谷氨酰胺对梗阻性黄疸大鼠小肠黏膜组织Akt活性的影响
尚海涛,李忠廉,张西波(天津医科大学,天津30000;天津市南开医院)
谷氨酰胺对梗阻性黄疸大鼠小肠黏膜组织Akt活性的影响
尚海涛1,李忠廉2,张西波2
(1天津医科大学,天津300100;2天津市南开医院)
摘要:目的观察梗阻性黄疸大鼠小肠组织中蛋白激酶B(Akt)活性,探讨谷氨酰胺肠保护的作用机制。方法将64只SD大鼠随机分为4组各16只,模型组、甘氨酸组、谷氨酰胺组行梗阻性黄疸造模,假手术组游离上段胆总管后关腹;造模后1d,甘氨酸组、谷氨酰胺组均给予同等热量的肠内营养剂灌胃,同时分别给予甘氨酸、谷氨酰胺1 g/(kg·d),模型组、假手术组给予等量生理盐水灌胃。各组分别于术后第3、7天处死大鼠8只,采用Western blotting法检测小肠组织Akt总蛋白及p-Akt,实时PCR检测肠组织AktmRNA。结果与假手术组比较,模型组、甘氨酸组、谷氨酰胺组术后第3、7天小肠组织中AktmRNA及p-Akt蛋白增加,且谷氨酰胺组高于模型组、甘氨酸组,P均<0.05;模型组、甘氨酸组间比较,P均>0.05。各组小肠组织Akt总蛋白比较,P均>0.05。结论谷氨酰胺通过促进Akt信号通路的活化,发挥对小肠上皮细胞的保护作用。
关键词:梗阻性黄疸;小肠黏膜;谷氨酰胺;蛋白激酶B;肠内营养;大鼠
Effect of glutamine on Akt activity in small intestinemucosa of rats with obstructive jaundice
SHANG Hai-tao1,LI Zhong-lian,ZHANG Xi-bo
(1 Tianjinmedical University,Tianjin 300100,China)
Abstract:Objective To observe the activity changes of protein kinase B(Akt)in the small intestine of rats with obstructive jaundice,and to investigate themechanism of glutamine in intestinal protection.Methods Sixty-four SD rats were randomlydivided into four groups,16 rats in each group.The obstructive jaundicemodels weremade in the groups A,B and C.After freeing the upper common bileduct and then we closed the abdomen of rats in the groupd.Oneday aftermodeling,rats in the groups B and C were given the same amount of heat enteral nutrition by gavage,and at the same time,the glycine and glutamine 1 g/(kg·d)was added.Rats in the groups A andd were given the same volume of normal saline by gavage.Eight rats were sacrificed atday 3 and 7 after surgery.Western blotting was used todetect the small intestine tissue’s total protein of Akt and p-Akt,RT-PCRmethod was used todetect AktmRNA of intestine tissue.Results Compare with groupd,the AktmRNA and p-Akt protein was increased atday 3 and 7 after surgery in the groups A,B and C,and group C was higher than groups A and B(all P<0.05).No significantdifference was found between group A and group B(all P>0.05).No significantdifference was found in Akt total protein of small intestine among these groups(all P>0.05).Conclusion The glutamine protects the epithelial cells of small intestine by promoting the activation of Akt signaling pathway.
Key words:obstructive jaundice; small intestinemucosa; glutamine; protein kinase B; enteral nutrition; rats
研究表明,梗阻性黄疸可致肠黏膜屏障功能障碍,继而引起肠道细菌易位[1],从而发生肠源性内毒素血症[2]。谷氨酰胺可维护肠黏膜的正常结构和功能[3],但其具体保护机制尚不完全清楚。2014 年4~12月,我们观察了早期肠内补充谷氨酰胺对梗阻性黄疸大鼠小肠组织蛋白激酶B(Akt)活性的影响,现分析结果并探讨其肠保护的作用机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料成年雄性SD大鼠64只,体质量250~280 g,由天津市中西医结合急腹症研究所动物研究
中心提供;谷氨酰胺(安凯舒,重庆药友医药有限公司),肠内营养混悬液(能全力,Nutricia公司),甘氨酸(Sigma公司);低温台式高速离心机(Eppendorf 5415R,Germany),蛋白电泳槽、蛋白转膜系统(Bio-Rad,USA),BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(Pierce Rockford,USA);兔抗大鼠Akt抗体、兔抗大鼠p-Akt抗体(Cell Signaling Tech,USA),HRP标记羊抗兔二抗(中杉金桥生物技术有限公司,北京)。
1.2模型制作及干预将64只大鼠随机分为四组各16只,模型组、甘氨酸组、谷氨酰胺组按张西波等[4]的方法制作梗阻性黄疸模型,假手术组游离上段胆总管后关腹。造模后1天,甘氨酸组、谷氨酰胺组均给予同等热量的能全力灌胃,同时分别给予甘氨酸、谷氨酰胺1 g/(kg·d)。每日总热量731.5 kJ/kg[5],分3~5次给予,期间自由饮水。模型组、假手术组给予等量生理盐水灌胃。各组于术后第3、7天,分别处死大鼠8只;取末段回肠4 cm,液氮速冻,-80℃冰箱储存。
1.3小肠组织Akt总蛋白及p-Akt蛋白检测采用Western blotting法。取小肠组织70mg,按说明书进行蛋白定量,SDS-PAGE垂直凝胶电泳,电转移至PVDF膜; TBS室温封闭洗膜后加Akt一抗、二抗处理,ECL化学发光试剂盒曝光显影,以GAPDH作为对照。用BOI-RAD Chemodoc XRS凝胶成像系统及Image J v1.42图像分析软件进行灰度分析,以目的蛋白与对照蛋白条带灰度比值表示目的蛋白表达量。
1.4小肠组织AktmRNA检测采用实时PCR法。用TaKaRa公司提供的试剂提取RNA,转录为cDNA后进行PCR反应。采用SYBR GreenⅠ荧光染料嵌合法,分别扩增目的基因Akt和管家基因βactin,通过比较目的基因和管家基因进行定量。Akt上游引物5'-GAGGTTGCCCACACGCTTA-3',下游引物5'-GGCGTACTCCATGACAAAGCAG-3';β-actin上游引物5'-GGAGATTACTGCCCTGGCTCCTA-3',下游引物5'-GACTCATCGTACTCCTGCTTGCTG-3'。反应条件: 95℃5min; 95℃30 s,60℃1min,共45个循环; 60~95℃10 s,退火温度为60℃。PCR产物经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,用凝胶成像系统和Quantity one软件进行图像分析。计算Akt与β-actin灰度比值,以此表示其mRNA相对表达量[6]。
1.5统计学方法采用SPSS17.0统计软件。计量资料以珋x±s表示,各组间比较用单因素方差分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1小肠组织Akt总蛋白及p-Akt蛋白表达各组小肠组织Akt总蛋白及p-Akt蛋白比较见表1。2.2小肠组织AktmRNA相对表达各组小肠组织AktmRNA相对表达比较见表2。
表1 各组小肠组织Akt总蛋白及p-Akt蛋白表达比较(n =8,)
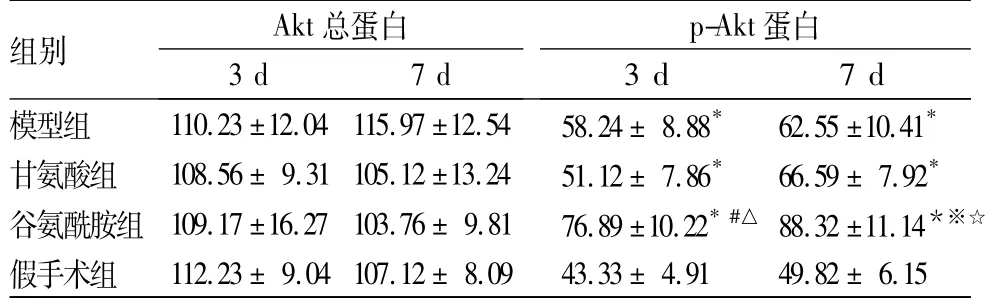
表1 各组小肠组织Akt总蛋白及p-Akt蛋白表达比较(n =8,)
注:与假手术组比较,*P<0.05;与模型组比较,#P<0.05,※P <0.01;与甘氨酸组比较,△P<0.05,☆P<0.01。
组别 Akt总蛋白p-Akt 蛋白3d 7d3d 7d模型组 110.23±12.04 115.97±12.54 58.24±8.88* 62.55±10.41*甘氨酸组 108.56±9.31 105.12±13.24 51.12±7.86* 66.59±7.92*谷氨酰胺组 109.17±16.27 103.76±9.81 76.89±10.22* #△88.32±11.14*※☆假手术组 112.23±9.04 107.12±8.09 43.33±4.91 49.82±6.15
表2 各组小肠组织AktmRNA相对表达量比较(n =8,)

表2 各组小肠组织AktmRNA相对表达量比较(n =8,)
注:与假手术组比较,*P<0.05;与模型组比较,#P<0.05;与甘氨酸组比较,△P<0.05。
组别AktmRNA 3d 7d模型组 3.75±0.11* 3.67±0.03*甘氨酸组 4.56±0.09* 4.98±0.13* #谷氨酰胺组 6.16±0.15* #△ 6.62±0.09* #△假手术组1.45±0.07 1.52±0.11
3 讨论
Akt信号转导通路作为细胞的主要存活通路,参与肠上皮细胞的增殖。既往研究表明,Akt是激活NF-κB的上游分子,而NF-κB是LPS所介导的信号转导通路中最重要的下游通路,活化的NF-κB可诱导多种炎症介质的表达[7]。
谷氨酰胺是血液循环和组织中含量最丰富的一种氨基酸[8],是肠黏膜增生的细胞的主要能量来源[9]。既往研究表明,谷氨酰胺可从保护肠黏膜屏障、调节肠免疫功能以及抗氧化等方面起到肠保护作用[10];适当剂量谷氨酰胺肠内营养,可加快肠上皮细胞增值,抑制肠上皮细胞凋亡,阻止肠黏膜萎缩及炎症所致的通透性增加。研究发现,梗阻性黄疸发生时p-Akt蛋白表达水平增高,考虑为梗阻性黄疸后的应激反应[11]。本研究显示,谷氨酰胺组小肠组织AktmRNA及p-Akt蛋白增高较A、甘氨酸组更明显。推断谷氨酰胺是通过激活Akt信号途径后,从而引活其下游分子而发挥肠保护作用。研究证实,谷氨酰胺不仅是蛋白质合成的底物,还是促进mRNA翻译和蛋白质合成的调节因子[12];mori等[13]发现,危重患者早期感染状态下应用谷氨酰胺,即可促进蛋白质合成;术后给予富含谷氨酰胺二肽的全胃肠外营养后第3天可以显著抑制其累计氮平衡[14]。在脓毒症、全胃切除术及烧伤患者等的研究中发现,给予谷氨酰胺后可显著抑制血浆中前白蛋白和转铁蛋白的下降[15]。由此可见,谷氨酰胺不
但能促进蛋白质合成,还可抑制蛋白质降解。
综上所述,谷氨酰胺可通过活化梗阻性黄疸时小肠Akt信号通路,促进肠上皮细胞增殖,修复肠黏膜,保护肠屏障功能。
参考文献:
[1]Assimakopoulos SF,Tsamandas AC,Louvros E,et al.Intestinal epithelial cell proliferation,apoptosis and expression of tight junction proteins in patients with obstructive jaundice[J].Eur J Clin Invest,2011,41(2): 117-125.
[2]Chen J,Dong JT,Li XJ,et al.Glucagon-like peptide-2 protects impaired intestinalmucosal barriers in obstructive jaundice rats [J].World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(2): 484-490.
[3]Noth R,Hsler R,Stüber E,et al.Oral glutamine supplementation improves intestinal permeabilitydysfunction in amurine acute graft-vs.-hostdiseasemodel[J].Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2013,304(7): 646-654.
[4]张西波,段启龙,李忠廉,等.急性胆道梗阻大鼠肝脏iNOS的表达及意义[J].山东医药,2013,53(29): 19-24.
[5]Zhaod,Letterman J,Schreiber BM.beta-Migrating very lowdensity lipoprotein(beta VLDL)activates smoothmuscle cellmitogen-activated protein(MAP)kinase via G protein-coupled receptor-mediated transactivation of the epidermal growth factor(EGF)receptor: effect ofmAP kinase activation on beta VLDL plus EGF-induced cell proliferation[J].J Biol Chem,2001,276(33):30579-30588.
[6]王思,曹旭,刘冬妍.新生大鼠高氧动物模型肠道Akt的变化[J].中国医科大学学报,2013,42(7): 577-581.
[7]Abarikwu SO.Anti-inflammatory effects of kolavironmodulate the expressions of inflammatorymarker genes,inhibit transcription factors ERK1/2,p-JNK,NF-κB,and activate Akt expressions in the 93RS2 Sertoli cell lines[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2015,401(1-2): 197-208.
[8]刘秀香,郭金将,赵国英,等.谷氨酰胺对高氧肺损伤的干预效果观察[J].山东医药,2011,51(18): 7-9.
[9]Xu CL,Sun R,Qiao XJ,et al.Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment[J].World J Gastroenterol,2014,20(16): 4662-4674.
[10]Shu XL,Yu TT,Zhong JX,et al.Effect of glutamine on intestinal barrier function following liver transplantation in rats[J].Eur Revmed Pharmacol Sci,2014,18(14): 2058-2064.
[11]Liu Z,Jahn LA,Wei L,et al.Amino acids stimulate translation initiation and protein synthesis through an Akt-independent pathway in human skeletalmuscle[J].J Clin Endocrinolmetab,2002,87(12): 5553-5558.
[12]Jefferson LS,Kimball SR.Amino acids as regulators of gene expression at the level ofmRNA translation[J].J Nutr,2003,133(6): 2046-2051.
[13]Morim,Rooyackers O,Smedbergm,et al.Endogenous glutamine production in critically ill patients: the effect of exogenous glutamine supplementation[J].Crit Care,2014,18(2): 72.
[14]Tsai JJ,Kuo HC,Lee KF,et al.Glycyrrhizin represses total parenteral nutrition-associated acute liver injury in rats by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress[J].Int Jmol Sci,2013,14(6): 12563-12580.
[15]Cunha HF,Rocha EE,Hissam.Protein requirements,morbidity andmortality in critically ill patients: fundamentals and applications[J].Rev Bras Ter Intensiva,2013,25(1): 49-55.
·基础研究·
收稿日期:( 2015-03-12)
通信作者简介:李忠廉(1963-),男,主任医师,博士研究生导师,主要研究方向为肝脏、胆道、胰腺等腹部疾病的临床与基础工作。E-mail: nkyylzl@163.com
作者简介:第一尚海涛(1978-),男,硕士研究生,主要研究方向为各种胆道、胰腺疾病的治疗和临床研究。E-mail: nkyysht@126.com
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(81273952)。
文章编号:1002-266X(2015)36-0021-03
文献标志码:A
中图分类号:R657.4
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.36.007

