肥料重金属含量状况及施肥对土壤和作物重金属富集的影响
王 美, 李书田
(中国农业科学院农业资源与农业区划研究所, 北京 100081)
土壤中重金属除源于其母质外,主要来源于工业、 农业、 交通、 大气沉降等[1-4],其中农业上施肥对土壤中重金属累积量产生直接影响[5-6]。虽然肥料尤其是化肥在增加作物产量、 提高品质和保证粮食安全方面起到了不可替代的作用,但其在补充作物生长必需营养元素的同时,不可避免地会将一些有毒有害物质如重金属带入到土壤中[7-8],一旦这些有害物质积累到一定程度,势必会影响植物的营养生长和生殖生长,从而影响产品品质[9-10]。土壤中重金属的累积是一个漫长的过程,因此了解长期施肥对土壤和作物产品重金属含量的影响,对肥料产品的安全生产和科学施用,防止农产品污染,保证农产品安全和农业可持续发展都具有十分重要的意义。
1 肥料中重金属含量现状
1.1 化肥
不同种类化肥中重金属的种类和数量具有很大差异(表 1)。整体上看,过磷酸钙的重金属如锌(Zn)、 铜(Cu)、 镉(Cd)、 铅(Pb)含量高于氮肥、 钾肥和三元复合肥,有机-无机复混肥料中的Pb含量高于除过磷酸钙之外的其他化肥。尿素和氯化钾中Pb、 Cd含量均小于1 mg/kg,远低于我国水溶性肥料有害元素限量标准 (Pb≤50 mg/kg,Cd≤10 mg/kg),这可能与生产原料重金属含量低以及合成工艺过程中的流失有关[11]。过磷酸钙中Cu、 Zn、 Cd、 Pb含量高于钙镁磷肥[12],除与生产原料磷矿石成分有关外(表2),还可能与生产工艺有关,过磷酸钙是通过酸法(硫酸、 硝酸、 盐酸或磷酸)分解磷矿石制成,而钙镁磷肥是通过高温加热分解磷矿石制成,后者在高温煅烧过程中会挥发掉部分重金属[12]。有机-无机复混肥料中重金属含量高于三元复混肥,可能与有机原料中重金属含量高有关。有关化肥中重金属的资料有限,因此从现有数据还不足以说明以上问题。
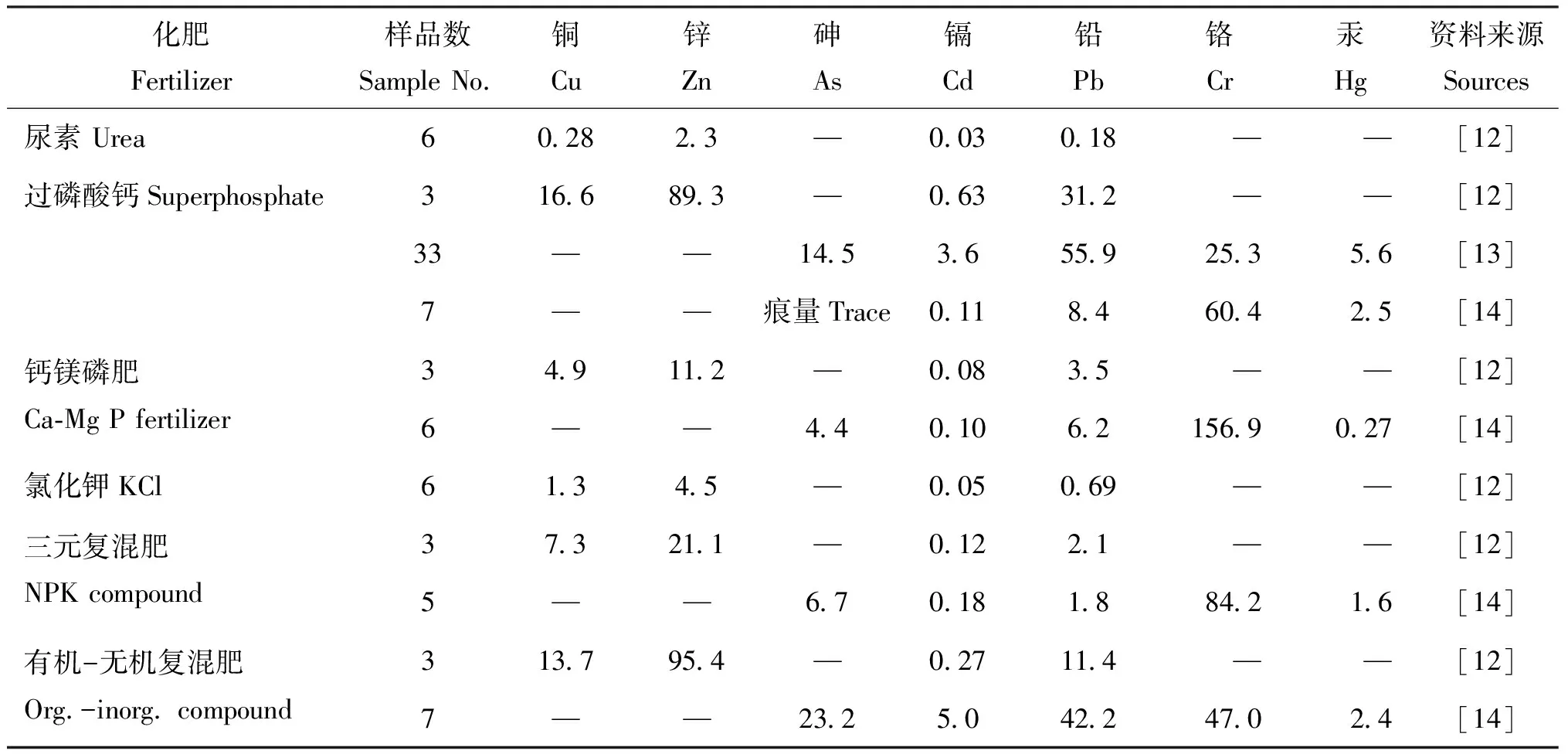
表1 化肥中重金属的含量状况(平均值, mg/kg)Table 1 Heavy metal contents in chemical fertilizers(mean)

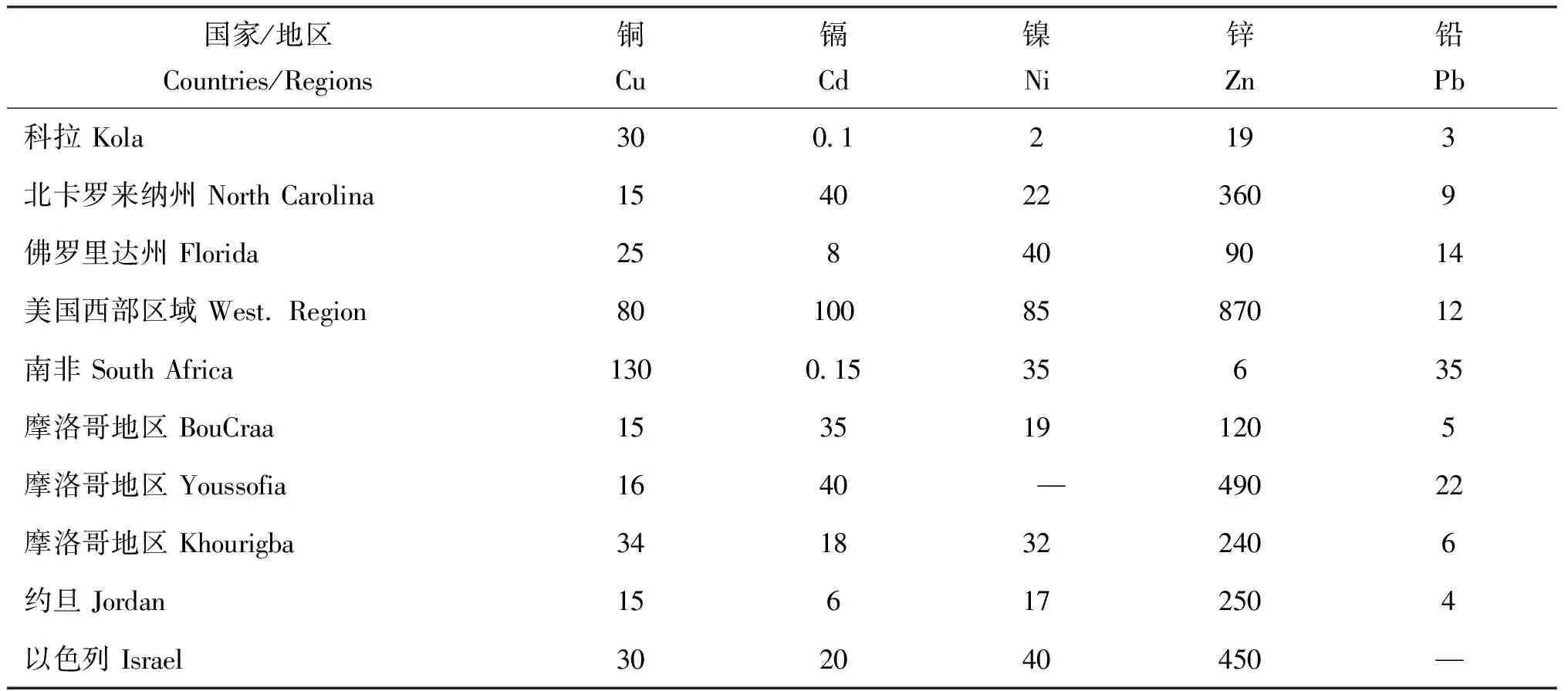
表2 不同国家和地区磷灰岩矿床中重金属含量 (mg/kg)Table 2 Heavy metal contents of phosphate rock deposits in different countries and regions
注(Note): 资料来源于Kongshaug 等(1992)[17]Materials come from Kongshaugetal(1992)[17].
1.2 有机肥料
有机肥料的成分和来源复杂,按其来源和制作方式可分为工农业有机废弃物、 一种或多种有机废弃物堆肥和经过加工的商品有机肥。
1.2.1 有机废弃物 有机废弃物主要包括畜禽粪便、 污泥、 作物秸秆等。这些废弃物中除含大量有机质外,还含有一定量的养分。因此,有机废弃物的应用可以增加土壤有机质、 改善土壤结构、 增加土壤养分、 提高土壤肥力等。但有机废弃物中通常含有一定量的重金属[21-22]等有害物质。表 3总结了国内外有机废弃物中重金属的含量状况。从表3几种废弃物中重金属的加权平均值来看,畜禽粪便中的Zn、 Cu、 Cd,尤其是Cd含量高于其他废弃物,污泥中汞(Hg)含量高。秸秆的资料较少,但可以看出其各种重金属含量低于其他有机废弃物(表3)。
畜禽粪便中猪粪的Cu、 Zn、 As、 Cd含量较高,鸡粪中铬(Cr)含量较高,羊粪中各种重金属的含量相对较低。不同畜禽粪便中的重金属含量变异较大,可能与饲喂方式和饲料添加剂使用量有关。例如英国Nicholson发现猪饲料中Zn、 Cu添加量是其它动物饲料的15倍、 4倍多,因此导致猪粪中Cu、 Zn含量高于其它种类粪便[23]。
1.2.2 堆肥 堆肥是由一种或多种有机废弃物经过堆积高温发酵而制成的有机肥料,通过高温堆置虽可在一定程度上降低重金属的生物有效性[24-25],但其总量不变。表3总结了一些国家和地区污泥堆肥和垃圾堆肥中的重金属含量状况。从现有数据的加权平均值看,污泥堆肥和垃圾堆肥中Cu、 Zn、 Pb的含量较高。
污泥堆肥中的重金属含量范围很大,即使同一个国家或地区差异也很大。例如意大利Pinamonti等[26]研究的污泥堆肥中Cu和Zn含量是Goi 等[27]研究的堆肥中的3倍;加拿大污泥堆肥中Pb含量相差十几倍[28-29];西班牙污泥堆肥中Zn含量相差6倍多[30-31];我国广州[32]、 佛山[32]污泥堆肥中Cu、 Zn、 Cd含量均高于北京[33]、 河北[34]和天津[35]地区。这种差异主要与污泥来源和堆肥方法有关系[36]。

表3 不同种类有机废弃物中重金属含量状况(平均值, mg/kg)Table 3 Heavy metal contents various organic wastes (mean)
续表3Table3continuos
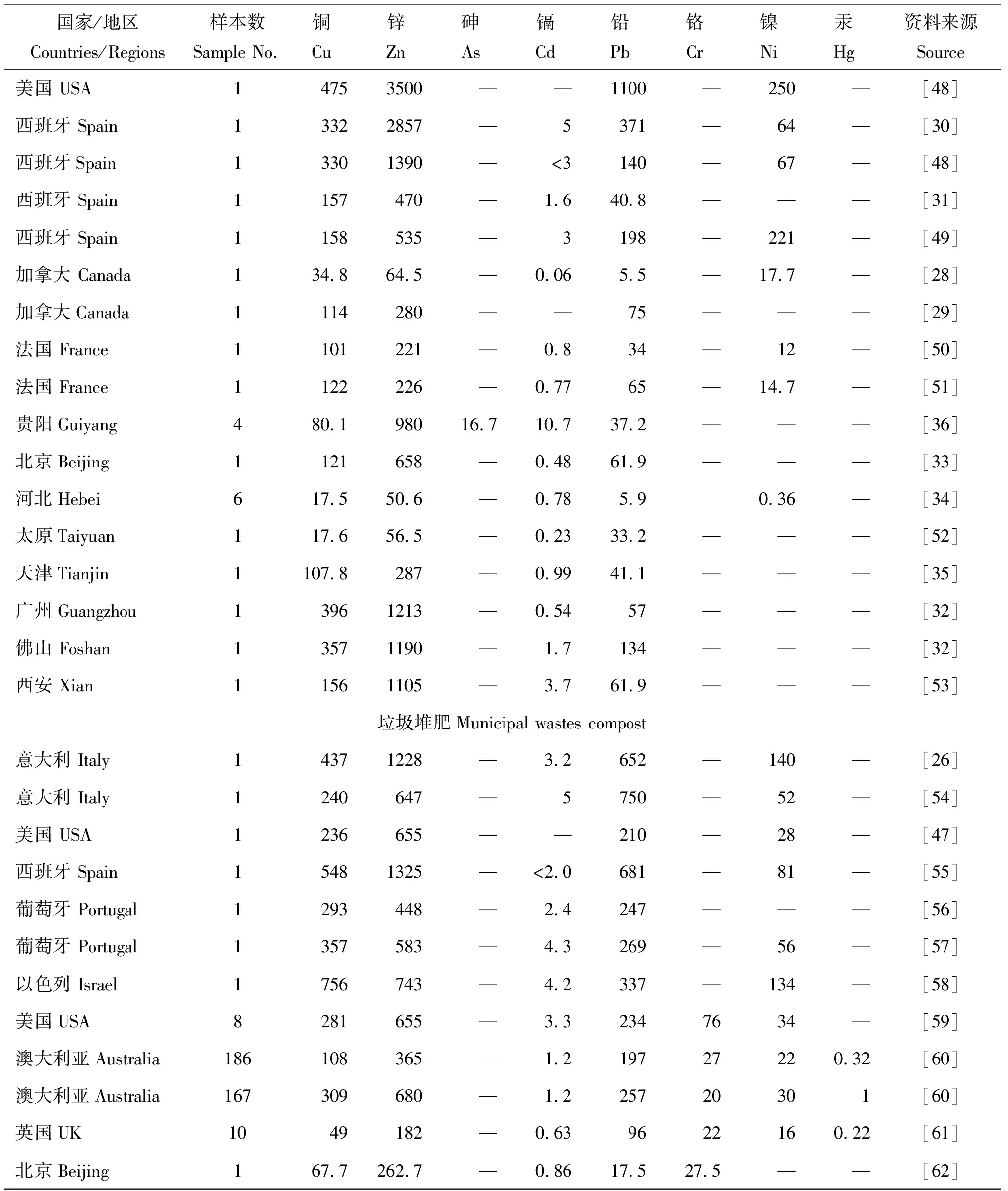
国家/地区Countries/Regions样本数Sample No.铜Cu锌Zn砷As镉Cd铅Pb铬Cr镍Ni汞Hg资料来源Source美国 USA14753500——1100—250—[48]西班牙 Spain13322857—5371—64—[30]西班牙Spain13301390—<3140—67—[48]西班牙 Spain1157470—1.640.8———[31]西班牙 Spain1158535—3198—221—[49] 加拿大 Canada134.864.5—0.065.5—17.7—[28]加拿大Canada1114280——75———[29]法国 France1101221—0.834—12—[50]法国 France1122226—0.7765—14.7—[51]贵阳Guiyang480.198016.710.737.2———[36]北京Beijing1121658—0.4861.9———[33]河北Hebei617.550.6—0.785.90.36—[34]太原Taiyuan117.656.5—0.2333.2———[52]天津Tianjin1107.8287—0.9941.1———[35]广州Guangzhou13961213—0.5457———[32]佛山 Foshan13571190—1.7134———[32]西安 Xian11561105—3.761.9———[53] 垃圾堆肥Municipal wastes compost 意大利 Italy14371228—3.2652—140—[26]意大利 Italy1240647—5750—52—[54]美国 USA1236655——210—28—[47]西班牙 Spain15481325—<2.0681—81—[55]葡萄牙 Portugal1293448—2.4247———[56]葡萄牙 Portugal1357583—4.3269—56—[57]以色列 Israel1756743—4.2337—134—[58]美国USA8281655—3.32347634—[59]澳大利亚Australia186108365—1.219727220.32[60]澳大利亚Australia167309680—1.225720301[60]英国UK1049182—0.639622160.22[61]北京Beijing167.7262.7—0.8617.527.5——[62]
1.2.3 商品有机肥 目前,国内外对商品有机肥并没有一个明确的定义,国内的商品有机肥料大多是畜禽粪便, 农业有机废弃物(如作物秸秆、 饼粕等), 工业有机废弃物(如糖醛渣、 味精下脚料、 造纸废液提取物、 污泥等)以及草(泥)炭、 腐植酸、 风化煤等单独或混合发酵熟化后直接生成,或混配一定量的无机肥料如尿素、 二铵、 硫酸钾或氯化钾等造粒而成的肥料[63-64]。商品有机肥的物料来源广泛,因此重金属含量有很大差异(表 4)。畜禽粪便[38,65]为主要原料的商品有机肥Cu、 Zn含量高于造纸废弃物、 腐植酸、 作物秸秆等[38]为原料的商品有机肥,而不同种类商品有机肥中As和Cr含量差别不大。不同畜禽粪便为原料的商品有机肥重金属含量也有差异,猪粪为主要原料的有机肥Cu、 Zn含量分别比牛粪混合鸡粪为原料的有机肥高出15、 5.7倍[65],很大原因是猪饲料比其它饲料添加更多的Cu和Zn[38]。虽然Cu、 Zn是作物必需的微量营养元素,但过量使用对土壤和农作物产品质量也有一定的风险,而且我国并没有针对这两种元素的相关限量标准,因此生产和施用商品有机肥时,要根据其物料来源, 土壤中Cu、 Zn含量, 施肥和种植历史监测其Cu、 Zn含量,防止含量过高对农产品构成污染。
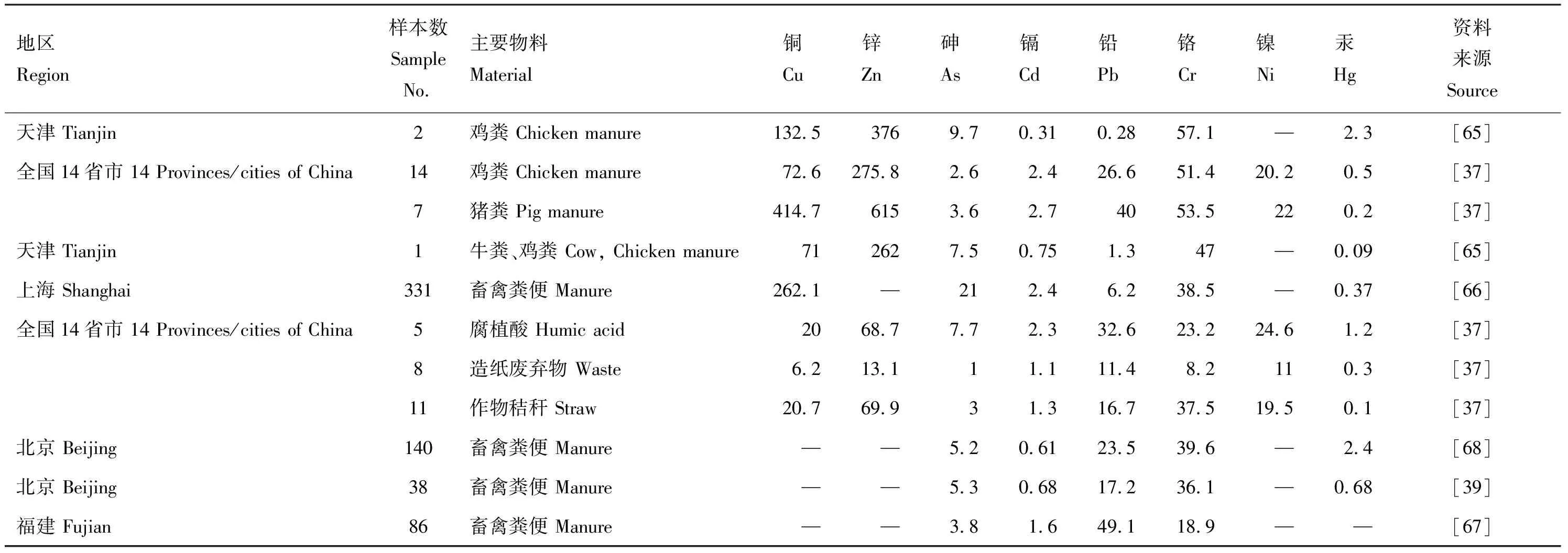
表4 商品有机肥中的重金属含量状况(mg/kg)Table 4 Heavy metal contents in organic commercial fertilizers

商品有机肥Zn、 Pb和Ni的加权平均比堆肥低,分别比污泥堆肥低486.5 mg/kg、 105 mg/kg、 27 mg/kg,比垃圾堆肥低296.3 mg/kg、 208 mg/kg、 7.4 mg/kg。Cu的加权平均含量分别比污泥堆肥和垃圾堆肥高101.5 mg/kg、 37 mg/kg。Hg加权平均值比畜禽粪便高,是鸡粪、 羊粪和牛粪的9倍,猪粪含量的4.5倍。
2 施肥对土壤重金属含量的影响
2.1 施用化肥的影响
化肥中含有一定量的重金属,长期施用可导致土壤中重金属含量发生变化[69-71],但不同种类化肥产生的影响不同。有研究表明[72],单施尿素25年相比不施肥对照没有显著提高土壤Cd、 Cr、 As、 Hg含量;氮磷钾配施和氮磷配施28年后土壤Cr、 Hg、 As含量没有显著差异[73],这表明氮肥和钾肥对土壤重金属累积的影响不大,主要是因为氮、 钾肥含有的重金属较少[74]。大量研究表明,磷肥能够增加土壤Cd含量,如封丘农业试验站12年肥料长期定位试验条件下,NPK处理相比NK处理土壤Cd含量升高了8.2%,差异显著(P≤0.05)[70];莱阳非石灰性土壤上施肥25年[71],NPK处理土壤中Cd含量为0.48 mg/kg,比NK处理土壤Cd含量高出0.43 mg/kg。新西兰一农田在50年的耕作期间,施用了大量的磷肥,酸溶Cd含量由原来的0.39 mg/kg上升到0.85 mg/kg,CaCl2提取的Cd含量从0.02 mg/kg增加到0.11 mg/kg,相当于肥料中80%的Cd留在了土壤中[75]。可见,施用化肥使土壤重金属含量增加主要与施用磷肥有关,与氮、 钾肥关系不大,因此,要注意磷肥的来源和用量,防止通过磷肥的施用带入土壤中过多的重金属而影响土壤环境质量。

2.2 施用有机肥的影响

2.3 施肥对土壤重金属有效态含量的影响
重金属毒性大小不仅与其总量有关,还与其化学形态有关。不同形态[86]的重金属对植物的有效性不同,有效态的含量决定了植物所能吸收利用的重金属数量,其中植物对可交换态重金属利用程度最大。因此,了解施肥后土壤中重金属不同形态含量的变化对于指导安全合理施肥具有重要意义。
研究表明,单施化肥不影响或降低土壤重金属有效态含量[87-90,91]。如湖南七个稻田试验施用氮、 磷、 钾18年并没有增加土壤Zn、 Cu、 Cd、 Pb的有效态(0.1 mol/L HCl提取)含量[87];棕壤上20多年的长期定位试验NP处理土壤有效态Cu、 Zn(0.1 mol/L HCl提取)平均含量分别比不施肥对照降低27%和26.7%[89];红壤上16年定位试验单施化肥有效态Cu、 Cd(0.1 mol/L HCl提取)含量与不施肥相比没有显著差异[91]。这可能是因为肥料促进作物生长,提高作物对有效态重金属的吸收量,从而减少了土壤中重金属有效态累积量[89]。
有机肥对土壤重金属有效态含量的影响比较复杂,与有机肥种类、 施用量、 土壤类型有关。如在石灰性土壤和红壤上施用秸秆可增加土壤交换态Cd的含量,猪粪则降低交换态Cd含量[92];在污泥施用量为10 t/hm2和30 t/hm2时,土壤Pb可还原态和可氧化态含量增幅不大,而在施污泥量为60 t/hm2的土壤上,这两种形态的Pb则显著增加[93]。土壤重金属形态与土壤性质,如pH值、 氧化还原电位、 有机质、 全氮、 全磷等密切相关,有机肥施入土壤,通过分解可产生有机酸、 糖类、 酚类、 及含氮、 硫的杂环等化合物改变土壤理化性质,从而影响土壤中重金属形态。一些研究发现,同一施肥措施对不同种类重金属的有效态含量产生的影响不同,如谭启玲等发现潮土上施用污泥,Pb、 Cr、 Cd、 Ni交换态含量没有显著增加,而交换态Cu含量显著提高[94]; Kidd指出,与不施肥对照处理相比,连续施用污泥土壤Cu的酸提取态含量下降,而Zn的酸提取态含量升高[95]。
3 施肥对作物可食部位重金属含量的影响
3.1 施用化肥的影响

化肥对农作物重金属富集的影响与多种因素相关。Singh[117]研究表明,壤土上施用磷肥对作物富集Cd的影响大于砂土;Grant[99]研究表明,大麦体内Cd含量升高与磷肥中Cd含量无关,而与土壤pH的降低、 离子强度升高以及土壤溶液中Zn含量的降低有关。因此,土壤类型、 肥料种类、 土壤pH、 有机质、 离子强度及土壤离子之间的相互作用等均可能对作物重金属富集产生影响,有关化肥对其它元素吸收的影响资料比较少,今后应加强这方面的研究。
3.2 施用有机肥的影响

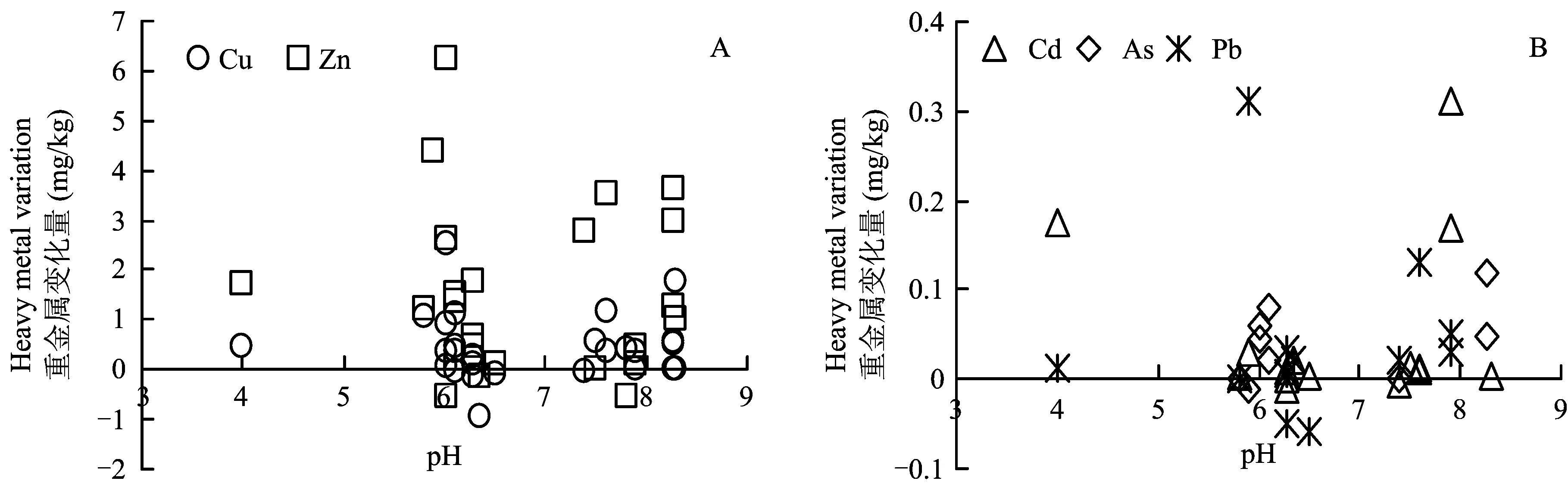
图2 施有机肥(A)与不施有机肥(B)相比作物可食部位重金属含量的变化Fig.2 Changes of heavy metal contents in edible parts of crops applied with organic fertilizers (A) compared with the control without organic fertilizers (B)[注(Note): 横坐标为不同试验土壤pH,纵坐标为不同研究试验中重金属变化量 Abscissa represents soil pH in different experiments, ordinate represents changes of heavy metals in different studies. ]
有机肥对作物可食部位重金属含量的影响,与有机肥种类、 用量、 土壤类型和pH以及作物种类等有很大关系。有关施用污泥对作物产品重金属的影响研究较多。如王新等[107]的研究结果表明,随着污泥施用量的增加,pH为6.5的棕壤上水稻籽粒中重金属略有升高,但差异不显著,只有在污泥施用量为120、 225 t/hm2时,籽粒中的Pb含量相比对照显著升高,但是并不超标(《粮食卫生标准》GB2715-2005,Pb≤0.2 mg/kg)。陈曦等[109]对小麦的研究表明,随污泥用量增加小麦籽粒Hg、 Cd、 Pb含量有升高的趋势,但是均在国家粮食卫生标准范围内。在蔬菜施肥研究中,金燕等[110]的研究指出,施用污泥复合肥使菜花和莴苣可食部位Pb含量超出了我国食品卫生标准(GB2715-2005,Pb≤0.2 mg/kg);黄雅曦等[111]发现,无论污泥施用量高低与否,青菜组织中Zn含量均超标,其它重金属含量在污泥施用量比较高时超出国家蔬菜食品卫生标准;刘善江等人[96]的研究结果中,油菜Hg、 As和Zn含量随污泥用量的增加呈上升趋势,以上结果表明Zn和Pb在蔬菜中的积累量较大,在施用污泥时应注意加强对这两种重金属的检测或者选择重金属富集能力低的作物种植[108]。此外不同种类的蔬菜对不同重金属的富集能力有一定差别,周艺敏等[120]发现,白菜对Pb、 Cd、 Ni、 Cr的吸收能力较强,韭菜对Cu、 Zn的吸收能力较强,菜豆对Cu、 Zn、 Pb、 Ni、 Hg的吸收能力较强,茄子对Cd、 Hg吸收能力较强。在进行蔬菜种植时应该针对不同种类蔬菜合理施肥,最大可能减少蔬菜对重金属的吸收量。
畜禽粪便作为主要有机肥料施用更加广泛,有田间试验表明[121],中量和高量有机肥与化肥配施时,糙米中Cd含量分别为0.20 mg/kg和0.19 mg/kg, 超出我国《粮食卫生标准》中Cd限量(GB2715-2005,Cd≤0.1 mg/kg);王瑾等[119]发现长期施用规模养殖厂的猪粪导致韭菜、 青菜、 芹菜、 萝卜的Cu、 Zn、 As含量显著升高,分别达到不施肥处理的4倍、 4倍、 3倍。然而。也有研究表明施用粪肥处理的番茄果实和青菜地上部重金属含量差异不显著[122]。国外也有研究报道,尽管在种植马铃薯的土壤上连续施用含大量Cu和Zn的猪粪,块茎中Cu和Zn的含量没有显著变化[118]。这种差异的产生可能与农作物类型以及作物的部位有关[123]。
上述结果表明,施用污泥或畜禽粪便等对农产品重金属含量有一定影响,但作物可食部位对重金属的富集因作物种类、 有机肥种类、 用量和重金属种类不同而有一定差异,在有机肥安全施用上应重点考虑,只要因地制宜地控制好有机肥的重金属含量和施用量,就可以避免对土壤和作物生产安全构成的威胁。
4 问题与展望
综上所述,磷肥和有机肥中含有一定量的重金属,不同有机肥种类或同一种类不同来源的有机肥中重金属种类和含量具有很大差异,没有一定的规律。施用化肥和有机肥对土壤和农作物重金属累积的影响因土壤类型和作物种类而不同,研究主要集中在以下几方面: 1)不同肥料种类和用量对土壤重金属累积的影响;2)施用化肥和有机肥尤其是畜禽粪便和污泥对作物重金属吸收和富集的影响;3)施用有机肥如污泥对土壤重金属生物有效性的影响。这些研究仅考虑施肥引起土壤重金属含量和有效性的变化,且大多采用盆栽试验或短期田间试验,而对长期不同施肥措施对重金属累积和投入产出平衡影响的差异性以及不同施肥措施下土壤重金属的变化规律缺乏系统研究。因此,针对国内外研究现状和存在的问题,今后应该在以下几个方面开展研究: 1)典型种植体系下土壤重金属的投入/产出平衡;2)长期不同施肥措施对土壤重金属含量、 形态和有效性的影响;3)土壤对重金属的承载年限和在一定承载年限下肥料中重金属的最高限量。这些问题的解决将从源头上控制重金属进入农田的数量,指导安全施肥和保证农产品质量安全。
参考文献:
[1] Tu C, Zheng C R, Chen H M. Effect of applying chemical fertilizers on forms of lead and cadmium in red soil[J]. Chemosphere, 2000, 41: 133-138.
[2] Selene C H, Chou J, De Rosa C T. Case studies—Arsenic[J]. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health, 2003, 206: 381-386.
[3] Nouri J, Mahvi A H, Jahed G Retal. Regional distribution pattern of groundwater heavy metals resulting from agricultural activities[J]. Environ. Geol., 2008, 55: 1337-1343.
[4] 李芳, 钱秋芳. 土壤重金属污染研究进展[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2011, 17(10): 80-82.
Li F, Qian Q F. Advances in pollution of heavy metals in soil[J]. Anhui Agric. Sci. Bull., 2011, 17(10): 80-82.
[5] Jiao W T, Chen W P, Chang A Cetal. Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: A review[J]. Environ. Pollut., 2012, 168: 44-53.
[6] 张乃明, 陈建军, 常晓冰. 污灌区土壤重金属累积影响因素研究[J]. 土壤, 2002, (2): 90-93.
Zhang N M, Chen J J, Chang X B. Influence factors of soil heavy metals in wastewater irrigation regions[J]. Soils, 2002, (2): 90-93.
[7] Soumaré M, Tack F M G, Verloo M G. Effects of a municipal solid waste compost and mineral fertilization on plant growth in two tropical agricultural soils of Mali[J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2003, 86: 15-20.
[8] Uprety D, Hejcman M, Száková Jetal. Concentration of trace elements in arable soil after long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers[J]. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst., 2009, 85: 241-252.
[9] 毕淑芹, 谢建治, 刘树庆, 等. 土壤重金属污染对植物产量及品质的影响研究[J]. 河北农业科学, 2006, 10(2): 107-110.
Bi S Q, Xie J J, Liu S Qetal. The review of effects of heavy metal pollution in soil on the plant[J]. J. Hebei Agri. Sci., 2006, 10(2): 107-110.
[10] 李秀珍, 李彬.重金属对植物生长发育及其品质的影响[J]. 四川林业科技, 2008, 29(4): 59-65.
Li X Z, Li B. Effects of heavy metals on growth development and quality of plants[J]. J. Sichuan For. Sci. Tech., 2008, 29(4): 59-65.
[11] 王起超, 麻壮伟.某些市售化肥的重金属含量水平及环境风险[J]. 农村生态环境, 2004, 20(2): 62-64.
Wang Q C, Ma Z W. Heavy metals in chemical fertilizer and environment risks[J]. Rural Eco-environ., 2004, 20(2): 62-64.
[12] 陈林华, 倪吾钟, 李雪莲, 等. 常用肥料重金属含量的调查分析[J]. 浙江理工大学学报, 2009, 26(2): 223-226.
Chen L H, Ni W Z, Li X Letal. Investigation of heavy metal concentrations in commercial fertilizers commonly-used[J]. J. Zhejiang Sci.-Tech. Univ., 2009, 26(2): 223-226.
[13] 封朝晖, 刘红芳, 王旭. 我国主要肥料产品中有害元素的含量与评价[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009, (4): 44-47.
Feng Z H, Liu H F, Wang X. Toxic substances contents in fertilizers and its environmental risk assessment in China[J]. China Soils Fert., 2009, (4): 44-47.
[14] 陈海燕, 高雪, 韩峰. 贵州省常用化肥重金属含量分析及评价[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2006, (4): 18-19.
Chen H Y, Gao X, Han F. Contents of heavy metal in chemical fertilizer in Guizhou province[J]. Till. Cult., 2006, (4): 18-19.
[15] 马榕. 重视磷肥中重金属镉的危害[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2002, 17(6): 5-6.
Ma R. Pay attention to the hazardous cadmium in phosphate fertilizer[J]. Phos. Comp. Fert., 2002, 17(6): 5-6.
[16] 高阳骏, 张乃明. 施用磷肥对环境的影响探讨[J]. 土壤肥料科学, 2003, 19(6): 162-165.
Gao Y J, Zhang N M. Study on the influence of phosphorus fertilizer on environment[J]. Sci. Soil Fert., 2003, 19(6): 162-165.
[17] Kongshaug G, Bφckman O C, Kaarstad Oetal. Paper presented at the international symposium for chemical climatology and geomedical problems[R], Oslo, Norway, 1992. 21-22.
[18] 鲁如坤, 时正元, 熊礼明. 我国磷矿磷肥中镉的含量及其对生态环境影响的评价[J]. 土壤学报, 1992, 29(2): 150-156.
Lu R K, Shi Z Y, Xiong L M. Cadmium contents of rock phosphates and phosphate fertilizers of China and their effects on ecological environment[J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 1992, 29(2): 150-156.
[19] 王江平. 化肥行业镉问题的进展与建议[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2004, 19(5): 4-7.
Wang J P. The development and suggestions on cadmium problem in fertilizer industry[J]. Phos. Comp. Fert., 2004, 19(5): 4-7.
[20] 周南华. 化肥施用与农产品质量安全[J]. 西南农业学报, 2004, 17(1): 126-130.
Zhou N H. Fertilizer application and quality safety of farrm products[J]. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci., 2004, 17(1): 126-130.
[21] 樊文华, 刘晋峰, 王志远. 施用沼肥对温室土壤养分和重金属含量的影响[J]. 山西农业大学学报, 2011, 31(1): 1-4.
Fan W H, Liu J F, Wang Z Y. Effects of biogas fertilizer on the contents of nutrients and heavy metals in soil of greenhouse[J]. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ., 2011, 31(1): 1-4.
[22] 黄鸿翔, 李书田, 李向林, 等. 我国有机肥的现状与发展前景分析[J]. 土壤肥料, 2006, (1): 3-8.
Huang H X, Li S T, Li X Letal. Analysis on the status of organic fertilizer and its development strategies in China[J]. Soil. Fert., 2006, (1): 3-8.
[23] Nicholson F A, Chambers B J, Williams J Retal. Heavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales[J]. Bioresour. Tech., 1999, 70: 23-31.
[24] 何增明, 刘强, 谢桂先, 等. 好氧高温猪粪堆肥中重金属砷、 铜、 锌的形态变化及钝化剂的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2010, 21(10): 2659-2665.
He Z M, Liu Q, Xie G Xetal. Changes of heavy metals form during aerobic high temperature composting of pig manure and the effects of passivators[J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2010, 21(10): 2659-2665.
[25] 黄国锋, 张振钿, 钟流举, 等. 重金属在猪粪堆肥过程中的化学变化[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(1): 94-99.
Huang G F, Zhang Z T, Zhong L Jetal. Chemical changes of heavy metals in the process of pig manure composting[J]. China Environ. Sci., 2004, 24(1): 94-99.
[26] Pinamonti F, Stringari G, Gasperi Fetal. The use of compost: its effects on heavy metal levels in soil and plants[J]. Resour. Conser. Recycl., 1997, 21: 129-143.
[27] Goi D, Tubaro F, Dolcetti G. Analysis of metals and EOX in sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants: a case study[J].Waste Manage, 2006, 26: 167-175.
[28] Hackett G A R, Easton C A, Duff S J B. Composting of pulp and paper mill fly ash with wastewater treatment sludge[J]. Bioresour. Tech., 1999, 70: 217-224.
[29] Zheljazkov V D, Astatkie T, Caldwell C Detal. Compost, manure, and gypsum application to timothy/red clover forage[J]. J. Environ. Qual., 2006, 35: 2410-2418.
[30] Millares R, Beltrán E M, Porcel M Aetal. Emergence of six crops treated with fresh and composted sewage sludge from waste treatment plants[J]. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient., 2002, 18: 139-146.
[31] Casado-Vela J, Sellés S, Díaz-Crespo Cetal. Effect of composted sewage sludge application to soil on sweet pepper crop (Capsicumannuumvar. annuum) grown under two exploitation regimes[J]. Waste Manage., 2007, 27: 1509-1518.
[32] Cai Q Y, Mo C H, Wu Q Tetal. Concentration and speciation of heavy metals in six different sewage sludge-composts[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 147: 1063-1072.
[33] 陈同斌, 李艳霞, 金燕, 等. 城市污泥复合肥的肥效及其对小麦重金属吸收的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(5): 643-648.
Chen T B, Li Y X, Jin Yetal. The effects of compound fertilizer made from municipal sewage sludge compost on N P K and heavy metals uptake of wheat[J]. Acta Ecol. Sin., 2002, 22(5): 643-648.
[34] 杨玉荣, 穆国俊, 魏静. 重金属在污泥堆肥过程中的变化[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(增刊): 226- 228.
Yang Y R, Mu G J, Wei J. Dynamics of heavy metals during composting process of sewage sludge[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2006, 25(Sup.): 226- 228.
[35] 周艺敏, 王正祥, 任顺荣, 等. 城市垃圾肥农用对土壤生态环境的影响[J]. 土壤肥料, 1992, (1): 7-10.
Zhou Y M, Wang Z X, Ren S Retal. The effects of municipal solid waste on soil ecological-environgment[J]. Soil Fert., 1992, (1): 7-10.
[36] 冯春, 杨光, 杜俊, 等. 污水污泥堆肥重金属总量及形态变化[J]. 环境科学研究, 2008, 21(1): 97-102.
Feng C, Yang G, Du Jetal. Study on the changes of total contents and the forms of heavy metals for sewage sludge composting[J]. Res. Environ. Sci., 2008, 21(1): 97-102.
[37] 刘荣乐, 李书田, 王秀斌, 等. 我国商品有机肥料和有机废弃物中重金属的含量状况与分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2005, 24(2): 392-397.
Liu R L, Li S T, Wang X Betal. Contents of heavy metal in commercial organic fertilizers and organic wastes[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2005, 24(2): 392-397.
[38] 彭来真, 刘琳琳, 张寿强, 等. 福建省规模化养殖场畜禽粪便中的重金属含量[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 39(5): 523-527.
Peng L Z, Liu L L, Zhang S Qetal. Heavy metals content in manure of commercial animal farms in Fujian Province[J]. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. (Nat. Sci Ed.), 2010, 39(5): 523-527.
[39] 梁金凤, 齐庆振, 贾小红, 等. 京郊有机肥料的质量状况分析[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2009, (6): 79-83.
Liang J F, Qi Q Z, Jia X Hetal. Investigation of quality in organic fertilizers in Beijing suburb[J]. China Soils Fert., 2009, (6): 79-83.
[40] 陈丽娜, 张晓芳, 赵全利, 等. 保定市郊养殖场畜禽粪中重金属含量调查分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(5): 357-362.
Chen L N, Zhang X F, Zhao Q Letal. Investigation of heavy metals in the excretions of the livestock and poultry in the suburbs of Baoding city[J]. Chin. Agri. Sci. Bull., 2008, 24(5): 357-362.
[41] McBride M B, Spiers G. Trace element content of selected fertilizers and dairy manures as determined by ICP-MS[J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 2001, 32(1-2): 139-156.
[42] Ihnat M, Fernandes L. Trace elemental characterization of composted poultry manure[J]. Bioresour. Tech., 1996, 57: 143-156.
[44] 杨军, 郭广慧, 陈同斌, 等. 中国城市污泥的重金属含量及变化趋势[J]. 中国给水排水, 2009, 25(13): 122-124.
Yang J, Guo G H, Chen T Betal. Concentrations and variation of heavy metals in municipal sludge of China[J]. China Water Waterwaste., 2009, 25(13): 122-124.
[45] Chen M, Li X M, Qi Yetal. Total concentrations and speciation of heavy metals in municipal sludge from Changsha, Zhuzhou and Xiangtan in middle-south region of China[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 160: 324-329.
[46] Haroun M, Idri A, Omar S. Analysis of heavy metals during composting of the tannery sludge using physicochemical and spectroscopic techniques[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 165: 111-119.
[47] Pichtel J, Anderson M. Trace metal bioavailability in municipal solid waste and sewage sludge compost[J]. Bioresour. Tech., 1997, 60: 223-229.
[48] Lopes C, Herva M, Franco-Uria Aetal. Inventory of heavy metal content in organic waste applied as fertilizer in agriculture: evaluating the risk of transfer into the food chain[J]. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. Int., 2011, 18(6): 918-939.
[49] Pascual J A, Hernandez T, Garcia Cetal. Enzymatic activities in an arid soil amended with urban organic wastes: laboratory experiment[J]. Bioresour. Tech., 1998, 64: 131-138.
[50] Korboulewsky N, Dupouyet S, Bonin G. Environmental risks of applying sewage sludge compost to vineyards: carbon, heavy metals, nitrogen, and phosphorus accumulation[J]. J. Environ. Qual., 2002, 31: 1522-1527.
[51] Larchevêque M, Ballini C, Korboulewsky N. The use of compost in afforestation of Mediterranean areas: effects on soil properties and young tree seedlings[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2006, 369: 220-230.
[52] 梁丽娜, 黄雅曦, 杨合法, 等. 污泥农用对土壤和作物重金属累积及作物产量的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2009, 25(6): 81-86.
Liang L N, Huang Y X, Yang H Fetal. Effects of farmland application of sewage sludge on crop yields and heavy metal accumulation in soil and crop[J]. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng., 2009, 25(6): 81-86.
[53] Gao P C, Tang X B, Tong Y Netal. Application of sewage sludge compost on highway embankments[J]. Waste Manage., 2008, 28: 1630-1636.
[54] Businelli D, Massaccesi L, Said-Pullicino Detal. Long-term distribution, mobility and plant availability of compost derived heavy metals in a landfill covering soil[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2009, 407: 1426-1435.
[55] García-Gil J C, Plaza C, Soler-Rovira Petal. Long-term effects of municipal solid waste compost application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass[J]. Soil Biol. Biochem., 2000, 32: 1907-1913.
[56] Sebastiaò J M, Queda A C C. Composting of urban solid wastes: agronomic interest vs environmental impact. Application to potato production[J]. Residuos, 2003, 13: 98-104.
[57] Alvarenga P, Gonçalves A P, Fernandes R Metal. Evaluation of composts and liming materials in the phytostabilization of a mine soil using perennial ryegrass[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2008, 406: 43-56.
[58] Kaschl A, Römheld V, Chen Y. The influence of soluble organic matter from municipal solid waste compost on trace metal leaching in calcareous soils[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 2002, 291: 45-57.
[59] He X T, Logan T J, Traina S J. Physical and chemical characteristics of selected US municipal solid waste composts[J]. J. Eviron. Qual., 1995, 24: 543-552.
[60] Smith S R. A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge[J]. Environ. Int., 2009, 35(1): 142-156.
[61] Dimambro M E, Lillywhite R D, Rahn C R. The physical, chemical and microbial characteristics of biodegradable municipal waste derived composts[J]. Comp. Sci. Util., 2007, 15: 243-52.
[62] 秦莉, 李玉春, 尹莉, 等. 城市生活垃圾工厂化堆肥过程中理化指标的变化研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(2): 501- 506.
Qin L, Li Y C, Yin Letal. Variations of physical and chemical indexes during MSW plant-scale composting[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2006, 25(2): 501- 506.
[63] 奚振邦, 王寓群, 杨佩珍. 中国现代农业发展中的有机肥问题[J]. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(12): 1874- 1878.
Xi Z B, Wang Y Q, Yang P Z. The issue on organic manure in developing modern agriculture in China[J]. Sci. Agric. Sin., 2004, 37(12): 1874- 1878.
[64] 李书田, 刘荣乐. 国内外关于有机肥料中重金属安全限量标准的现状与分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(增刊): 777- 782.
Li S T, Liu R L. Establishment and evaluation for maximum permissible concentration of heavy metals in biosolid wastes as organic manure[J]. J. Agro-Environ Sci., 2006, 25(Sup.): 777-782.
[65] 任顺荣, 邵玉翠, 王正祥. 利用畜禽废弃物生产的商品有机肥重金属含量分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2005, 24(增刊): 216 - 218.
Ren S R, Shao Y C, Wang Z X. Analyze on heavy metals content of merchandise compost produced by animal wastes[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2005, 24(Sup.): 216-218.
[66] 朱建华, 杨晓磊, 严瑾, 等. 上海商品有机肥料中重金属含量及影响因素研究[J]. 上海农业学报, 2010, 26(4): 113-116.
Zhu J H, Yang X L, Yan Jetal. Contents and influencing factors of heavy metals in commercial organic fertilizers in Shanghai[J]. Acta Agric. Shanghai, 2010, 26(4): 113-116.
[67] 吴凌云. 福建省商品有机肥料重金属含量的分析与研究[J]. 福建农业科技, 2010, (1): 67-69.
Wu L Y. Research on heavy metal contents of commercial organic fertilizers in Fujian[J]. Fujian Agri. Sci. Tech., 2010, (1): 67-69.
[68] 谭晓冬, 董文光. 商品有机肥中重金属含量状况调查[J]. 农业环境与发展, 2006, 23(1): 50-51.
Tan X D, Dong W G. Investigation of heavy metal contents in merchandise compost[J]. Agro-Environ. Devel., 2006,23(1): 50-51.
[69] Atafar Z, Mesdaghinia A, Nouri J. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration[J]. Environ. Monit. Assess., 2010, 160: 83-89.
[70] 陈芳, 董元华, 安琼, 等. 长期肥料定位试验条件下土壤中重金属的含量变化[J]. 土壤, 2005, 37(3): 308-311.
Chen F, Dong Y H, An Qetal. Changes of soil heavy metal content in long-term fertilization trial[J]. Soils, 2005, 37(3): 308-311.
[71] 刘树棠, 赵永厚, 孙玉林, 等. 25年长期定位施肥对非石灰性潮土重金属状况的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(1): 164-167.
Liu S T, Zhao Y H, Sun Y Letal. Effects of25 years long-term fertilization on status of heavy metals in non-calcareous fluro-aqic soil[J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2005, 19(1): 164-167.
[72] 任顺荣, 邵玉翠, 高宝岩. 长期定位施肥对土壤重金属含量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(4): 96-99.
Ren S R, Shao Y C, Gao B Y. Effects of long-term located fertilization on heavy metal content of soil[J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2005, 19(4): 96-99.
[73] 王颖, 韩晓日, 孙杉杉, 等. 长期定位施肥对棕壤重金属的影响及其环境质量评价[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2008, 39(4): 442-446.
Wang Y, Han X R, Sun S Setal. Effects of long term fertilization on the heavy metals in brown soil and environmental quality evaluation[J]. J. Shenyang Agric. Univ., 2008, 39(4): 442- 446.
[74] 崔德杰, 张玉龙. 土壤重金属污染现状与修复技术研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2004, 35(3): 366-370.
Cui D J, Zhang Y L. Current situation of soil contamination by heavy metals and research advances on the remediation techniques[J]. Chin. J. Soil Sci., 2004, 35(3): 366-370.
[75] Taylor M D. Accumulation of cadmium derived from fertilizers in New Zealand soils[J]. Sci. Total Environ., 1997: 123-126.
[76] 李本银, 汪鹏, 吴晓晨, 等.长期肥料试验对土壤和水稻微量元素及重金属含量的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2009, 46(2): 281-288.
Li B Y, Wang P, Wu X Cetal. Effects of long-term fertilization on content of trace elements and heavy metals in soil and rice[J]. Acta Pedol. Sin., 2009, 46(2): 281-288.
[77] Adeli A, Sistany K R, Tewolde Hetal. Broiler litter application effects on selected trace elements under conventional and no-till systems[J]. Soil Sci., 2007, 172: 349-365.
[78] Schomberg H H, Endale D, Jenkins Metal. Poultry litter induced changes in soil test nutrients of a Cecil soil under conventional tillage and no-tillage[J]. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 2008, 73: 154-163.
[79] Novak J M, Watts D W, Stoke K C. Copper and zinc accumulation, profile distribution and crop removal in coastal plain soils receiving long-term intensive applications of swine manure[J]. Trans. ASAE., 2004, 47: 1513-1522.
[80] Berenguer P, Cela S, Santivery Fetal. Copper and zinc soil accumulation and plant concentration in irrigated maize fertilize with liquid swine manure[J]. Agron. J., 2008, 100: 1056-1061.
[81] Lipoth S L, Schoenau J J. Copper, zinc, and cadmium accumulation in two prairie soils and crops as influenced by repeated applications of manure[J]. Plant Nutr. Soil. Sci., 2007, 170: 378-386.
[82] Benke M B, Indraratne S P, Hao Xetal. Trace element changes in soil after long-term cattle manure applications[J]. Environ. Qual., 2008, 37: 798-807.
[83] Chang A C, Warneke J E, Page A Letal. Accumulation of heavy metals in sewage-treated soil[J]. Environ. Qual., 1984, 13: 87-91.
[84] McGrath S P, Chaudri A M, Giller K E. Long-term effects of metals in sewage sludge on soils, microorganisms and plants[J]. J. Ind. Microbiol., 1995, 14(2): 94-104.
[85] Mantovia P, Baldonib G, Toderib G. Reuse of liquid, dewatered, and composted sewage sludge on agricultural land: effects of long-term application on soil and crop[J]. Water Res., 2005, 39: 289-296.
[86] Tessier A, Campbell P G C, Bisson M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals[J]. Anal. Chem., 1979, 51(7): 844-851.
[87] 王开峰, 彭娜, 王凯荣, 等. 长期施用有机肥对稻田土壤重属含量及其有效性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2008, 22(1): 105-108.
Wang K F, Peng N, Wang K Retal. Effects of long-term manure fertilization on heavy metal content and availability in paddy soils[J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2008, 22(1): 105-108.
[88] Ajayi S O, Odesanya B O, Avwioroko A Oetal. Effects of long term fertilizer use on trace metal levels of soils in a farm settlement[J]. J. Agric. Res. Develop., 2012, 2(2): 44-51.
[89] 李双异, 刘赫, 汪景宽. 长期定位施肥对棕壤重金属全量及其有效性影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2010, 29(6): 1125-1129.
Li S Y, Liu H, Wang J K. Effects of long-term fertilization on heavy metals and their availability in brown earth[J]. J. Agro-Environ. Sci., 2010, 29(6): 1125-1129.
[90] Jones C A, Jacobsen J, Lorbeer S. Metal concentrations in three Montana soils following 20 years of fertilization and cropping[J]. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 2002, 33(9-10): 1401-1414.
[91] 刘景, 吕家珑, 徐明岗, 等. 长期不同施肥对红壤Cu和Cd含量及活化率的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 2009, 18(3): 914-919 .
Liu J, Lü J L, Xu M Getal. Effect of long-term fertilization on content and activity index of Cu and Cd in red soil[J]. Ecol. Environ. Sci., 2009, 18(3): 914-919 .
[92] 陕红, 刘荣乐, 李书田. 施用有机物料对土壤镉形态的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(1): 136 - 144.
Shan H, Liu R L, Li S T. Cadmium fractions in soils as influenced by application of organic materials[J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2010, 16(1): 136 - 144.
[93] 王喜艳, 聂振江. 施用污泥对土壤中重金属含量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008, 24(12): 432-435.
Wang X Y, Nie Z J. The effect of the application of sludge on content of heavy metal in soil[J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2008, 24(12): 432-435.
[94] 谭启玲, 胡承孝, 赵斌. 两种污泥连续施用对潮土重金属含量及酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2004, 3(15): 497-500.
Tan Q L, Hu C X, Zhao B. Effect of continual application of two kinds sludge on enzyme activities and heavy metal concentrations in alluvial soil[J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2004, 3(15): 497-500.
[95] Kidd P S, Dominguez-Rodriguez M J, Diez Jetal. Bioavailability and plant accumulation of heavy metals and phosphorus in agricultural soils amended by long-term application of sewage sludge[J]. Chemosphere, 2007, 66(8): 1458-1467.
[96] 刘善江, 康少杰, 孙昊, 等. 污泥施用对油菜生长和土壤重金属积累的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2011, 27(27): 135-140.
Liu S J, Kang S J, Sun Hetal. Effects of sludge on rape growth and heavy metals accumulation in soil[J]. Chin. Agri. Sci. Bull., 2011, 27(27): 135-140.
[97] Lo′pez-Mosquera M E, Moiro′n C, Carral E. Use of dairy-industry sludge as fertilizer for grasslands in northwest Spain: heavy metal levels in the soil and plants[J]. Resour., Conser. Recycl., 2000, 30: 95-109.
[98] 温明霞, 高焕梅, 石孝均. 长期施肥对作物铜、 铅、 铬、 镉含量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2010, 24(4): 119-122.
Wen M X, Gao H M, Shi X J. Effect of long-term fertilization on accumulation of Cu, Pb, Cr and Cd in crop[J]. J. Soil Water Conserv., 2010, 24(4): 119-122.
[99] Grant C A, Bailey L D, Harapiak J Tetal. Efffect of phosphate source, rate and cadmium content and use of penicillium bilaii on phosphorus, zinc and cadmium concentration in durum wheat grain[J]. J. Sci. Food Agri., 2002, 82: 301-308
[100] Huang B, Kuo S, Bembenek R. Cadmium uptake by cucumber from soil amended with phosphorus fertilizers[J]. J. Am. Soc. Horti-cultur. Sci., 2003, 128(4): 615-620.
[101] Mortvedt J J, Mays D A, Osborn G. Uptake by wheat of cadmium and other metal contaminants in phosphate fertilizers[J]. J. Environ. Qual., 1981, 10: 193-197.
[102] Mitchell L G, Grant C A, Racz G J. Effect of nitrogen application on concentration of cadmium and nutrient ions in soil solution and in durum wheat[J]. Can. J. Soil Sci., 2000, 80: 107-115.
[103] Gray C W, Moot D J, McLaren R Getal. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer applications on cadmium concentrations in durum wheat (Triticumturgidum) grain[J]. New Zealand. J. Crop Horti-cultur. Sci., 2002, 30(4): 291-299.
[104] Wångstrand H, Eriksson J, Öborn I. Cadmium concentration in winter wheat as affected by nitrogen fertilization[J]. Eur. J. Agron., 2007, 26: 209-214.
[105] Perilli P, Mitchell L G, Grant C Aetal. Cadmium concentration in durum wheat grain(Triticumturgidum) as influenced by nitrogen rate, seeding date and soil type[J]. J. Sci. Food Agric., 2010, 90: 813-822.
[106] Li X L, Ziadi N, Be′langer Getal. Cadmium accumulation in wheat grain as affected by mineral N fertilizer and soil characteristics[J]. Can. J. Soil Sci., 2011, 91: 521-531.
[107] 王新, 陈涛. 梁仁禄. 污泥土地利用对农作物及土壤的影响研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(2): 163-166.
Wang X, Chen T, Liang R L. Effects of land utilization of sewage sludge on crops and soils[J]. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol., 2002, 13(2): 163-166.
[108] 丁文, 王海勤. 城市污泥有机肥对马铃薯产量和品质及重金属吸收的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(12): 254-256.
Ding W, Wang H Q. Effect of municipal sludge organic fertilizer on potato yield, quality and heavy metal uptake[J]. Chin. Agri. Sci. Bull., 2005, 21(12): 254-256.
[109] 陈曦, 杨丽标, 王甲辰, 等. 施用污泥堆肥对土壤和小麦重金属累积的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(8): 278-283.
Chen X, Yang L B, Wang J Cetal. Effect of sewage sludge compost application on heavy metals accumulation in soil and wheat shoots[J]. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull., 2010, 26(8): 278-283.
[110] 金燕, 李艳霞, 陈同斌, 等. 污泥及其复合肥对蔬菜产量及重金属含量积累的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2002, 8(3): 288-291.
Jin Y, Li Y X, Chen T Betal. Effects of sewage sludge compost and compound fertilizers on vegetable yield and heavy metal accumulation[J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2002, 8(3): 288-291.
[111] 黄雅曦, 李季, 李国学, 等. 施用污泥堆肥对土壤和生菜重金属积累特性的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2005, (6): 15-18.
Huang Y X, Li J, Li G Xetal. Heavy metal accumulation in lettuce in soil amended with sewage sludge compost[J]. Heilongjiang Agric. Sci., 2005, (6): 15-18.
[112] Reuss J O, Dooley H L, Griffis W. Uptake of cadmium from phosphate fertilizers by peas, radishes, and lettuce[J]. J. Environ. Qual., 1978, 7(1): 128-133.
[113] He Q B, Singh B R. Crop uptake of cadmium from phosphorus fertilizers: I. Yield and cadmium content[J]. Water Air Soil Poll., 1994, 74(3-4): 251-265.
[114] Grant C A, Bailey L D. Nitrogen, phosphorus and zinc management effects on grain yield and cadmium concentration in two cultivars of durum wheat[J]. Can. J. Plant. Sci., 1998, 78(1): 63-70.
[115] Guttormsen G, Singh B R, Jeng A S. Cadmium concentration in vegetable crops grown in a sandy soil as affected by Cd levels in fertilizer and soil pH[J]. Fert. Res., 1995, 41(1): 27-32.
[116] Mortvedt J J. Plant uptake of heavy metals in zinc fertilizers made from industrial by-products[J]. J. Environ. Qual., 1985, 14(3): 424-427.
[117] Singh B R. Cadmium and fluoride uptake by oats and rape from phosphate fertilizers in two different soils[J]. Norwegian J. Agric. Sci., 1990, 4(3): 239-249.
[118] Petršrek, Hejcman M, Kunzová E. Multivariate analysis of relationship between potato yield, amount of applied elements, their concentrations in tubers and uptake in a long-term fertilizer experiment[J]. Field Crops Res., 2010, 118: 183-193.
[119] 王瑾, 韩剑众. 饲料中重金属和抗生素对土壤和蔬菜的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2008, 24(4): 90-93.
Wang J, Han J Z. Effects of heavy metals and antibiotics on soil and vegetables[J]. J. Ecol. Rur. Environ., 2008, 24(4): 90-93.
[120] 周艺敏, 张金盛, 任顺荣, 等. 天津市园田土壤和几种蔬菜中重金属含量状况的调查研究[J]. 农业环境保护, 1990, 9(6): 30-34.
Zhou Y M, Zhang J S, Ren S Retal. Investigation of heavy metal content in soil and vegetables of Tianjin[J]. Agro-Environ. Prot., 1990, 9(6): 30-34.
[121] 孔文杰, 倪吾钟. 有机无机肥配合施用对土壤-水稻系统重金属平衡和稻米重金属含量的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2006, 20(5): 517-523.
Kong W J, Ni W Z. Effects of integrated fertilization with commercial organic manure and chemical fertilizers on heavy metal balance in soil-rice cropping system[J]. Chin. J. Rice Sci., 2006, 20(5): 517-523.
[122] 孔文杰. 有机无机肥配施对蔬菜轮作系统重金属污染和产品质量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 977-984.
Kong W J. Risk of heavy metal pollution and product quality in tomato-radish-green grocery cropping system under applications of commercial organic manure and chemical fertilizers[J]. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci., 2011, 17(4): 977-984.
[ 123] 荆旭慧, 李恋卿, 潘根兴. 不同环境条件下土壤-作物系统中重金属元素迁移分配特点[J]. 生态环境, 2007, 16(3): 812- 817.
Jing X H, Li L Q, Pan G X. Movement and partitioning of some heavy metals in soil-crop system under different environmental impacts[J]. Ecol. Environ., 2007, 16(3): 812-817.

