革兰氏阴性益生菌大肠杆菌Nissle 1917益生机理及其在仔猪方面的应用
邓 欢 赖 星 孙志洪 陈 澄 石宝石 唐志如
(西南大学动物科技学院,生物饲料与分子营养实验室,重庆 400715)
1917年,志贺菌痢爆发,德国医生 Alfred Nissle从疫区一位未患肠炎的士兵粪便中分离了1株无致病性的大肠杆菌(E.coli)菌株,命名为 E.coli Nissle1917(EcN)。随后,科学家分离到一些新的益生E.coli菌种,如 SK22(保存于德国菌种中心,编号为DSM6601),并探索了它们对动物健康的益生机理[1-2]。作为一种肠道微生物,EcN能定植于肠道中并与其他微生物抗衡。了解EcN特殊的表型、定植机理、免疫调节机理和在仔猪方面应用的研究现状对其他益生革兰氏阴性杆菌在肠道中的研究具有重要参考意义。
1 EcN的基本特征
在琼脂固体营养培养基上,EcN菌落呈半粗糙型,较光滑、透明、黏稠,易挑取,大而平坦,菌落正反面或边缘与中央部位的颜色一致。EcN的O6抗原聚合酶wzy基因终止子上的点突变使得O6抗原多糖侧链很短,由单个寡糖骨架“重复单位”组成O6抗原,其低聚糖骨架直接与“重复单位”相连,而不与长链多糖相连[3]。这种古怪脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)结构决定了 EcN的菌落半粗糙表型(图1),又称为半粗糙 O6-LPS表型。这种表型决定了EcN的血清敏感性和免疫调节性[4]。EcN具有K5型荚膜(图1),在与肠上皮细胞相互作用时,K5型荚膜产生特异性趋化因子反应[4]。EcN基因组编码F1A、F1C和卷曲菌毛(图1),这3种菌毛替代了P-和S-菌毛(具有血凝反应因子,是致病大肠杆菌代表性特征)[4-5]。
虽然EcN血清型为 O6∶K5∶H1,但无致病性。而与尿道感染相关的大肠杆菌菌种血清型也为O6∶K5∶H1,却具有致病性。原因在于EcN基因组缺少其他大肠杆菌的毒力因子致病基因[3]。EcN适应性因子位于基因组的4个染色体组小岛上,有助于定植于宿主(图1)。
EcN最大的特点是具有获取铁营养素的多重机制(图1)。EcN的6种铁摄取系统能产生铁螯合剂肠菌素、杆菌素、产气菌素、铁摄取有关气菌素、枸橼酸铁运输系统和储血红素运输场所,有利于其利用环境中的 Fe3+[3,6]。EcN 具有氯高铁血红素和柠檬酸盐依赖性铁摄取系统[7]。EcN能产生EfeU[一种氧化酶依赖性铁转运(OFeT)家族的亚铁系统摄取系统][8]。EcN也能分泌小菌素M、小菌素H47、溶血素和细胞毒素坏死因子,从而抑制致病微生物[9]。

图1 EcN的表型特征及其在基因组上的位置Fig.1 Phenotypical characteristics of EcN and its location in genome[3]
2 EcN的益生机理
2.1 EcN在肠道中的定植机制
EcN表达3种菌毛有利于其定植于肠上皮细胞,形成生物被膜,最终形成自然屏障来抵御致病菌的入侵[4-5]。EcN的K5型荚膜对黏附和定植起重要作用(图 2)[10]。K5不产生血清抗性,同时EcN在血清抗性试验中很快被杀死[11]。EcN表达的K5型荚膜能在肠上皮细胞和体内鼠小肠中激活Toll样受体5(TLR5)产生化学增活素[12-13]。
EcN特有的6种铁摄取系统有利于其在肠道中定植。EcN能提高猪的小肠钙网蛋白(calprotectin),这提示了钙网蛋白可能在EcN的益生作用中发挥了作用[14]。EcN能促进炎症肠道中抗菌的脂质运载蛋白-2(lipocalin-2)和钙网蛋白高表达,但EcN的定植和益生功能是否增强有待进一步研究。高亲和力金属运载体可以增强EcN在炎症的肠道中的定植力,并为其与包括病原菌在内的其他微生物之间竞争提供手段。
研究发现EcN能分泌抵抗菌物质(小菌素H47和小菌素M 等)来抵抗病原体[15]。小菌素是一种低分子质量的抗菌肽,类似于革兰氏阳性杆菌的细菌素,对于补偿免疫蛋白不足的细菌在种族发育中发挥了有力的杀菌作用[15]。小菌素H47和小菌素M与铁螯合剂salmochelin结合,并为受体所感应,从而展示一种进入菌体的“Trojan horse”机制(图 2)[6,16]。因此小菌素 H47 和小菌素M可增强EcN与肠道中其他微生物之间的竞争力。
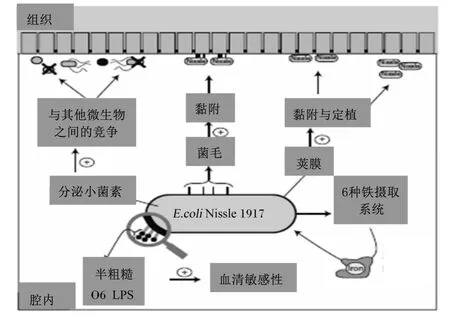
图2 益生菌EcN所具备的多种适应性因子Fig.2 The multiple fitness factors of probiotic EcN[16]
2.2 提高黏膜屏障
EcN通过鞭毛蛋白经核转录因子-κB(NF-κB)和AP-1-依赖性途径产生人抗菌肽β-防御素2(β-defensin 2),从而增强结肠上皮细胞化学防御(图 3)[14,17-18]。通过上调肠上皮细胞紧密连接蛋白 ZO-2水平,EcN 能提高黏膜屏障(图 3)[19]。EcN能阻碍致肠病的大肠杆菌感染引起ZO-2表达下降。EcN通过上调闭锁小带(OZ-1、OZ-2)的表达,增强肠上皮细胞的紧密连接,减少因为肠漏引起的细菌异位与代谢产物穿过肠上皮细胞[20]。
2.3 调节致炎和抗炎细胞因子之间的平衡
EcN能下调炎症,研究发现EcN具有调节致炎和抗炎的局部细胞因子的平衡(图3)[21-22]。体外试验表明,EcN的生物学功能与在肠道微生物的调控和肠内细胞因子引起免疫反应相关联[23]。EcN抑制炎症反应维持肠道免疫稳态的机理之一在于EcN能通过激活T细胞诱导天生性和记忆性外周血CD4+T细胞同源细胞的生长(图3)[24]。EcN也能加速γδT细胞周期和细胞因子分泌(图3)。γδT细胞的激活和脱噬作用是限制肠道炎症的一种可能方式[25]。在变应原诱导的Th2反气管炎症,EcN被发现通过诱导不产生免疫球蛋白E(IgE)的 Th1模型来减轻症状[26]。许多研究发现,EcN通过提高分泌型免疫球蛋白A(sIgA)[2],改变致炎和抗炎细胞因子[27-28]及调节T细胞的分化[29]来进行免疫调控。EcN能减少试验小鼠大肠杆菌数量,降低通过 Toll样受体 4(TLR4)和TLR5产生的炎症细胞因子和干扰素-γ(IFN-γ)(图3)[30]。口服EcN能产生黏膜特异性免疫球蛋白G(IgG)与免疫球蛋白M(IgM)抗体而诱导婴儿体液免疫(图3)[31]。EcN的免疫调控作用也被发现在结肠上皮细胞,EcN提取物能促进细胞白介素-8(IL-8)的分泌[2],降低结肠致癌指示物环氧酶-2(COX-2)和前列腺素E2(PGE2)的表达水平(图 3)[32]。
3 EcN在仔猪方面的应用现状
3.1 在肠道黏膜屏障方面
Kleta等[33]从仔猪肠内容物中筛选到EcN,证实了EcN也存在于猪小肠中,表明EcN是猪肠道微生物的一部分。同时Kleta等[33]研究了EcN对仔猪肠相关淋巴组织的影响,试验中采用109和1011CFU/d EcN饲喂仔猪21 d,定量分析了肠免疫细胞(粒性白细胞、肥大细胞 CD4+、CD8+、CD25+、IgA+淋巴细胞)的数量和分布及黏膜细胞因子[IFN-γ、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、转化生子因子-β(TGF-β)、细胞白介素-10(IL-10)]和抗菌肽 (PR-39、NK-lysin、pre-defensin-β1、protegrins)mRNA的表达水平,结果表明,各组中肠免疫细胞(粒性白细胞、肥大细胞 CD4+、CD8+、CD25+和IgA+淋巴细胞)的数量和分布小肠与结肠存在较大的差异,低剂量EcN各组间差异不显著,高剂量EcN(1011CFU/d)使结肠升段黏膜CD8+细胞数量显著增加。mRNA分析表明,饲喂EcN对黏膜细胞因子(IFN-γ、TNF-α、TGF-β、IL-10)和抗菌肽(PR-39、NK-lysin、pre-defensin-β1、protegrins)mRNA的表达水平无显著影响,EcN对健康仔猪肠免疫细胞的分布影响较小。EcN的预防作用可能与除肠免疫细胞的分布的单一调节以外的其他机制有关。仔猪口服109CFU/d的EcN不会引起小猪结肠炎和泌尿生殖器感染[34]。唐志如等[35]研究发现,在大肠杆菌Abbottstown攻毒的断奶仔猪中,口服1010CFU/d的EcN显著下调空肠黏膜双链RNA依赖的蛋白质激酶(PKR)、真核生物翻译起始因子5A(eIF-5A)和TLR2 mRNA相对表达丰度,显著降低空肠黏膜淋巴细胞数量,显著提高空肠黏膜occludin蛋白水平,显著上调空肠黏膜胰岛素样生长因子-Ⅰ(IGF-Ⅰ)、肝细胞生长因子(HGF)、三叶草肽-3(TFF-3)和表皮生长因子(EGF)mRNA相对表达丰度,提示EcN能维持肠道功能完整性,并保护肠道屏障。

图3 益生菌EcN对宿主免疫系统的调节途径Fig.3 The probiotic EcN modulates the host immune system in multiple ways[31]
3.2 在促进生长与治疗腹泻方面
EcN对传染性腹泻具有良好的治疗效果。Duncker等[36]对EcN预防21日龄断奶仔猪急性分泌性腹泻进行研究,试验分为以下4组:1组[-肠毒性大肠杆菌(EcA)/-EcA,n=6]、2组(-EcN/+EcA,n=7)、3 组(+EcN/-EcA,n=4)和4组(+EcN/+EcA,n=4);将 1010CFU/d EcA 和EcN通过口胃管饲喂21日龄断奶仔猪,攻毒48 h后,屠宰取空肠上皮置于Ussing chambers上测定空肠上皮电生理的参数的变化,结果表明,EcN预处理后的仔猪能完全控制仔猪急性分泌性腹泻。唐志如等[35]研究发现,在大肠杆菌Abbottstown攻毒的断奶仔猪中,口服1010CFU/d的EcN能显著降低腹泻率,显著改善生长性能。Splichalova等[37]研究发现,猪感染沙门氏菌后血浆中 IL-10、TNF-α和肠道TNF-α浓度显著增加,但在感染沙门氏菌前口服 EcN,血浆中IL-10、TNF-α和肠道TNF-α浓度无显著影响,这提示了EcN能竞争性阻碍沙门氏菌的入侵。Schroeder等[38]研究表明提前口服EcN能预防断奶仔猪受产毒型大肠杆菌的感染。
4 小结
EcN由于其特殊的基因型,决定了其半粗糙O6-LPS 表型、O6∶K5∶H1F1A 的血清型、特殊的菌毛与荚膜、适应性因子和铁摄取系统,从而使得EcN在肠道中具有稳定定植机制和免疫调节功能。以仔猪为对象的研究发现口服EcN能维护肠道形态结构,提高肠黏膜紧密连接性,维持肠道功能完整性,保护肠道屏障,进而提高断奶仔猪生长性能和降低断奶仔猪腹泻率。
[1] SMITH F,CLARK J E,OVERMAN B L,et al.Early weaning stress impairs development of mucosal barrier function in the porcine intestine[J].American Journal of Physiolog:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2010,298(3):G352-G363.
[2] CUKROWSKA B,LODLNOVA-ZADNLKOVA R,ENDERS C,et al.Specific proliferative and antibody responses of premature infants to intestinal colonization with nonpathogenic probiotic E.coli strain Nissle 1917[J].Scandinavian Journal of Immunology,2002,55(2):204-209.
[3] GROZDANOV L,RAASCH C,SCHULZE J,et al.A-nalysis of the genome structure of the nonpathogenic probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917[J].Journal of Bacteriology,2004,186(16):5432-5441.
[4] BLUM G,HACKER J,MARRE R.Properties of Escherichia coli strains of serotype O6[J].Infection,1995,23:234-236.
[5] LASARO M A,SALINGER N,ZHANG J,et al.F1C fimbriae play an important role in biofilm formation and intestinal colonization by the Escherichia coli commensal strain Nissle 1917[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2009,75:246-251.
[6] VALDEBENITO M,CRUMBLISS A L,WINKELMANN G,et al.Environmental factors influence the production of enterobactin,salmochelin,aerobactin,and yersiniabactin in Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917[J].International Journal of Medical Microbiology,2006,296:513-520.
[7] LÉVEILLÉ S,CAZA M,JOHNSON J R,et al.Iha from an Escherichia coli urinary tract infection outbreak clonal group A strain is expressed in vivo in the mouse urinary tract and functions as a catecholate siderophore receptor[J].Infection and Immunity,2006,74:3427-3436.
[8] HANCOCK V,VEJBORG R M,KLEMM P.Functional genomics of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and 83972,and UPEC strain CFT073:comparison of transcriptomes,growth and biofilm formation[J].Molecular Genetics and Genomics,2010,284:437-454.
[9] PATZER S I,BAQUERO M R,BRAVO D,et al.The colicin G,H and X determinants encode microcins M and H47,which might utilize the catecholate siderophore receptors FepA,Cir,Fiu and IroN[J].Microbiology,2003,149(9):2557-2570.
[10] BURNS SM,HULL SI.Comparison of loss of serum resistance by defined lipopolysaccharide mutants and an acapsular mutant of uropathogenic Escherichia coli O75∶K5[J].Infection and Immunity,1998,66:4244-4253.
[11] HUGHES C,PHILLIPS R,ROBERTS A P.Serum resistance among Escherichia coli strains causing urinary tract infection in relation to O type and the carriage of hemolysin,colicin,and antibiotic resistance determinants[J].Infection and Immunity,1982,35:270-275.
[12] HAFEZ M,HAYES K,GOLDRICK M,et al.The K5 capsule of Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 is important in mediating interactions with intestinal epithelial cells and chemokine induction[J].Infection and Immunity,2009,77:2995-3003.
[13] HAFEZ M,HAYES K,GOLDRICK M,et al.The K5 capsule of Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 is important in stimulating expression of Toll-like receptor 5,CD14,MyD88,and TRIF together with the induction of interleukin-8 expression via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in epithelial cells[J].Infection and Immunity,2010,78:2153-2162.
[14] SPLICHAL I,FAGERHOL M K,TREBICHAVSKY I,et al.The effect of intestinal colonization of germfree pigs with Escherichia coli on calprotectin levels in plasma,intestinal and bronchoalveolar lavages[J].Immunobiology,2005,209:681-687.
[15] BAQUERO F,MORENO F.The microcins[J].FEMS Microbiology Letters,2006,23:117-124.
[16] VASSILIADIS G,DESTOUMIEUX-GARZON D,LOMBARD C,et al.Isolation and characterization of two members of the siderophore-microcin family,microcins M and H47[J].Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy,2010,54:288-297.
[17] WEHKAMP J,HARDER J,WEHKAMP K,et al.NF-κB-and AP-1-mediated induction of human beta defensin-2 in intestinal epithelial cells by Escherichia coli Nissle 1917∶a novel effect of a probiotic bacterium[J].Infection and Immunity,2004,72:5750-5758.
[18] SCHLEE M,WEHKAMP J,ALTENHOEFER A,et al.Induction of human beta-defensing 2 by the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is mediated through flagellin[J].Infection and Immunity,2007,75:2399-2407.
[19] UKENA S N,SINGH A,DRINGENBERG U,et al.Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 inhibits leaky gut by enhancing mucosal integrity[J].PLoS One,2007,2:e1308.
[20] ZYREK A A,CICHON C,HELMS S,et al.Molecular mechanisms underlying the probiotic effects of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 involve ZO-2 and PKCζ redistribution resulting in tight junction and epithelial barrier repair[J].Cellular Microbiology,2007,9:804-816.
[21] CROSS M L,GANNER A,TEILAB D,et al.Patterns of cytokine induction by gram-positive and gram-negative probiotic bacteria[J].FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology,2004,42:173-180.
[22] UKENA S N,WESTENDORF A M,HANSEN W,et al.The host response to the probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917:specific up-regulation of the proinflammatory chemokine MCP-1[J].BMC Medical Genetics,2005,6:43.
[23] SKAAR E P.The battle for iron between bacterial pathogens and their vertebrate hosts[J].PLoS Pathogens,2010,6:e1000949.
[24] STURM A,RILLING K,BAUMGART D C,et al.Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 distinctively modulates T-cell cycling and expansion via Toll-like receptor 2 signaling[J].Infection and Immunity,2005,73:1452-1465.
[25] GUZY C,PACLIK D,SCHIRBEL A,et al.The probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 inducesγδ T cell apoptosis via caspase-and FasL-dependent pathways[J].International Immunology,2008,20:829-840.
[26] BICKERT T,TRUJILLO-VARGAS C M,DUECHS M,et al.Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 suppresses allergen-induced Th2 responses in the airways[J].International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,2009,149:219-230.
[27] HELWIG U,LAMMERS K M,RIZZLLO F,et al.Lactobacilli,Bifidobacteria and E.coli Nissle induce pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells[J].World Journal of Gastroenterology,2006,12:5978-5986.
[28] ARRIBAS B, RODRIGUEZ-CABEZAS M E,CAMUESCO D,et al.A probiotic strain of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917,given orally exerts local and systemic anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharideinduced sepsis in mice[J].British Journal of Pharmacology,2009,157:1024-1033.
[29] AGRAWAL S,AGRAWAL A,DOUGHTY B,et al.Cutting edge:different Toll-like receptor agonists instruct dendritic cells to induce distinct Th responses via differential modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos[J].The Journal of Immunology,2003,171:4984-4989.
[30] GRABIG A,PACLIK D,GUZY C,et al.Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 ameliorates experimental colitis via toll-like receptor 2-and toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathways[J].Infection and Immunity,2006,74:4075-4082.
[31] LAMMERS K M,HELWIG U,SWENNEN E,et al.Effect of probiotic strains on interleukin 8 production by HT29/19A cells[J].The American Journal of Gastroenterology,2002,97:1182-1186.
[32] OTTE JM,MAHJURIAN-NAMARI R,BRAND S,et al.Probiotics regulate the expression of COX-2 in intestinal epithelial cells[J].Nutrition and Cancer,2008,61:103-113.
[33] KLETA S,STEINRUCK H,BREVES G,et al.Detection and distribution of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 clones in swine herds in Germany[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2006,101(6):1357-1366.
[34] GUNZER F,HENNIG-PAUKA I,WALDMANN K H,et al.Gnotobiotic piglets develop thrombotic microangiopathy after oral infection with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli[J].American Journal of Clinical Pathology,2002,118(3):364-375.
[35] 唐志如,邓欢,孙卫忠,等.口服益生菌 Escherichia coli Nissle 1917调控断奶仔猪空肠粘膜屏障功能的机理研究[J].畜牧兽医学报,2014,45(1):78-86.
[36] DUNCKER S C,LORENTZ A,SCHROEDER B,et al.Effect of orally administered probiotic E.coli strain Nissle 1917 on intestinal mucosal immune cells of healthy young pigs[J].Veterinary Immunology Immunopathology,2006,111:239-250.
[37] SPLICHALOVA A,TREBICHAVSKY I,RADA V,et al.Interference of Bifidobacterium choerinum or Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 with Salmonella Typhimurium in gnotobiotic piglets correlates with cytokine patterns in blood and intestine[J].Clinical and Experiment Immunology,2011,163:242-249.
[38] SCHROEDER B,DUNCKER S,BARTH S,et al.Preventive effects of the probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 on acute secretory diarrhea in a pig model of intestinal infection[J].Digestive Diseases and Sciences,2006,51:724-731.

