附件
1 微生物群落结构分析
Meta-Mesh工作中心的微生物群落分析基于元基因组分析软件 Parallel-META[1],并提供可配置的分析参数。Parallel-META[1]由本文作者开发,使用HMM(Hidden Markov Model)[2]提取16S rRNA和18S rRNA的生物标记基因片段,然后将其映射到 GreenGenes[3]、RDP[4]、Silva[5]及 Oral Core[6],数据库中进行物种识别、注释、进化分析,并使用MetaSee[7]引擎进行分析数据的可视化。所有提供的可配置参数如表S1所示。
2 样本搜索
Meta-Mesh工作中心的样本搜索基于元基因组数据引擎Meta-Storms[8]来搜索与待查询样本群落结构相似的数据库样本。根据Meta-Storms[8]的 p-value测试我们建议大于等于 85%的相似度即可认为两个样本有着非常明显相似的结构。
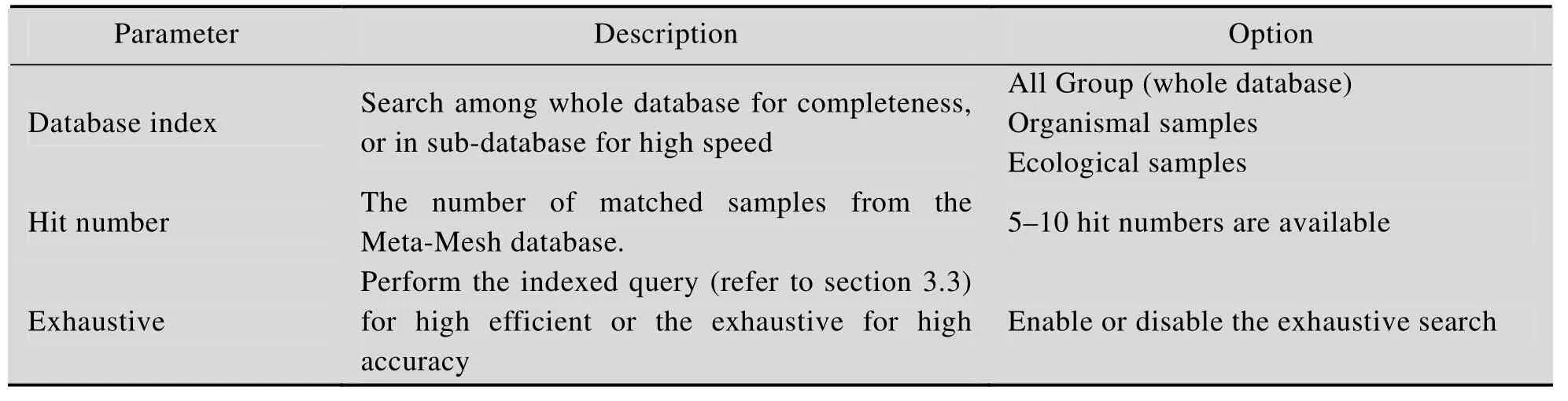
表S2 样本搜索的可配置参数Table S2 Configurable parameters of sample search
3 Meta-Mesh系统登录
Meta-Mesh系统中我们创建了系统共用帐号用来进行登录操作,登录用户名为“metamesh”,密码是“metamesh”。在此帐号下,名 为 “Human_associate_habitat”的 工 作 平 台(Workshop)即为正文部分所使用的人体微生物群落应用案例。其中保存了所有的原始数据、群落结构分析结、样本搜索以及样本比较的计算结果。

表S3 案例中数据库匹配样本的项目来源详细信息Table S3 Details of projects of matched samples in Meta-Mesh database for case studies
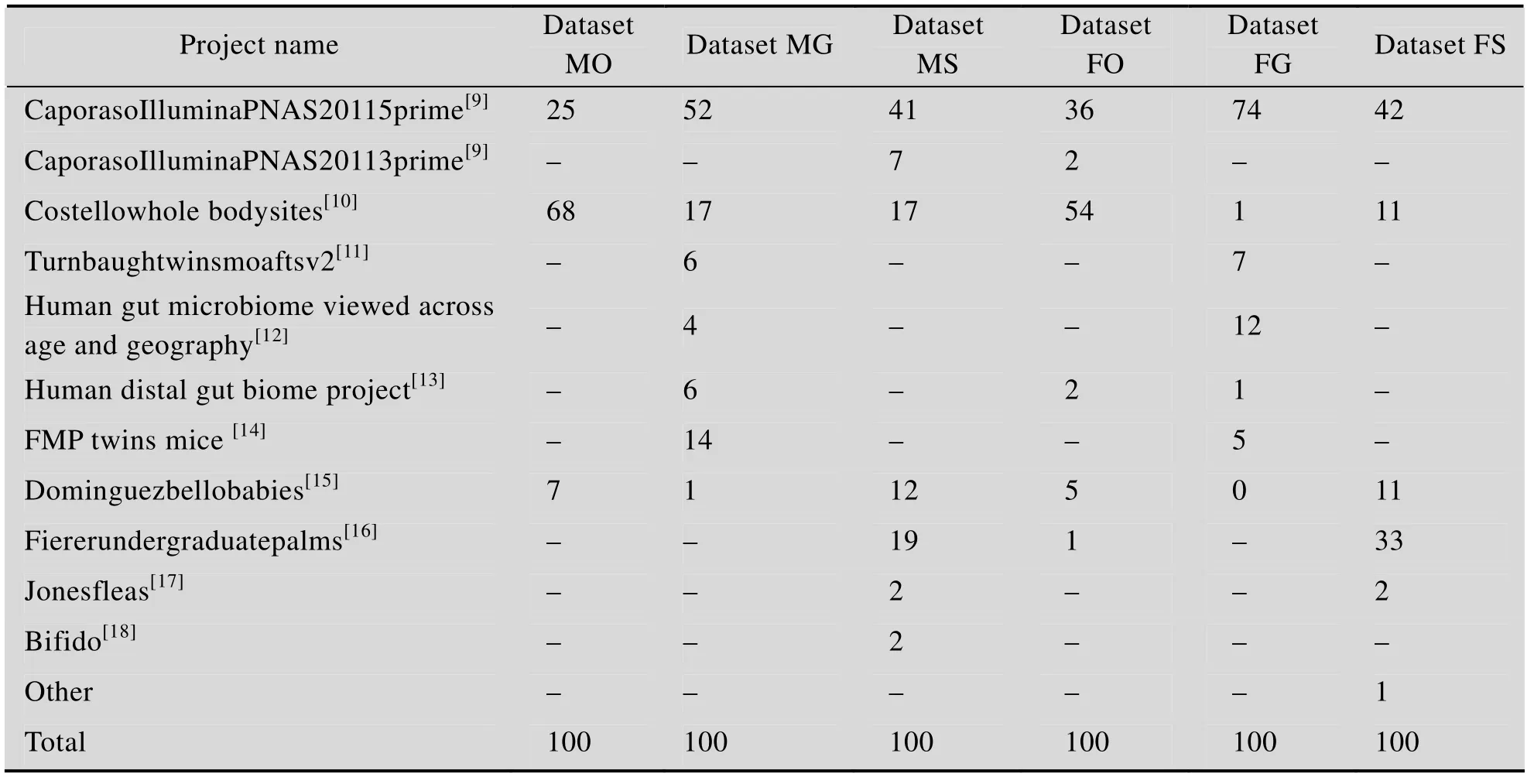
表S4 案例中数据库匹配样本的项目来源分布Table S4 Matched samples number of each project in Meta-Mesh database of case studies

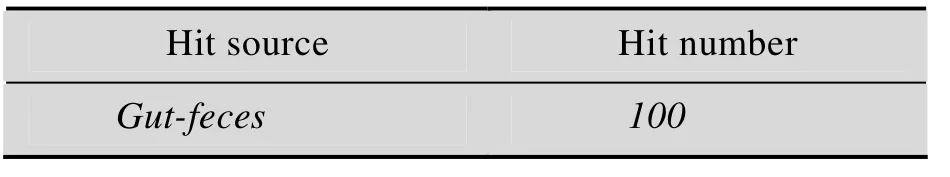
表 S5 案例样本的数据库搜索结果匹配详细信息(斜体所标注的匹配样本来源表示与案例中搜索样本来源相同,即正确匹配)Table S5 Details of search results of case studies. Hit sources marked in italic font indicate matched samples from the same source with the queries, which also means the correct hitsA. Dataset MO(query samples from male oral cavity)

B. Dataset FO (query samples form female oral cavity)

C. Dataset MG (query samples from male gut)
D. Dataset FG (query samples from female gut)

E. Datasets MS (query samples form male palm skin)
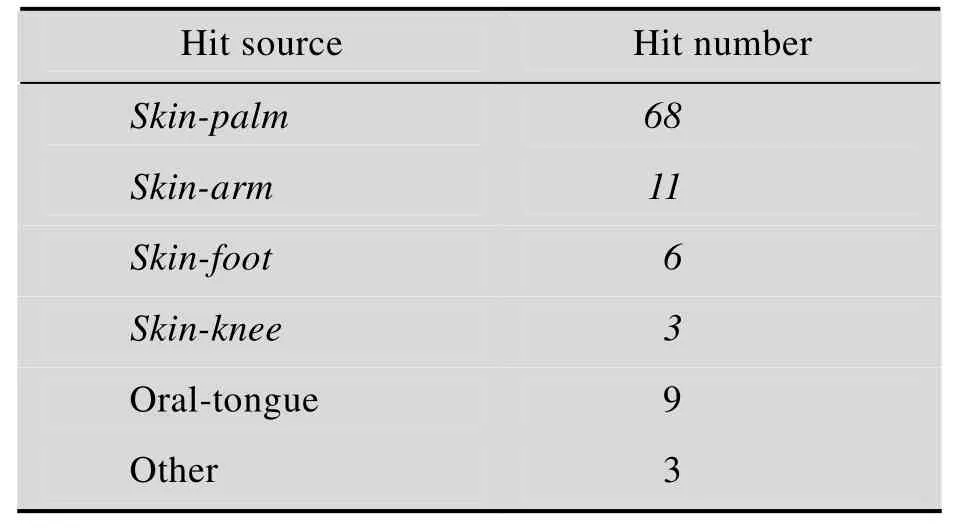
F. Dataset FS (query samples from female palm skin)
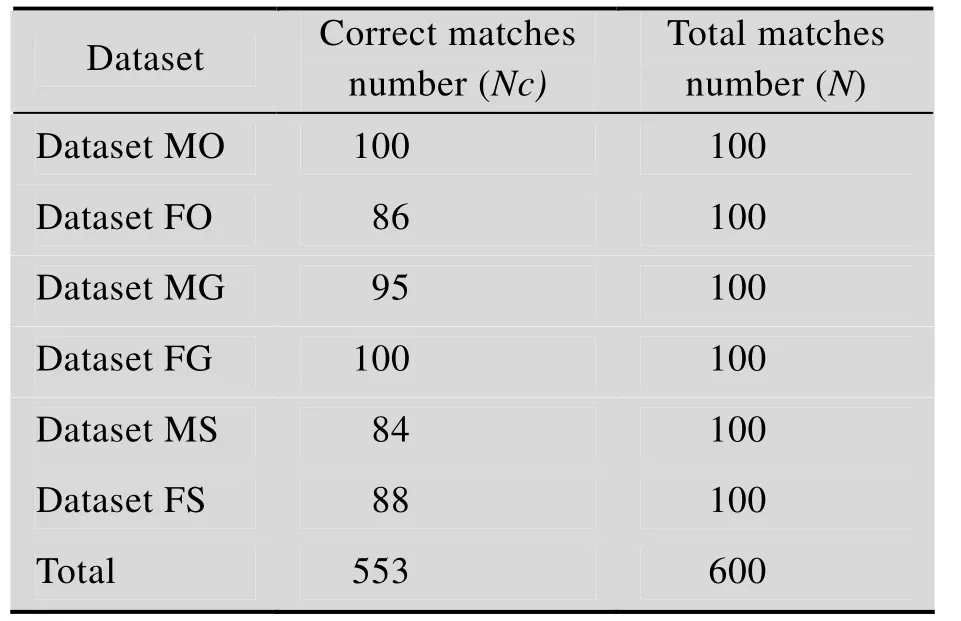
表S6 案例中样本的平均识别率Table S6 Overall average rate of correct identification of case studies
[1]Su X, Xu J, Ning K. Parallel-META: efficient metagenomic data analysis based on high-performance computation.BMC Systems Biology, 2012, 6(Suppl 1): S16.
[2]Mukherjee S, Mitra S. Hidden Markov Models,grammars, and biology: a tutorial.J Bioinform Comput Biol, 2005, 3(2): 491–526.
[3]DeSantis, TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, et al.Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB.Appl Environ Microbiol, 2006, 72(7): 5069–5072.
[4]Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis.Nucleic Acids Res, 2009, 37(Database issue): D141–145.
[5]Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, et al. SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB.Nucleic Acids Res, 2007,35(21): 7188–7196.
[6]Griffen, AL, Beall CJ, Firestone ND, et al. CORE:a phylogenetically-curated 16S rDNA database of the core oral microbiome.PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(4):e19051.
[7]Song B, Su X, Xu J, et al.MetaSee: An Interactive and Extendable Visualization Toolbox for Metagenomic Sample Analysis and Comparison.PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(11): e48998.
[8]Su X, Xu J, Ning K. Meta-Storms: Efficient Search for Similar Microbial Communities Based on a Novel Indexing Scheme and Similarity Score for Metagenomic Data.Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(19):2493–2501..
[9]Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, et al.Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 108: 4516–4522.
[10]Costello EK, Lauber CL, Hamady M, et al.Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time.Science, 2009,326(5960): 1694–1697.
[11]Turnbaugh, PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins.Nature, 2009, 457(7228): 480–484.
[12]Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography.Nature, 2012, 486(7402): 222–227.
[13]Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome.Science, 2006, 312(5778): 1355–1359.
[14]McNulty NP, Yatsunenko T, Hsiao A, et al. The impact of a consortium of fermented milk strains on the gut microbiome of gnotobiotic mice and monozygotic twins.Sci Transl Med, 2011, 3(106):106ra106.
[15]Dominguez-Bello MG, Costello EK, Contreras M,et al. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107(26): 11971–11975.
[16]Fierer N, Hamady M, Lauber CL, et al. The influence of sex, handedness, and washing on the diversity of hand surface bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(46): 17994–17999.
[17]Jones RT, Knight R, and Martin AP. Bacterial communities of disease vectors sampled across time, space, and species.ISME J, 2010, 4(2):223–231.
[18]Sim K, Cox MJ, Wopereis H, et al. Improved detection of bifidobacteria with optimised 16S rRNA-gene based pyrosequencing.PLoS ONE,2012, 7(3): e32543.

