Research on the Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices
LI Fei, BI Kai-shun, YUAN Peng
Research on the Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices
LI Fei1,2, BI Kai-shun1, YUAN Peng3
Objective To study the IMDRF essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices and to provide a reference for medical devices premarket evaluation in China. Methods Literature review of essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices and filling out EP checklist were studied. Result and Conclusion EP checklist is a recognized method for implementing the essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices. The principles, methods, and evidences should be combined with EP checklist to form the premarket approval application system for medical devices in China.
medical device; EP checklist; application; premarket evaluation
International Medical Device Regulatory Forum (IMDRF) has proposed “the essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices” as the core, the “principles of conformity assessment” as the management methods, and the “application documentation” as a medium between government and enterprises, forming a trinity premarket review system of medical device. Its aim is to provide a reference for the reform of market access path and the improvement of registration management for medical devices so as to achieve the ultimate goal of scientific review and be in line with international standards[1].
In order to implement the essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices in the registration evaluation, IMDRF designed “the essential principles checklist of safety and performance of medical devices” (hereinafter referred to as “EP checklist”) in the premarket evaluation application documentation. EP checklist has been widely used for many years in the world. As “Declaration of Conformity and Summary Reports” of the FDA 510 (k) application requirements, “Essential Requirements Checklist” of the EU application requirements for medical devices, Japan began to use comprehensively IMDRF application documentation requirements from 2005, including EP checklist; Other countries, such as Canada and Australia, also used EP checklist as the premarket evaluation application documentation. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the essential principles of EP checklist for perfecting premarket evaluation application documentation and improving the scientific and systemic of registration review in China.
1 Introduction of the essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices
Based on “Medical Device Registration and Filing Management Measures” (draft), medical device registration refers to the application and approval process made by the Food and Drug Administration department. After getting the application for medical devices from the applicant, the Food and Drug Administration department will evaluate systematically the safety and effectiveness of the research and its result for premarket medical devices in accordance with legal procedures to determine whether to approve the application.
Since the safety and effectiveness of systematical evaluation is the core of product registration, we need to clarify what safety and effectiveness are and how to evaluate them systemically. China has carried out medical device registration work for nearly 20 years, and 14 years have passed since the implementation of “Medical Devices Regulations” in 2000, but we have not gotten the answer to the safety and effectiveness of products. After many years of research, Europe and other countries with more experience in medical device regulatory proposed solutions and they reached a consensus after jointly establishing “the Global Harmonization Task Force” (IMDRF predecessor) (hereinafter referred to as “GHTF”). Then they issued “the Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices”[2]and “the technical summary documents accordance with the basic requirements”[3].
Medical device is the object of the essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices (hereinafter referred to as the basic requirements), and it clearly stated that the safety and performance must meet 65 basic requirements in the whole life cycle of medical devices.
The implementation of 65 basic requirements through EP checklist is a recognized method. EP checklist is mainly composed of three parts, the first is the basic requirement, the second is the method that demonstrates it is in compliance with the basic requirements; the third is the evidence that demonstrates it is in compliance with the basic requirements, too. By organizing requirement, methods and evidence together, we can have the relevant documents to form the basis for systematic evaluation.
2 Investigation of EP checklist preparation
We still have no experience on how to prepare EP checklist in China (there is no experience to follow in our country for preparing EP checklist until now), the research team organized relevant departments and persons to study the essential principles of safety and performance of medical devices.
Research program includes the eligibility criteria, the number of surveys and the statistical indicators.
Criteria for the design are as follows: (1) based on product’s risk classification, the second class and the third class products are selected; (2) based on product’s energy classification, active products and passive products are selected; (3) based on product’s economic scale, product with annual revenue over billions of dollars and product with no more than billions are selected; (4) based on product’s region, developed regions such as Beijing and medium-developed regions such as Liaoning are selected.
The number of investigations is designed as follows: according to four criteria aspects, two samples are selected for each aspect and the total of 2x2x2x2 =24= 16 samples are selected. In order to avoid the lost survey, two samples are added to it, therefore, there are a total of 18 samples.
Statistical indicators mainly have three aspects: ① the percentage of products in accordance with the preparation requirements; ②the percentage of evidence for applicable products according to EP checklist requirements; ③ the main project of the evidence in the registration dossier.
According to the above criteria, the inventory survey of 18 products was completed. The category of product is shown in Table 1; the economy and regional conditions of product are shown in Table 2.
Table 1 Category of products
Active products Non-active products Products of Class Ⅱ Ultrasonic diagnostic device Zirconium oxide porcelain pieces X-ray diagnosis device Medical surgical protective dressings Medical atomizer Products of Class Ⅲ Computed tomography (CT) Intravascular stent Cardiac pacemaker Intrauterine device
Table 2 Products economy and regional situation
Products of developed region Products of medium-developed region Output value more than 1 $billion 6 4 Output value less than 1 $billion 4 4
According to the requirements, the inventory survey of 18 products is completed. The completion rate is 100% and all products fulfill the requirement. All submitted evidences are in application material and quality management system documents. The results are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Investigation results
Active productsNon-active products Completed EP checklist108 The applicable requirements4034 Corresponding evidence requirements in the registration application documentation3831 The percentage of evidence in the registration application documentation (%)9591
The results show that the requirements for application documentation include: physical, chemical and biological properties; environmental characteristics; protection against device risk, mechanical risk and radiation risk; products with diagnostic or measuring function; protection for non-professional users; risks from providing energy or matter for patients; medical devices with software or independent software; instructions and labels; requirements for clinical evaluation.
Based on the above research results we can make the following conclusions: (1) to prepare EP checklist is feasible in China and the time required depends on corporate research foundation which in general takes 2 to 5 days; (2) the content of EP checklist requirements should be reflected 90% in the registration data, the approved document for safety and effectiveness usually embodies in risk management reports, research materials, registration inspection reports, clinical evaluation data, instruction and labels; (3) the content of EP checklist requirements which is not in the registration documentation usually include the safety and effectiveness of product in its life cycle, the safety and effectiveness of product under certain conditions, requirements for purifying environment, report of specific risk control measures and verification reports, etc.
The purpose of the study is to fill out EP checklist. Based on the results of the study, the author compiled “introduction on completing EP checklist” to pave the way for filling the content in. The essential principles of safety and effectiveness of medical devices can be proved with following methods: (1) To get the published regulations from medical device department, regulatory documents, registration review guidance and other normative documents. (2) To get the medical device-related national standards, industry standards and international standards. (3) To get the generally accepted testing methods. (4) To get methods which meet the need of corporate. (5) To compare with the similar products which have been approved. (6) Clinical confirmation.
There are three conditions which can demonstrate the evidences provided are in compliance with the basic requirements: (1) Files in the product registration application documentation should explain their specific application serial numbers as well as their exact location. For example, the registration inspection report (medical electrical safety: protective part against the mechanical risks); Manual Chapter 4.2; (2) If the information is not included in the product registration application documentation, then it would not be provided, but it shall indicate the evidence file name and its quality management system number for future reference, such as the inspection report on workshop purification (quality management system file number); (3) If the measures and results of the risk control are reflected in the risk management report and the validation evidences are presented in the quality management system documentation, then the evidence file name and system numbers should be indicated (such as Risk Management Report 5-1 “Software Compatibility Assessment Data” (Quality Management System File Number)).
3 The role of EP checklist in the registration application for medical devices
“Medical Device Registration and Filing Management Measures (Draft)” required that the applicant should be liable for the product. Therefore, the applicant should comply with the basic requirements of safety and effectiveness for medical devices in the development and production of product. Now most of the applicants do not know what they should do to ensure the safety and effectiveness, which result in a lot of defects. EP checklist can help the applicant clarify his work to ensure product safety and effectiveness, which will comprehensively reduce product risk and improve the level of the entire industry. Before submitting registration application documentation, filling out EP checklist will truly reflect the applicant must be responsible for product safety and effectiveness.
EP checklist is the core file of registration documentation and its important roles are as follows. First, EP checklist can guide reviewers to evaluate product safety and effectiveness scientifically. Second, EP checklist can provide the logical directory to ensure the systematic review.
The revised registration application documentation, non-clinical evidence (product research materials, product technical requirements, product inspection reports, risk management reports, manufacturing information, etc.) and clinical evidences (clinical evaluation data) are corresponding to EP checklist settings, which ensure the registration application documentation scientifically and to provide the basis for registration review work.
Compared with other countries, the main difference for China’s medical device registration is the classification review mode. 32 registration and examination institutions have had two problems for a long time. First, the censors are poorly organized with many new reviewers. As a guiding tool, EP checklist can help reviewers quickly grasp what safety and effectiveness are and how to review systematically. Second, it is difficult to unify the standards for various institutions. One of the main reasons is the lack of a unified examination requirements or guidelines. In recent years, China Food and Drug Administration issued the product guidance to achieve a good result. EP checklist can be regarded as the guidelines for the preparation of guiding principles, and it is of significance for the implementation of registration review.
EP checklist has been widely used for medical device supervision in developed countries. The United States, European Union, Japan, Canada, Australia and other countries have adopted EP checklist as the application documentation. As the first annex of EU directives, EP checklist has played an important role in guiding the industry to design and produce effectively for more than 10 years as well as guiding the certification bodies to evaluate the product.
China has joined IMDRF and it is necessary to meet its basic requirements. It has a long-term significance for China to improve the supervision level and keep in line with international management.
4 Suggestions on applying EP checklist to the registration review
Through the above studies, “the Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices” has explained what safety and effectiveness of the products is. “EP checklist” provides a method of conducting the review systematically. Combined with China's actual situation, EP checklist is recommended to be used in the future registration review.
Currently, the issue of EP checklist is “whether we need it and review it”. Study shows that EP checklist is helpful to improve the level of product safety and effectiveness for enterprises, which can promote the implementation of enterprises as the first responsible person. In addition, EP checklist can guide the reviewers to evaluate the product and ensure a systematic review. EP checklist does not need to have a substantive review; registration application documentation should be focused on and if some information is not in the application document, it will be marked in the EP checklist.
With reference to the international experience, the formation of registration documents should include EP checklist as the core of the registration and other materials. It can be roughly divided into three levels. The first level is EP checklist which has played an important role in framing. The second level is the technical documentation requirements according to the key point categories, and the third level is the detailed documentation requirements, as shown in Figure 1.
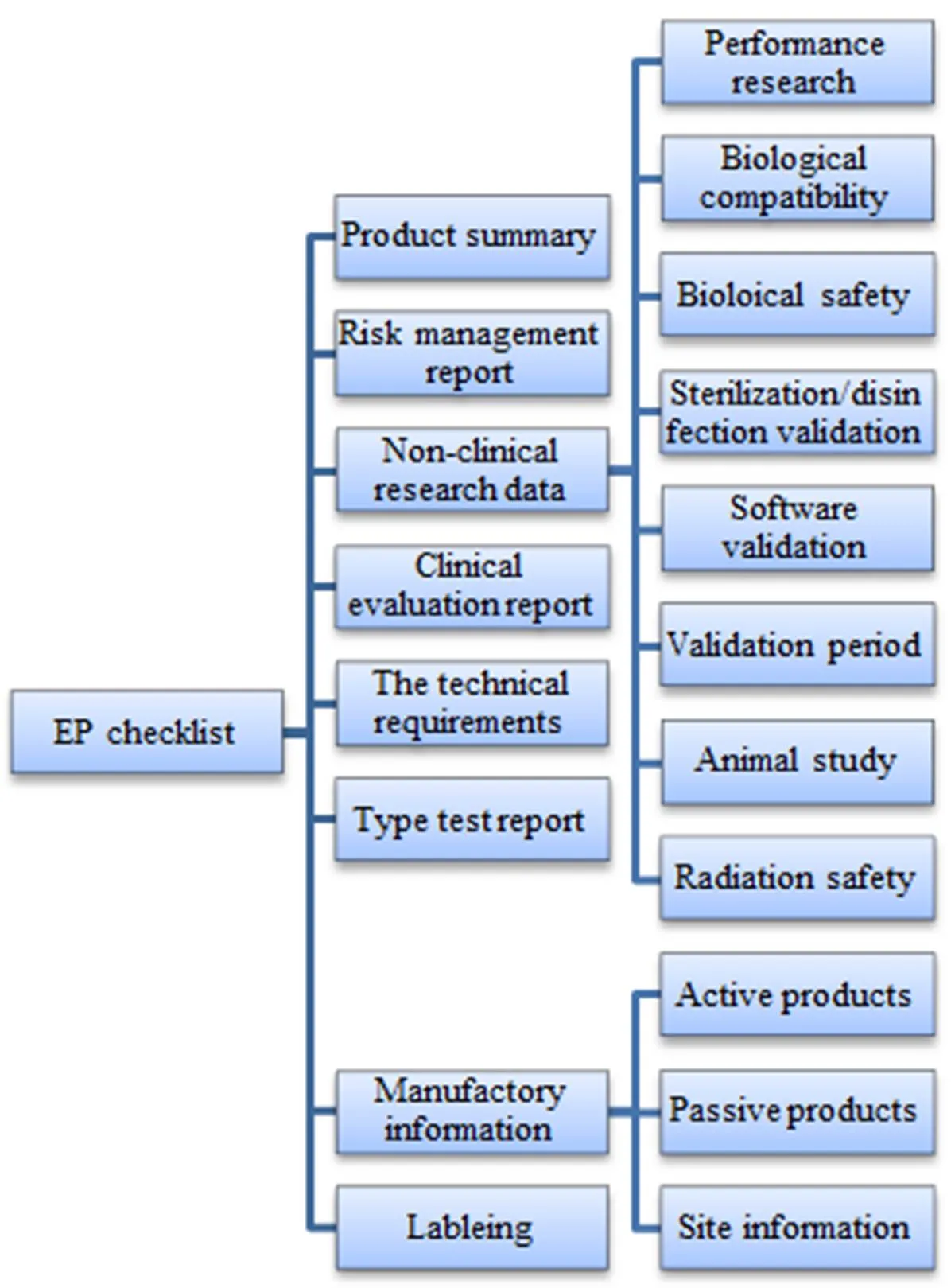
Figure 1 Hierarchy diagram of registration review with EP checklist as core element
Medical devices registration is to get an administrative license which should follow the principle of permission combined with supervision[4]. As to the problems from on-site verification, one is the inconsistency of the registration application document with the real condition. But the administration department does not supervise properly; the other is the lack of registration information support from administration department for the applicant’s on-site inspection, which results in the lack of targeted on-site inspections risk.
Through the study of EP checklist, we found that 5% to 20% of the required evidences are not contained in the registration application document, but they should be kept in the quality management system documents. Therefore, EP checklist can be applied to the on-site inspection to further verify the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. At the same time, the inspectors should carry the registration application documents and EP checklist to participate in the on-site inspection which can both help them get necessary information support and check the consistence and authenticity of the documents.
In the process of investigation, we found that some of the production enterprises, especially enterprises without global market, misunderstand the relationship between the article 65 requirements of EP checklist and product features, and they need further guidance. To develop guidelines document is an effective measure for the production enterprises apply EP checklist. FDA has set more than 800 guiding principles, and China has also published 115 guiding principles from 2006 to now[5]. The guidance of EP checklist should include at least three aspects: instructions of the basic requirements for safety and effectiveness of medical devices; the explanation and example of 65 specific requirements; paradigm of EP checklist for each kind of representative medical device.
There are about 300 review centers in China including the China Food and Drug Administration review center, provincial review centers and municipal review centers. The level of evaluation is different among them. Although EP checklist has been in use in the developed countries for years, most reviewers for EP checklist in China have not yet fully understood it. Therefore, we should focus on training so that the system staff and the industry personnel can understand the role of EP checklist. Then they can correctly apply EP checklist to assessing the safety and effectiveness of each medical device.
The starting point of risk management of medical device is to analyze the product risk. Based on analysis of risk, the measures taken by production enterprises are used to control the risk in the process of design and production[6]. Similarly, the design of EP checklist also follows the principle of risk, the second requirement of EP checklist is to ensure that each hazardous residual risk is acceptable.
(1) To identify the known or predictable hazards, and evaluate risk for intended use or improper use.
(2) To eliminate the risk in the process of design and production as much as possible.
(3) To use protective measures as much as possible to reduce residual risk.
(4) To inform the residual risk.
There are differences between EP checklist and risk management. The risk assessment of EP checklist includes 12 aspects, such as chemical, physical and biological properties, infection and microbiological contamination, environmental characteristics. Medical device risk management should follow the standard of YY/T0316 “Medical Device Risk Management for Medical Device Applications”, risk assessment of the product includes eight aspects, such as electrical hazards, biological hazards and mechanical hazards. Therefore, it is necessary to further study the relationship between EP checklist and risk management so that the common principles and differences can be fully understood. EP checklist will be better applied to enterprise risk management activities, rather than an isolated requirement.
[1] LI Fei, YUAN Peng. The Application to GHTF Essential Principles of Safety and Performance for the Medical Devices Conformity Assessment in China [J]. China Medical Device Information, 2013, 18 (4): 1-8.
[2] GHTF. Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices [EB/OL]. http://www.imdrf.org, 2012-11-02.
[3] GHTF. Summary Technical Documentation for Demonstrating Conformity to the Essential Principles of Safety and Performance of Medical Devices (STED) [EB/OL]. http://www.imdrf.org, 2008-02-21.
[4] YING Song-nian, YANG Xie-jun. The Theory and Systematic Interpretation of the Administrative Permit Law [M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2004: 90-112.
[5] YUAN Peng, LI Fei. Study on the New Submission Documents for Medical Device Registration [J]. China Medical Information, 2014, 19 (12): 5-8.
[6] XU Yan-ruo.A Theory on Systematicness of Medical Devices Evaluation (Registration Technical Review) [J]. China Medical Information, 2011, 17 (6): 46-48.
Author’s information: BI Kai-shun, Professor. Major research area: National drug system. Tel:024-23986012, E-mail: bikaishun@126.com

