IL-29对胰蛋白酶诱导的肥大细胞PARs表达的调节作用①
隋 丽 陈 冬 张慧云 何韶衡 (辽宁医学院附属第一医院耳鼻咽喉科,锦州 121001)
IL-29对胰蛋白酶诱导的肥大细胞PARs表达的调节作用①
隋 丽 陈 冬 张慧云②何韶衡③(辽宁医学院附属第一医院耳鼻咽喉科,锦州 121001)
目的:检测白细胞介素29(Interleukin-29,IL-29)对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞蛋白酶激活受体(Protease activated receptor,PAR)-1,2,3,4表达的调节作用。方法:P815肥大细胞培养后,用不同浓度的IL-29、胰蛋白酶单独或联合激发肥大细胞,在不同时间点收集激发细胞,用流式细胞术(FCM)及实时定量PCR检测P815肥大细胞蛋白酶激活受体的表达。结果:IL-29单独作用能够下调肥大细胞PAR-1蛋白及mRNA水平的表达,上调PAR-3、PAR-4 mRNA的表达,与对照组相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);以IL-29预处理肥大细胞后,IL-29对胰蛋白酶诱导的肥大细胞PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4表达起促进作用,与对照组相比差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:IL-29能够调节胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PARs表达,从而参与肥大细胞相关的炎症反应。
肥大细胞;白细胞介素29(IL-29);胰蛋白酶;蛋白酶激活受体(PARs);流式细胞术
随着过敏性疾病呈明显上升趋势,近几年有关过敏反应领域的研究也进展迅速,而肥大细胞脱颗粒反应被认为是过敏性炎症过程中主要细胞反应之一,其作为初级效应细胞参与过敏性疾病的发病机制,肥大细胞一旦被过敏原激活后即释放细胞内预先形成的及新合成的介质而发挥其生物学作用,但其确切机制仍需进一步探讨。
IL-29是近年发现的一种细胞因子,又称为干扰素 λ1(Interferon λ1,IFNλ1),主要在上皮细胞及肝细胞中表达,不同起源的造血和非造血细胞被各种病毒感染后,可诱导表达IL-29,新近的研究发现大部分人的肥大细胞表达IL-29,并且蛋白水解性变应原能刺激肥大细胞释放大量的IL-29,在过敏性哮喘患者外周血浆中存在高水平的IL-29[1-4],因此,血浆中高水平的IL-29很可能来源于肥大细胞,而肥大细胞是参与过敏反应的核心细胞,IL-29可能是过敏反应中的重要促炎性细胞因子。蛋白酶激活受体(Protease activated receptors,PARs)是G蛋白偶联受体(G-protein coupled receptors,GPCRs)家族中的新成员,目前在人和小鼠体内共发现4种PARs的存在,即 PAR-1、2、3、4,胰蛋白酶作为 PARs激活酶,通过PARs相关机制诱导人肥大细胞组胺释放[5],在过敏性炎症中发挥重要作用。因此我们拟通过流式细胞术及实时定量PCR研究IL-29对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PARs表达的调节,期待为与肥大细胞相关的过敏性疾病的发病机制相关研究提供实验依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 主要试剂 青链霉素、多聚甲醛、牛血清白蛋白均购于Sigma公司,含25 mmol/L羟乙基哌嗪乙磺酸的培养基、达尔伯克改良伊格尔培养基、胎牛血清购于Gibco公司,重组人 IL-29、小鼠抗人IL-29单克隆抗体购于美国R&D公司,胰蛋白酶(Trypsin)购于Promega公司,FITC标记的兔抗鼠PAR-1单克隆抗体、羊抗鼠 PAR-2单克隆抗体、兔抗鼠PAR-3多克隆抗体、兔抗鼠PAR-4多克隆抗体购于Santa Cruz公司。PCR引物由Invitrogen公司合成,Trizol试剂购自Invitrogen公司,逆转录试剂及试剂盒由TaKaRa公司提供。
1.1.2 主要仪器 台式高速冷冻离心机购于Expender公司,细胞培养箱购于Heraeus公司,生物安全柜HFsafe1200购于Heal Force公司,FACS Calibur流式细胞仪购于Becton Dickinson公司。紫外分光光度计及电泳仪购于Bio-Rad公司,PCR扩增仪购于M J Research公司,凝胶成像分析系统购自SYNGENE公司,型荧光定量PCR扩增仪购于ABI-PE公司。
1.1.3 细胞株 小鼠肥大细胞株P815购于美国标准培养物保藏中心(ATCC)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 细胞培养、激发 肥大细胞的培养按参考文献[6]进行。1.2×106个/ml的 P815肥大细胞采用无血清基础培养基培养6 h后,PBS洗涤细胞2次,分别用 IL-29(0.1、1、10、100 ng/ml)及 trypsin (0.001、0.01、0.1、1 μg/ml)单独或联合处理 P815肥大细胞,于2、6、16 h后终止反应,于4℃条件下450 r/min离心10 min,收集并用PBS重悬细胞后,待流式细胞术(FCM)及实时定量PCR分析。
1.2.2 肥大细胞 PAR-1、2、3、4表达的检测 上述激发后的肥大细胞经20 g/L的多聚甲醛固定30 min后,用含10 g/L牛血清白蛋白的PBS洗涤、重悬细胞。PAR-1、PAR-3及PAR-4的标记:加兔抗鼠PAR-1单克隆抗体或兔抗鼠PAR-3、PAR-4多克隆抗体及同型对照2 mg/L,37℃孵育1 h后,用含10 g/L牛血清白蛋白的PBS洗涤2次后加入FITC标记的羊抗兔多克隆抗体1 mg/L,37℃孵育 1 h。PAR-2的标记:加FITC标记的羊抗鼠PAR-2单克隆抗体以及同型对照4 mg/L,37℃孵育1 h后,用含10 g/L牛血清白蛋白的PBS洗涤2次,PBS重悬细胞,与相应的二抗孵育后,以FCM检测肥大细胞PARs的表达情况。
1.2.3 实时定量逆转录聚合酶链式反应(q-RTPCR) 激发后的P815肥大细胞实时定量PCR按参考文献[7]进行。PARs及β-actin内参引物序列详见表1。
1.3 统计学处理 全部数据均采用SPSS21.0软件分析,数据均以±s表示。统计学方法为单因素方差分析或t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 IL-29对肥大细胞PARs蛋白表达的调节作用浓度为0.1、1、10、100 ng/ml的 IL-29 单独作用于肥大细胞2、6、16 h后,FCM结果显示:肥大细胞PAR-1平均荧光强度下降幅度分别达39%、45%、31%,与对照组相比差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4平均荧光强度与对照组比较,差异均无统计学意义;应用1.0 μg/ml的IL-29单克隆抗体封闭 IL-29 后,PAR-1、PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4平均荧光强度与对照组比较,差异均无统计学意义(P >0.05,图 1)。
2.2 IL-29对肥大细胞PARs mRNA的调节作用浓度为0.1、1、10、100 ng/ml的 IL-29 单独作用于肥大细胞2、6、16 h后,实时定量PCR结果显示:IL-29呈浓度依赖性下调肥大细胞PAR-1 mRNA的表达,与对照组相比差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),在作用16 h时下调强度最大达79.4%;IL-29对肥大细胞PAR-2 mRNA的表达与对照组相比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);IL-29对肥大细胞 PAR-3、PAR-4 mRNA的表达起促进作用,与对照组相比差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),在6 h及16 h时作用最强,分别达9.5 倍,11.2 倍(图2)。

表1 实时定量PCR的引物序列Tab.1 Primer sequences for mouse PARs used in real time PCR
2.3 IL-29对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PARs蛋白表达的调节 用0.1 ng/ml的IL-29预处理肥大60 min 后,用 0.001、0.01、0.1 和 1 μg/ml的胰蛋白酶激发细胞16 h,FCM检测结果显示:IL-29对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PAR-1平均荧光强度表达与基础培养液对照组、单纯IL-29作用组、单纯trypsin作用组相比差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4 平均荧光强度分别增强 2.1、1.6、1.8倍,与基础培养液对照组、单纯IL-29作用组、单纯trypsin作用组相比差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.05),IL-29对胰蛋白酶作用的肥大细胞表面PARs表达的促进作用与胰蛋白酶的浓度无关(图3)。
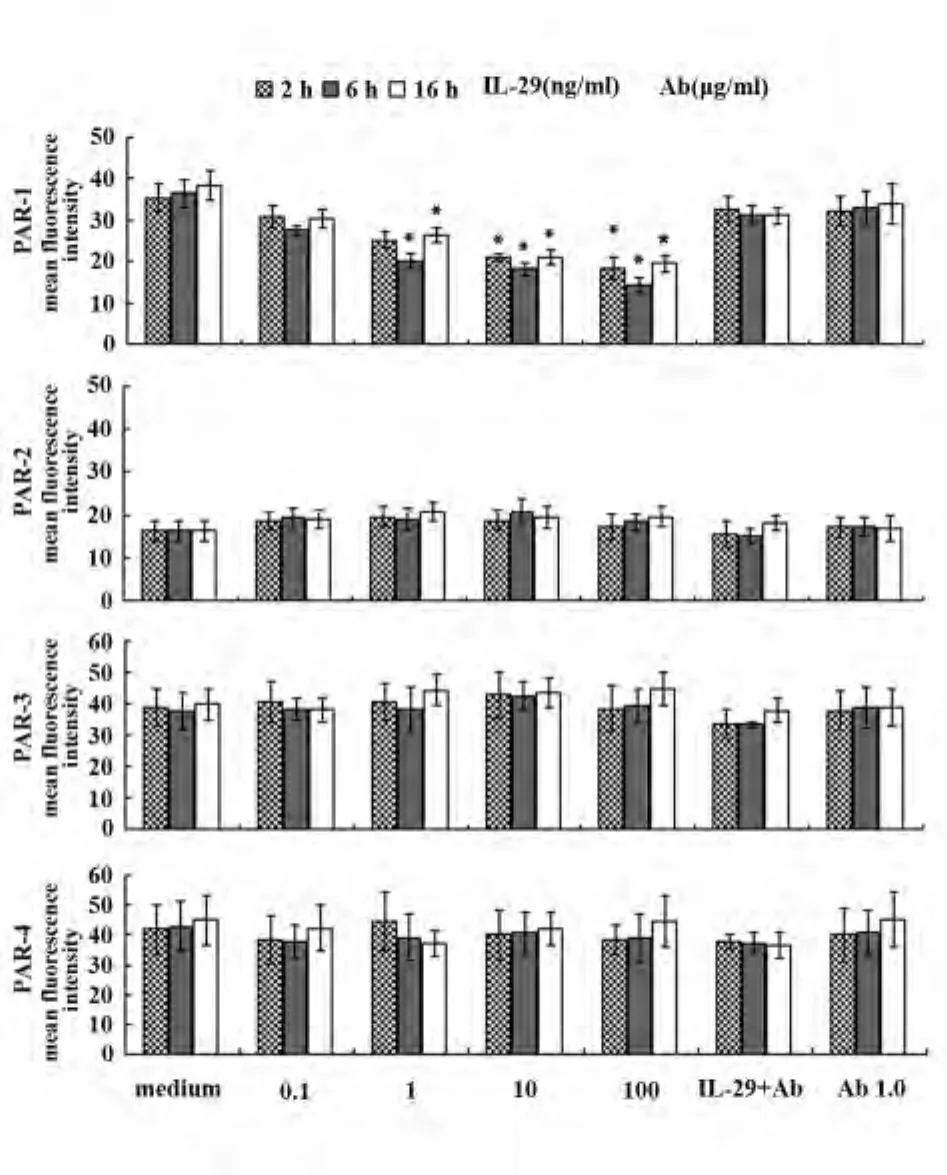
图1 IL-29 对 P815 肥大细胞 PAR-1、PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4蛋白表达的调节作用Fig.1 Effect of IL-29 on expression of protease activated receptor(PAR)-1,PAR-2,PAR-3,PAR-4 protein on P815 cells

图2 IL-29 对 P815 肥大细胞 PAR-1、PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4 mRNA表达的调节作用Fig.2 Effect of IL-29 on expression of protease activated receptor(PAR)-1,PAR-2,PAR-3,PAR-4 mRNAs on P815 cells

图3 IL-29对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PAR-1、PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4表达的调节作用Fig.3 Effect of IL-29 on trypsin-induced expression of protease activated receptor PAR-1,PAR-2,PAR-3 and PAR-4 on P815 cells
3 讨论
PARs为丝氨酸蛋白酶受体,目前共发现4种PARs的存在,即 PAR-1、2、3、4。其中 PAR-1 是胰蛋白酶和凝血酶受体[8],本研究发现IL-29单独作用时能够下调肥大细胞PAR-1蛋白及mRNA的表达,而胰蛋白酶和凝血酶已经被证实积极参与炎症过程[9-10],由此可以推测IL-29也可能通过下调肥大细胞PAR-1表达来参与和调节炎症反应过程,相关的其他细胞因子对PAR-1表达的调节作用的研究发现[11]支持本研究结果;PAR-2是胰蛋白酶、类胰蛋白酶和弹性蛋白酶受体,PAR-3和PAR-4是凝血酶受体[8,12],PAR-2 已经证实在过敏性疾病中具有正性调节作用,例如PAR-2在哮喘及过敏性鼻炎患者气道的表达增强[13,14],PAR-2 能够促进德国小镰过敏患者的呼吸道中Th2及Th17类细胞因子的释放等[15],在本实验发现 IL-29对肥大细胞 PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4蛋白的表达几乎均没有作用,但在mRNA水平,能够增强肥大细胞PAR-3、PAR-4的表达,IL-29 对肥大细胞 PAR-1、PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4表达调节作用的不同可能与细胞内池募集不同类型PARs的动员及释放情况不同有关[16],此外,也可能与转录后调控机制的改变有关[17]。
本研究中发现IL-29对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PAR-1表达几乎没有作用,对 PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4表达起促进作用,说明胰蛋白酶对IL-29引起的PAR-1下调有抑制作用,同时与IL-29协同诱导PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4蛋白的表达,这可能提示肥大细胞活化过程中存在一种放大机制:IL-29存在于未激活的肥大细胞中[3],过敏原能够诱导肥大细胞聚集和激活,激活后的肥大细胞能够分泌胰蛋白酶和IL-29,分泌的IL-29不但募集肥大细胞向炎症部位聚集,还能够使邻近的肥大细胞在胰蛋白酶的作用下表达更多的PARs,而肥大细胞PARs的过量表达使之更容易与蛋白酶作用,从而导致肥大细胞活化。IL-29通过激活肥大细胞内PI3K/Akt和JAK/ STAT3信号转导通路,诱导肥大细胞释放Th2类细胞因子如IL-4、IL-13等,这些Th2细胞因子进一步作用于其他炎症细胞而使过敏性炎症反应放大[18]。CD18及细胞间黏附分子-1可能参与IL-29诱导的肥大细胞募集[3],但因肥大细胞黏附及迁移机制并不清楚,IL-29对肥大细胞募集作用的确切机制还需进一步研究。之前的研究发现低浓度的趋化因子CCL5能够增强胰蛋白酶诱导的肥大细胞PAR-1、PAR-2和PAR-4表达,类胰蛋白酶诱导的PAR-2的表达和凝血酶诱导的PAR-1和PAR-4也支持上述观点[19]。肥大细胞产生的细胞因子具有增敏作用,如IL-29对肥大细胞PARs表达的调节并且促进胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞释放促炎细胞因子,这些都有助于过敏性炎症的发展。而IL-29对胰蛋白酶作用的肥大细胞PARs表达的促进作用与胰蛋白酶浓度无关,这可能与胰蛋白酶的含量达到阈值有关。
综上,IL-29能够选择性地下调肥大细胞PAR-1蛋白及mRNA水平的表达,增强PAR-3、PAR-4 mRNA水平的表达,也能够通过促进胰蛋白酶引起肥大细胞PAR-2、PAR-3、PAR-4表达参与过敏性炎症反应,但多种理化刺激、病理过程能调节PARs的表达情况[20],且转录翻译、膜表面转运和溶酶体降解都与PARs表达的调节密切相关,所以仍期待深入探究各种因素包括IL-29对胰蛋白酶引起的肥大细胞PARs表达调节的确切机制。
[1]Dolganiuc A,Kodys K,Marshall C,et al.Type III interferons,IL-28 and IL-29,are increased in chronic HCV infection and induce myeloid dendritic cell-mediated FoxP3+regulatory T cells[J].PLoS One,2012,7(10):e44915.
[2]Park H,Serti E,Eke O,et al.IL-29 is the dominant type III interferon produced by hepatocytes during acute hepatitis C virus infection[J].Hepatology,2012,56(6):2060-2070.
[3]He S,Zhang H,Chen H,et al.Expression and release of IL-29 by mast cells and modulation of mast cell behavior by IL-29 [J].Allergy,2010,65(10):1234-1241.
[4]He S,Li T,Chen H,et al.CD14+cell-derived IL-29 modulates proinflammatory cytokine production in patients with allergic airway inflammation[J].Allergy,2011,66(2):238-246.
[5]He SH,Xie H,Fu YL.Activation of human tonsil and skin mast cells by agonists of proteinase activated receptor-2[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2005,26(5):568-574.
[6]Zhang H,Lin L,Yang H,et al.Induction of IL-13 production and upregulation of gene expression of protease activated receptors in P815 cells by IL-6[J].Cytokine,2010,50(12):138-145.
[7]Zhang H,Yang X,Yang H,et al.Modulation of mast cell proteinase-activated receptor expression and IL-4 release by IL-12[J].Immunol Cell Biol,2007,85(7):558-566.
[8]Ossovskaya VS,Bunnett NW.Protease-activated receptors:contribution to physiology and disease[J].Physiol Rev,2004,84 (2):579-621.
[9]Ma L,Dorling A.The roles of thrombin and protease-activated receptors in inflammation [J].Semin Immunopathol,2012,34 (1):63-72.
[10]Adams MN,Ramachandran R,Yau MK,et al.Structure,function and pathophysiology of protease activated receptors[J].Pharmacol Ther,2011,130(3):248-282.
[11]Colognato R,Slupsky JR,Jendrach M,et al.Differential expression and regulation of protease activated receptors in human peripheral monocytes and monocyte-derived antigen-presenting cells[J].Blood,2003,102(7):2645-2652.
[12]张慧云,何韶衡.蛋白酶激活受体在过敏反应中的作用及检测方法[J].中华检验医学杂志,2007,30(3):339-342.
[13]D′Agostino B,Roviezzo F,De Palma R,et al.Activation of protease-activated receptor-2 reduces airways inflammation in experimental allergic asthma[J].Clin Exp Allergy,2007,37(10): 1436-1443.
[14]Dinh QT,Cryer A,Trevisani M,et al.Gene and protein expression of protease-activated receptor 2 in structural and inflammatory cells in the nasal mucosa in seasonal allergic rhinitis[J].Clin Exp Allergy,2006,36(8):1039-1048.
[15]Page K,Ledford JR,Zhou P,et al.Mucosal sensitization to German cockroach involves protease-activated receptor-2[J].Respir Res,2010,11(1):1-10.
[16]Hirano K,Yufu H,Hirano M,et al.Physiology and pathophysiology of proteinase-activated receptors(PARs):regulation of the expression of PARs[J].Pharmacol Sci,2005,97(1):31-37.
[17]Esnault S,Malter JS.Hyaluronic acid or TNF-alpha plus fibronectin triggers granulocyte macrophage-colony-stimulating factor mRNA stabilization in eosinophils yet engages differential intracellular pathways and mRNA binding proteins[J].Immunology,2003,171(12):6780-6787.
[18]Feng BS,Zheng PY,Chen X,et al.Investigation of the role of cholera toxin in assisting the initiation of the antigen-specific Th2 response[J].Immunol Invest,2008,37(8):782-797.
[19]Zhang H,Yang H,Ma W,et al.Induction of IL-13 production and upregulated expression of protease activated receptor-1 by RANTES in a mast cell line[J].Cytokine,2011,53(2):231-238.
[20]Zhang H,Lin L,Yang H,et al.Induction of IL-13 production and upregulation of gene expression of protease activated receptors in P815 cells by IL-6[J].Cytokine,2010,50(2):138-145.
[收稿2013-12-07 修回2014-01-13]
(编辑 张晓舟)
Effect of IL-29 on trypsin-induced protease-activated receptor expression on P815 mast cells
SUI Li,CHEN Dong,ZHANG Hui-Yun,HE Shao-Heng.Department of ENT,the First Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning Medical University,Jinzhou 121001,China
Objective:To investigate the modulatory effect of IL-29 on trypsin-induced protease activated receptors(PARs)expression on P815 mast cell.MethodsAfter P815 mast cells were challenged with different concentrations of IL-29 alone or combined with trypsin for 2 h,6 h and 16 h,the challenged cells were collected and analysed by flow cytometry to detect the protein expression of PARs on P815 cells,and analysed by real time RT-PCR to detect the mRNA expression of PARs on P815 cells.ResultsCompared with the corresponding control,IL-29 induced significantly decreased expression of PAR-1 at protein and mRNA level on P815 cells,and upregulated PAR-3,PAR-4 mRNA level on P815 cells,whereas IL-29 did little effect on the expressions of PAR-2,3,4 at protein level on P815 cells accordingly.Preincubation of mast cell with IL-29 did not alter trypsin-induced PAR-1 expression on P815 cells,whereas up-regulated expression of PAR-2,3,4 were detected when P815 cell were pre-treated with IL-29 before being challenged with trypsin compared with the corresponding control.ConclusionIL-29 can upregulate trypsin-induced PARs expression on mast cells through which participated in mast cell related inflammation.
Mast cell;Interleukin-29(IL-29);Trypsin;Protease activated receptors(PARs);Flow cytometry
R329.8
A
1000-484X(2014)05-0609-05
10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2014.05.008
①本文为 国 家 自 然 科 学基 金 (81241135,81060250,81172836,
81030054)和辽宁省博士科研启动基金资助项目(20101063)。②海南医学院病理生理学教研室,海口571101。
③辽宁医学院附属第一医院变态反应与临床免疫研究中心,锦州121001。
隋 丽(1981年-),女,主要从事过敏性鼻炎发病机制的研究,E-mail:suili1018@163.com。
及指导教师:陈 冬(1972年-),男,博士,主任医师,教授,硕士生导师,主要从事过敏性鼻炎发病机制的研究,E-mail:entdoctorchen@163.com。

