国家所有者的权益几乎没有考虑。目前收取的水资源费实际上是水资源管理部门对水资源的管理维护费,而不是体现所有者权益的收益。因此,水资源所有者收益p5要纳入工业水价之中,这是一个调控空间比较大的变量。
可见,污水治理成本、水生态保护补偿成本、水资源所有者权益是工业水价中发挥价格杠杆作用、促进工业节水的主要部分。
4.促进工业节水的水资源定价方式
利用水价杠杆实现工业节水同时具有经济、社会和环境三重含义。在水资源日益紧缺的情况下,恰当、合理的水价政策可以起到促进工业节水效果,进而保证工业经济的持续健康增长,提高社会各部门的用水效率,促进水资源生态环境的不断改善。这三重含义在工业节水的水资源定价中是一个有机整体。
边际成本定价、平均成本定价和两部制定价都不适用于工业节水定价。边际成本定价虽然最优但要求水价费率变化极为灵活,可操作性差,在实践中并不可行。单纯以供水企业的边际生产成本定价忽视了基于水循环和水环境自净化过程的水资源生态价值,当用水需求不能得到有效抑制时,这一定价方式难以实现工业节水和水生态保护目标。平均成本定价和两部制定价尽管操作性较强,但并不能达到工业节水目的。所以,适用于工业用水的定价方式应是内含生态水价、污染水价和资源水价的阶梯定价,并且为了达到控制用水需求的目的,应以递增的方式予以加价,即递增的阶梯定价。
早在20世纪90年代,在水资源不充裕的国家和地区就已广泛使用递增的阶梯水价作为工业节水的定价方式,比如意大利、墨西哥、葡萄牙、西班牙和美国中西部地区,见表1。在西班牙,受水资源稀缺的限制,大多数地区水价的从量费按照递增的两阶梯设计。美国洛杉矶地区全年少雨而冬季降雨较多,为了节水,其工业水价不仅采用递增的阶梯水价,而且联合使用季节性水价和超额用水加价,其中超额用水加价部分根据工业用水户的历史平均用水量核定。
总之,依照需求侧管理原则,实施科学合理的水价政策有利于综合实现环境保护、经济发展和工业节水目标。工业水价应当准确地反映经济发展中遭遇的水资源紧缺危机,反映水资源在生产、生活和生态环境中的稀缺价值,反映工业取水和污水排放对生态环境的负外部性影响。尽管依照社会和生态环境供水的总边际成本制定工业水价政策是最优定价方式,但其可行性差。递增的阶梯定价是较好的次优选择。明确区分水资源费、商品水价、生态水价和污染水价等各组成部分的递增阶梯水价既能针对原水抽取的数量效应起到减量化用水作用,又能针对废水排放的数量和质量效应起到降低污染排放数量和强度的作用。
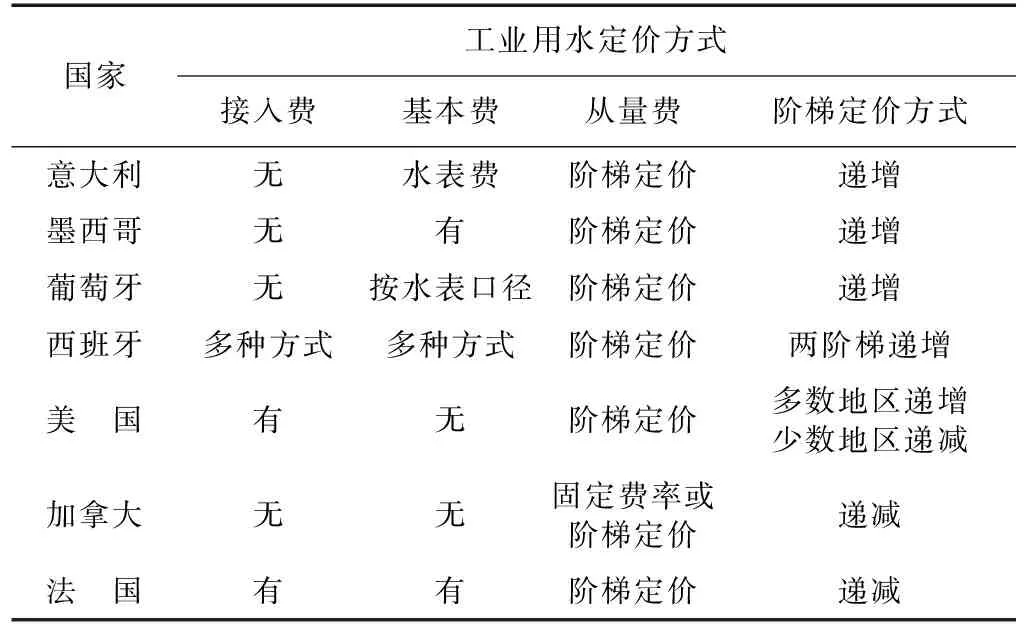
表1 部分国家的工业用水定价方式(以公共供水为例)
资料来源:根据The Price of Water: Trends in OECD Countries (Paris: OECD Publications, 1999)整理[17]。
三、促进我国工业节水的水价调控战略
价格机制是市场机制的核心。水价调控在促进工业节水中具有关键作用。促进我国工业节水的水价调控战略是一个战略体系。
1.体现资源稀缺程度的工业水价调控战略
在工业水价的内涵组成中,体现水资源稀缺价值的资源水价和体现水资源所有者权益的水资源费是工业节水价格调控的主要变量。当前,我国工业水价调控应以充分体现国家作为水资源所有者的权益为重点。在未来一段时期,我国工业水价政策的制定应把资源水价和实行阶梯式计量定价作为深化工业水价改革的主要方向。
2.体现外部性内部化的工业水价调控战略
在工业用水的污染水价和生态水价中,完全、准确的外部性内部化定价政策不直接以工业节水为目的,但足额到位的排污收费机制和兼顾效率公平的生态补偿机制具有重要的工业节水效果。随着水生态保护和水环境污染的产权界定技术的突破,尤其是水资源和污水的计量成本的下降,在使用者和污染者付费原则下实现工业用水外部性内部化已经成为可能。在工业用水的上端——取水端,要实施“谁保护,谁受益”和“谁使用,谁补偿”的生态补偿机制,在工业用水的下端——排水端,要体现“谁污染,谁治理”和“谁污染,谁付费”的排污收费机制。
3.体现产业管制要求的工业水价调控战略
制水企业的管控是水价调控战略有效实施的保障条件之一,商品水价是主要管控变量,其调控思路是“该涨的涨,该降的降”:一要管控制水成本,通过创新管理出效益;二要管控供水品质,通过多样供水降成本;三要管控水厂利润,通过控制收入促公平。水厂要想方设法降低制水成本、增加供水种类,满足用水需求多样化的要求,满足工业用水价廉达标不超标的要求。要防止出现工业水价与供水企业的收入齐头并进但工业节水效果不明显的现象。
4.体现各种供水统筹的工业水价调控战略
工业节水的价格调控战略不仅要反映在公共供水的水价之中,更要反映在自备供水的水价之中。如果对自备供水不加控制,工业节水最终会一场空。因此,必须要加强自备供水的监管。首先,对于自备供水的企业都要申请登记,取得取水许可;第二,取水数量要纳入区域社会的总量控制之中,绝对不能游离于总量之外;第三,政府部门要加强企业取水和排污的检测监管,坚决杜绝偷采偷排现象;第四,根据企业取水和排污的情况收取体现水资源所有者权益的水资源费、体现水生态保护的生态补偿费、体现水环境治理的污水治理费等。
如此,自备供水的水价调控应从四方面深化改革:取水许可收费——基本费和管理费、取水计量收费——水资源费和生态补偿费、总量控制收费——递增的阶梯定价和超额用水加价、排污计量收费——(分级的)污水治理费。
5.体现因地制宜原则的工业水价调控战略
工业节水的价格调控战略须因地制宜,注重调整水价结构,细化水价组成功能。水资源严重短缺的地区实施递增的阶梯式水价制度重在体现用水的稀缺价值和用水的公平原则——即以资源水价中的生态水价部分对给定的由其他地区或其他主体生态保护的水资源进行生态补偿。水资源短缺但不严重或水生态脆弱的地区也应实施递增的阶梯式水价制度,但重在通过提升水价努力实现本地区的水资源供需平衡和工业经济良性发展。水资源比较富余同时水生态又良好的地区既可以采取固定费率的计量水价也可以采取递增的阶梯式水价,灵活的水价政策重在协调地区工业经济发展和水生态保护的正外部性——如果正外部性高于地区工业经济的直接发展收益而且正外部性又能通过受益地区的水价政策得到补偿,那么水资源富余且水生态良好的地区应采用递增的阶梯式水价制度。
这样,基于大调控观的差异化政策,可发挥水价调控的全国性作用。在统一推进节水的前提下,合理调配水资源供给那些节水潜力有限但工业用水效益突出的地区和省份,应从整体上提高全国的工业用水效率。按照用水地区补偿供水地区的角度,应深化水价中的生态补偿水价改革;按照国家大调控的角度,应在水价中深化国家作为水资源所有者的权益改革,即水资源费改革。按照两步走的观点,工业用水的水价改革应先进行水资源费改革再进行生态水价改革。
[1] 杜斌. 中国工业节水的潜力分析与战略导向[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2008.
[2] 贾绍凤,张士锋,杨红,夏军. 工业用水与经济发展的关系:用水库兹涅茨曲线[J].自然资源学报,2004,19(3):279-284.
[3] 贾绍凤,张士锋. 北京市水价上升的工业用水效应分析[J].水利学报,2003(4):108-113.
[4] 李眺. 我国城市供水需求侧管理与水价体系研究[J].中国工业经济,2007(2):43-51.
[5] DEROOY J. Price responsiveness of the industrial demand for water[J]. Water Resources Research, 1974, 10(3): 403-406.
[6] ZIEGLER J, BELL S. Estimating the demand for intake water by self-supplied firms[J]. Water Resources Research, 1984, 20(1): 4-8.
[7] RENZETTI S. An econometric study of industrial water demands in British Columbia, Canada[J]. Water Resources Research, 1988, 24(10): 1569-1573.
[8] 毛春梅. 工业用水量的价格弹性计算[J].工业用水与废水,2005,36(3):1-4.
[9] 刘昕,李继伟,朱崇辉,刘俊民. 工业用水量的价格弹性分析[J].节水灌溉,2009(10):68-70.
[10] 张宁,张媛媛. 浙江省工业用水的节水潜力及影响因素分析[J].给水排水,2011,37(8):62-67.
[11] WANG H, LALL S. Valuing water for chinese industries: A marginal productivity analysis[J]. Applied Economics, 2002, 34(6): 759-765.
[12] FUJII H, MANAGI S, KANEKO S. A water resource efficiency analysis of the chinese industrial sector[J]. Environmental Economics, 2012, 3(3): 82-91.
[13] 郑新业,李芳华,李夕璐,郭琎. 水价提升是有效的政策工具吗?[J].管理世界,2012(4):47-59.
[14] 姜翔程,周迅,宋夏阳. 我国城市水价定价方法研究进展[J]. 河海大学学报:哲学社会科学版,2013,15(3):51-55.
[15] 沈满洪,陈庆能. 水资源经济学[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社, 2008.
[17] ORGANIZATION FOR ECONOMIC COOPERATION AND DEVELOPMENT. The price of water: Trends in OECD countries[M]. Paris: OECD Publications, 1999.
Abstract: In China, industrial water has the problems of price deficiency and price distortion. Optimizing industrial water price has four significant effects, including direct price effects, structural adjustment effects, water recycling effects and technological progress effects. Industrial water price mainly consists of five sections: water construction and production costs, the profit of water providers, sewage treatment costs, water ecological protection costs and income of water resources owners. Therefore, regulation strategies of water price should abide by the following principles: reflecting the degree of water resources scarcity, internalization of water resources externalities, industrial regulation requirements of water control enterprises, overall planning on various water prices and pricing water according to local conditions.Key words: industrial water; industrial water conservation; water price regulation
Globalization of Contemporary Capitalism: A Critical Interpretation
TANG Zhengdong
(Department of Philosophy, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China)
Lisbon group regards globalization as a new social economic phenomenon from the perspective of central power sprawl. Gray regards globalization as a complex historical process from the perspective of the interaction between globalization and localization. Harvey regards globalization as a geopolitical plan from the perspective of spatial production of capitalism. Although these interpretations indicate different fields of vision, they have a common shortcoming: they fail to regard globalization of contemporary capitalism as a form of production relationship of capitalism of the present stage. Therefore, it is impossible for them to deeply understand the essential connotation of globalization from the perspective of historical materialism.Key words: globalization; capitalism; historical materialismFalse Noumenon of Law Justice in the Context of Interest Malediction: Rereading of Marx’sTheArgumentaboutActofWoodStealYAN Bing,et al(Business College of Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225009, China)
The Argument about Act of Steal Wood is a transition text of youth Marx’ thought “on the way”. Reappearance its historic condition and narrate logic is necessary for significances of thought history and realistic functions. Seeking immoral behind Steal Wood “imputation”, opening out reversal of nation essence with self-interest and vassal and taking apart illegitimacy symptom of lawmaker were not only a intention trend in the article but also a value assume and an origin that Marx overturned classic liberalism later and made for the true historic depth and realistic mother earth. Also in this paper also Marx unannotated“material benefit to express an opinion on the difficult”details were explained in detail, to Lenin’s“change”to do the dialectical analysis, and from ontology, methodology and value theory of triple perspective to identify the text meaning.
law justice; politics; act of steal wood ; Marx
Research into Social Management Thoughts of Marx and Engels
SHEN Jie
(School of Marxism,Hohai University,Nanjing 210098,China)
Abstract: Marx and Engels ’ criticism of capitalist social management and the summary of the proletarian revolutionary practice , in particular the experience of the Paris Commune, contains many theories on social management. Social management showing the dual nature of class and social has the dual functions of the political domination and the social administration. With the means of production being transformed from the private possession into the socially owned, the social management converted from the class nature into service ultimately. Social management in the future is the concrete practice reflecting people’s principal status and focusing on the people’s livelihood-oriented ,and also is the democratic management which requires the participation of all members, pursuits the equity and justice and the social governance This democratic administration needs political, economic, ideological and institutional conditions, and also needs to be run through a systematic public powers in response to the demands of the public interest.Marx and Engels ’ thoughts has important implications for social management innovation and the national and social governance in our country’s modernization .
Keywords: Marx and Engels; social management; social governance, democracy and people’s livelihood
On Knowledge Production of Ideological and Political Education
YE Fangxing
(School of Marxism,Fudan University, Shanghai200433,China)
Abstract: The main point for discipline construction ,theoretical and practical innovation of Ideological and Political Education lies in the knowledge production.Knowledge production is the important indicators of the scientific ideological and political education ,the basis of theoretical innovation, and improve the ideological and political education.Knowledge of ideological and political education with scientific concept, category, principle, law as the basic elements, such as in principle and method of ideological and political education as the basic form. On the ideological and political education particularity of cognition and grasp of knowledge, help to reveal the ideological and political education characteristic and mechanism of knowledge production. The value of ideological and political education knowledge production to political guidance as the guidance, to pay attention to the reality of social problems, in state financing, organization and system guarantee, the complete analysis of the problems with the crack. Ideological and political education knowledge to produce polymer effect need to focus on building and developing academic community ideological and political education, focusing on strengthening the ideological and political education academic research team construction, cultivate the ideological and political education academic culture, ideological and political education to promote academic exchanges and strengthen ideological and political education academic ethics and system construction. Key words: the knowledge of ideological and political education; knowledge production; scientific research; The academic community
Strategy and Justification of Famers’ Resistance in China: Two dimensional analysis of Rightful Resistance Theory
XIAO Tangbiao
(Research Center of Public Affairs and Local Governance, Nanjing University,Nanjing 210093,China)
Abstract: In recent years, “rightful resistance” is the most competitive theory and received widely response and approval in the study on contentious politics in China. This paper shows that “Rightful resistance” is more struggle justification than struggle strategy. As performance and tactics of contentious, the concept of “rightful resistance” has an inner conflict, because it not only may be non-violence, but also violent, it not only may be legal, but also between legal and illegal, not necessarily true legitimate. This strategic struggle fall in between legal and illegal boundaries is hard to say that it is the truly rightful resistance. As legitimate justification of contentious, the concept of “rightful resistance” is very appropriate to highlight the current national laws, policies and ideologies gives the legitimacy of public protest, and show the contrast in the actual operation and implementation. For these “law”, no matter whether the trust or not, all protesters take it as a justification of the struggle. Because the concept of rights as a universal value and ethical demand is to be self-evident in the western society, western social movement theory neglect the legitimate justification of contentious have a rightful reason. In today’s China, however, when people need make great efforts to justification them contentious action in social context, our theoretical research no reason not to focus on the deeper problems that include ethical and moral element.Key words: rightful resistance; struggle strategy; struggle justification; political legitimacy; contentious politics
Income Disparity between Urban Residents and Descendants of Migrant Workers: An Analysis Based on Improved Oaxaca-Blinder Decomposition Method
WAND Yijie,et al
(Department of Sociology, Hohai University, Nanjing 211100,China)
Abstract: The majority of current studies about descendants of rural migrants focus on school education, but few concern the labor market. Base on the sample survey data from Nanjing, this paper finds that, the social and economic status of descendants of rural migrants is higher than those without migration experience, but lower than urban residents. With the improved Oaxaca-Blinder decomposition, this paper explores how the income differentials are influenced by human capital, social capital and household registration discrimination. The result shows that human capital is the most important factor. Household registration discrimination and social capital are also important for the differentials.
Keywords: descendant of rural migrants workers; income differentials; household registration discrimination; human capital; social capita
Impact of Human Capital, Political Capital, Social Capital on Income Inequality
HE Zhaiping
(Department of applied sociology, School of politics and administration, Tianjin Normal university, Tianjing 300387, China)
Abstract: On the basis of CGSS2006 data,using Regression-based inequality decomposition technique, the paper compares the contribution of human capital, political capital and social capital on the income inequality of Chinese urban residents between the eastern and midwest. The total impact of human capital on inequality of china has slight difference. In which the level of education in the eastern affects income greater than midwestern. experienc is the opposite. Impact of social capital of midwestern urban resident on inequality , by contrast, is more than the eastern, but the impact of political capital on income inequality is greater than in the eastern. Refuting market monism of income inequality, this paper considers that the role of the market and the state all have impact on income inequality.
Keywords: human capital; political capital; social capital; income inequality; regression decomposition technique
The Vortex of Reproduction in School Education: Research into Education of Migrant Workers’ Children
SHI Qiuxia,et al
(Law and Politics School ,Jiangsu Normal University,Xuzhou 221116,China)
Abstract: Reviewing and combing the relationship between education and social inequality, this paper analyzes the education mechanism of class reproduction, and gives further explanation about this mechanism for the education process of a designated public school named “fly” to recruit migrant workers’ children. Research shows that there are many reproduction vortexes in school education that make intomigrant workers’ children has three characteristics:low learning ability, low education expectation and low Labor market competitiveness, and make this children have the risk of copy their Parents’ life path. Vortexes contain a deep understanding of class reproduction. On the one hand, school education influenced by education and social structure and has its own operating logic is very important on a class reproduction chain. On the other hand, Structural factors impact on education,it is through the actors’ understanding of their own living environment and ultimately effect on behavior, and concentrate in schools, teachers and students of all kinds of replication strategy.
Key words: migrant workers’ children; education; reproduction; actor; vortex
Interest Game and Group Power: A Study of Formation Mechanism of Mass Incidents and Solution to Social Conflicts
Hua Jian,et al
(Business School of Hohai Universtiy, Nanjing 211100, China)
Abstract: Mass incidents are the result of game between different interest groups. In the mass incidents, the change of group power especially the people’s strength plays an important role in the evolution course of social conflicts. In this thesis, we use evolutionary game model to illustrate the evolution course of social conflicts depending on the change of group power, and divide it into four stages: incubation, acute, outbreak and recession. The most effective way to deal with mass incidents is to try to reach a compromise agreement between the people and the local government, which can be realized by active negotiation between the two groups or an intervention of a third party. In addition, in order to prevent the mass incidents, the government should strengthen the information collection system, promptly solve the people’s interest problem, using media to guide, and increase the transparency of the government’s work.Key words: mass incidents; evolutionary game; group power
Rethinking of the Strictest Water Resources Management System
ZUO Qiting
(Center for Water Science Research, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, 450001, China)
Abstract: To deal with the increasingly serious water resources problems, the strictest water resources management system was proposed by our government, and it has been implemented throughout the country up to now as a new move to intensify water resources management. However, there are some problems concemed. Based on the preliminary studies, some problems discussed and thought in the preliminary times were presented, some related issues were further rethought, and some thinkings for several major issues of the strictest water resources management system were stated, including the concept of the strictest water resources management system, the relationship with river harnessing of human-water harmony, the relations with ecological civilization construction, the relations with deepening of water conservancy reform, key issues for system implementation and evaluation, theory system problems, support system issues, et al. It can provide a reference for further scientific understanding and improving the implementation of the strictest water management system.Key words: the strictest water resources management system; water resources management; integrated water resources management; theory system; core system.
Research into Dilemmas and Countermeasures of Functional Transformation of Government in the Process of the Strictest Water Resource Management
WANG Huiming,et al
(State Key Laboratory of Hydrology-Water Resources and Hydraulic Engineering,Hohai University,Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: It is of great significance for Chinese government to transform its functions to effectively implement the system reform of water resource management, because governmental functions and behaviors are shown in the holistic process of the strictest water resource management. Then, the establishment of water market system and the implementation of the strictest water resource management are available. According to the six dilemmas pertaining to the transformation of governmental functions, the paper proposes the countermeasures to promote the smooth transformation of the governmental functions in the process of the strictest water resource management, namely, system innovation, fostering of water market, participation of multi-subjects and publicity education.
Key words: the strictest water resource management; functional transformation of government; d ̄i ̄l ̄e ̄m ̄ma; countermeasures
Research into the Mode of Governmental Cooperation in Floods Emergency Management
TONG Jinping,et al
(School of Business,Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: A relatively perfect organizational system of floods emergency management has been established in China. However, no-timely response and procrastination still exist in practical actions of the grassroots organizations. In this paper, evolutionary game (EG) theory is applied to floods emergency management, and to research the modality for intergovernmental cooperation from the vertical governmental relationship and the horizontal governmental relationship. Game models are founded respectively and a conclusions are inferred based on evolution results that: the superior government in the vertical governmental relationship insists on strengthening supervision is a necessary condition for promoting a positive cooperation between governments in floods emergency management.
Key words: floods; emergency management; intergovernmental cooperation; evolutionary game
Research into Implementation Difficulties in the Process of the Strictest Water Resources Management Based on Internet Information
LIU Gang, et al
(State KeyLaboratory of Hydrology Water Resource and Hydraulic Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China)
Abstract: Based on internet information, the paper analyzes the implementation and policy execution dilemma of the strictest water resources management in China and the relevant issues of the local government.. On the basis of the predicament of the strictest water resources management in the process of implementation and the analysis of the core issue and the conflict concerned, it discusses the deep reasons of the predicament. Finally, from the perspective of dealing with man-water conflict, low efficiency of management, core issues, practical problems and external conditions, the paper systematically proposes the countermeasures on coping with the implementation predicament of the strictest water resources management in China. Key words: the strictest water resources management; internet information; execution dilemma
Research into Regulating Strategies of Water Pricing for Industrial Water Conservation
LI Tailong ,et al
(School of Economics and Management, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou 310018, China)
10.3876/j.issn.1671-4970.2015.04.014
2014-10-27
国家社会科学基金项目(12AJY003)
李太龙(1981—),男,山东泰安人,副教授,博士,从事数量经济学和资源经济学研究。
F205
A
1671-4970(2015)04-0082-07

