Introduction Test of Flue-cured Tobacco Varieties from Abroad in Heilongjiang Province
Enjian QIU,Chunjun WANG,Zhiquan ZHAO,Yong CHEN,Kunyu SHANG,Peng CHI,Xin ZHONG,Zunqiang LI,Ke SONG
1.Mudanjiang Tobacco Science Research Institute of Heilongjiang Province Tobacco Corporation,Northeast Agricultural Experiment Station,CNTC,Mudanjiang 157011,China;
2.Harbin Tobacco Corporation,Harbin 150000,China;
3.Zhaodong Branch of Harbin Tobacco Corporation,Zhaodong 151100,China
Responsible editor:Nanling WANG Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
Tobacco leaf is the basis of its industry development,and variety is the basis of tobacco production.At present,although the fluecured tobacco varieties bred and generalized at home had high yield and strong adaptability,there was a relatively small number of breakthrough varieties,especially in the quality,and it still existed a large gap comparing with America and Brazil,etc.Therefore,in order to meet the development needs of Chinese-style cigarette and sustainable development of Chinese tobacco production,we should not only focus on independent innovation,accelerate the breeding of new tobacco varieties with both Chinese and foreign varieties’ merits and fine comprehensive characters,but also carry out introduction.The research showed that tobacco was sensitive to environment,the adaptability of the same variety in different environmental conditions had some differences[1-14].Hence,only organically combining varietal characteristics with local ecological conditions,can give play to the potential productivity of fine varieties[15].In order to solve the problems of ageing and single tobacco variety in Heilongjiang,a comparative trail on introduced flue-cured tobacco varieties from America and Brazil was carried out in 2013 to screen out fine varieties suitable for planting in the ecological environment of Heilongjiang Province,and improve the layout of tobacco varieties in the whole province.
Materials and Methods
The general situation of experimental field
The experiment was carried out in the trial field of Mudanjiang Tobacco Science Research Institute in 2013(the geographical location is 129°06′E and 44°58′ N,the altitude is 230 m).The agrotype is warp soil,and the soil texture is medium loam,the preceding crop is wheat,the ground is flat and the land fertility is moderate,so it is easy for irrigation and drainage.Soil organic matter,available nitrogen(N),available phosphorus (P) and rapidly available potassium(K)contents of the experimental field were 25.3 g/kg,79.6 mg/kg,69.3 mg/kg and 278.6 mg/kg,respectively.
Experimental materials
The testing varieties were PVH2248,PVH2269,PVH2291,PVH2310,NC196,NC-YATAS2,NCYATAS6 and NC89(CK).
Experimental design
There were 10 treatments in the experiment,namely one variety for one treatment,NC89 was taken as check (CK).The experiment was designed by random grouping with 3 repetitions,each plot had four lines and 68 plants,and the line length was 10.2 m,the planting space was 0.6 m×1.1 m,the plot area was 44.88 m2.
Experimental methods
Each tobacco variety had same fertilization and quantity,pure N application was 45 kg/hm2,pure N:P2O5:K2O=1:2:3,thefertilizerswereapplied10 d before transplanting as single base fertilizer.The seeds were sowed on March 14,and tray seedling was carried out;on May 13,the seedlings were transplanted,then carrying out field management according to Comprehensive Standard System of Heilongjiang Fluecured Tobacco.
Measuring items and methods
The investigation and analysis on agronomic traits was carried out based on Chinese Tobacco Industry Criteria YC/T142-1998[16].The morbidity and disease index of each disease should be recorded.According to the plot,harvesting,baking,classifying and calculating the yield,so as to count leaf yield,output value,average price and ratio of first-class tobacco.30 plants of each variety (including CK) in each plot were chosen,and tobacco leaves of central section(the 8th-12thleaf positions down from parietal lobe) were got to appraise appearance quality according to Appraisal of Tobacco Sample Appearance Quality GB2635-92.Excel 2003 and DPS data processing[17]were adopted to carry out statistical analysis on experimental results,Duncan’s new multiple range method was used to carry out multiple comparisons on economic characters,other characters were also compared and analyzed.
Results and Analyses
Growth period
As seen in Table1,fr om transplant to budding,NC-YATAS-6 spent 69 d,which was the longest; PVH-2269,PVH2248 and NC89 (CK) all spent 62.7 d,which was the shortest,and other varieties spent among 63.3-65.7 d.From transplant to heart flowering,NC-YATAS-6 was also the longest,namely 73.3 d,PVH2248 and PVH2269 were shorter,namely 66.3 and 68.7 d,respectively,other varieties were among 69.3-72.0 d.For growth duration after transplant,PVH2310 was the shortest,namely 103.3 d,and NC89 was the longest,namely 110.3 d,other varieties were among 105.7-108.7 d.
Botanical characters
As shown in Table2,the plant shape of check variety NC89 and NCYATAS-2 was tower shape,and leaf colour was dark green;the plant shape of other varieties was barrel-type,and leaf colour was green.The leaf shape of each variety was oblong,the angle of stem leaf was moderate.The main vein of check variety NC89 and NCYATAS-6 was thicker,and that of other varieties was medium.The plant uniformity of PVH2310 was the best,and that of other varieties was neater.From mature characters of each variety,blades of PVH2248 and PVH2291 turned yellow and became mature most quickly,the yellowing area was most concentrated and had no tolerance in mature; blades of PVH2310,NC196 and NC-YATAS-2 turned yellow and became mature more quickly,the yellowing area was more concentrated and also had no tolerance in mature;blades of NC-YATAS-6 turned yellow hierarchically,and the yellowing speed was medium and the matureintolerance degree was also medium;blades of other varieties also turned yellow hierarchically,and the yellowing speed was relatively slow,the matureintolerance degree was good.Growth potential of NC-YATAS-6,NC-YATAS-2 and check variety NC89 at seedling stage was stronger,and that of other varieties was strong; for 25 d after planting,growth potential of NC89 was moderate,that of PVH2269 and PVH2291 was among strongerstrong,and that of other varieties was stronger;for 50 d after planting,growth potential of PVH2269,PVH2310,PVH2291 and NC89 was stronger,and that of other varieties was among strong-stronger.
Economical characters
From Table3,we inferred that plant height of PVH2248 was the highest,namely 108.6 cm,followed byNC-YATAS-6 and NC89,which were 103.8 and 103.6 cm,respectively,that of other varieties was among 95.8-99.6 cm; the number of harvestable leaves of each variety was among 19.1-20.5,and stem girth of each variety was among 9.5-10.3 cm,the differences were smaller.The pitch,length of lumbar leaf and width of lumbar leaf of each testing variety were slightly less than these of NC89.

Table1 Comparison on main growth period of each variety
?
Natural morbidity
From Table4,for the natural morbidity of the field,every variety had TMV slightly except PVH2269 and PVH2310,the morbidity was among 0.49%-2.94%,the disease index was among 0.25-1.35.For PVY,except NC-YATAS-2,PVH2310,PVH2248 and NC89,the others slightly infected,the morbidity was among 0.49% -6.80%,the disease index was among 0.12-2.57.
Economic characters
YieldAs seen in Table5,tobacco yield of check variety NC89 was 3 099.00 kg/hm2,ranking third in all varieties,but the differences with other testing varieties were not remarkable; tobacco yields of PVH2310 and NC-YATAS-2 were higher,namely 3 266.85 and 3 181.35 kg/hm2,respectively,which separately increased 5.41% and 2.66% than CK; yields of other varieties were among 2 789.10-3 074.55 kg/hm2.
Output valueAs shown in Table5,output value of check variety NC89 was 44 358.75 Yuan/hm2,ranking fourth in all varieties,but the differences with other testing varieties were not remarkable; output values of PVH2310,PVH2248 and NC-YATAS-2 were higher,namely 55 485.30,45 168.45 and 44 645.85 Yuan/hm2,respectively,which separately increased 25.08%,1.82% and 0.65%than CK; output values of other varieties were among 34 957.20-43 692.90 Yuan/hm2.
Average priceFrom Table5,we drew that average price of check variety NC89 was 14.30 Yuan/kg,ranking fourth in all varieties,but the differences with other testing varieties were not remarkable; the top three varieties in order were PVH2310,PVH2248,PVH2291,and the average prices of them were 17.02,15.07,14.37 Yuan/kg,respectively,which separately increased 19.02%,5.38% and 0.48%than CK; average prices of other varieties were among 12.28 -14.21 Yuan/kg.

Table3 Comparison on main economical characters of each variety
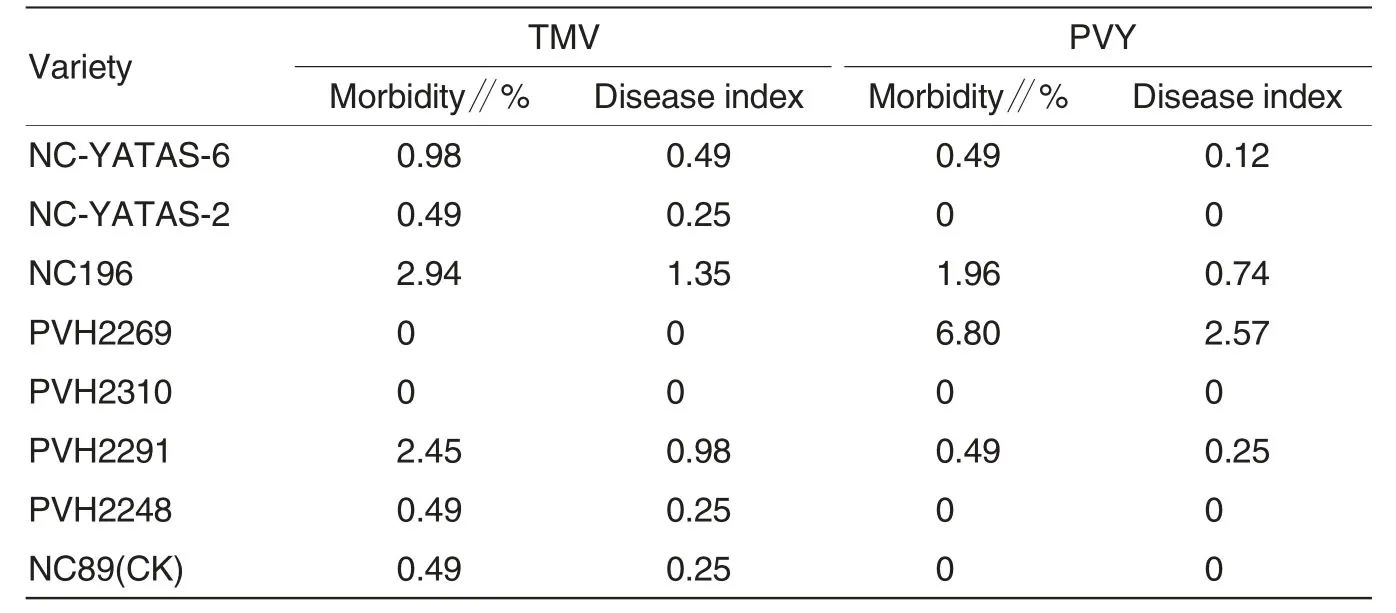
Table4 Natural morbidity of each variety
Ratio of first-class tobaccoFrom Table5,we inferred that ratio of firstclass tobacco of check variety NC89 was 10.91%,ranking second in all varieties,and that of PVH2310 was the highest,namely 24.16%,and increased 13.25 percentage point than CK; the differences between CK and other testing varieties were not significant.
Comparison on appearance quality of raw tobacco
From Table6,we can see that tobacco colors of PVH2310 and check variety NC89 were mainly among golden-deep yellow,tobacco color of NC-YATAS-2 was mainly golden,thatof PVH2269 and PVH2248 was mainly yellow,and that of other varieties was mainly among light yellow-yellow,in which NC-YATAS-6 had many variegated blades; each variety had good maturity,and leaf structure was open;the tobacco body of NC196,PVH2291 and PVH2248 was less thin,and that of other varieties was mainly medium;for oil,PVH2310 was better and mainly among oily-rich,NC-YATAS-6 and PVH2291 were low and just less oily,and other varieties were in the grade of oily;color intensity of PVH2310 was mainly strong,and that of NC196 was mainly among weak-moderate,in which moderate level took the most part,other varieties’ color intensity was also moderate.Synthesizing each indicator of appearance quality of each tobacco variety,the appearance quality of PVH2310 was superior to that of CK NC89,and that of NC-YATAS-2 was comparable to CK group,and that of other varieties was inferior to CK group.
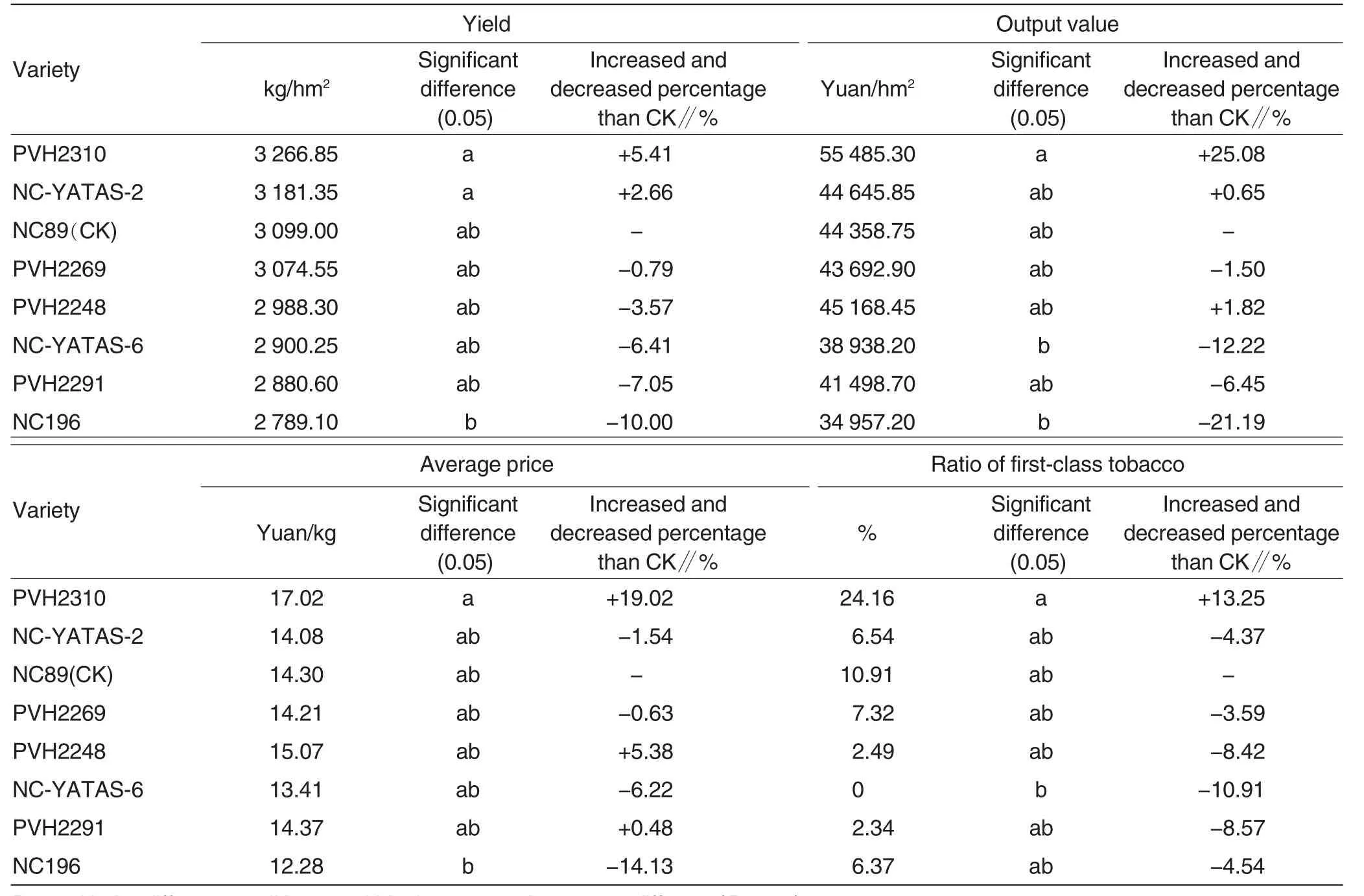
Table5 Comparison on main economic characters of each variety
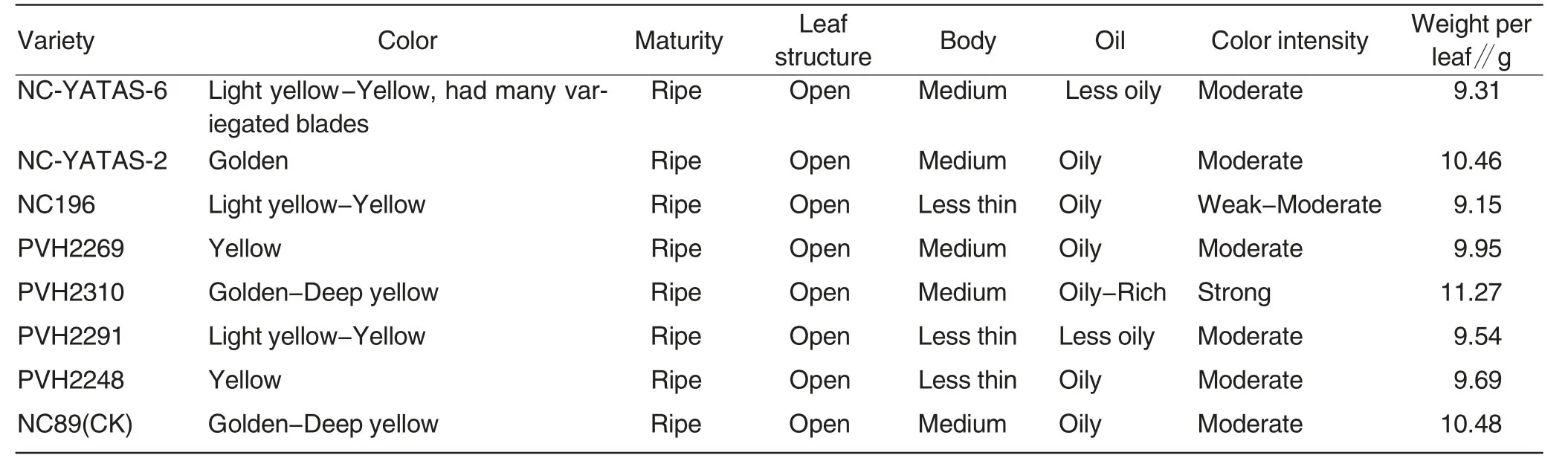
Table6 Identification of appearance characters of raw tobacco
Conclusions
(1)PVH2310 was an early-maturing variety,so its growth duration after transplant was shorter,this feature had vitally important significance for Heilongjiang flue-cured tobacco areas where air temperature was low,frostfree season was short and active accumulated temperature was less.The variety had not infected disease in the field,its yield,output value,ratio of first-class tobacco,average price and appearance quality of raw tobacco were all superior to check variety NC89,moreover,it had merits in many important characters,such as growth period,disease-resistance,main economic characters and appearance quality,etc.,in addition,its comprehensive characters were fine,which were better than check variety NC89,thus it had better adaptation in the ecological condition of Heilongjiang flue-cured tobacco areas; the variety was tested in the second year,and the experimental results in 2012[18]and 2013 were basically same,the general performance was better in the continuous two years,so further experiment and demonstration should be carried out and matching cultivation and modulation technique should be studied.
(2) NC-YATAS-2 had slightly shorter field growth period than check variety NC89,and its yield and output value were slightly higher than CK,average price and ratio of first-class tobacco were slightly lower than CK,disease,main economic characters and appearance quality were comparable to CK,thus it can be further demonstrated and verified in Heilongjiang flue-cured tobacco areas.
[1]XI BL(奚柏龙),DANG JZ(党军政),ZHU F (朱峰),et al.Research on the adaptability of new flue-cured tobacco varieties(lines) in Ankang tobacco growing area(安康烟区烤烟新品种(系)适应性研究) [J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin (中国农学通报),2013,29(25):80-86.
[2]SHANG ZQ (尚志强),JI H (冀 浩),ZHANG XM (张晓海),et al.Study on adaptability of tobacco varieties in Jingdong(不同烤烟品种在云南景东的适应性研究)[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin (中国农学通报),2013,29(10):114-118.
[3]MA WG (马文广),XU ZC (许自成),LI YP (李永平),et al.Stability analysis of economic traits and smoking quality of flue-cured tobacco varieties(lines)(烤烟品种(系)经济性状和评吸品质的稳定性分析)[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural University(河南农业大学学报),2002,36(2):111-116.
[4]LV F(吕芬),DENG SB(邓盛斌),LI ZL(李卓膦).A report on comparative test of tobacco variety(烤烟品种小区比较试验)[J].Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences(西南农业学报),2005,18(6):724-727.
[5]YANG TZ (杨铁钊).Tobacco Breeding Science(烟草育种学)[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press (北京:中国农业出版社),2003:67-72
[6]YI JH (易建华),PU WY (蒲文宜),ZHANG XY(张新要),et al.Study on the regional trial of different tobacco varieties(不同烤烟品种区域性试验研究)[J].Chinese Countryside Well-off Technology(作物栽培),2006(6):21-24.
[7]ZHOU JX (周金仙).Yield and quality changes of tobacco varieties in different ecological zones (不同生态条件下烟草品种产量与品质的变化)[J].Tobacco Science&Technology(烟草科技),2005(9):32-35.
[8]WEI JY(韦建玉),JIN YB(金亚波),WU F(吴峰),et al.Experiment on the adaptability of flue-cured tobacco varieties(烤烟品种K326 云烟85 及云烟87 的适应性研究)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences (安徽农业科学),2008,36(6):2362-2363,2372.
[9]LIN K(林昆),YANG HW(杨焕文),MA L (马林),et al.Preliminary study on location and development of feature highquality tobacco leaves in Kunming(昆明烟区特色优质烟叶定位及开发的研究初报)[J].Journal of Kunming Teachers College (昆明学院学报),2009,3l(6):23-27.
[10]WANG B (王兵),SHEN YJ (申玉军),ZHANG YM (张玉海),et al.Comparison of routine chemical components between zimbabwean and domestic flue-cured tobaccos (国产烤烟与津巴布韦烟叶常规化学成分比较)[J].Tobacco Science&Technology (烟草科技),2008(8):33-37.
[11]SHAO HF (邵惠芳),GUO B (郭波),REN XH (任晓红),et al.Comparative analysis on chemical components in hue-cured tobacco leaf from the main tobacco growing areas of Yunnan Province(云南烤烟主产烟区烟叶化学成分比较分析)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences (安徽农业科学),2007,35(7):1957-1959.
[12]SHAO Y (邵岩),FANG DH (方敦煌),DENG JH (邓建华),et al.The difference in the aroma of flue-cured tobacco between Yunnan and Zimbabwe(云南与津巴布韦烤烟致香物质含量差异研究)[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin (中国农学通报),2007,23(8):70-74.
[13]ZHANG XY(张新要),YI JH(易建华),PU WX (蒲文宣),et al.A preliminary report on flue-cured tobacco variety trail(烤烟新品种(系)试验初报)[J].Chinese Tobacco Science (中国烟草科学),2006,27(4):38-41.
[14]QIAN SX(钱时祥),CHEN XP(陈学平),GUO JM (郭家明).The application of cluster analysis in tobacco-planting regionalization(聚类分析在烟草种植区划上的应用)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural University(安徽农业大学学报),1994,21(1):21-25.
[15]XIE XQ(谢秀晴),WANG HQ(王汉琼),ZHANG DM (张东明).Study on the layout of tobacco variety in Shaanxi Province (陕西省烤烟品种布局研究)[J].China Tobacco (中国烟草),1995,16(4):16-18.
[16]State Tobacco Monopoly Administration(国家烟草专卖局).Investigating methods of agronomical character of tobacco (中华人民共和国烟草行业标准烟草农艺性状调查方法YC/T 142-1998)[S].Beijing:Standards Press of China(北京:中国标准出版社),1998.
[17]TANG QY (唐启义),FENG MG (冯明光 ).DPS Data Processing System——Experimental Design,Statistical Analysis and Data Mining(DPS 数据处理系统——实验设计 统计分析及模型 优 化)[M].Beijing:Science Press(北京:科学出版社),2006:85-98.
[18]QIU EJ (邱恩建),LIU W (刘伟),WANG CJ (王春军),et al.Research on the adaptability of new flue-cured tobacco varieties introduction from foreign in Heilongjiang tobacco growth area(国外引进烤烟品种在黑龙江的适应性研究)[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences (安徽农业科学),2014,42(6):1641-1643,1646.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年5期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Exogenous Glycine Betaine on Oxidation Metabolism in Cucumbers during Low-temperature Storage
- A Preliminary Study on Genetic Variation of gE Gene of an Epidemic Pseudorabies Virus Strain and Its Pathogenicity to Piglets
- Development and Application of a Quantitative Competitive PCR Assay for Detecting Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
- A New Rapid and Batch-oriented Crushing Method for DNA Extraction from Maize Leaves
- Effects of Reducing Application Amount of Base Fertilizer and Increasing Application Time of Leaf Fertilizer on Corn Yield
- Screening,Identification and Fermentation Property of a Yeast Strain R6 Accumulating Alpha-ketoglutaric Acid
