盐酸右美托咪啶对非体外循环冠脉搭桥患者血流动力学及血浆NT-proBNP的影响
王 曙, 吉 林, 于广东
(江苏省盐城市第三人民医院 麻醉科, 江苏 盐城, 224001)
盐酸右美托咪啶对非体外循环冠脉搭桥患者血流动力学及血浆NT-proBNP的影响
王曙, 吉林, 于广东
(江苏省盐城市第三人民医院 麻醉科, 江苏 盐城, 224001)
摘要:目的探讨盐酸右美托咪啶(DxM)对非体外循环冠脉搭桥(OPCAB)患者血流动力学及心肌功能的影响。方法20例拟行OPCAB患者随机分为盐酸右美托咪啶组(实验组)和生理盐水组(对照组),分别于麻醉用药前(T0)、术后1 h(T1)、24 h(T2)、48 h(T3)测定血清肌钙蛋白I (Troponin I)含量、心肌肌酸激酶同工酶(CK-MB)和血浆NT-proBNP浓度;并同时记录血流动力学参数。结果与T0比较,2组患者MBP、HR均明显降低(P<0.05); 与对照组比较,实验组T1~T3时点HR和MAP显著降低(P<0.05); 2组患者T1~T3时点肌钙蛋白I、CK-MB、NT-proBNP浓度较T0明显升高(P<0.01),且实验组较对照组浓度低(P<0.05)。结论盐酸美托咪啶能减轻OPCAB患者心肌损害,有助于维持OPCAB患者围术期血流动力学的稳定。
关键词:盐酸右美托咪啶; 脑利钠肽; 冠状动脉分流术
Influence of dexmedetomidine on level of plasma
非体外循环冠状动脉搭桥术患者都存在比较严重的心肌缺血,手术、麻醉刺激引起交感神经兴奋,释放儿茶酚胺,引起血压升高、心率增快等不良心血管反应,可加重心肌缺血导致严重后果,尤其是老年冠心病患者心脏储备差,更应该格外重视[1-3]。右美托咪啶(Dex)是一种新型高选择性α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂具有镇静、镇痛以及抗交感神经的作用,适用于老年冠心病手术患者的麻醉[4-5]。本研究探讨盐酸右美托咪啶连续输注对OPCAB患者血流动力学及血浆NT-proBNP的影响。
1资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
择期行OPCAB患者20例,年龄58~76岁,体质量55~82 kg, 心功能Ⅱ~Ⅲ级。排除情况:严重肝肾疾患,严重房室传导阻滞,凝血功能障碍,手术中涉及第二种器官的。入选病例随机分为右美托咪啶组(实验组)和生理盐水组(对照组),每组10例。
1.2 方法
麻醉术前用药:肌肉注射吗啡0.1 mg/kg和东莨菪碱0.005 mg/kg。所有患者采用咪达唑仑0.05 mg/kg、舒芬太尼0.5~1 μg/kg、哌库溴铵0.15 mg/kg及异丙酚0.5~1 mg/kg行全麻诱导,气管内插管。同时穿刺左桡动脉和右颈内静脉,连续监测动脉血压和中心静脉压,实验组于诱导前给予0.8 μg/kg右美托咪啶10 min泵注,诱导后加用0.6 μg/(kg·h)右美托咪啶维持麻醉,对照组则泵注相同剂量生理盐水。麻醉维持采用丙泊酚和七氟醚静吸复合麻醉,间断静脉注射舒芬太尼、哌库溴铵。
监测参数和指标:分别于麻醉诱导前(T0)、术后1 h(T1)、24 h(T2)和术后48 h(T3)取患者静脉血2 mL,免疫荧光法测定血清肌钙蛋白Ⅰ; 速率法全自动生化分析仪测定CK-MB,罗氏Cobas e601型全自动免疫分析仪采用电化学发光法测定血浆NT-proBNP浓度(试剂盒购自美国Roche公司)。
1.3 统计学分析
使用SPSS 13.0软件进行统计处理,计量数据用均数±标准差表示,符合正态分布的计量资料采用方差分析和t检验,偏态分布的行对数转换后采用上述检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2组患者在性别构成、年龄、身高、体质量、术前左心室射血分数、搭桥的冠状动脉支数及手术时间等差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
表1 2组患者一般情况比较
与T0比较,2组患者MBP、HR均明显降低(P<0.05); 与对照组比较,实验组T1~T3时点HR和MAP降低有明显差异(P<0.05); 2组患者T1~T3时点肌钙蛋白I、CK-MB、NT-proBNP浓度较T0明显升高(P<0.01), 而实验组较对照组浓度低(P<0.05)。见表2。
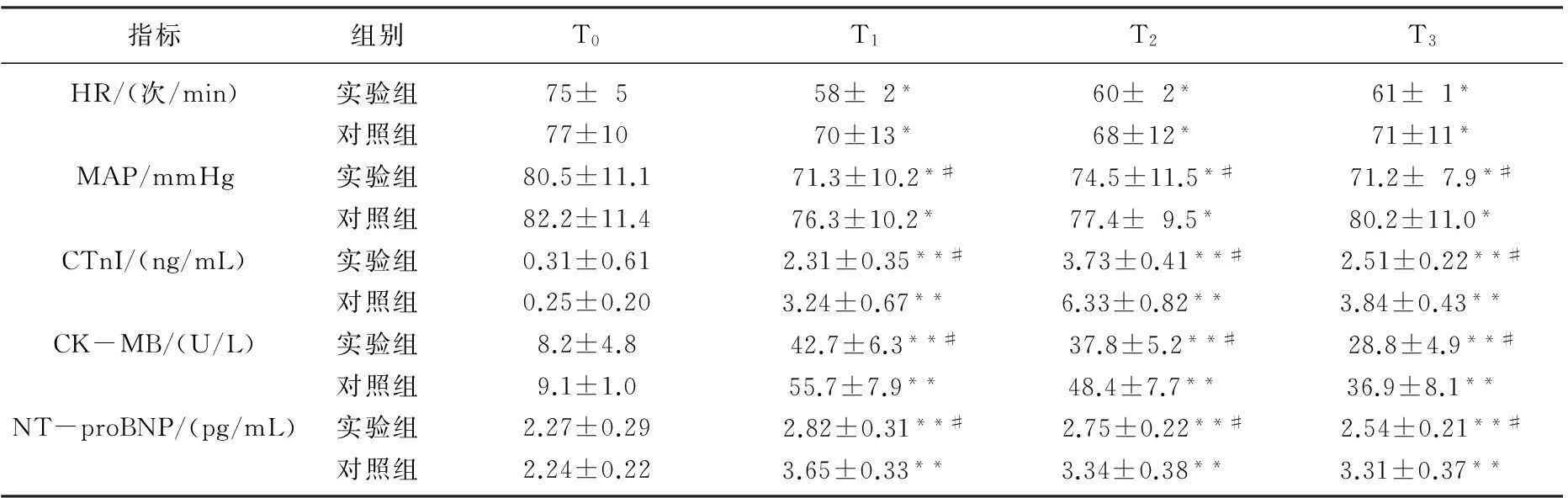
表2 2组围术期MAP、HR和血肌钙蛋白I、CK-MB、NT-proBNP变化
与T0比较,*P<0.05, **P<0.01; 与对照组比较, #P<0.05。
3讨论
近年来,非体外循环冠脉搭桥手术成为治疗终末期冠心病患者的有效手段之一。但手术、麻醉刺激引起系统炎性反应介质的释放增加和交感神经兴奋从而增加心脏负担,加重心肌损害。心肌细胞受损后,肌钙蛋白I, CK-MB释放增加,由此判断心肌坏死的情况。以往NT-proBNP应用于充血性心力衰竭等疾病的诊断,是反映心肌损伤的又一经典指标[6-8], 盐酸右美托咪啶是一种新型α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂,α1与α2的效能比为1∶1 620, 半衰期6 min, 克服了可乐定选择性不高、可控性差的弱点,已广泛应用于临床麻醉中的各个环节[9-10]。
本研究发现,盐酸右美托咪啶在辅助全身麻醉方面可减少全麻药物的用量,本研究中2组患者血浆NT-proBNP水平在术后1、24、48 h均比术前明显增高,与CK-MB变化趋势类似,说明NT-proBNP血浆水平与非体外循环冠脉搭桥患者心功能损伤程度密切相关。与对照组相比,右美托咪啶组患者围术期心率、血压均较对照组平稳,心率控制在理想范围,更加有利于术者操作,减少了操作时间和术后并发症的发生,患者血浆NT-proBNP浓度升高比对照组低,其原因可能有: ① 盐酸右美托咪啶能有效地抑制交感神经兴奋,减慢心率,降低心肌氧耗,心肌缺血再灌注时间减少有关; ② 通过抑制体内去甲肾上腺素,肾上腺素,皮质醇等神经递质的释放有关; ③ 通过蓝斑核和下丘脑的神经体液调节[11-15]。
总之,血浆NT-proBNP浓度与非体外循环冠脉搭桥术心肌损害程度密切相关。盐酸右美托咪啶可明显降低非体外循环冠脉搭桥术患者血浆NT-proBNP浓度,提高患者围术期血流动力学稳定性,减轻心肌损害。
参考文献
[1]王嵘. 右美托咪定持续输注对不停跳冠脉搭桥患者麻醉效果的影响[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2013, 17(21): 24.
[2]Borsook D, George E, Kussman B, et al. Anesthesia and perioperative stress: consequences on neural networks and postoperative behaviors[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2010, 92(4): 601.
[3]Tullio Palmerini, Giuseppe Biondi-Zoccai, Diego Della Riva, et al. Risk of stroke with percutaneous coronary intervention compared with on-pump and off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery: Evidence from a comprehensive network meta-analysis[J]. American Heart Journal, 2013, (6): 21.
[4]李云, 洪彬源, 赖晓红, 等. 右美托咪定复合地佐辛术后镇痛对开颅手术患者血浆儿茶酚胺及内皮素-1的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2013, 29( 12): 211.
[5]刘玲, 纪风涛, 刘付宁, 等. 右美托咪定对老年患者腰-硬联合麻醉的镇静效应[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2011, 27(1): 49.
[6]S. B.Elíasdóttir, G. Klemenzson, B.Torfason, et al. Brain natriuretic peptide is a good predictor for outcome in cardiac surgery[J]. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica, 2007, (2): 51.
[7]Thanos Athanasiou, Sharif Al-Ruzzeh,Pankaj Kumar,et al. Off-pump myocardial revascularization is associated with less incidence of stroke in elderly patients[J]. The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, 2004, (2): 125.
[8]杨曙光, 王爱萍, 汤学超, 等. 血浆N-末端脑钠肽前体水平与急性冠状动脉综合征近期预后的关系[J]. 实用医药杂志, 2007, 4(9): 31.
[9]Carlollo D S, Nossaman B D, Ramadhyani U. Dexmedetomidine: a review of clinical applications[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2008, 32: 31.
[10]Gerlach A T, Murphy C V, Dasta J F. An updated focused review of dexmedetomidine in adults[J]. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 2009, 13: 231.
[11]Hülya Basar, Serpil Akpinar, Nur Doganci, et al. The effects of preanesthetic, single-dose dexmedetomidine on induction, hemodynamic, and cardiovascular parameters[J]. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia, 2008, (6): 21.
[12]Hall J E, Uhrich T D, Barney J A, et al. Sedative,amnestic,and analgesic properties of small-dosedexmedetomi-dine infusions[J]. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 2000, 2(23): 51.
[13]Venn R M, Bradshaw C J, Spencer R, et al. Preliminary UK experi-ence of dexmedetomidine,a novel agent for postoperative sedation inthe intensive care unit[J]. Anaesthesia, 1999, (31): 103.
[14]方仲蓉, 赵晓琴, 王古岩, 等. 右美托咪定对冠状动脉旁路移植术患者麻醉诱导期BIS和血流动力学的影响[J]. 中国微创外科杂志, 2011, (02): 31.
[15]莫伟波, 黎必万, 檀文好, 等. 右美托咪定对心脏手术麻醉诱导期间血流动力学的影响[J]. 中国误诊学杂志, 2011,(07): 71.
N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide and
hemodynamic in patient with off-pump
coronary artery bypass grafting
WANG Shu, JI Lin, YU Guangdong
(DepartmentofAnesthesiology,YanchengThirdPeople′sHospital,Yancheng,Jiangsu, 224001)
ABSTRACT:ObjectiveTo investigate the influence of dexmedetomidine on the level of plasma NT-proBNP and hemodynamics in patients with off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (OPCAB). MethodsTwenty patients underwent OPCAB were randomly divided into dexmedetomidine group (experimental group) and saline group (control group). Venous blood samples were taken before induction (T0), 1 hour (T1), 24 hours (T2) and 48 hours (T3) after operation for determination of concentrations of Troponin I, CK-MB and plasma N-terminal-pro-brain natriuretic peptide. Hemodynamics parameters were recorded at the same time. ResultsCompared with those indexes at T0, HR and MAP reduced at T1to T3in both groups, and those indexes in the experimental group were significantly lower than the control group (P<0.05). Plasma Troponin I, CK-MB and NT-proBNP concentrations in both groups increased significantly at T1to T3when compared with T0, and the levels of these indexes in the experimental group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.01). ConclusionDexmedetomidine can effectively reduce cardiac injury, and it is helpful in maintaining stable hemodynamics of patients with OPCAB.
KEYWORDS:dexmedetomidine; brain Natrluretic peptide; coronary artery bypass
通信作者:吉林
收稿日期:2015-01-22
中图分类号:R 654
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-2353(2015)15-075-03
DOI:10.7619/jcmp.201515022

