Purification and Antimicrobial Assay of an Antimicrobial Protein from a Biocontrol Bacterium Strain K2-1 against Aquatic Pathogens
Xu TANG,Yuansen LIU,Ling LIN,Shixin HUANG,Weidong FANG,Changan XU*
1.Third Institute of Oceanography,State Oceanic Administration,Xiamen 361005,China;2.Fishery Department,Jimei University,Xiamen 361015,China
Antimicrobial agents from chemical synthesis are still in prevalence in the control and prevention of aquatic and animal husbandry diseases.However,this behavior has been questioned,and more and more synthetic antimicrobial agents have been restricted because of environmental and human health hazards[1]for this reason,alternative antimicrobials are needed in urgent[2],and the antimicrobial proteins/peptides have been proved to be the new potential source of antibiotics[3-4].a wide variety of living organisms can produce antimicrobial proteins,among those organisms,bacteria have been found to be an important source for producing antimicrobial proteins which display a wide spectrum of antimicrobial activity against different species of pathogens like viruses,bacteria and fungi etc.This paper describes the purification and antimicrobial assay of a protein from a biocontrol bacterium strain K2-1.
Materials and Methods
Strains and media
Biocontrol bacterium strain K2-1 was screened by the Research Engineering Centre of Marine Biological Resource Comprehensive Utilization,SOA.Strain K2-1 was identified asBacillus cereus(accession number in GenBank:KM892855)based on 16S rDNA sequence and the analysis of morphological,physiological and biochemical characteristics,
Vibrioalginolyticus,Aeromonas hydrophila,Aeromonas.Sobria,Pseudomonas fluorescens,Vibrio Parahaemolyticus,Vibrio harveyiand Vibrio anguillarumwere applied for antibacterial assay,andAeromonas hydrophilawas used as the test microor-ganism in antibacterial activity test,those pathogenic bacteria were obtained from the Biological Department of Fujian Normal University,China.
These strains were incubated in LB medium (peptone 10 g,yeast extract 5 g,NaCl 10 g,agar 20 g,H2O 1 000 ml)at 37℃.
Antibacterial activity test
The antibacterialactivity was conducted using an agardiffusion technique[5]and tests were made in triplicate.20 μl of test liquid was added to the hole of agar plate seeded with the test bacterium stated above,control plate was added with 20 μl LB medium,plates were incubated at 37℃for 36 h.The zones of inhibition around the holes were recorded and measured.
Purification of antimicrobial protein
Strain K2-1 was cultured under aerobic condition in LB medium for 36 h at 37℃and 180 rpm,fermentation broth was centrifuged at 10 000 g for 10 min,then (NH4)2SO4was added slowly into the supernatant to 75%saturation,the mixture was kept for 18 h,.and then was centrifuged to get precipitate which was subsequently dialyzed and freeze-dried to crude powder.The freeze-dried crude powder was dissolved in 0.2 mot/L sodium Acetate,and was loaded onto a 60 cm×3 cm Sephadex G-50(Pharmacia Biotech)column,the column was equilibrated and eluted with 0.02 mot/L sodium acetate at a flow rate of 24 ml/h and the absorbance at a wavelength of 254 nm was monitored.The fraction corresponding to each peak was collected,and its antimicrobial activity was conducted.All the fractions were mixed and immersed into hot water(80℃)for 10 min,then applied to Sephadex G-50 chromatography again.The peak with antibacterial activity was collected and used as the purified protein for subsequent experiments.All procedures above were carried out at room temperature.
Antimicrobial assay
The antimicrobial activities of the purified protein against the growth of the given pathogenic microorganisms were conducted by the method of agar diffusion stated above,the values are means±standard deviation of three replicate experiments.
Results and Discussion
Purification of Antimicrobial Component
54 mg of crude powder was obtained from 100 ml of fermentation supernatant by (NH4)2SO4precipitation,two components(APK1,APK2),corresponding to peak K1 and peak K2,were obtained from a Sephadex G-50 column chromatography (Fig.1).The fraction of peak K2 exhibited strong antimicrobial activity againstAeromonas hydrophila(Fig.2).
Two fractions of APK1 and APK2 were mixed and applied to Sephadex G-50 column chromatography again,one component was obtained(Fig.3),which showed strong antimicrobial activity against Aeromonas hydrophila.
This active component was collected and free-dried to powder as the purified protein,the final yield of the antimicrobial component is approximately 0.08%(Table 1).
Antimicrobial assay
The antimicrobial activity of purified protein APK2 was conducted against 7 strains of popular aquatic pathogenic bacteria,the results are given in Table 2.APK2 showed strong antimicrobialactivity againstmost pathogenic bacteria but less effect of inhibition on the growth ofPseudomonas fluorescens.
Discussions
In recent years,many antimicro-bial proteins or peptides have been found and purified[6-8],which are used as new antibiotics to treat pathogens,especially multi-drug resistant pathogens(MDRP),and a quite good result have been harvested.In this study an antimicrobial protein APK2 was isolated from the fermentation broth of strain K2-1,the purification process included (NH4)2SO4precipitation and Sephadex G-50 column chromatography combined with bath heat,the target protein with antimicrobial activity was got with a yield of approximately 0.08%.

Table 1 Yield of APK2 purified from fermentation broth
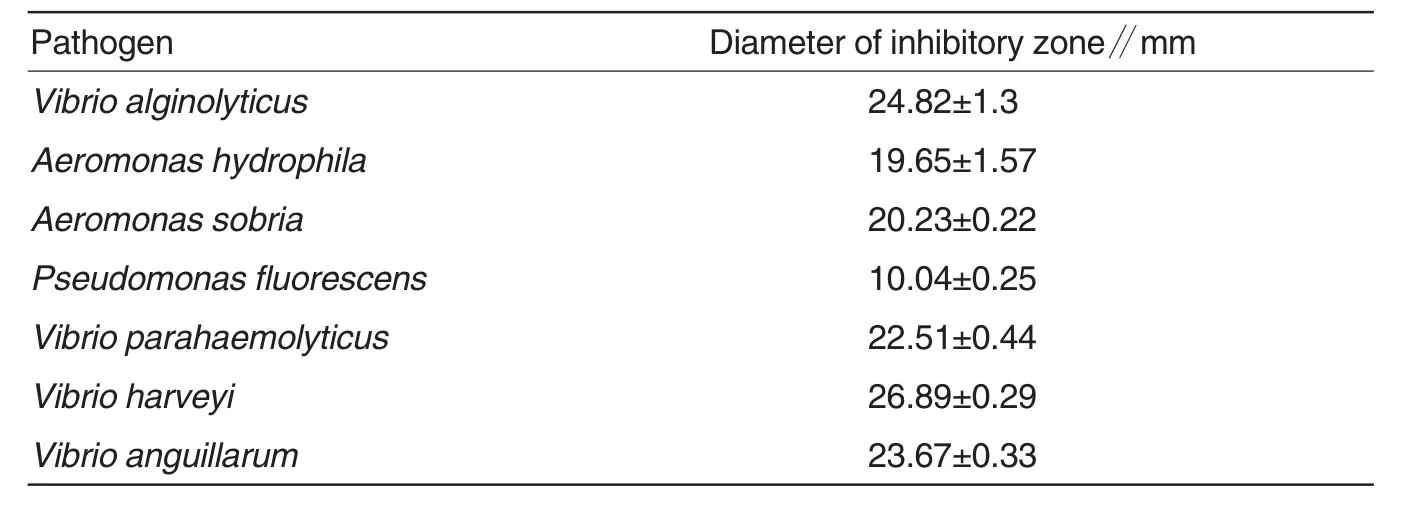
Table 2 Inhibitory effect of APK2 to selected aquatic pathogens
The antimicrobial assay indicated that this protein APK2 has strong antagonistic activity against most popular aquatic pathogens.From the measure of inhibitory zone showed in Table 3,APK2 has even more inhabitation effect on vibrios:includingVibrio harveyi VibrioanguillarumVibrioparahaemolyticusandVibrio alginolyticus.Vibrios own a lot of hosts,among about 30 kinds of identified vibrios,more than half of which are pathogenic to farmed fish,shell fish and shrimp[9],Vibrio harveyiandVibrio alginolyticusare the top 2 pathogenic vibrios which often result in heavy mortality of yellow croaker(Pseudosciaena crocea)[10],an important commercial fish farmed in net cage in the south of China,this study showed that APK2 had strong ability to inhibit the growth of these two kinds of vibrio pathogens in laboratory experiment,revealing the prospect of APK2 being used as highly effective antimicrobial protein in the prevention and control of vibrio pathogen disease happening in farmed fish.
[1]SAMBASIVAM S,CHANDRAN R,KHAN S.A.Role of probiotics on the environment of shrimp pond[J].Environ Biol.2003,24(1):103-106.
[2]SONG J H.What’s new on the antimicrobial horizon Int.J.Antimicrob Agents.2008,32(Suppl4):S207-S213.
[3]YEAMAN MR.,YOUNT NY,Nat Rev.Microbial.,2007,(5),727.
[4]HU Z,YE M Q,XIA L Q,et al.Purification and Characterization of an Antibacterial Protein from the Cultured Mycelia ofCordycepssinensis[J].Wuhan University Nature Science 2006,11(3):709-71
[5]TAGG J R,McGIVEN A R.Assay systems for bacteriocins.Appl.Microbio.1971:121-125.
[6]VAN DER GOOT F G,LAKEY J,PATTUS F,et al.Sectroscopic Study of the Activation and Oligomerization of the Channel-FormingToxin Aerolysin:Identification of the Site of Proteolytic Activation[J].Biochemistry,1992,31:8566-8570.
[7]ZHOU J,MENG Q F,XU X S,et al.Purification and in vitro Activity of an Antimicrobial Peptide from Skin of RanaTemporariaChensinensis,Davi[J].CHEM RES CHINESE U,2007,23(4):433-43.
[8]ZHANG Y X,ZOU A H,MANCHU R,et al.Purification and Antimicrobial Activity of Antimicrobial Protein from Brownspotted Grouper,Epinephelus fario[J].Zoological Research.2008,Dec.29(6):627?632
[9]AUSTIN B,AUSTIN DA.Bacterial fish pathogens:Disease in farmed and wild fish[M].2nded.Chichester,UK:Ellis Horwood Ltd.,1993,p.265-314.
[10]JIN S,WANG G L,ZHAO Q S,et al.Epidemiology of Vibrios in Large Yellow CroakerPseudosciaena croceain Marine Cage Culture[J].Fish.Sci.2005,24(1):17-19.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年8期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Simplified Cultivation Technology of Hua’an No.513——A New Summer Maize in Suixi County
- Research Progress on Heavy Metals Detoxification in Human Body
- The Strategies of Rainfall Accumulation and Utilization in New Countryside
- Advances in the Study of Protein Quality Traits and Main Influencing Factors of Wheat in China
- DNA Extraction from Half-grain Wheat Seeds without Using Chloroform
- Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in Dairy Food by Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification(LAMP)
