Effects of Mixed Solvents on the High-Rate Performance of Li3V2(PO4)3/C Prepared by Sol-Gel Method
TANG Yan ZHONG Ben-He,* GUO Xiao-Dong LIU Heng ZHONG Yan-JunNIE Xiang TANG Hong
(1College of Chemical Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,P.R.China;2College of Materials Science and Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,P.R.China)
Effects of Mixed Solvents on the High-Rate Performance of Li3V2(PO4)3/C Prepared by Sol-Gel Method
TANG Yan1ZHONG Ben-He1,*GUO Xiao-Dong1LIU Heng2ZHONG Yan-Jun1NIE Xiang1TANG Hong1
(1College of Chemical Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,P.R.China;2College of Materials Science and Engineering,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,P.R.China)
Abstract: A Li3V2(PO4)3/C composite cathode material was obtained by a sol-gel method using deionized water and organic solvents as mixed solvents.Ethanol,ethylene glycol,and 1,2-propylene glycol were used as the organic solvents and polyacrylic acid(PAA)was used as the chelating agent and carbon source.The structure,morphology,and electrochemical performance of the synthesized materials were studied by X-ray diffraction(XRD),scanning electron microscopy(SEM),charge-discharge tests,and cyclic voltammetry.XRD analysis showed that all the materials were well crystallized and that the addition of organic solvents did not affect the crystal structure of Li3V2(PO4)3.The results of galvanostatic cycling showed that the electrochemical performance of the products was improved by the addition of organic solvents.The material synthesized using 1,2-propylene glycol had the best electrochemical performance.It exhibited an initial discharge capacity of 132.89 mAh·g-1at 0.1C(1C=150 mA·g-1)in the voltage range of 3.0-4.5 V.The initial discharge capacity was as high as 125.42 mAh·g-1upon discharging at 10C,and it had a capacity retention of 95.79%after 700 cycles.These results indicate a good rate and cycling performance in the voltage range of 3.0-4.5 V;while in the voltage range of 3.0-4.8 V,it exhibits a bad rate performance.SEM images indicated that the sample prepared using the mixed solvents had a flake-like and needle-like shape,which facilitates the interface ion-transfer process and thus improves the overall electrochemical properties.
Key Words:Lithium ion battery;Cathode material;Li3V2(PO4)3;Sol-gel method;Mixed solvents
1 Introduction
Lithium ion batteries have become the most promising energy storage devices for portable electronics.Some poly-anionic phosphate materials,such as the olivine-type LiFePO41-3and monoclinic Li3V2(PO4)3(LVP)4-10,have attracted much interest in the past decade.The reversible cycling of all three lithium ions from LVP would correspond to a theoretical capacity of 197 mAh·g-1,which is the highest for all phosphate that have been reported11-13.Owing to good ion mobility,high lithium capacity,and a high operating voltage,LVP has been proposed to be a potential candidate of cathode materials for Li-ion batteries.LVP has good high-rate performance and good cycling stability.14,15It may play an important role in the expanding demand of electric vehicles(EVs)and hybrid electric vehicles(HEVs)in the future.
In the literature,carbon-coated LVP powders have been synthesized via various methods such as solid-state reaction,16-18sol-gel process,19-21and microwave solid-state reaction.22,23Among them,the solid-state reaction is simple,environment friendly,and reaction efficient,but the particle size of the material is non-uniform.By using microwave,the reaction time can be greatly shortened;however,the preparation condition is difficult to control.Although the sol-gel process is complex,this method allows reactants to mix at the atomic or molecular level,thus reducing the calcination temperature and time of the products.Therefore,the sol-gel process is a promising method to synthesize higher purity material with uniform particle size.
So far,nearly all the LVP synthesized by the sol-gel method used pure deionized water as solvent.A few studies have been reported to use some organic solvents,but paper16did not specify the role of organic solvent.Surface tension of an organic solvent is smaller than that of water.Therefore,the organic solvent is not only used as solvent,but also would play the role of surfactant,which has an impact on the growth of the particle.Also,during the drying process,the gel is not easy to reunite,thereby reducing the particle size.In this work,LVP precursor was synthesized by the sol-gel method with an organic solvent in water.Ethanol,ethylene glycol,and 1,2-propylene glycol were used as organic solvents.The effects of different organic solvents on the performance of LVP samples were evaluated.
2 Experimental
The LVP/C composites were prepared by a sol-gel method.The stoichiometric ratio of LiOH·H2O(99%(w,mass fraction)),NH4VO3(99%),H3PO4(85%)were used as raw materials.Polyacrylic acid(PAA)(30%)was used as carbon source and chelating reagent.Organic solvents(in this work,ethanol,ethylene glycol,and 1,2-propylene glycol were chosen as organic solvents)and deionized water were mixed in proportion of 40:60(volume ratio).First,LiOH·H2O and NH4VO3were dissolved in deionized water at room temperature.Then organic solvent and 10%(w)of PAA were added into the solution.Finally,H3PO4was added to the mixture.This solution was constantly stirred for 2 h at 80°C,and then the excess solvent was removed by vacuum distillation.The resulting gel precursor was dried in a vacuum oven at 90°C for 15 h.After drying,the precursors were decomposed in tube furnace at 350°C for 4 h,then heated at 700°C for 6 h under flowing argon.The final product was a black powder.
The carbon content was verified by CS-902 analytical instrument(Wanlianda Xinke,Beijing,China).The crystalline structure of each product was analyzed by X-ray diffraction(XRD,D/max-rB,Rigaku,Cu Kαradiation)(λ=0.15046 nm)operated at 40 kV and 40 mA.The particle morphology and particle size of the LVP powders were observed by scanning electron microscopy(SEM,SPA400 Seiko Instruments).
The specific surface areas(SSA)were measured with Brunauer-Emmett-Teller(BET)method by N2physisorption at 77 K on Quanachrome automated surface area&pore size analysizer(Autosorb SI).The samples were pretreated at 300°C for 3 h prior to the measurement.
The cathode was fabricated by pressing a mixture of 80%(w)LVP/C,13%(w)acetylene black(conducting additive),and 7%(w)PVDF(binder)onto an Al foil.The anode was lithium foil and the electrolyte was 1 mol·L-1LiPF6solution in ethylene carbonate:propylene carbonate:diethyl carbonate[1:1:1(volume ratio)].Galvanostatic charging/discharging tests were operated in the voltage range of 3.0-4.5 V and 3.0-4.8 V at room temperature(25°C)with a battery test system(Neware BTS-610).Cyclic voltammetry(CV)was performed on the positive electrode in the cells described above by a CHI 660C electrochemical work station.CV tests were carried out in voltage ranges 3.0-4.5 V and 3.0-4.8 V at a scanning rate of 0.10 mV·s-1.
3 Results and discussion
Fig.1 shows the X-ray diffraction patterns of the LVP/C composites synthesized with different organic solvents;they are similar to those reported by Rui24and Saidi25et al.The characteristic peaks of all the LVP/C samples are sharp and without any impurity peaks.The carbon left in the LVP can not be detected because the residual carbon is only about 3%and in amorphous form.It can be concluded that the samples with all solvents have produced a single phase of LVP/C with monoclinic structure.Table 1 shows the cell parameters of LVP/C samples,and it can be seen that the cell volumes of the four samples are close to each other.It indicates that different solvents do not have significant effects on the cell parameters of the products.In addition,the mean coherent domain sizes of the samples were calculated by Jada 5.0 software which takesaccount of all the major diffraction peaks in the XRD pattern.It can be seen that the mean coherent domain sizes of the samples synthesized by mixed solvents are smaller than that using pure deionized water;and the grain size of sample D is the smallest one,which may facilitate the electron transport and ions diffusion.
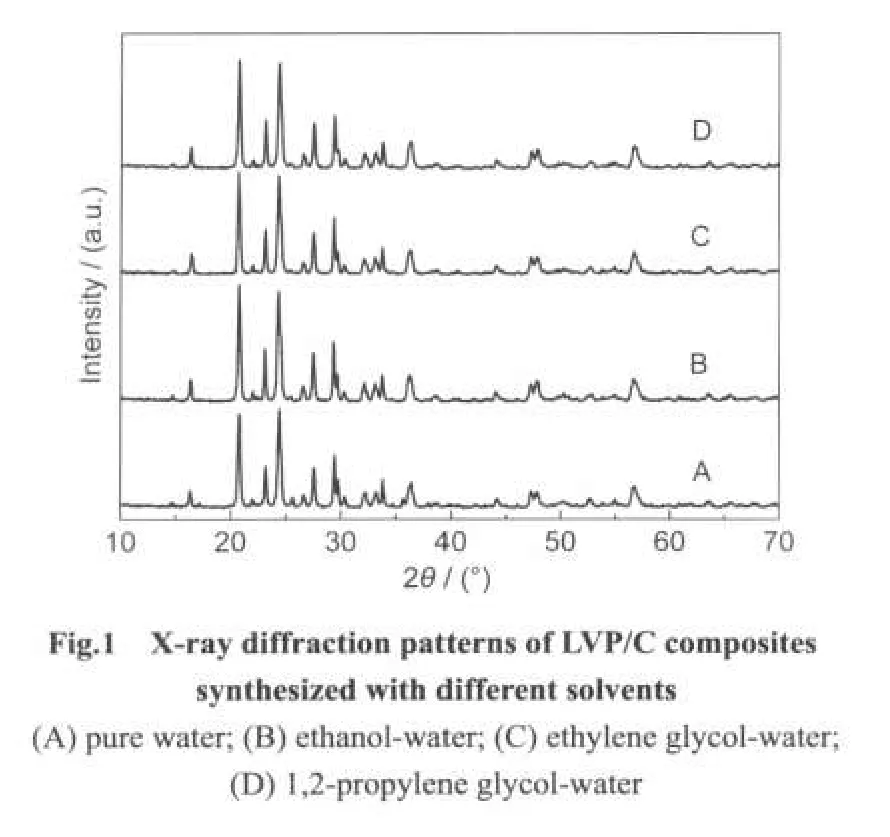
Fig.2 shows the first charge/discharge curves of LVP/C samples in the voltage range of 3.0-4.5 V at 0.1C.It can be seen that all the initial charge curves of the samples exhibit three stable voltage plateaus at 3.57,3.65,and 4.08 V.These plateaus correspond to the two-phase transitions between the single phases of LixV2(PO4)3(x=2.5,2.0,1.0).The initial discharge capacities of samples A,B,C,and D are 123.59,127.60,130.51,and 132.89 mAh·g-1,respectively.Compared with sample A,samples B,C and D,which are synthesized with mixed solvents,have higher discharge capacity.Fig.3 displays the average discharge capacity of samples A,B,C,and D at 0.1C,0.2C,0.5C,1C,3C,5C,10C,and 20Crates,respectively.It can be seen that the capacity of the samples basically possesses better retention,only fading faster at higher rates for sample A.The discharge capacities of samples A,B,C,and D at 20Crates are 95.92,110.85,116.92,and 119.99 mAh·g-1,which are 77.61%,86.87%,89.30%,and 90.29%of the capacity at 0.1Crate,respectively.Obviously,the electrochemical performance of products can be improved by adding organic solvents during the reaction of precursors,especially at high discharge rate.
In order to explain why the samples obtained by adding organic solvents have better electrochemical performance,the SEM images of samplesAand D in Fig.4 are compared carefully.As shown in Fig.4(a,b),the sample synthesized by pure deionized water presents an irregularity of shape with particle size of 1-3 μm.This kind of shape with a small specific surface area does not favor lithium-ion diffusion.When the current increases,the diffusion of lithium ion is blocked and the capacity decreases.The sample synthesized in the mixed solvent by adding some 1,2-propylene glycol,to some extent,is part of the particle agglomerate,but the original particle size is small and most of the particles are distributed in the range of 1-2 μm(Fig.4(c,d)).Most of the particles have a flake-like shape,as mentioned previously;26the morphology of flake-like shape has a large specific surface area and results in good electrochemical performance.There are also particles in needlelike shape that are about 0.1 μm in diameter and 1 μm in length;meanwhile these particles also have a large specific surface area.We believe that the flake-like and needle-like shape leads to the better performance of sample D.It can be concluded that the existence of organic solvent can affect the shape ofthe particle.The surface tension of organic solvents is smaller than that of water;the solvent can selectively control the surface energy of different particle faces in the process of gel formation.PAA is a long-chain molecule,so that the LVP precursor particle can grow along its long-chain direction to give flake-like and needle-like particles.

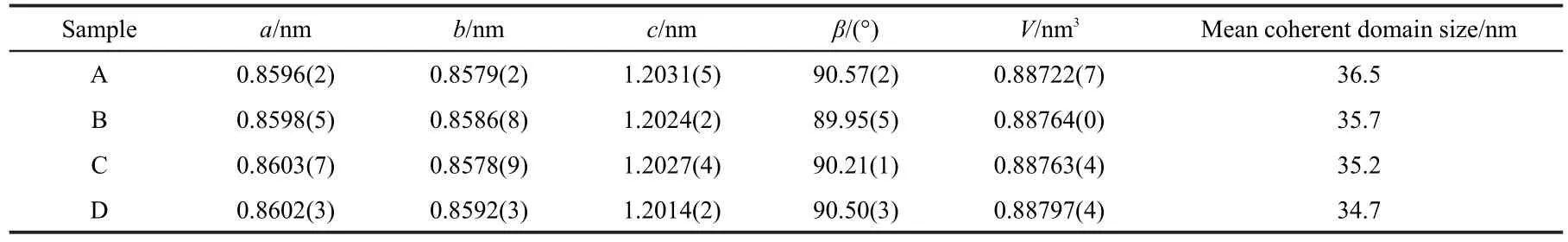
Table 1 Cell parameters of the samples

A confirmation,quite valuable being quantitative,of the positive influence of the solvent on the grain characteristics comes from specific surface area measurements with the BET method.The data reported in Table 2 show that 1,2-propylene glycolwater mixed solvents markedly enhance the specific surface area of the powders.The sample D shows a specific surface area almost 1.5 times that of the sample prepared by pure deionized water.Therefore,it can be concluded that the solvents have great effects on the specific surface area of the samples.
Among the samples,sample D gave the best performance.Fig.5 demonstrates the cycle and rate performance of sample D at various discharge rates.It can be seen that its cycling stability is excellent at each rate.The discharge capacity does not decrease at each rate after several cycles.As the rate increases,the discharge capacity decreases only a little;when the current comes to 20C,the specific capacity is still as high as 119.99 mAh·g-1.The discharge voltage decreases as the rate increases since the polarization becomes heavier with increasing the rate.From Fig.6,we can clearly see that sample D shows a good cycling stability at 10Crate.The initial specific capacity is 125.42 mAh·g-1and decreases to 120.14 mAh·g-1after 700 cycles(the ratio of 95.79%of the initial capacity).The good performance of LVP/C obtained in this experiment,combined with its high safety,implies that it can be a candidate cathode material for the lithium ion battery of HEVs and EVs in the future.

Table 2 Specific surface area(S)of the sample synthesized with different solvents

Monoclinic lithium vanadium phosphate contains three independent lithium sites with a theoretical discharge capacity of 197 mAh·g-1,while three Li ions are completely released from the cathode.Fig.7 shows the electrochemical performance of sample D in the voltage range of 3.0-4.8 V.Sample D presents an initial charge specific capacity of 196.14 mAh·g-1at 0.1C,equivalent to the theoretical capacity(Fig.7(a)).The initial discharge capacity is 165.96 mAh·g-1,which is only 84.61%ofthe initial charge capacity.When keeping the charge rate at 1C rate and increasing the discharge rate,the polarization becomes heavy and the voltage decreases a lot.The discharge specific capacity decreases from 117.80 to 105.06 mAh·g-1when discharge rate increasing from 10C to 20C rate.It can be seen from Fig.7(b)that the fading seems to be unavoidable since the capacity of sample D is 139.69 mAh·g-1after six cycles at 0.1C and 0.2C rates,respectively,a capacity decrease of about 26.27 mAh·g-1.However,it is obvious that the major decay exists in the first 12 cycles with a fading rate of 2.19 mAh·g-1per cycle.With the increase of discharge rate,the latter 60 cycles remain stable,especially at 10Cand 20Crate.The initial specific capacity is 117.80 mAh·g-1and is also as high as 116.21 mAh·g-1after 20 cycles at 10Crate.Compared with the stable cycle ability presented in LVP samples in the voltage range of 3.0-4.5 V(Fig.5),there is a significant fading of capacity in the voltage range of 3.0-4.8 V,which might be due to the following reasons.One is the oxidation of electrolyte in this high electrochemical window(3.0-4.8 V).The other is that the crystal structures of LVP is distorted during the phase transition process at the high voltage(>4.6 V).The resistance of Li3V2(PO4)3sample might be increased during the extraction/reinsertion process,which results in the poor cycle ability.
In order to compare the behavior of LVP at different voltage ranges,the CV curve obtained in the voltage ranges of 3.0-4.5 V and 3.0-4.8 V are shown in Fig.8.Fig.8(A)shows the CV curves of sample D from 3.0 to 4.5 V.The voltage range to 4.5 V exhibits typical oxidative peaks near 3.63,3.72,and 4.14 V(vs Li/Li+)as well as reductive peaks 3.53,3.60,and 3.99 V(vs Li/Li+),respectively.It corresponds to lithium extraction and insertion in the stoichiometric ranges:x=0.0-0.5,0.5-1.0,1.0-2.0 in Li3-xV2(PO4)3,respectively.Among the three CV curves,the first cycle has the weakest peak intensities;as the cycle number increases,the peak intensities become stronger and the oxidative/reductive peaks are approaching to each other,promising a good cycle stability.The CV profile of LVP in the voltage range of 3.0-4.8 V is shown in Fig.8(B).There are four oxidation and three reduction peaks present in the CV curve.The oxidation peak at 4.58 V is the extraction of the third Li+ion associated with the phase transition process from LiV2(PO4)3to V2(PO4)3.From Fig.8(B),it can be seen that peakintensities gradually decrease with increasing cycle number,especially from the first to the second cycle.This change corresponds to a significant capacity fading charging to 4.8 V.


4 Conclusions
In this work,the electrochemical performance of the LVP/C cathode material,especially the high-rate performance,was greatly improved by using an organic/water as mixture solvent.The precursor of LVPwas prepared by a sol-gel method using PAA as the chelating agent and carbon source.Electrochemical tests show that the discharge capacity of the samples is increased by adding the organic solvents.The sample with adding 1,2-propylene glycol gave the best electrochemical performance.In the voltage range of 3.0-4.5 V,the discharge capacity is 132.89,128.59,125.07,119.99 mAh·g-1at 0.1C,1C,10C,20C,respectively.The specific capacity of sample D is as high as 120.14 mAh·g-1after 700 cycles at 10C rate.In the voltage range of 3.0-4.8 V,the capacity of the materials has a significant fading and poor cycle stability.
(1)Guo,X.D.;Zhong,B.H.;Liu,H.;Wu,D.Q.;Tang,Y.;Tang,H.J.Electrochem.Soc.2009,156,A787.
(2)Tang,Y.;Guo,X.D.;Zhong,B.H.;Liu,H.Inorganic Chemicals Industry 2010,42,12.[唐 艳,郭孝东,钟本和,刘 恒.无机盐工业,2010,42,12.]
(3)Wu,D.Q.;Zhong,B.H.;Xu,R.;Guo,X.D.;Liu,H.;Song,Y.;Tang,Y.New Chemical Materials 2010,38,37.[吴德桥,钟本和,徐 瑞,郭孝东,刘 恒,宋 杨,唐 艳.化工新型材料,2010,38,37.]
(4) Li,Y.Z.;Zhou,Z.;Gao,X.P.;Yan,J.Electrochimica Acta 2007,52,4922.
(5)Jiang,T.;Wei,Y.J.;Pan,W.C.;Li,Z.;Ming,X.;Chen,G.;Wang,C.Z.J.Alloy.Compd.2009,488,L26.
(6)Li,L.J.;Li,X.H.;Wang,Z.X.;Guo,H.J.;Wu,L.;Hao,Y.;Zheng,J.C.J.Alloy.Compd.2010,497,176.
(7)Guo,X.D.;Zhong,B.H.;Tang,Y.;Liu,H.;Wu,D.Q.;Yang,H.L.J.Chem.Eng.Chin.Univ.2009,23,701.[郭孝东,钟本和,唐 艳,刘 恒,吴德桥,杨海兰.高校化学工程学报,2009,23,701.]
(8)Guo,X.D.;Zhong,B.H.;Tang,Y.;Liao,W.H.;Wu,D.Q.Chemical Research and Application 2008,20,625. [郭孝东,钟本和,唐 艳,廖文华,吴德桥.化学研究与应用,2008,20,625.]
(9) Hou,C.P.;Yue,M.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2007,23,1954.[侯春平,岳 敏.物理化学学报,2007,23,1954.]
(10) Zheng,J.C.;Li,X.H.;Wang,Z.X.;Li,J.H.;Wu,L.;Li,L.J.;Guo,H.J.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.2009,25,1916.[郑俊超,李新海,王志兴,李金辉,伍 凌,李灵均,郭华军.物理化学学报,2009,25,1916.]
(11)Chen,Q.Q.;Wang,J.M.;Tang,Z.;He,W.C.;Shao,H.B.;Zhang,J.Q.Electrochimica Acta 2007,52,5251.
(12)Tan,L.;Luo,Z.M.;Liu,H.W.;Yu,Y.J.Alloy.Compd.2010,502,407.
(13) Jang,I.C.;Lim,H.H.;Lee,S.B.;Karthikeyan,K.;Aravindan,V.;Kang,K.S.;Yoon,W.S.;Cho,W.I.;Lee,Y.S.J.Alloy.Compd.2010,497,321.
(14)Wang,L.;Zhang,L.C.;Lieberwirth,L.;Xu,H.W.;Chen,C.H.Electrochem.Commun.2010,12,52.
(15)Wang,J.W.;Zhang,X.F.;Liu,J.;Yang,G.L.;Ge,Y.C.;Yu,Z.J.;Wang,R.S.;Pan,X.M.Electrochimica Acta 2010,55,6879.(16)Wang,L.J.;Zhou,X.C.;Guo,Y.L.J.Power Sources 2010,195,2844.
(17)Fu,P.;Zhao,Y.M.;Dong,Y.Z.;Hou,X.M.J.Phys.Chem.Solid 2010,71,394.
(18) Zhou,X.C.;Liu,Y.M.;Guo,Y.L.Electrochimica Acta 2009,54,2253.
(19) Jiang,T.;Pan,W.C.;Wang,J.;Bie,X.F.;Du,F.;Wei,Y.J.Electrochimica Acta 2010,55,3864.
(20) Huang,J.S.;Yang,L.;Liu,K.Y.;Tang,Y.F.J.Power Sources 2010,195,5013.
(21) Dai,C.S.;Wang,F.P.;Liu,J.T.;Wang,D.L.;Hu,X.G.Chin.J.Inorg.Chem.2008,24,381.[戴长松,王福平,刘静涛,王殿龙,胡信国.无机化学学报,2008,24,381.]
(22)Yang,G.;Liu,H.D.;Ji,H.M.;Chen,Z.Z.;Jiang,X.F.J.Power Sources 2010,195,5374.
(23)Yang,G.;Liu,H.D.;Ji,H.M.;Chen,Z.Z.;Jiang,X.F.Electrochimica Acta 2010,55,2951.
(24) Rui,X.H.;Li,C.;Chen,C.H.Electrochimica Acta 2009,54,3374.
(25) Saidi,M.Y.;Barker,J.;Huang,H.;Swoyer,J.L.;Adamson,G.J.Power Sources 2003,119-121,266.
(26)Fu,P.;Zhao,Y.;Dong,Y.;An,X.;Shen,G.Electrochimica Acta 2006,52,1003.
混合溶剂对溶胶-凝胶法制备的Li3V2(PO4)3/C高倍率性能的影响
唐 艳1钟本和1,*郭孝东1刘 恒2钟艳君1聂 翔1唐 红1
(1四川大学化学工程学院,成都610065;2四川大学材料科学与工程学院,成都610065)
以有机-水为混合溶剂,采用溶胶-凝胶法制备锂离子电池正极材料Li3V2(PO4)3/C,选取乙醇、乙二醇和1,2-丙二醇为有机溶剂,聚丙烯酸(PAA)为碳源和螯合剂.通过X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电镜(SEM)、恒流充放电以及循环伏安测试等方法,研究了产物的结构形貌及电化学性能.XRD测试结果表明所有溶剂制备的样品结晶良好,有机溶剂的加入不影响Li3V2(PO4)3材料的晶型结构.恒流充放电结果表明有机溶剂的加入改善了材料的电化学性能.以1,2-丙二醇-水为溶剂的样品电化学性能最好,在3.0-4.5 V电压范围内,0.1C(1C=150 mA·g-1)倍率首次放电比容量为132.89 mAh·g-1,10C倍率首次放电比容量达125.42 mAh·g-1,循环700周后容量保持率为95.79%,具有良好的倍率性能与循环性能;在3.0-4.8 V电压范围内倍率性能较差.扫描电镜结果表明混合溶剂制备的样品呈片状和针状,这种形状有利于锂离子的扩散,因此提高了材料的电化学性能.
锂离子电池; 正极材料;Li3V2(PO4)3; 溶胶-凝胶法; 混合溶剂
O646;O614.1;TM912.9
Received:January 3,2011;Revised:February 14,2011;Published on Web:March 7,2011.
∗Corresponding author.Email:Zhongbenhe@hotmail.com;Tel:+86-28-85406702;Fax:+86-28-85405517.
The project was supported by the National Science&Technology Pillar Program of China(2007BAQ01055).
国家科技支撑计划(2007BAQ01055)资助项目

