Therapeutic Efficacy Observation on Acupoint Sticking for Edema Due to Chronic Cardiac Failure
Cardiology Department No.1, Tongde Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang 310012, China
CLINICAL STUDY
Therapeutic Efficacy Observation on Acupoint Sticking for Edema Due to Chronic Cardiac Failure
Xu Jia-li
Cardiology Department No.1, Tongde Hospital of Zhejiang Province, Zhejiang 310012, China
Author:Xu Jia-li, bachelor of medicine, Lecturer.
E-mail: fgcaihui@163.com
Objective: To evaluate the therapeutic effect of acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs for edema due to chronic cardiac failure.
Methods: One hundred and seventy patients in conformity with the diagnostic criteria of edema due to chronic cardiac failure were randomly divided into two groups, 85 cases in each group. The observation group was treated by oral administration of diuretics plus acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs. The control group was treated just by oral administration of diuretics same as the observation group. The therapeutic effects were evaluated after continuous intervention for 14 d.
Results: The total effective rate was 90.6% in the observation group, remarkably higher than 67.1% in the control group. The difference of overall therapeutic effect between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.01).
Conclusion: The therapeutic effect of acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs plus oral administration of diuretics is better than simple oral administration of diuretics in treatment of edema due to chronic cardiac failure.
Drugs, Chinese Herbal; Acupoint Therapy; Acupoint Sticking Therapy; Heart Failure; Complications; Edema, Cardiac
Edema is commonly seen in chronic cardiac failure. Clinically, diuretics are often used to improve edema. Among them, Furosemide is one of the most commonly used diuretics[1]. However, diuretics alone cannot effectively alleviate edema in chronic cardiac failure. Under some circumstances, even the large dose of diuretics cannot eliminate edema, and edema is easy to recur after the stop of administration[2]. From 2013, we have tried to treat edema due to chronic cardiac failure with acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs in combination of diuretics. Now, the report is given as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
1.1.1 Diagnostic criteria of chronic cardiac failure[3]
Major criteria: Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, pulmonary rales, neck vein distension, acute pulmonary edema, S3 gallop, radiographic cardiomegaly, increased central venous pressure.
Minor criteria: Bilateral ankle edema, dyspnea on exertion, nocturnal cough, pleural effusion, hepatomegaly, tachycardia.
The diagnosis of chronic cardiac failure can be confirmed by the conformity with two items in the major criteria, or with one item in the major criteria and two items in the minor criteria.
1.1.2 Diagnosis and grading of edema
Edema is classified into four grades.
No edema.
Mild edema: Edema only in the eyelid, infraorbital soft tissue, subcutaneous tissue of tibia and ankle, mild indentation by finger pressure, quickly disappears.
Moderate edema: Visible edema in the loose tissues of the whole body, obvious or deep indentation by finger pressure, slowly disappears.
Severe edema: Severe edema in the whole body, tense and shining skin in the indentation area, and even fluid exudation.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
In conformity with the above diagnostic criteria; hospitalized patients at the age of 18-65, with mild edema; and voluntarily participate in the clinical trial.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those not met the above diagnostic and inclusion criteria; those with serious diseases of malignant tumors and respiratory failure; women in pregnancy and lactation; and those allergic to medications in this study.
1.4 Statistical methods
The SPSS 13.0 version software was used for statistical analysis. The rates were compared by Chi-square test.
1.5 General data
From 2013, 170 patients in conformity with the inclusion criteria of edema due to chronic cardiac failure were recruited and treated in our clinic. They were numbered by their visiting order and randomly divided into an observation group and a control group, 85 cases in each group. The differences in comparison of gender, age, duration and edema grade between the two groups were not statistically significant (allP>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).
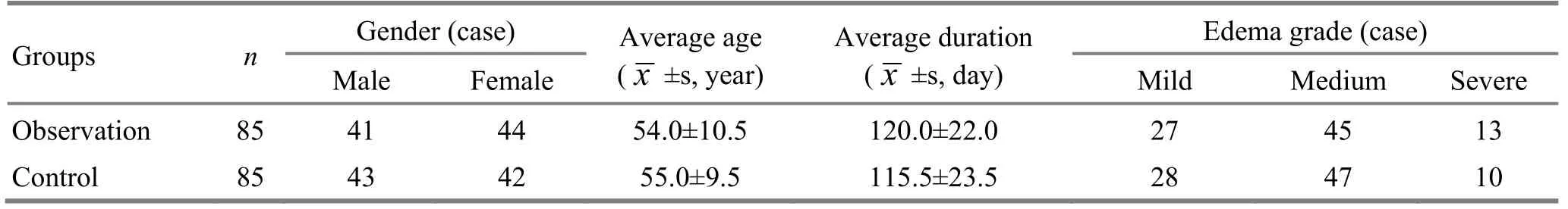
Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Therapeutic Methods
The original treatment with medications for cardiac failure was maintained for patients in the two groups. There was no statistical difference in administration of medications between the two groups.
2.1 Observation group
2.1.1 Acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs
Composition: Equal proportion ofFu Zi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) andFu Ling(Poria).
Usage: The above Chinese herbs were ground into powder and stored in the bottle. Each time, 12 g herbal powder was mixed with ginger juice into a paste, and then the paste was applied to Guanyuan (CV 4) of the patient. Then, the acupoint was covered with clean gauze and fixed with a medical plaster. The acupoint sticking was applied for one hour each session, once per day, for 14 d continuously.
2.1.2 Diuretics
Furosemide Tablets, 20 mg, once per day, oral administration.
2.2 Control group
The patients in the control group were treated with same diuretics as those used in the observation group, and the dose and usage were as same as those in the observation group.
3 Observation of Therapeutic Effects
3.1 Criteria of therapeutic effects
The criteria of the therapeutic effects were stipulated upon the changing situation of edema.
Remarkable effect: Edema disappeared. Effect: Edema was relieved. Failure: No change in edema.
3.2 Results
After 14-day treatments, the total effective rate was 90.6% in the observation group and 67.1% in the control group. The difference in the total effective rate between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.01), (Table 2).
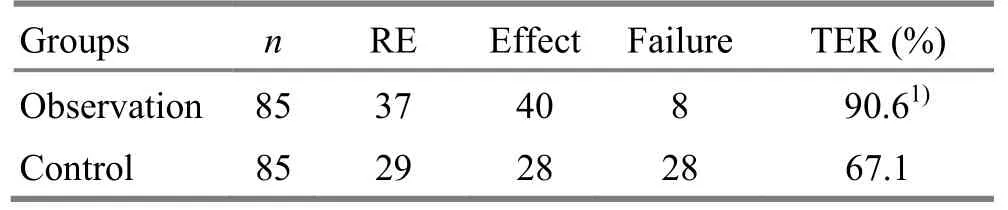
Table 2. Comparison of therapeutic effect between the two groups (case)
4 Discussion
Furosemide is the most commonly used diuretics for edema due to cardiac failure, and it can improve retention of water due to cardiac failure and reduce the cardiac burden[4]. But, it is found out in the clinical practice that the diuretic alone has limitation in treatment of edema due to chronic cardiac failure. Even, the large dose of diuretics is still unable to eliminate edema in some cases, and moreover, chronic cardiac failure accompanied by diuretic resistance is a commonly encountered clinical phenomenon[5]. Therefore, it is especially important to explore a safe and effective method for edema due to cardiac failure.
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that chronic cardiac failure belongs to the scope of ‘panting cough’and ‘edema’, and its pathogenesis is mostly related to deficiency in root cause and excess in symptoms. The deficiency in root cause is the key for breakout of chronic cardiac failure and also a main reason to cause dysfunction of water metabolism[6]. Considering from pathogenic characteristics, the acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs has been combined with Guanyuan (CV 4) based upon administration of routine medication from January of 2013. In the used Chinese herbal medicine,Fu Zi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata), in spicy and warm property, has the effects to restore yang for resuscitation, disperse cold and stop pain and has been proved to have the effect to reduce cardiac burden and strengthen the cardiac functions[7].Fu Ling(Poria) has the diuretic effect, and has been proven to be able to enhance the immunity, increase the cardiac output volume and alleviate water retention[8]. Ginger juice is in spicy property. When the powder ofFu Zi(Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata) andFu Ling(Poria) is prepared with ginger juice into paste and applied to the sick area, it is able to promote discharge of retained water fluid[9]. Guanyuan (CV 4) is the Front-Mu acupoint of the small intestine and a crossing acupoint of the Governor Vessel and three yin meridians of foot. The acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs can be used to replenish Yuan-Primordial qi greatly, to realize the effects to warm up yang, disperse cold, secrete water and diminish swelling[10].
It has been proven by the results of this study that edema has been remarkably improved in the observation group, and the difference in the total effective rate between the two groups was statistically significant, indicating that the therapeutic effect is better in the routine administration of medication plus the acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs than the singular administration of medication for edema due to cardiac failure. Moreover, the acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs is safe, effective, convenient and cheap, and will be able to provide an effective method for edema due to cardiac failure. Therefore, it needs to be further studied.
[1] Meng YM, Wang W, Ye HL. Research on Chinese medicine on chronic heart failure. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2012, 27(3): 270-274.
[2] Yu RH. Observation of Furosemide plus acupoint sticking with Chinese herbs for edema due to chronic cardiac failure. Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi, 2014, 23(11): 1222-1223.
[3] Kannel WB, D’Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Belanger AJ, Wilson PW, Levy D. Profile for estimating risk of heart failure. Arch Intern Med, 1999, 159(11): 1197-1204.
[4] Zhen YZ, Deng YD, Liu KS. Development of research in chronic heart failure accompanying diuretic resistance. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue, 2012, 15(4B): 1290-1292.
[5] Deng ZB, Wang Y. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine on chronic cardiac failure. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xinxueguan Zazhi, 2014, 12(3): 353-354.
[6] Yan L, Xue WH, Yin LJ.Yi Xin Tangclinical study of cardiac function in patients with chronic heart failure. Shiyong Zhongyi Neike Zazhi, 2012, 26(9): 1-2.
[7] Wu MP, Dong YR, Xiong XD, Zhao Y, Wang JL, Xing JD. Effects and dose-effect relationship ofAconit Lateralis Radix in Praeparataon ventricular remodeling in rats with heart failure following myocardial infarction. Zhonguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi, 2012, 18(16): 187-190.
[8] Chen G, Ai J, Xiao J. Clinical observation on promoting flow and alleviating water retention in heart failure of chronic pneumocardial disease. JETCM, 2013, 22(8): 1314-1316.
[9] Zuo WM, Shen GH. Observation of diuretic effect of Chinese herbs for congestive cardiac failure. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2010, 28(3): 71-72.
[10] Cai H, Mao JY, Wang Q, Cui XL, Wang HH, Wang XL, Liu HW, Li GZ, Zhang FL. Literature analysis of syndrome differentiation on traditional Chinese medicine of chronic heart failure. Sichuan Zhongyi, 2011, 29(7): 22-24.
Translator:Huang Guo-qi
R245.9
: A
Date:August 20, 2014
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2014年6期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2014年6期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Personal Experience on Palpation of the Spine
- Tuina plus Ultrasonic Therapy for Infantile Muscular Torticollis
- Efficacy Observation of Tuina Therapy for Fibromyalgia Syndrome
- Warm Needling Moxibustion at Zhongji (CV 3) and Zusanli (ST 36) for Urinary Retention after Gynecological Surgery
- Acupoint Massage in Relieving Pain after Ureteroscopic Holmium Laser Lithotripsy
- Therapeutic Efficacy Analysis of Balancing Yin-yang Manipulation for Post-stroke Upper Limb Spasticity
