Application Effects of Photosynthesis Synergist in Early Hybrid Rice
You XU,Xuehua WANG*,Qisheng QIU,Bin SHEN
1.College of Agronomy,Hunan Agricultural University,Changsha 410128,China;
2.Hengyang Bureau of Agriculture,Hengyang 421200,China;
3.Hunan Benzhi Biotechnology Co.,Ltd,Changsha 410011,China
Responsible editor:Xiaoxue WANG Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
Photosynthesis lays foundation for growth and development of early hybrid rice and yield formation,as well as a factor deciding productivity[1].Yield of early hybrid rice,co-contributed by yield components,is decided by Photosynthetic material production capacity and operation and distribution of photosynthetic assimilation products[2].The process of early hybrid rice yielding is actually a process of accumulation and distribution of dry matters,and 90%-95% of the increases of dry matter are from photosynthesis of leaf[3].What’s more,any physiological metabolism,which improves photosynthetic efficiency of rice groups and net photosynthetic rate of leaf area per unit area,extending leaf photosynthetic period,accelerating transportation and distribution of photosynthate,and increasing storage of starch,would all enhance rice yield[4-5].
Currently,highly-qualified early hybrid rice applied in production performs not so satisfied in some areas in terms of yield,disease or lodging resistance,due to climate,soil and management differences[6].It is key for stabilization and improvement of total yield of early hybrid rice to increase yield per unit area,which can be accomplished by enhancing photosynthetic capacity and efficiency for solar energy utilization."Yezhiyuan",a photosynthesis synergist developed by Hunan Benzhi Biotechnology Co.Ltd.,proves well in improving the content of chlorophyll in functional leaf and photosynthetic rate,reducing transpiration rate,and increasing yield per unit area[7-9].In order to further demonstrate the effects of Yezhiyuyan in early hybrid rice in Hunan,a test was conducted in farmlands in Yunyuan Teaching and Testing Base of Hunan Agricultural University and Meihua Village,Xidu Town,Hengyang County,National Crop Yielding S&T Engineering Demonstration,which provides references for extension of Yezhiyuan in other areas.
Materials and Methods
Materials
The test was conducted in farmlands in Yunyuan Teaching and Testing Base of Hunan Agricultural University and Meihua Village,Xidu Town,Hengyang County,National Crop Yielding S&T Engineering Demonstration.In Hunan Agricultural University,the test material was Lingliangyou No.211,and test material was Lingliangyou No.268 in Hengyang.Both test materials were provided by Longping Seed,and Yezhiyuan was supplied by Hunan Benzhi Biotechnology Co.Ltd.
Methods
Test designThe test was conducted in experimental sites in Hunan Agricultural University and Hengyang,respectively,with two treatments.Specifically,treatment 1 involved Yezhiyuan of 450 g/hm2(×1 000) and treatment 2 was a control(CK).The test was conducted as per randomized block design,with three repetitions,and the test region totaled 13.3 m2.At first,rice in the test plots were sprayed in the end of tillering stage in treatment 1 and rice in treatment 2 was not sprayed.Subsequently,seedlings were sprayed at 16:00 in a sunny day and rice should be covered with films,avoiding spraying to other test plots.On March 30,2012,seeds were sown and transplanted on May 2 at 16.7 cm×20 cm.On June 15,Yezhiyuan was sprayed and transplanting should be conducted in a field with shallow water.Other preventions of disease and insect damages were conducted as per local highly-qualified fields.
Measured itemsThe number of tiller was surveyed once every 3 d after turning green to record basic seedlings; photosynthetic rate and transpiration rate were measured on June 30 with photosynthesis equipment (LI6400) of two leaves in every test plot to get an average; the content of chlorophyll of the 1stleaf in upper part was measured on July 8 with a portable chlorophyll instrument(HK/SPAD-502Plus) and the leaves with similar values were averaged; in ripening stage,the number of productive ear in surveyed areas was measured and rice samples were collected from 5 holes in every test plot to explore seeds and compute theoretical yield; rice was harvested in different test plots to measure practical yield.
Data processingThe test data were settled and analyzed with Excel and DPS.
Results and Analysis
Photosynthetic rate
As shown in Table1,photosynthetic rate of flag-leaf reached 16.96 μmol/(m2·s) in treatment 1 in Hunan Agricultural University,which was significantly higher than that of control; in Hengyang,the photosynthetic rate reached 14.34 μmol/(m2·s),accordingly,which was also higher compared with control.It is obvious that Yezhiyuan would improve photosynthetic rate in the same term.
Transpiration rate
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant,accelerating transportation rate of inorganic salt to ground parts and reducing plant temperature,which prevents leaves from hurt by photosynthesis.Nevertheless,self-grown green plants have to exchange gases with surroundings at photosynthesis,so that water in plants would lose upon water potential gradient.Hence,it is necessary to inhibit transpiration properly and reduce water consumption to promote plant growth.As shown in Table2,in the experimental site in Hunan Agricultural University,transpiration rate of flag-leaf was 8.73 g/(m2·h),which was lower compared with control group,showing little differences.In Hengyang experimental site,the transpiration rate of flag-leaf reached 9.77 g/(m2·h),which was lower than that of control,showing insignificant differences.In the two sites,although the differences between treatments were not so significant,transpiration rate in the treatment sprayed with Yezhiyuan kept declining,suggesting that Yezhiyuan would reduce transpiration rate of early hybrid rice in the same term.
The content of chlorophyll
The content and components of chlorophyll have significant effects on photosynthesis and high content of chlorophyll relies on photosynthesis of leaf in later stage.Therefore,a highcontent of chlorophyll in later period would enhance rice yield.As shown in Table3,the content of chlorophyll in experimental site in Hunan Agricultural University was 44.57,which was higher than that of control,showing significant differences.In Hengyang experimental site,in contrast,the content of chlorophyll reached 42.59,which was higher compared with control,also showing significant differences.It can be concluded that Yezhiyuan would increase the content of chlorophyll of early hybrid rice in the same term.

Table1 The effect of Yezhiyuan photosynthesis synergist on photosynthetic rate μmol/m2·s

Table2 The effects of Yezhiyuan photosynthesis synergist on transpiration rate g/m2·h
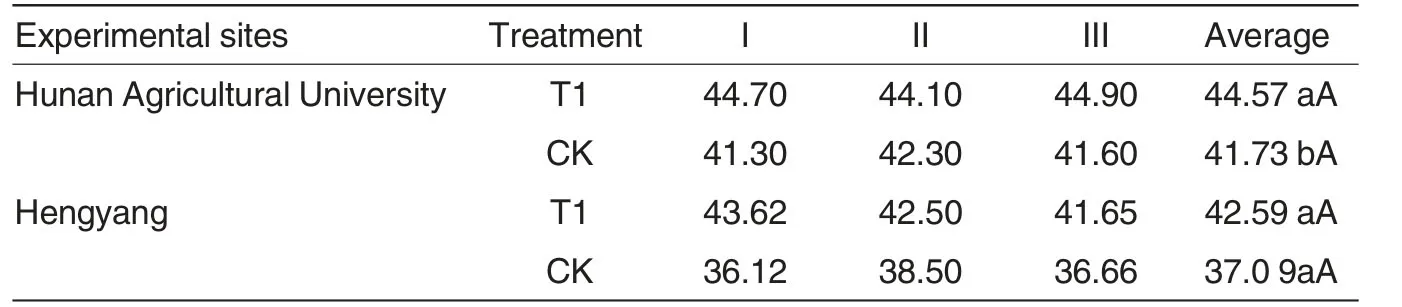
Table3 The effect of Yezhiyuan photosynthesis synergist on SPAD
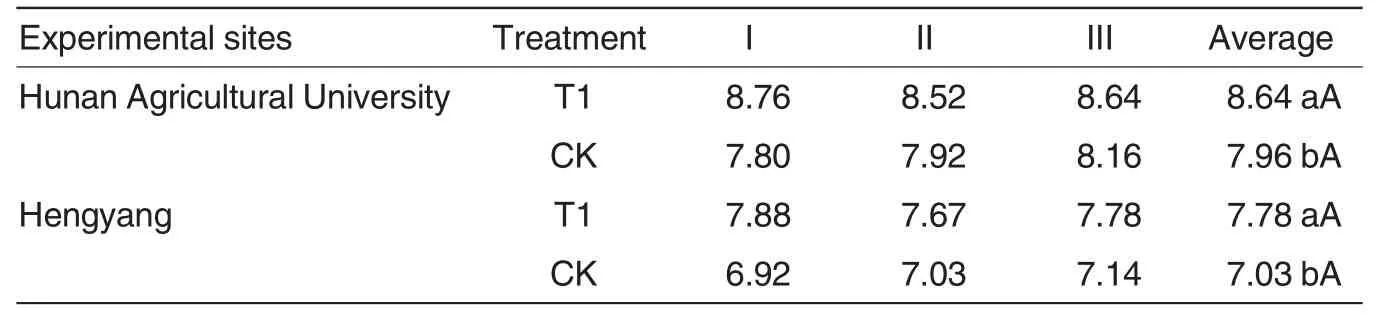
Table4 The effect of Yezhiyuan photosynthesis synergist on yield per unit area kg
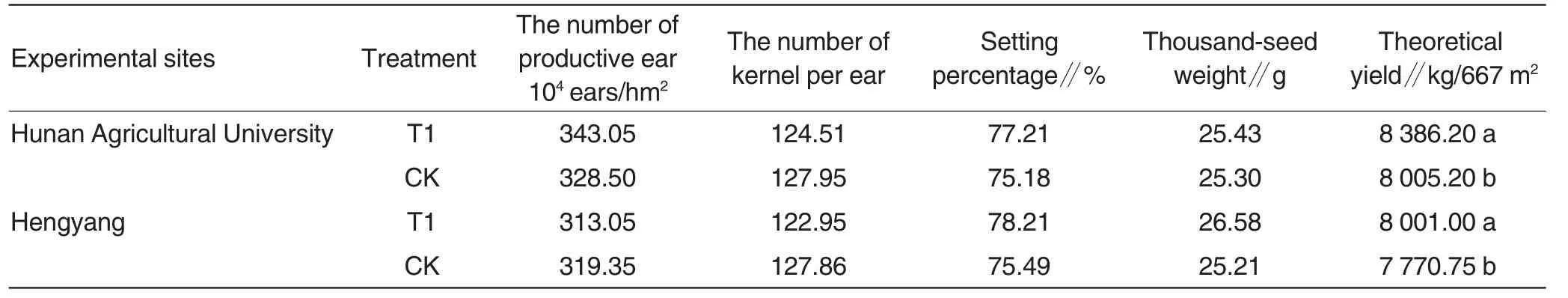
Table5 The effect of Yezhiyuan photosynthesis synergist on rice theoretical yield and its influence factors
Yield
In treatment 1 in Hunan Agricultural University,rice yiled was 8.64 kg,which was 8.54% higher compared with control group,showing significant differences.In contrast,in treatment 1 in Hengyang experimental site,rice yield was 7.78 kg,which was 10.67%higher compared with control,showing significant differences.It can be concluded that Yezhiyuan would increase yield of early hybrid rice in the same term(Table4).
Yield component factors
The yield of early hybrid rice is determined by the number of ear per unit area,the number of kernel per ear,setting percentage and thousandseed weight.It can be concluded from Table5 that after application of Yezhiyuan,both of setting percentage and thousand-seed weight increased,and theoretical yield grew considerably.Furthermore,the theoretical yield in Hunan Agricultural University increased by 4.76% in Hunan Agricultural University compared with control and 2.96% in Hengyang experimental site.
Conclusions and Discussions
The test showed that with Yezhiyuan applied in the end of tillering stage,photosynthetic rate and yield of Lingliangyou No.211 and Lingliangyou No.268 were both higher compared with control group,which indicated that Yezhiyuan would improve photosynthetic rate and yield.Meanwhile,considering from SPAD,it can be concluded that Yezhiyuan would increase the relative content of early hybrid rice,possibly caused by the reduced degradation rate of chlorophyll and extended photosynthesis after Yezhiyuan was applied,which actually provides abundant photosynthate and is conductive to growth of early hybrid rice.However,the application effect of Yezhiyuan is definitely under influence of climate,soil fertility,and crop variety.In future,therefore,further attention should be paid to application term,concentration,and times of Yezhiyuan in order to precisely understand the work mechanism and provide more accurate references for its application.
[1]PAN RC (潘瑞炽).Plant physiology(the 5th edition)(植物生理学 (第五版))[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press (北京:高等教育出版社),2005.
[2]LV J(吕 军),WANG BL(王伯伦),MENG WR (孟维韧),et al.The characteristics of photosynthesis and dry matter production in japonica rice cultivars with different type panicles (不同穗型粳稻的光合作用与物质生产特性)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学),2007,(5):902-908.
[3]WANG W(王 卫),XIE XL(谢小立),XIE YH (谢永宏).Key factors of high yields of early hybrid rice and its mechanism(杂交早稻高产的关键因子及其作用机理)[J].Hunan Agricultural Sciences (湖南农业科学),2010,(5):42-46,49.
[4]GAO Y(高 宇),TIAN T(田 恬).Research progress on physiological breeding of super-high yielding early hybrid rice (超高产杂交早稻生理育种研究进展)[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin(中国农学通报),2004,(3):1-3.
[5]WANG SX(王少先),PENG KQ(彭克勤),XIAO LT(萧浪涛),et al.The application and mechanism of synergist for early hybrid rice(杂交早稻专用配方肥增效剂的应用及其作用机理研究)[J].Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science (植物营养与肥料学报),2003,(3):294-298.
[6]NIU ZG(牛兆国).Production and development strategies of highly-qualified early hybrid rice in China(我国优质杂交早稻生产现状及发展对策)[J].Modern Agricultural Science and Technology(现代农业科技),2010,(23):343-344,347.
[7]WANG BF (汪本福),HUANG JP (黄金鹏),JIANG S (姜 仕),et al.Effect of“Yezhiyuan” photosynthesis biological synergist applied on rice(作用生物增效剂在杂交早稻上的应用效果研究)[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences(湖北农业科学),2012,(11):2180-2183.
[8]MEI ZD(梅正鼎),LI RL(李瑞莲),HE YX(贺云新),et al.Influences of photosynthesis biological synergist on growth,yield and quality of cotton(光合作用生物增效剂对棉花生长及产质量的影响)[J].Hunan Agricultural Sciences (湖南农业科学),2012,(19):34-36.
[9]LU CD(卢成达),GUO ZL(郭志利),Li Y(李 阳),et al.Application effects of two photosynthesis synergists on millets(两种光合增效剂在谷子上的应用效果研究)[J].Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology (农业科技通讯),2013,(9):33-35.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Exogenous Glycine Betaine on Oxidation Metabolism in Cucumbers during Low-temperature Storage
- A Preliminary Study on Genetic Variation of gE Gene of an Epidemic Pseudorabies Virus Strain and Its Pathogenicity to Piglets
- Development and Application of a Quantitative Competitive PCR Assay for Detecting Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
- A New Rapid and Batch-oriented Crushing Method for DNA Extraction from Maize Leaves
- Effects of Reducing Application Amount of Base Fertilizer and Increasing Application Time of Leaf Fertilizer on Corn Yield
- Screening,Identification and Fermentation Property of a Yeast Strain R6 Accumulating Alpha-ketoglutaric Acid
