一米新真空太阳望远镜离焦对高分辨太阳观测图像重建的影响*
方玉亮,金振宇,刘 忠,戴懿纯,黄善杰
(1. 中国科学院云南天文台,云南 昆明 650011;2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049)
CN 53-1189/P ISSN 1672-7673
一米新真空太阳望远镜离焦对高分辨太阳观测图像重建的影响*
方玉亮1,2,金振宇1,刘 忠1,戴懿纯1,黄善杰1
(1. 中国科学院云南天文台,云南 昆明 650011;2. 中国科学院大学,北京 100049)
由于太阳辐射、环境温度等因素,太阳望远镜在一个观测日内往往有较明显的像差变化,而离焦是其中的主要像差。针对抚仙湖1 m太阳望远镜的高分辨成像观测系统,对其离焦像差及变化进行了简要分析,在此基础上模拟分析了离焦像差对图像高分辨统计重建的影响。分析结果表明,离焦像差对高分辨重建图像的相位传递函数影响不大,但对调制传递函数有明显的影响,进而造成像质衰减,应当进行补偿。
1 m太阳望远镜;温度变化;离焦;高分辨统计重建
抚仙湖1 m新真空太阳望远镜(New Vacuum Solar Telescope, NVST)是国内口径最大的地基太阳望远镜,主要用于对太阳光球和色球的高分辨率成像观测[1]。众所周知,地球的湍流大气会造成地基望远镜的严重像质衰减,采用基于斑点干涉术[2]和斑点掩模法[3-4]的图像统计重建技术对1 m太阳望远镜进行观测图像的高分辨率重建。望远镜的像差会影响高分辨率图像重建的效果,太阳辐射及较大的日温差等因素,使太阳望远镜产生显著的离焦像差,且离焦量随着望远镜的热量累积及外界温度的变化而改变。观测经验和数值分析均表明,离焦像差是地基太阳望远镜观测过程中不可忽略的像差。
文[5-9]作者研究了望远镜静态像差对图像高分辨统计重建的影响,研究结果表明,在望远镜具有一定静态像差的情形下,算法仍可采用,但重建结果将受到影响。在实际使用中发现,1 m太阳望远镜的离焦像差及其日变化给观测结果带来的影响是不可忽略的。 本文首先采用简化模型估算了1 m太阳望远镜在观测过程中可能产生的离焦量及其变化,在此基础上模拟分析了离焦像差对高分辨图像重建的影响,为下一步研制1 m太阳望远镜离焦像差的快速补偿系统提供了设计依据。
1 1 m太阳望远镜离焦像差估计
太阳望远镜观测中的像差变化主要由主副镜等光学部件及机械支撑系统的热变形引起的。文[5]分析了太阳热辐射对1 m太阳望远镜主镜的影响,得到了形变在允许范围内的结论,因此本文不考虑主副镜及封窗的形变对时变离焦像差的影响,只考虑机械支撑系统的热变形。图1是1 m太阳望远镜的光路示意图,是格里高利结构加折轴光路,其中M1是抛物面镜,M2和M3是椭球面镜,F3是第三焦点位置[1,6]。考虑到M1和M2间距对焦点位置的敏感性,之间用热膨胀系数很小的铟钢连接。将离焦量的变化简化为线性模型,以(1)式描述温度变化和F3的焦点位置变化量的关系:
(1)
其中ΔF是F3的位置变化量;L12=3 024 mm是M1到M2的距离;L24=2 588 mm是M2到M4的距离;L43=1 636 mm是M4到M3的距离;β2=13.4是M2镜的轴向放大率;β3=26.3是M3镜的轴向放大率;α1=1.8×10-6/℃是铟钢的热膨胀系数[10];α2=12.2×10-6/℃是普通钢的热膨胀系数[10]。将这些参数代入(1)式,即可计算出F3的位置随温度的变化率是δF=2.57 mm/℃。离焦距离与离焦像差的关系
可以用下式表示:
(2)
1 m太阳望远镜的系统焦比F/45,在光球观测(中心波长705.8 nm)的离焦像差随温度的变化率为δw=0.225λ/℃。
从2014年1月31日到2014年3月31日,对1 m太阳望远镜的镜筒温度进行了测量,共得到38天的有效测量数据。测试到1 m太阳望远镜的镜筒温度在一个观测日内的最大温差为12.4 ℃,

图1 1 m太阳望远镜光学系统图
Fig.1 A light-ray diagram of the optical system of the NVST
最小温差为5.57 ℃,38天的平均温差为7.99 ℃。将这些结果代入(2)式,估算一天观测时段内的离焦像差变化量,得到平均的离焦像差变化量是1.8λ,最大可能的变化量是2.8λ,最小的变化量是1.25λ。图2是3月16日测量的温度变化曲线及其对应的离焦像差的变化曲线(假设20 ℃时望远镜聚焦,离焦像差的正负表示F3焦点前后偏移)。测量结果表明,在温度变化快的时段,在1 h内可能出现接近1λ的离焦像差的变化。

图2 2014年3月16日测量的1 m太阳望远镜镜筒温度和对应的离焦像差
Fig.2 The measured temperatures of the tube of the NVST and corresponding defocus aberrations induced by the temperature variations in March 16, 2014
2 离焦像差对太阳高分辨观测的影响
1 m太阳望远镜的高分辨重建采用斑点干涉术重建目标的功率谱和斑点掩模法重建目标相位的模式。利用湍流大气成像过程的数值模拟方法[11]分析离焦像差对图像高分辨率重建的影响。考虑到抚仙湖太阳观测站的平均视宁度是10 cm[1],因此在r0=10 cm情况下分析离焦像差对重建的影响。
大气-望远镜综合系统成像的数值模拟方法如下:
(1)利用(3)式模拟大气-望远镜成像系统的广义光瞳函数:
(3)
式中,P(x,y)是望远镜的光瞳函数;φA(x,y)是湍流大气的瞬时相位;Z4(x,y)是泽尼克(Zernike)多项式表示离焦像差的第4项;a4是离焦量。
(2)对光瞳函数进行逆傅里叶变换,再对其模进行平方获得点扩展函数。
(3)点扩展函数与目标卷积,获得目标斑点图。
获得有离焦像差的序列目标斑点图后,采用斑点干涉术统计重建目标的模,斑点掩模法重建目标的相位的模式对图像进行重建。将有离焦像差的重建结果与没有离焦像差的重建结果进行比较来分析离焦像差对重建结果的影响。
在不考虑湍流大气非等晕效应的前提下,大气-望远镜综合成像系统满足(4)式的空域线性卷积关系和频域乘积关系:
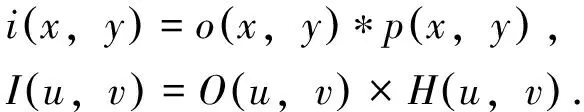
(4)
(5)式和(6)式分别是斑点干涉术和重谱的统计过程的描述公式:
(5)
(6)
由于重建算法不同,离焦像差对斑点干涉术重建的模和斑点掩模法重建的相位的影响需要分别进行分析。下式反映离焦像差对斑点干涉术重建的影响:
(7)
式中HD(u,v)是有离焦像差的斑点干涉术传递函数。图3是离焦像差分别为0.2λ、0.5λ、1λ和2λ的斑点干涉术传递函数与没有离焦像差的斑点干涉术传递函数的比较结果。结果表明,离焦像差对模的重建产生影响,小于0.2λ时影响较小,大于1λ时影响比较严重。图4是有离焦像差时斑点掩模法重建的相位减掉无像差时重建的相位的结果,表明离焦像差对相位重建有影响。离焦像差对重建结果的模和相位都有影响,对其影响表现比较直观的是重建的点扩展函数,(8)式是重建点扩展函数的定义:
(8)
其中,R(u,v)是(7)式的计算结果;φ(u,v)是由离焦像差引入斑点掩模法传递函数的相位;F-1是傅里叶逆变换;H0(u,v)望远镜的理想光学传递函数,主要作用是滤波,降低高频噪声的影响。图5是重建的点扩展函数,纵坐标是对数坐标,随着离焦像差的增加,点扩展函数的斯特列尔比降低,点扩展函数的全峰半宽(FWHM)变大,旁瓣也有变化但是并不明显。表1是不同离焦像差下的重建点扩展函数的斯特列尔比和全峰半宽。太阳米粒图像的强度均方根能在一定程度上反映图像的分辨率,强度均方根的定义如(9)式所示:
(9)

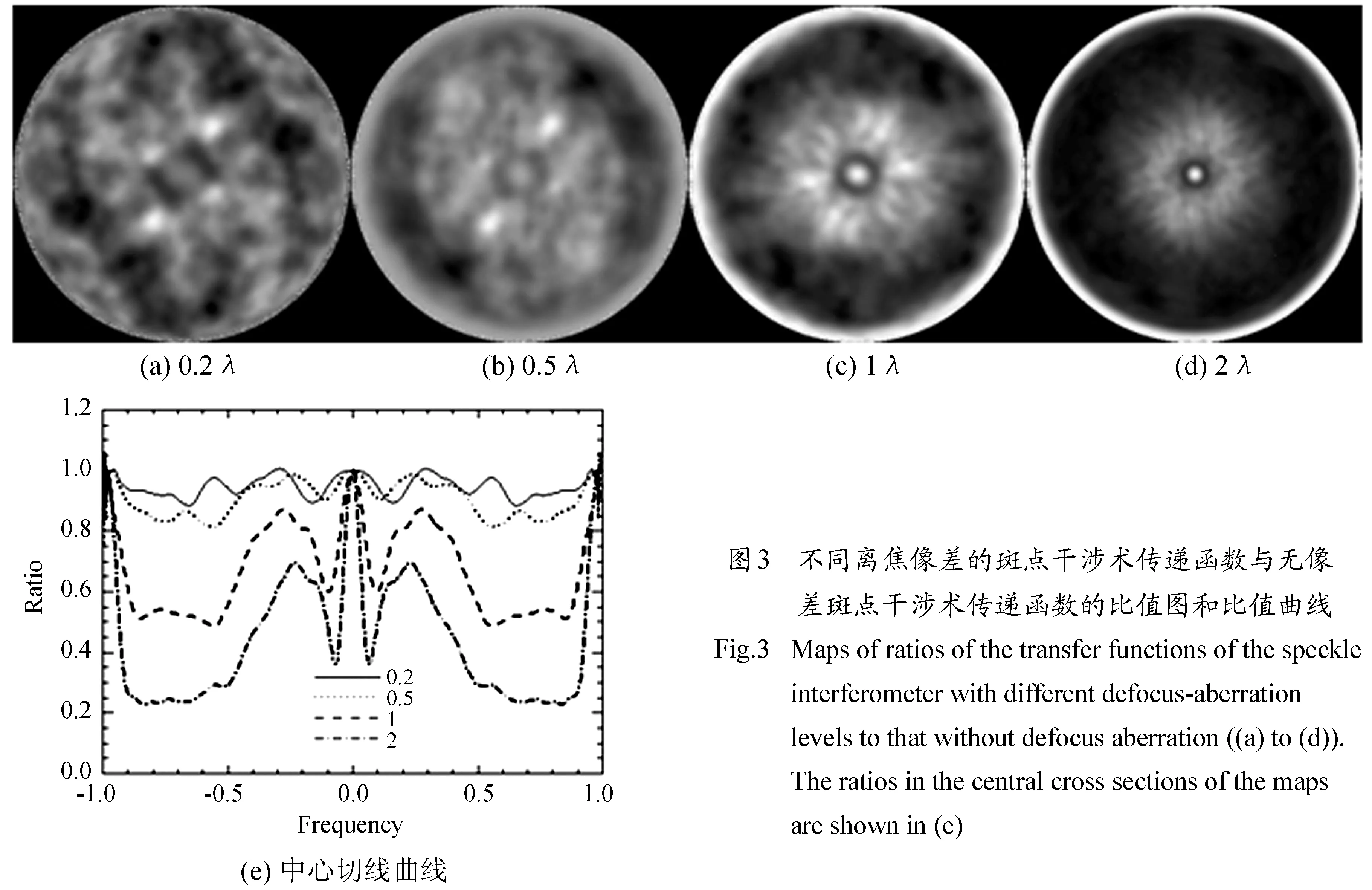
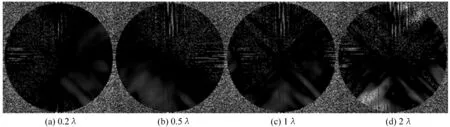
图4 有离焦像差与无像差斑点掩模法重建的相位之差
Fig.4 The maps of the differences of the phases reconstructed by the speckle masking with different defocus-aberration levels from the reconstructed phases without defocus aberration

图5 不同离焦像差下重建的点扩展函数
Fig.5 Plots of the Point Spread Functions reconstructed under different defocus levels 表1 不同离焦像差下的重建点扩展函数的 斯特列尔比和全峰半宽
Table 1 The Strehl ratios and Full Widths at Half Maximum of the Point Spread Functions reconstructed under different defocus levels

离焦像差λ斯特列尔比全峰半宽/″0100144020990146050880148100690154200370192

图6 不同离焦像差下重建的太阳米粒图像与理想重建的太阳米粒图像的差值
Fig.6 The difference images of the reconstructed solar images at different defocus-aberration levels from that without defocus aberration
3 结 论
利用1 m太阳望远镜镜筒温度测量数据估算了观测时间段内的时变离焦像差的变化,并利用数值模拟方法分析了离焦像差对太阳高分辨观测的影响。分析结果表明,平均每天估计有1.8λ的离焦像差的变化。在此范围内的离焦像差对斑点干涉术重建模的影响较大,对斑点掩模法重建相位的影响较小,对重建图像的综合影响主要是空间分辨率下降,使望远镜达不到衍射极限分辨率。当离焦像差小于0.2λ时对高分辨重建的影响可以忽略。因此需要针对1 m太阳望远镜高分辨观测系统研制离焦像差的测量系统,结合M3镜的调焦机构,实现对离焦像差的实时测量和修正。
表2 有离焦像差重建图像强度均方根与无像差 重建图像强度均方根比值
Table 2 Ratios of intensity RMS values of the reconstructed images at different defocus aberration levels to those of the reconstructed image without defocus aberration

离焦像差λ灰度RMS比值0209673170509288401074560220512546
[1] Liu Z, Xu J. 1-meter near-infrared solar telescope[C]// First Asia-Pacific Solar Physics Meeting ASI Conference Series. 2011: 9-17.
[2] Labeyrie A. Attainment of diffraction limited resolution in large telescope by fourier analysing speckle patterns in star images [J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 1970, 6(1): 85-87.
[3] Lohmann A W, Weigelt G, Wirnitzer B. Speckle masking in astronomy: triple correlation theory and applications[J]. Applied Optics, 1983, 22(24): 4028-4037.
[4] Weigelt G, Wirnitzer B. Image reconstruction by the speckle-masking method[J]. Optics Letters, 1983, 8(7): 389-391.
[5] Barakat R, Ebstein S. Bispectral diffraction imagery. I. the bispectral optical transfer function[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1987, 4(9): 1756-1763.
[6] 顾伯忠, 左恒. 云南天文台1 m 红外望远镜的主镜热力学分析[J]. 天文研究与技术——国家天文台台刊, 2008, 5(1): 83-90. Gu Bozhong, Zuo Heng. The thermal analysis of the primary mirror of 1m infrared solar telescope at Yunnan Observatory[J]. Astronomical Research & Technology——Publications of National Astronomical Observatories of China, 2008, 5(1): 83-90.
[7] Zhang J Y, Dainty J C. Effects of aberrations on transfer functions used in high angular resolution astronomical imaging[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 1992, 39(12): 2383-2404.
[8] Roddier F, Ricort G, Roddier C. Defocusing effects in astronomical speckle interferometry[J]. Optics Communications, 1978, 24(3): 281-284.
[9] Barakat R, Nisenson P. Influence of the wave-front correlation function and deterministic wave-front aberrations on the speckle image-reconstruction problem in the high-light-level regime[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1981, 71(11): 1390-1402.
[10]宫雪非, 崔向群. LAMOST 焦面板的结构分析[J]. 天体物理学报, 2000, 20(B12): 58-64. Gong Xuefei, Cui Xiangqun. Structural analysis of the LAMOST focal plate[J]. Acta Astrophysica Sinica, 2000, 20(B12): 58-64.
[11]McGlamery B L. Computer simulation studies of compensation of turbulence degraded images[C]// Proceedings of SPIE: the International Society for Optics Engineering. 1976: 225-233.
A Study of Influences of Defocus Aberrations on High-ResolutionImage Reconstruction for Data from the New VacuumSolar Telescope of the YNAO
Fang Yuliang1,2, Jin Zhenyu1, Liu Zhong1, Dai Yichun1, Huang Shanjie1
(1. Yunnan Observatories, Chinese Academic of Sciences, Kunming 650011, China, Email: fyul@ynao.ac.cn;2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China)
The 1m New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) in the Fuxian Solar Observatory (FSO) of the Yunnan Observatories is currently the largest ground-based solar telescope in China. The primary scientific task of the NVST is high-resolution observation of the sun. Images from the ground-based NVST are inevitably blurred by atmospheric turbulences, and some high-resolution statistical reconstruction techniques (such as the speckle interferometry and speckle masking) need to be adopted to remove effects from atmospheric turbulences. However, reconstruction results with the techniques are affected by aberrations of the NVST. Due to solar radiations and environmental temperature variations there are appreciable aberration changes in a day. Changes of defocus aberrations have major contributions to overall aberration changes. In this paper we present analyses of defocus aberrations of the NVST and their temporal variations using the NVST high-resolution imaging system. We subsequently investigate influences of defocus aberrations on high-resolution statistical reconstruction of NVST data. Our preliminary estimation shows that in a typical day of observation the average and maximum variations of defocus aberrations of the NVST are about 1.8λ and 1λ, respectively. Our numerical simulations illustrate that defocus aberrations significantly influence the Module Transfer Functions (MTFs) of reconstructed images, but affect little the Phase Transfer Functions (PTFs) of the images. If defocus aberrations are above about 2λ spatial resolutions of reconstructed images for the NVST decrease rapidly as defocus aberrations increase. We conclude from these that defocus aberrations should be appropriately compensated to make reconstructed images of the NVST to have sufficient quality.
1m New Vacuum Solar Telescope; Temperature variation; Defocus; High-resolution statistical reconstruction
国家自然科学基金 (11303090) 资助.
2014-05-01;修定日期:2014-06-03 作者简介:方玉亮,男,硕士. 研究方向:天文技术与方法. Email: fyul@ynao.ac.cn
P111
A
1672-7673(2015)02-0183-06

