攀枝花岩体钛铁矿成分特征及其成因意义*
郑文勤 邓宇峰 宋谢炎** 陈列锰 于宋月 周国富 刘世荣 向建新
1.中国科学院地球化学研究所,矿床地球化学国家重点实验室,贵阳 550002
2.合肥工业大学资源与环境工程学院,合肥 230009
3.攀钢集团矿业有限公司,攀枝花 617000
钛铁矿是火成侵入岩体的主要氧化物之一,尽管常常是以副矿物的形式出现,但具有重要的成因指示意义。在镁铁-超镁铁侵入体中,钛铁矿和磁铁矿都是主要的氧化物矿物,甚至形成钒钛磁铁矿矿床。钒钛磁铁矿成矿主要产于大型层状岩体或斜长岩套,前者如著名的南非Bushveld岩体、格陵兰Skaergaard岩体和加拿大Sept Iles岩体等 (Klemm et al.,1985;Reynold,1985;Hunter and Sparks,1987;Toplis and Carrol,1996;Cawthorn and Ashwal,2009;Namur et al.,2010),后者如著名的挪威Tellnes铁钛矿床 (Wilmart et al.,1989;Charlier et al.,2006,2007)。钛铁矿不仅是钒钛磁铁矿矿床的主要氧化物矿物,相对于磁铁矿而言,其固相线以下的固溶体分离现象较弱,能够更好地保留其结晶时的成分特点,因此,可以为矿床成因探讨提供重要信息。
峨眉大火成岩省内带是世界上最大的钒钛磁铁矿聚集区,巨厚的钒钛磁铁矿矿层赋存于几个大型镁铁-超镁铁层状岩体的中下部,钛铁矿是仅次于磁铁矿的主要矿石矿物。近年来,不少作者对这些矿床的磁铁矿成分及其成因意义进行了较多的探讨,例如Pang et al.(2008,2009)和Song et al.(2013)在攀枝花岩体及其钒钛磁铁矿矿床的研究中,都从磁铁矿的成分中获得了重要的成因信息,但对钛铁矿成分的系统数据较少,成因意义的关注不够。作者选择开采最早、剥露最充分的攀枝花岩体,对其中、下部岩相带进行了系统采样和钛铁矿成分的电子探针分析,试图阐明钛铁矿成分的变化规律及其与分离结晶过程及岩浆补充的关系。
1 地质背景
峨眉大火成岩省(ELIP)指峨眉山玄武岩所覆盖的扬子板块西部的广大区域。近年来的研究表明峨眉火成岩省的西界应为青藏高原东缘金沙江缝合带(Song et al.,2004),向东延伸到广西北部(范蔚茗等,2004),向南扩展至越南北部“Song Da”地块(Hanski et al.,2004)。考虑到中新生代以来松潘-甘孜造山带的剧烈褶皱、向东推覆和横向收缩,峨眉火成岩省当时的面积应该超过50万平方千米(Song et al.,2004),为晚二叠世地幔柱活动产物(Chung and Jahn,1995;Xu et al.,2001;Zhang et al.,2006,2008,2009)。
根据峨眉山玄武岩系厚度、成分、岩性变化、以及侵入岩的岩石组合的规律性变化可以将峨眉火成岩省具分为内带和外带(图1)。内带玄武岩厚度超过2000m,在云南宾川一带最厚达5000m;而在ELIP的边缘,玄武岩减薄为数十至百余米。尽管峨眉大火成岩省的喷出岩以高钛玄武岩为主,但在内带玄武岩系的中下部可以发现多层低Ti玄武岩,而在外带的玄武岩系中低钛玄武岩较少(徐义刚和钟孙霖,2001;Song et al.,2001,2009;Xu et al.,2001,2004;Zhou et al.,2002;徐义刚等,2003;肖龙等,2003;He et al.,2003;Zhong et al.,2003;郝艳丽等,2004;Xiao et al.,2004;侯增谦等,2005;宋谢炎等,2005)。由于中新生代以来的隆升,内带攀西地区峨眉山玄武岩往往因后期强烈剥蚀而缺失,从而使含V-Ti磁铁矿矿床的大型层状岩体和含Ni-Cu-(PGE)硫化物矿床的小型镁铁-超镁铁岩体得以出露;外带则仅发现了含铜镍硫化物矿床或矿化的镁铁-超镁铁杂岩体,如火成岩省北缘四川丹巴地区和南缘云南金平-越南北部地区(图1)(王登红,1998;胡瑞忠等,2005;宋谢炎等,2005)。
大型-超大型的V-Ti磁铁矿矿床只出现在峨眉火成岩省内带,从北向南包括太和、白马、新街、红格和攀枝花(图1),这些岩体沿攀枝花断裂、磨盘山-元谋断裂和安宁河断裂等南北向深断裂分布,如:攀枝花岩体位于攀枝花断裂东侧。多数岩体侵入于新元古代(震旦系灯影组)大理岩、云母石英片岩中(如:攀枝花和红格岩体)或古生代砂岩中(如:白马岩体),个别岩体侵入峨眉山玄武岩中(如新街岩体)。近年来的锆石U-Pb年代学研究表明这些岩体形成于~260Ma(Zhou et al.,2002,2005;Zhong and Zhu,2006,Hou et al.,2012,2013),是峨眉山大火成岩省的重要组成部分(Zhang et al.,2009,2014)。其中钒钛磁铁矿矿石总储量超过100亿吨,V2O5储量约1580万吨、TiO2约8.7亿吨,V和Ti分别占世界储量的11.6%和35.17%,占我国总储量的62.6%和90.54%(攀西地质大队,1984)。
2 攀枝花岩体基本地质特征
如图2所示,攀枝花岩体侵入于新元古代白云质大理岩、片麻岩和片岩中,倾向北西,倾角约40°~60°,岩体顶部与三叠系陆相碎屑岩呈断层接触(攀西地质大队,1984)。该岩体长约19km,岩体最厚处达2000余米,被后期断层分为7个矿段(图2)。岩体的边缘相厚度介于几米至数十米,

图1 峨眉大火成岩省玄武岩以及各种岩浆矿床分布图(据攀西地质大队,1984① 攀西地质大队.1984.攀枝花-西昌地区钒钛磁铁矿共生矿成矿规律与预测研究报告;宋谢炎等,2005;Song et al.,2009)三个横贯内带近南北向断裂从西向东依次是攀枝花断裂、磨盘山-元谋断裂和安宁河断裂Fig.1 Distribution of the basalts and magmatic deposits in Emeishan large ignous province(after Song et al.,2004,2009)The three N-S trending faults crossing the central zone are the Panzhihua,Mopanshan-Yuanmou and Anninghe,respectively from the west to east

图2 攀枝花岩体地质简图(据攀西地质大队,1984;Song et al.,2013)Fig.2 Simplified geological sketch of the Panzhihua intrusion(after Song et al.,2013)
根据Song et al.(2013)的观察和详细描述,下部岩相带由5个旋回组成(I-V),除旋回I外,每个旋回都由下部的块状氧化物矿层和上部的中粗粒磁铁矿辉长岩构成,其中,旋回II和V块状矿层厚度达40~60m(图3)。块状矿石含有70%~90%的自形和半自形磁铁矿,3% ~15%的半自形钛铁矿和小于10%的橄榄石、单斜辉石和斜长石;磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值介于5~24,多大于10(表1、图3)。磁铁矿辉长岩含40%~70%的斜长石和单斜辉石,半自形磁铁矿及钛铁矿的含量最高达60%,橄榄石<10%;磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值介于4~11,多小于6。每一旋回从下至上不仅铁钛氧化物的含量减少,磁铁矿/钛铁矿的比值也显著降低。磁铁矿中钛铁矿出溶叶片以及钛铁矿中磁铁矿出溶叶片发育,单斜辉石席列构造非常发育(图4a,b),斜长石和单斜辉石往往定向排列显示韵律层理(Pang et al.,2008;Song et al.,2013)。岩石
结构特征的研究表明每个旋回的下部铁钛氧化物的结晶往往较早,稍晚于橄榄石,早于或与斜长石和单斜辉石同时发生,而在旋回的上部,铁钛氧化物的结晶常晚于硅酸盐矿物;中下部岩相带磁铁矿结晶稍早于钛铁矿,而上部岩相带钛铁矿结晶稍早于磁铁矿;块状和稠密浸染状矿石中的硅酸盐矿物常会因新岩浆的补充而发生一定程度的熔蚀(图4)(Song et al.,2013)。

表1 攀枝花岩体磁铁矿和钛铁矿含量统计Table 1 Modal abundances of magnetite and ilmenite of the Panzhihua intrusion

图3 攀枝花岩体中、下岩相带氧化物含量、比值及钛铁矿成分柱状图Fig.3 Stratigraphic composition variations of the ilmenite of the Lower and Middle zones of the Panzhihua intrusion

图4 攀枝花矿床典型矿石结构(a)-块状矿石,显示高的磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值,磁铁矿呈半自形粒状,钛铁矿呈半自形或他形粒状或填隙状,反光显微镜照片;(b)-稠密浸染状矿石中橄榄石和单斜辉石边缘不完整,说明受到一定程度的熔蚀,单斜辉石的席列构造发育.Ol-橄榄石;Cpx-单斜辉石;Oxieds-铁钛化物氧;Mt-磁铁矿;Ilm-钛铁矿Fig.4 Typical lithological structures of the Panzhihua intrusion(a)-massive ore shows high magnetite/ilmenite ratio and subhedral magnetite granins and subhedral or anhedral or interstitial ilmenite grains;(b)-olivine and clinopyroxene grains with melted margins in the densely disseminated ore and the clinopyroxene with magnetite exsolution lamina.Ol-olivine;Cpx-clinopyroxene;Oxieds-Fe-Ti oxides;Mt-magnetite;Ilm-ilmenite
中部岩相带有6个旋回(VI-XI),每个旋回由中粗粒磁铁矿辉长岩和辉长岩构成(图3)。磁铁矿辉长岩的特征与下部岩相带的同类岩石相似,但氧化物中钛铁矿的比例明显升高,磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值多介于1~6(表1、图3)。辉长岩则以较低的铁钛氧化物含量(10% ~20%),以及更高的单斜辉石(30% ~40%)和斜长石(40% ~50%)为特征,几乎不含橄榄石,韵律层理也非常发育。上部岩相带由中粗粒磷灰石辉长岩构成,该岩相带以磷灰石含量的突然增高(3% ~5%),铁钛氧化物含量一般低于10%,岩性旋回和韵律层理均不发育,单斜辉石无铁钛氧化物出溶为突出特点(图3)(Song et al.,2013)。
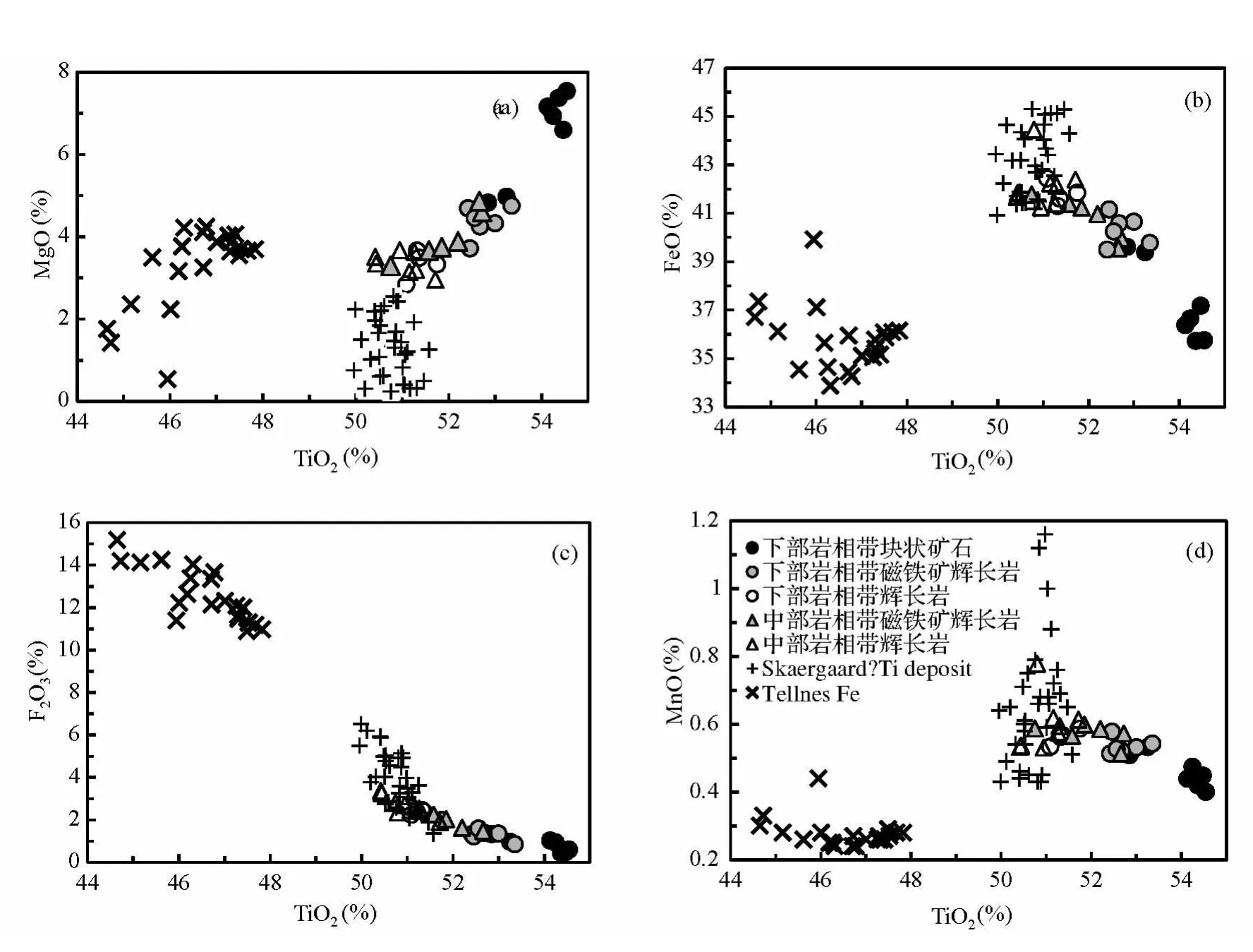
图5 攀枝花岩体钛铁矿TiO2与其它氧化物相关图Skaergaard岩体和挪威Tellnes铁钛矿床的钛铁矿成分数据分布据Jang and Naslund,2003和Charlier et al.,2007Fig.5 Binary plots of major oxide elements versus TiO2of ilmenite from the Panzhihua intrusionData of the ilmenite of the Tellnes deposit and Skaergaard intrusion are from Jang and Naslund,2003 and Charlier et al.,2007,respectively

表2 攀枝花岩体钛铁矿电子探针成分平均值(wt%)Table 2 Average composition of major elements of ilmenite in the Panzhihua intrusion(wt%)
3 分析方法及结果
本次研究样品采自攀枝花岩体的朱家包包矿段,采样路径如图2所示。由于上部岩相带氧化物较少,仅对中、下部岩相带的钛铁矿进行成分分析。钛铁矿的氧化物成分利用中国科学院地球化学研究所矿床地球化学国家重点实验室的EPMA-1600型电子探针仪分析,束斑直径为5μm,电流为25nA,加速电压为25kV。分析误差小于5%,分析结果列于表2。
如图5所示,下部岩相带块状矿石中的钛铁矿具有最高的MgO和TiO2含量,最低的FeO、Fe2O3和MnO含量;无论下部还是中部岩相带,其磁铁矿辉长岩中钛铁矿这些氧化物的含量都基本相同,而辉长岩中钛铁矿具有最低的MgO和TiO2含量及最高的FeO含量。同时,这些岩石和矿石中钛铁矿的TiO2都与MgO呈正比,而与FeO和Fe2O3及MnO呈反比。图6显示攀枝花岩体中、下部岩相带中钛铁矿的FeO含量随MnO的增加而增加,随MgO的增加而降低,而与Fe2O3的关系不明显。
此外,钛铁矿中的TiO2和MgO含量与磁铁矿中这两种氧化物的含量基本呈正比,而与Al2O3呈反比(图7)。块状矿石的钛铁矿和磁铁矿都具有较高的MgO和TiO2含量,辉长岩中这两种矿物的MgO和TiO2均较低。另一方面,钛铁矿的MgO含量更高,而Al2O3含量更低(图7b,c),这说明铁钛氧化物结晶时Mg更趋向于进入钛铁矿,而Al则趋于进入磁铁矿。此外,钛铁矿MgO的含量与同一样品中橄榄石的镁橄榄石牌号(Fo)呈正比(图8)。

图6 攀枝花岩体钛铁矿FeO与MnO(a)、Fe2O3(b)和MgO(c)的相关图Skaergaard岩体和挪威Tellnes铁钛矿床的钛铁矿成分数据分布据Jang and Naslund,2003和Charlier et al.,2007Fig.6 Binary plots of MnO(a),Fe2O3(b)and MgO(c)vs.FeOof ilmenite from the Panzhihua intrusionData of the ilmenite of the Tellnes deposit and Skaergaard intrusion are from Jang and Naslund(2003)and Charlier et al.(2007),respectively

图7 攀枝花岩体钛铁矿和磁铁矿的TiO2(a)、MgO(b)和Al2O3(c)的相关图(磁铁矿成分据Song et al.,2013)Fig.7 Binary plots of TiO2(a),MgO(b)and Al2O3(c)of ilmenite and magnetite from the Panzhihua intrusion(data of the magnetite after Song et al.,2013)
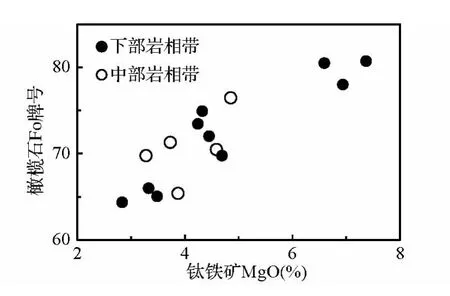
图8 钛铁矿MgO含量与橄榄石Fo牌号的关系橄榄石成分据张晓琪等,2011;图中橄榄石和钛铁矿的数据均为同一样品中若干电子探针点的平均值Fig.8 Binary plots of MgO of ilmenite vs.Fo of olivine from the Panzhihua intrusionData of the olivine component are from Zhang et al.,2011;the data of the olivine and ilmenite are the averages of several grains of these minerals in the same sample
4 钛铁矿成因意义分析
4.1 成矿背景及母岩浆成分特点
图5和图6的投影表明,攀枝花岩体和格陵兰Skaergaard岩体的钛铁矿氧化物成分的变化具有相似的趋势,暗示在成因上的相似性(Jang and Naslund,2003)。研究表明Skaergaard岩体是冰岛热点地幔柱幔源岩浆活动的产物(Tegner et al.,1998),而攀枝花等层状岩体与峨眉地幔柱的活动密切相关(Song et al.,2001;Xu et al.,2001,2004;侯增谦等,2005)。图5和图6的对比表明与地幔柱有关的幔源岩浆演化特征的相似性也反映在钛铁矿成分的变化中。另一方面,与挪威斜长岩套有关的Tellnes铁钛矿床钛铁矿的TiO2含量远低于攀枝花岩体和Skaergaard岩体的钛铁矿,同时,其 MgO、FeO和 MnO含量也相对较低(图5、图6),Charlier et al.(2006,2007)认为Tellnes岩体的母岩浆是特殊的富铁钛的闪长质岩浆,钛铁矿和斜长石(钙长石比例An牌号小于50,低于攀枝花岩体斜长石的An牌号=49~66,张晓琪等,2011)是主要堆积矿物,结晶早于磁铁矿,但由于母岩浆基性程度很低,钛铁矿不仅具有低的MgO含量,其TiO2含量也较低,而Fe2O3含量非常高(图5、图6)。这不仅说明Tellnes岩体母岩浆的成分与攀枝花岩体和Skaergaard岩体有很大差异,也说明母岩浆成分对岩浆的结晶顺序和矿物的成分都有决定性影响。一般认为斜长岩套形成与碰撞后伸展背景下的地幔或下地壳熔融有关,其岩浆的起源和演化过程及其成分特点与地幔柱背景有很大差异。攀枝花和Skaergaard岩体的钛铁矿与Tellnes铁钛矿床钛铁矿成分的差异,说明不同构造背景镁铁-超镁铁岩浆活动形成的铁钛氧化物矿床,其母岩浆成分有较明显的区别。
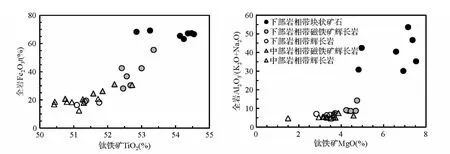
图9 攀枝花岩体钛铁矿TiO2-全岩Fe2O3(a)和钛铁矿MgO-全岩Al2O3/(K2O+Na2O)(b)的相关图(全岩成分据Song et al.,2013)Fig.9 Binary plots TiO2of ilmenite vs.Fe2O3of whole rocks(a)and MgO of ilmenite vs.Al2O3/(K2O+Na2O)of whole rocks(b)from the Panzhihua intrusion(data of the component of whole rocks after Song et al.,2013)
另一方面,尽管攀枝花岩体和Skaergaard岩体的钛铁矿氧化物成分的变化具有相似的趋势,但前者的TiO2和MgO含量显著高于后者,而FeO和Fe2O3的含量较低。研究表明Skaergaard岩体的氧化物包括钛铁矿结晶明显晚于硅酸盐矿物,因此,富铁钛氧化物层产于岩体上部,说明钛铁矿的结晶发生于分离结晶作用的晚期阶段(Jang et al.,2001)。攀枝花岩体钒钛磁铁矿矿层产于岩体中、下部岩相带的宏观现象、钛铁矿较高的MgO含量以及钛铁矿MgO含量与橄榄石Fo牌号的正相关关系,都说明铁钛氧化物的结晶发生于分离结晶较早的阶段,而其较高的TiO2含量表明攀枝花岩体的母岩浆是一种特殊的富铁钛的岩浆。这与Song et al.(2013)的研究结果相吻合,他们的研究表明攀枝花岩体的母岩浆是由高钛苦橄质岩浆经深部岩浆房硅酸盐矿物分离结晶产生的独特的富铁钛的岩浆。攀枝花岩体钛铁矿较低的FeO和Fe2O3含量与磁铁矿结晶稍早于钛铁矿有关。
4.2 钛铁矿分离结晶特点
图4表明尽管中、下部岩相带的每个旋回从下至上钛铁矿含量的变化较为复杂,但磁铁矿含量及磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值总体上是逐渐降低的。每个旋回从块状矿石或磁铁矿辉长岩到辉长岩,钛铁矿的TiO2和MgO含量有规律地逐渐降低,而FeO和Fe2O3含量则逐渐增高。尽管岩石结构关系及MELTs计算都表明攀枝花岩体钛铁矿开始结晶晚于橄榄石和磁铁矿(Song et al.,2013),但钛铁矿MgO含量与磁铁矿MgO含量及橄榄石Fo牌号的正相关关系(图7、图8)都表明,它们结晶的温度区间是有较大重叠的。块状矿石中个别磁铁矿样品较低的MgO含量可能与磁铁矿与橄榄石之间的Fe-Mg交换有关。钛铁矿的MgO含量与全岩Al2O3/(K2O+Na2O)比值的正相关关系指示钛铁矿的MgO含量与斜长石的An牌号呈正相关关系,也表明钛铁矿结晶较早(图9b)。这些特点反映出每个旋回的岩浆分异过程中氧化物结晶较早,随着氧化物的结晶,岩浆中TiO2和MgO的含量逐渐降低。每个旋回从下至上磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值逐渐降低的特点(图3)表明分离结晶过程中钛铁矿的结晶比例逐渐增高。
4.3 多次岩浆补充在钛铁矿成分上的反映
中、下部岩相带每个旋回钛铁矿成分的韵律式变化,特别是每个旋回底部钛铁矿成分的相似性(图2),都暗示旋回的形成与新的岩浆的周期性补充有着密切的关系。下部岩相带每个旋回底部钛铁矿更高的TiO2和MgO含量和较低的FeO含量,特别是块状矿石中钛铁矿和磁铁矿很高的MgO含量(图3、图5、表2),表明与中部岩相带相比,下部岩相带母岩浆演化程度更低。结合块状矿石极高的铁钛氧化物含量以及极高的磁铁矿/钛铁矿比值的特征(图3),下部岩相带母岩浆还具有更高的TiO2、FeO和Fe2O3含量。此外,II和V旋回底部块状矿石中钛铁矿较稳定的成分还暗示富铁钛岩浆非常频繁的补充为巨厚块状矿石层的形成提供了充足的物质条件。
5 结论
攀枝花岩体中、下部岩相带钛铁矿成分特征和变化说明每个旋回从下至上钛铁矿的成分具有规律性变化,这种规律性变化说明每个旋回可以代表一次比较明显的岩浆补充。尽管每次有新岩浆的补充,钛铁矿和磁铁矿及橄榄石都是结晶较早的矿物。此外,通过与挪威Tellnes铁钛矿床的钛铁矿成分比较说明地幔柱成因的幔源岩浆中结晶出的钛铁矿成分与元古宙斜长岩套中钛铁矿的成分有显著区别。因此,钛铁矿的成分对于分析岩体形成的地质背景以及岩浆结晶过程有重要的指示意义。
致谢 攀枝花集团有限公司张加飞高工等对于野外工作给予了大力支持和协助;戚华文研究员和官建祥参与了部分采样和测试工作;审稿人提出了宝贵的修改意见;在此一并感谢。
Cawthorn RG and Ashwal LD.2009.Origin of anorthosite and magnetitite layers in the Bushveld Complex,constrained by major element compositions of plagioclase.Journal of Petrology,50(9):1607-1637
Charlier B,Duchesne JC and Vander Auwera J.2006.Magma chamber processes in the Tellnes ilmenite deposit(Rogaland Anorthosite Province,SW Norway)and the formation of Fe-Ti ores in massiftype anorthosites.Chemical Geology,234(3-4):264-290
Charlier B,Skår ∅,Korneliussen A,Duchesne JC and Auwera JV.2007.Ilmenite composition in the Tellnes Fe-Ti deposit, SW Norway:Fractionalcrystallization,postcumulus evolution and ilmenite-zircon relation.Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology,154(2):119-134
ChungSL andJahnBM.1995. Plume-lithosphereinteractionin generation of the Emeishan flood basalts at the Permian-Triassic boundary.Geology,23(10):889-892
Fan WM,Wang YJ,Peng TP,Miao LC and Guo F.2004.Ar-Ar and UPb geochronology of Late Paleozoie basahs in western Guangxi and its constraints on the eruption age of Emeishan basalt magmatism.Chinese Science Bulletin,49(18):1892-1900(in Chinese)
Hanski E,Walker RJ,Huhma H,Polyakov GV,Balykin PV,Ngo TT and Phuong NT.2004.Origin of the Permian-Triassic komatiites,northwestern Vietnam.Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology,147(4):453-469
Hao YL,Zhang ZC,Wang FS and Mahoney JJ.2004.Petrogenesis of high-Ti and low-Ti basalts from the Emeishan Large Igneous Province.Geological Review,50(6):587-592(in Chinese with English abstract)
He B,Xu YG,Chung SL,Xiao L and Wang YM.2003.Sedimentary evidence for a rapid,kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,213(3-4):391-405
Hou T,Zhang ZC,Pirajno F.2012.A new metallogenic model of the Panzhihua giant V-Ti iron oxide deposit in the Emeishan large province:Based on high-Mg olivine-bearing wehrlites and new field evidence.International Geology Review,54(15):1721-1745
Hou T,Zhang ZC,Encarnacion J,Santosh M and Sun Y.2013.The role recycled oceanic crust in magmatism and metallogenesis:Os-Sr-Nd isotpes,U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of picritic dykes in the Panzhihua giant Fe-Ti oxide deposit,central Emeishan large igneous province.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,165(4):805-822
Hou ZQ,Lu JR and Lin SZ.2005.The axial zone consisting of pyrolite and eclogite in the Emei mantle plume:Major,trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotope evidence.Acta Geologica Sinica,79(2):200-219(in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu RZ, Tao Y, Zhong H, Huang ZL andZhangZW.2005.Mineralization systems of a mantle plume:A case study from the Emeishan igneousprovince, SouthwestChina. Earth Science Frontiers,12(1):42-54(in Chinese with English abstract)
Hunter RH and Sparks RSJ.1987.The differentiation of the Skaergaard intrusion.Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology,95(4):451-461
Jang YD,Naslund HR and McBirney AR.2001.The differentiation trend ofthe Skaergaard Intrusion and the timing of magnetite crystallization:Iron enrichmentrevisited.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,189(3-4):189-196
Jang YD and Naslund HR.2003.Major and trace element variation in ilmenite in the Skaergaard intrusion:Petrologic implications.Chemical Geology,193(1-2):109-125
Klemm DD,Henckel J,Dehm RM and von Gruenewaldt G.1985.The geochemistry of titanomagnetite in magnetite layers and their host rocks of the Eastern Bushveld Complex.Economic Geology,80(4):1075-1088
Namur O,Charlier B,Toplis J,Higgins MD,Liegeois JP and Auwera JV.2010.Crystallization sequence and magma chamber processes in the ferrobasaltic septiles layered intrusion, Canada. Journal of Petrology,51(6):1203-1236
Pang KN,Zhou MF,Lindsley D,Zhao DG and Malpas J.2008.Origin of Fe-Ti Oxide ores in mafic intrusions:Evidence from the Panzhihua Intrusion,SW China.Journal of Petrology,49(2):295-313
Pang KN,Li CS,Zhou MF and Ripley EM.2009.Mineral compositional constraints on petrogenesis and oxide ore genesis of the Late Permian Panzhihua layered gabbroic intrusion,SW China.Lithos,110(1-4):199-214
Reynolds IM.1985.The nature and origin of titaniferous magnetiterich layers in the Upper Zone of the Bushveld complex:A review and synthesis.Economic Geology,80(4):1089-1108
Song XY,Zhou MF,Hou ZQ,Cao ZM,Wang YL and Li YG.2001.Geochemical constraints on the mantle source of the Upper Permian Emeishan continental flood basalts, southwestern China.International Geology Review,43(3):213-225
Song XY,Zhou MF,Cao ZM and Robinson PT.2004.Late Permian rifting of the South China Craton caused by the Emeishan mantle plume?Journal of the Geological Society London,161(5):773-781
Song XY,Zhang CJ,Hu RZ,Zhong H,Zhou MF,Ma RZ and Li YG.2005.Genetic links of magmatic deposits in the Emeishan large igneous province with dynamics of mantle plume.Journalof Mineralogy and Petrology,25(4):35-44(in Chinese with English abstract)
Song XY,Keays RR,Long X,Qi HW and Ihlenfeld C.2009.Platinumgroup element geochemistry of the continental flood basalts in the central Emeisihan large igneous province,SW China.Chemical Geology,262(3-4):246-261
Song XY,Qi HW,Hu RZ,Chen LM,Yu SY and Zhang JF.2013.Formation of thick stratiform Fe-Ti oxide layers in layered intrusion and frequent replenishment of fractionated mafic magma:Evidence from the Panzhihua intrusion,SW China.Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems,14(3):712-732
Tegner C,Duncan RA,Bernstein S,Brooks CK,Bird DK and Storey M.1998.40Ar-39Ar geochronology of Tertiary mafic intrusions along the East Greenland rifted margin:Relation to flood basalts and the Iceland hotspot track.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,156(1-2):75-88
Toplis MJ and Carrol MR.1996.Differentiation of ferro-basaltic magmas under conditions open and closed to oxygen:Implications for the Skaergaard intrusion and other natural systems.Journal of Petrology,37(4):837-858
Wang DH.1998.Mantle Plume and Mineralization.Beijing:Seismic Press,1-160(in Chinese with English abstract)
Wilmart E,Demaiffe D and Duchesne JC.1989.Geochemical constraints on the genesis of the Tellnes ilmenite deposit,Southwest Norway.Economic Geology,84(5):1047-1056
Xiao L,Xu YG and He B.2003.Emei mantle plume-subcontinental lithosphere interaction:Sr-Nd and O isotopic evidences from low-Ti and high-Ti basalts.Geological Journal of China Universities,9(2):207-217(in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiao L,Xu YG,Mei HJ,Zheng YF,He B and Pirajno F.2004.Distinct mantle sources of low-Ti and high-Ti basalts from the western Emeishan large igneous province,SW China:Implications for plume-lithosphere interaction.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,228(3-4):525-546
Xu YG and Zhong SL.2001.The Emeishan large igneous province:Evidence formantle plume activity and melting conditions.Geochimica,30(1):1-9(in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu YG,Chung SL,Jahn BM and Wu GY.2001.Petrologic and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Permian-Triassic Emeishan flood basalts in southwestern China.Lithos,58(3-4):145-168
Xu YG,Mei HJ,Xu JF,Huang XL,Wang YJ and Chung SL.2003.Origin of two differentiation trends in the Emeishan flood basalts.Chinese Science Bulletin,48(4):383-387(in Chinese)
Xu YG,He B,Chung SL,Menzies MA and Frey FA.2004.Geologic,geochemical,and geophysical consequences of plume involvement in the Emeishan flood-basalt province.Geology,32(10):917-920
Zhang XQ,Zhang JF,Song XY,Deng YF,Guan JX and Zheng WQ.2011.Implications of compositions of plagioclase and olivine on the formation ofthe Panzhihua V-Timagnetite deposit,Sichuan Province.Acta Petrologica Sinica,27(12):3675-3688(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang ZC,Mahoney JJ,Mao JW and Wang FS.2006.Geochemistry of picritic and associated basalt flows of the western Emeishan flood basalt province,China.Journal of Petrology,47(10):1997-2019
Zhang ZC,Zhi XC,Chen L,Saunders AD.and Reichow MK.2008.Re-Os isotopic compositions of picrites from the Emeishan flood basalt province,China.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,276(1-2):30-39
Zhang ZC,Mao JW,Saunders AD,Ai Y,Li Y and Zhao L.2009.Petrogenetic modeling of three mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions in the Emeishan large igneous province,SW China,based on isotopic and bulk chemical constraints.Lithos,113(3-4):369-392
Zhang ZC,Hou T,Santosh M,Li HM,Li JW,Zhang ZH,Song XY and Wang M.2014.Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China:An overview.Ore Geology Reviews,57:247-263
Zhong H,Yao Y,Hu SF,Zhou XH,Liu BG,Sun M,Zhou MF and Viljeon MJ.2003.Trace-element and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry of the PGE-bearing Hongge layered intrusion,southwestern China.International Geology Review,45(4):371-382
Zhong H and Zhu WG.2006.Geochronology of layered mafic intrusions from the Pan-Xi area in the Emeishan large igneous province,SW China.Mineralium Deposita,41(6):599-606
Zhou MF,Malpas J,Song XY,Robinson PT,Sun M,Kennedy AK,Lesher CM and Keays RR.2002.A temporal link between the Emeishan large igneous province(SW China)and the end-Guandalupian mass extinction.Earth and Planetary Science Letters,196(3-4):113-122
Zhou MF,Robinson PT,Lesher CM,Keays RR,Zhang CJ and Malpas JM.2005.Geochemistry,petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Panzhihua gabbroic layered intrusion and associated Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits,Sichuan Province,SW China.Journal of Petrology,46(11):2253-2280
附中文参考文献
范蔚茗,王岳军,彭头平,苗来成,郭锋.2004.桂西晚古生代玄武岩Ar-Ar和U-Pb年代学及其对峨眉山玄武岩省喷发时代的约束.科学通报,49(18):1892-1900
郝艳丽,张招崇,王福生,Mahonet JJ.2004.峨眉山大火成岩省“高钛玄武岩”和“低钛玄武岩”成因探讨.地质论评,50(6):587-592
侯增谦,卢记仁,林盛中.2005.峨眉地幔柱轴部的榴辉岩-地幔岩源区:主元素、痕量元素及Sr、Nd、Pb同位素证据.地质学报,79(2):200-219
胡瑞忠,陶琰,钟宏,黄智龙,张正伟.2005.地幔柱成矿系统:以峨眉山地幔柱为例.地学前缘,12(1):42-54
宋谢炎,胡瑞忠,张成江,钟宏,周美夫,马润则,李佑国.2005.峨眉火成岩省岩浆矿床成矿作用与地幔柱动力学过程的耦合关系.矿物岩石,25(4):35-44
王登红.1998.地幔柱及其成矿作用.北京:地震出版社,1-160
肖龙,徐义刚,何斌.2003.峨眉地幔柱-岩石圈的相互作用:来自低钛和高钛玄武岩的Sr-Nd和O同位素证据.高校地质学报,9(2):207-217
徐义刚,钟孙霖.2001.峨眉山大火成岩省:地幔柱活动的证据及其熔融条件.地球化学,30(1):1-9
徐义刚,梅厚钧,许继峰,黄小龙,王岳军,钟孙霖.2003.峨眉山大火成岩省两类岩浆分异趋势及其成因.科学通报,48(4):383-387
张晓琪,张加飞,宋谢炎,邓宇峰,官建祥,郑文勤.2011.斜长石和橄榄石成分对四川攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿床成因的指示意义.岩石学报,27(12):3675-3688