Synthesis and Biological Properties of the Complex Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)
GU Mei,ZHONG Guo-qing
(State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for Nonmetal Composite and Functional Materials,School of Material Science and Engineering,Southwest University of Science and Technology,Mianyang 621010,China)
Many 2,3-pyrazinedicarboxylic acid complexes which were synthesized as linear chains or infinite networks are coordination polymers with special electronic and magnetic properties[1].In particular,2,3-pyrazinedicarboxylic acid had been studied extensively because of its versatile coordination sites and good candidate for the assembly of novel metal-organic complexes[2-3].The presence of two carboxyl groups in different orientations permits the construction of one-,two-or three dimensional frameworks,aside from the metal-ligand coordination bond,other relatively weak intermolecular interactions such as hydrogen-bonding and π-π stacking interactions can further reinforce supramolecular structure[4-5].It is known that 2,3-pyrazinedicarboxylic acid is an important chemical intermediate of pyrazinamide which has very good effect on tuberculosis[6],and pyrazine derivatives have potent antifungal and cytotoxic effect[6-8].The fifth main group metal compounds including inorganic and metallorganic complexes have been studied for decades thanks to the interesting medical,physical properties and functional materials[9-10].Bismuth is the heaviest stable element in the periodic table,and its compounds have been extensively studied in the past decades because of their potential applications in medicine[11],catalysis[12]and inorganic synthesis.The bismuth complexes have been diffusely used because of its nontoxic,antibacterial activity[13],anti-inflammatory[14]and anti-cancer property[15].The research on design and synthesis of metal-organic coordination polymers is an area of substantial interest due to the potential of these materials in various applications as functional materials.Therefore,the synthesis of bismuth complexes will be very important not only for the bioinorganic chemistry of main group metal elements,but also for medicine application.Moreover,the complexes of bismuth and 2,3-pyrazinedicarboxylic acid have been much less investigated.Therefore,we chose Bi(NO3)3·5H2O and biological function ligand of 2,3-H2pzdc to synthesize new bismuth complex Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH).We report herein the syntheses,spectroscopic properties,thermal properties and X-ray powder diffraction analysis of the complex.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials
1.2 Physical measurements
The bismuth content was determined by EDTA complexometric titration with xylenol orange as the indicator,and the carbon,hydrogen and nitrogen analyses were obtained using a Vario EL CUBE elemental analyzer(Germany elemental analysis Inc.).The infrared spectra were recorded on an FT-IR spectrophotometer(Nicolet-5700)in the region from 4 000 to 400 cm-1using KBr pellets.The thermogravimetric analysis of the complex was measured by a TA Q500 thermogravimetric analyzer under air.The measurement was recorded from 30 to 600 ℃at the heating rate of 10 ℃·min-1.X-ray powder diffraction was performed using a D/max-ⅡX-ray diffractometer(Japan Science Corporation),Cu Kαradiation(λ=0.154 056 nm,step width:2θ=0.2°,scan speed:8°/min).The UV-Vis spectra were recorded on a UNICO UV-210 PCS spectrophotometer and the fluorescence spectra on a LS-5500 luminescence spectrometer.
1.3 Synthesis of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)
A total of(0.504 3 g,3 mmol)2,3-H2pzdc was dissolved in 15 mL of distilled water at 100 ℃.After 2,3-H2pzdc was dissolved completely,then(0.503 2 g,1 mmol)of Bi(NO3)3·5H2O was added to the above mentioned solution,producing a white precipitate.The mixture was kept stirring for 3 days under solid liquid reflux reaction at 100 ℃.The resultant was separated from the reaction mixture by filtration at this temperature,then washed with boiling water,and dried at 60 ℃.As suggested by the thermogravimetric analysis and the chemical assay of bismuth,the stoichiometry of the resultant is close to Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH).Anal.Found for Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH):Bi 37.37%,C 25.63%,N 9.97%,H 1.14%;and calcd for Bi 37.31%,C 25.73%,N 10.00%,H 1.26%,respectively.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 X-ray powder diffraction analysis
The X-ray powder diffraction data of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)and 2,3-H2pzdc was collected in the diffraction angle range of 3°~80° in Fig.1.The main diffraction peaks appeared in 2θ=14.44°,22.98° and 33.78° for 2,3-H2pzdc,and in 2θ=10.36°,20.82°,12.74° and 16.44° for Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH).The diffraction angle,the distance of crystal plane and the diffraction intensity of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)were completely different from 2,3-H2pzdc.It indicated that Bi(NO3)3·5H2O and 2,3-H2pzdc had formed a new compound.Getting the index calculation of XRD data based on the computer program of least squares method[16],the results were shown in Tab.1.In Tab.1,all the peaks in the X-ray diffraction pattern of the complex can readily be indexed by a set of lattice parameters according to a monoclinic symmetry,and the calculated values of interplanar crystal spacing were close to the experimental values,and the maximum relative percentage error was less than 0.3%,it indicated that the resultant was a single phase compound.The crystal structure of the complex Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)belongs to monoclinic system with crystal cell parameters of a=1.714 3 nm,b=1.383 0 nm,c=1.832 1 nm and β=95.63°,respectively.
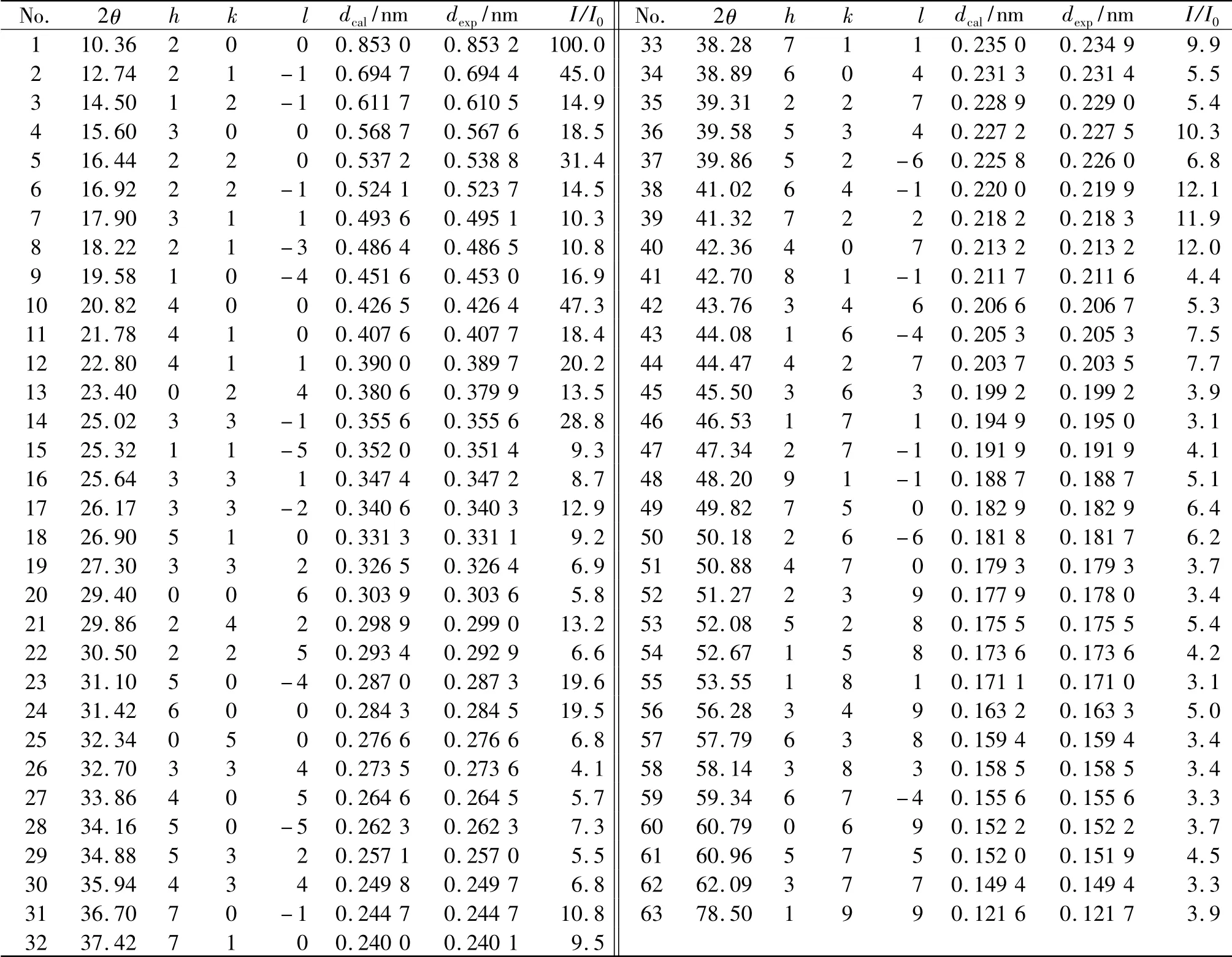
Tab.1 Experimental data and calculated results for powder X-ray diffraction pattern of the complex Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)(monoclinic system:a=1.714 3 nm,b=1.383 0 nm,c=1.832 1 nm,β=95.63°)
2.2 FT-IR spectra
The FT-IR spectra of the complex are compared with those of free ligand in order to determine the coordination sites that may involved in chelation.In Fig.2,a wide intense absorption band around 3 426.07 cm-1can be assigned to stretching vibration of hydroxyl.The absorption bands between 2 500 and 3 267 cm-1are stretching vibration of hydroxyl which belong to the dimmer of carboxylic acid.Similar absorption bands of the complex appear at 2 358.71 cm-1.The bands centred at 1 717~1 754 cm-1in the IR spectra of the free ligand can be assigned to stretching vibrations of the carboxyl group.The difference of 255.34 cm-1between the asymmetric(1 592.22 cm-1)and symmetric(1 336.88 cm-1)modes of the carboxylate group is in line with a monodentate type of coordination[17].The vibration peak found in the 446.19 cm-1region are assigned to the Bi-O(H)-Bi bonds[18].It indicates that each ligand molecule has one carboxylic function and coordinates to the metal ion through an oxygen atom of the carboxylate group.Thevibrations in 1 553.11 cm-1and ArC=O at 1 638.11 cm-1shifts towards lower frequencies,1 553.11 cm-1is the specific absorbing peak about the nitrogen atom of pyrazine coordinates to the metal ion,it confirms that the nitrogen atom is coordinated to the metal ion.The specific absorbing peak of pyrazine appears at 1 429.00,1 108.81 and 832.51 cm-1[19],and C—O vibrations at 1 337.23 cm-1[3].Therefore,it can conclude that the Bi(Ⅲ)ions are joined via two μ-OH bridging ligands.In the title complex,the central Bi(Ⅲ)ion may be coordinated by two oxygen and two nitrogen atoms from carboxylic and pyrazinyl groups of two the 2,3-H2pzdc ligands,and two oxygen atoms from two μ-OH bridging ligands,respectively.
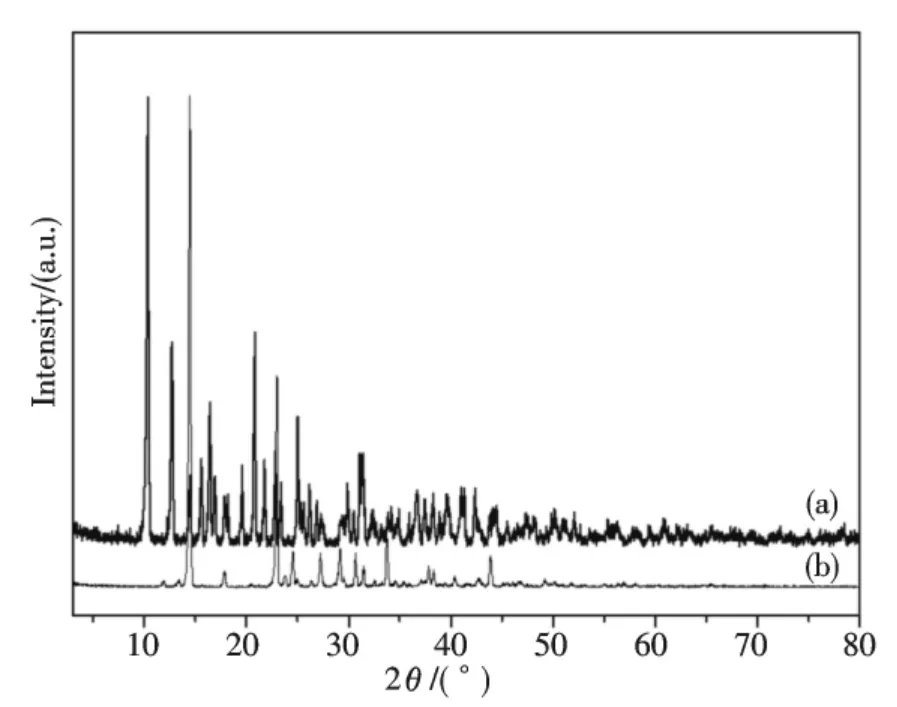
Fig.1 XRD patterns of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)(a)and 2,3-H2pzdc(b)
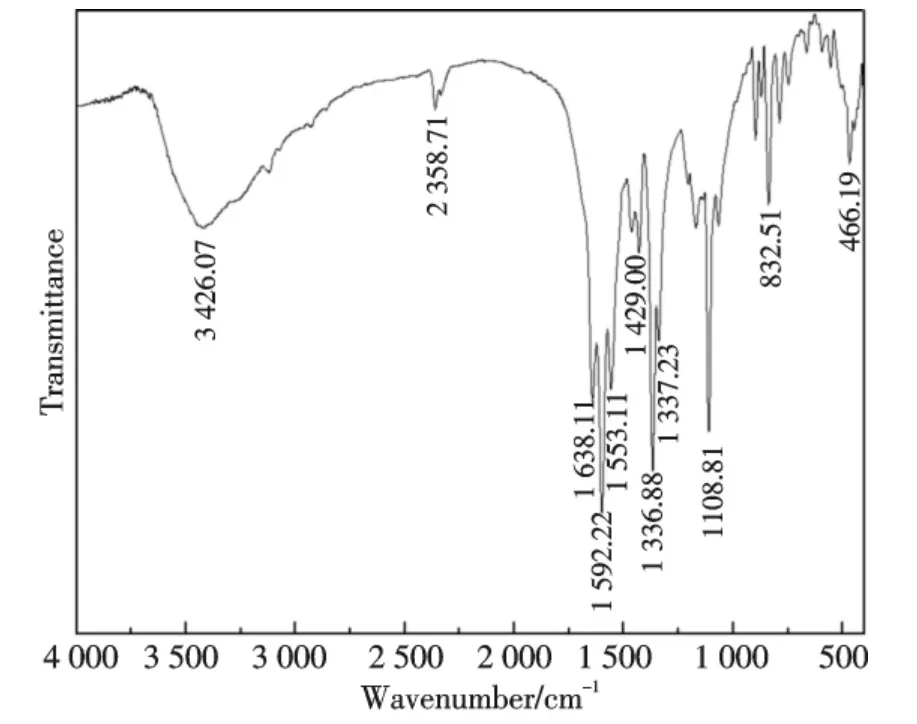
Fig.2 FT-IR spectra of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)
2.3 Thermal decomposition reaction
To study the thermal decomposition process of complexes is helpful to the understanding of the coordination structure of complexes[20].The TG and DSC curves of the complex were given in Fig.3.The denuded H2O of the complex took place in the first step,then the complex became to be Bi(Hpzdc)(pzdc).In this step the TG curve shows an obvious weight loss from 105.07 ℃to 163.58 ℃is observed about 3.36%,the experimental value was compared favourably with the theoretical value(calcd.3.21%;found 3.36%),the expected endothermic peak from 103.30 ℃to 172.18 ℃for the denuded H2O process associated with the complex has been observed in the DSC curve.As well as Bi(Hpzdc)(pzdc)was successively oxidized and decomposed from 167.83 ℃ to 481.02 ℃in the second step.The TG curve displays an obvious weight loss in this step that agrees with the simultaneous evolution of two ligands(calcd.55.20%,found 54.24%),among which the ligands are burnt completely,only inorganic compound Bi2O3was obtained and its weight content is 42.40%(calcd.41.59%).In Fig.3,the DSC curve shows three exothermic unresolved peaks in the temperature range 283~469 ℃.Thus we can conjecture that the oxidative decomposition of the complex takes place in four steps.These results further ascertain that the resultant is composed of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH).
2.4 UV-Vis spectra
The reaction was carried out in a quartz cell(1 cm)and place in the cell compartment of a UV-Vis spectrophotometer.In a typical experiment,3.00 mL of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)solution(4.0×10-6mol·L-1)was added in a quartz cell,and 10.00 μL of DNA(1.2×10-4mol·L-1)solution was gradually added in the solution(10 μL each time,the volume effect was so small that could be ignored.),using solvent(Tris-HCl)as reference.In Fig.4,the complex exhibits mainly two maxima absorption peaks at 227 nm(ε=515 000 L·mol-1·cm-1)and 256 nm(ε=522 500 L·mol-1·cm-1)due to π-π*and n-π*intraligand transitions of 2,3-H2pzdc.DNA is the primary intracellular target of anticancer drug,because of its specific structure and function,forming a new compound with coordination compound[21].In Fig.4,it showed that the intensity of the peaks larger than in absence of DNA.And in Fig.5,with the addition of DNA solution,the intensity of the UV-Vis peaks at 227 nm and 256 nm increase gradually,the spectral characteristics suggested that the absorption peaks did not generate bathochromic shift,and appeared hyperchromism.In summary,the experimental results indicated that there was an interaction between Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)and DNA at molecular level,and indicated that a beneficial hydrogen bond may be formed between OH of the complex and N of adenine or O of thymine in the DNA[22].The amount of complex bound to DNA is not available from this experiment.The biological target of this complex is unknown.However,we have known here that the complex is able to bind to hs-DNA physiological relevant conditions.
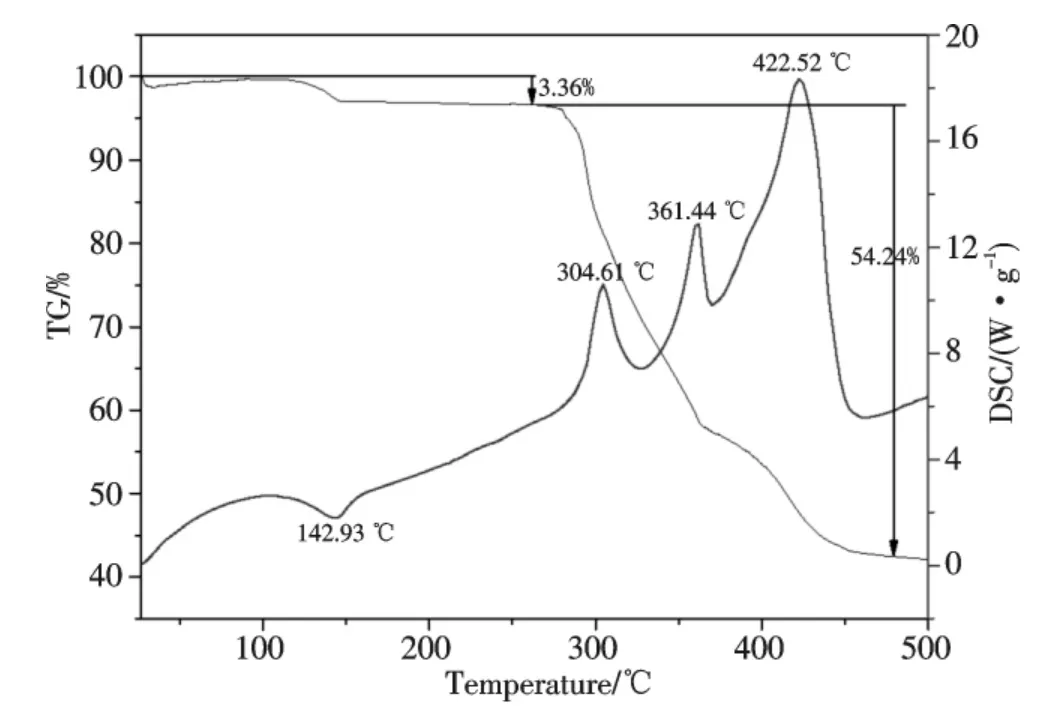
Fig.3 TG and DSC curves of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)
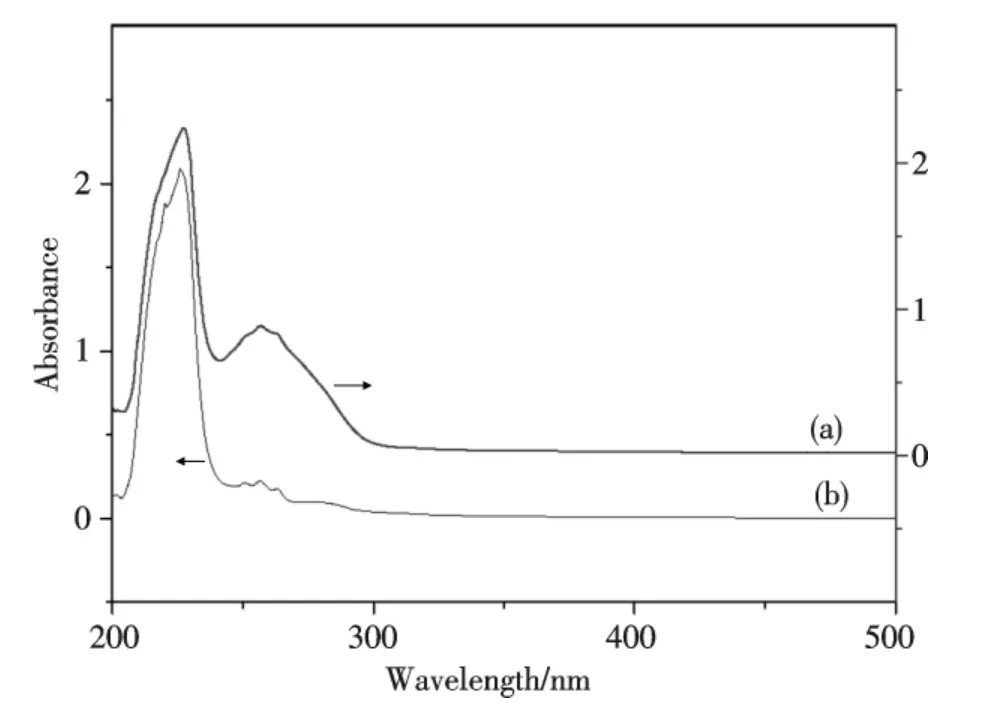
Fig.4 UV-Vis spectra of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)-DNA(a)and Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)(b)
2.5 Luminescent property
The bismuth cation in inorganic complexes or hosts exhibits considerable luminescence properties resulting from ligand to metal coordination[23].The luminescence properties of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)in Tris-HCl solvent at room temperature were analyzed in Fig.6 and Fig.7,the excitation spectra has a maximum at 243 nm with an emission 428 nm upon.The ligand of 2,3-H2pzdc gave an intense emission band at 439 nm upon excitation at 337 nm[24].The emission spectra of the complex had a large blue-shift relating to 2,3-H2pzdc,indicating an enhancement of the π-conjugation due to the complexation of 2,3-H2pzdc with Bi(Ⅲ).The emission may be assigned to the ligand-to-metal charge transition(LMCT)modified by metal coordination[25].

Fig.5 UV-Vis spectra of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)-DNA(UVVis spectra of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)in different molar quantity of DNA.c(DNA)=1.20×10 -4 mol·L -1(10 μL per scan),c[Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)]=4.00×10 -6 mol·L -1)
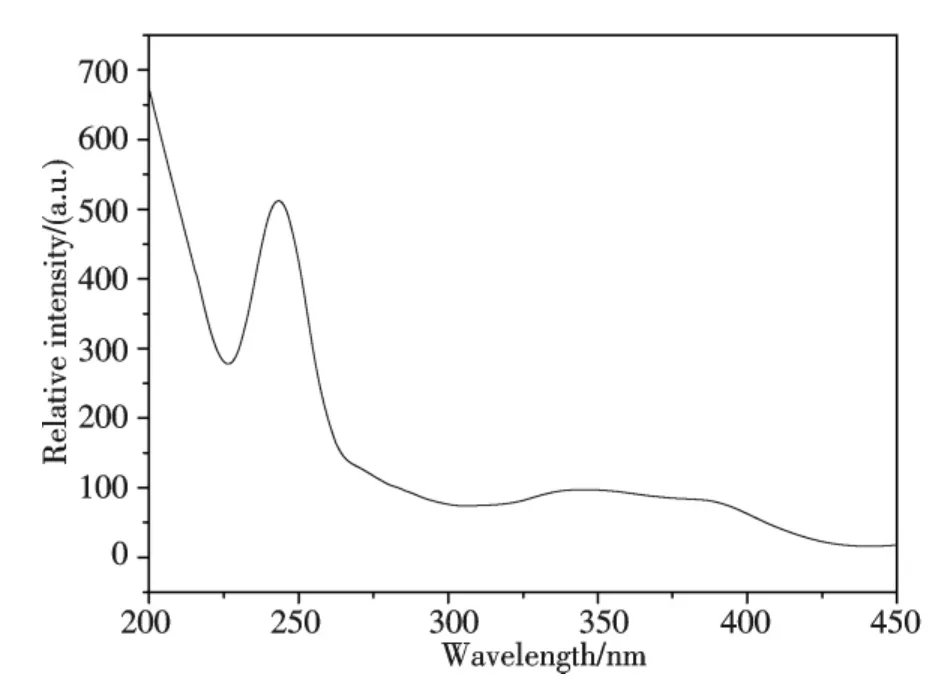
Fig.6 Excitation spectra of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)in Tris-HCl solvent at room temperature

Fig.7 Emission spectra of Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)in Tris-HCl solvent at room temperature
3 Conclusions
In summary,the complex Bi(2,3-Hpzdc)2(μ-OH)had been synthesized and characterized structurally.The crystal structure of the complex belongs to monoclinic system.The Hpzdc-anion acts as a bidentate ligand,its coordination sites being the carboxylate oxygen atom and nitrogen atom of pyrazine ring.The Bi(Ⅲ)ions may be joined with two centrosymmetric hydroxyl bridges.The UV-Vis spectra of the complex suggested that it may be a potential candidate for biological activity drug.Further research is continuing in this area.
[1]HU X D,XU Z,ZOU J Z.Synthesis and structure of 2,3-pyrazinedicaroxylate cobalt(Ⅱ)complex[J].Chin J Inorg Chem,1998,14(3):308-312.
[2]WANG F Q,ZHUANG W J,JIN L P.Self-assembly and structure of three new Zn(Ⅱ)complexes with pyrazine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid[J].J Mol Struct,2007,832(1-3):48-54.
[3]TANG Q,ZHANG C J,ZHANG C H,et al.Two sandwich-type compounds from Keggin polyoxometalate,d10metals and the product of in situ catalyzed decarboxylation of pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid[J].Inorg Chem Commun,2012,15:238-242.
[4]LI J X,DU Z X,WANG L Z,et al.Cobalt and cadmium complexes with N-heterocyclic dicarboxylic acid ligands:syntheses,structures,magnetic and fluorescent properties[J].Inorg Chim Acta,2011,376(1):479-485.
[5]WANG F Q,WENG D F,ZHENG X J,et al.3D supramolecular network assembly and thermal decomposition of new copper(Ⅱ)complexes with pyrazine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid[J].Inorg Chim Acta,2007,360(6):2029-2038.
[6]SEITZ L E,SULING J W,REYNOLDS C R.Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of pyrazine and quinoxaline derivatives[J].J Med Chem,2002,45(25):5604-5606.
[7]YEŞILEL O Z,MUTLU A,DARCAN C,et al.Syntheses,structural characterization and antimicrobial activities of novel cobalt-pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylate complexes with N-donor ligands[J].J Mol Struct,2010,964(1-3):39-46.
[8]DOLEZAL M,CMEDLOVA P,PALEK L,et al.Synthesis and antimycobacterial evaluation of substituted pyrazinecarboxamides[J].Eur J Med Chem,2008,43(5):1105-1113.
[9]JIANG Q Y,DENG H Q,ZHONG G Q,et al.Crystal structure and thermal decomposition of a 2D heterometallic coordination polymer{[NdBi(cydta)(NO3)2(H2O)4]·2.5H2O}n[J].Acta Chim Sinica,2008,66(12):1429-1434.
[10]SHEN J,JIN B,ZHONG G Q,et al.Synthesis,characterization,and magnetic properties of heterometallic trinuclear complex with Sb(Ⅲ)and Ho(Ⅲ)[J].Inorg Chim Acta,2012,385:158-163.
[11]CHEN M J,JIANG Q Y,ZHONG G Q.Synthesis and characterization of bismuth(Ⅲ)complexes with pyridinecarboxylic acid[J].J Synth Cryst,2008,37(2):322-326.
[12]BONVIN Y,CALLENS E,LAROSA I,et al.Bismuth-catalyzed benzylic oxidatons with tert-butyl hydroperoxide[J].Org Lett,2005,7(21):4549-4552.
[13]YANG S P,HAN L J,PAN Y,et al.Synthesis,crystal structure and antibacterial activity of a bismuth(Ⅲ)complex[Bi2(PPA)6·(Phen)2]with phenylacetic acid and 1,10-phenanthriline[J].Acta Chim Sinica,2012,70(4):519-524.
[14]PARRILHA G L,VIEIRA R P,CAMPOS P P,et al.Coordination of lapachol to bismuth(Ⅲ)improves its anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic activities[J].Biometals,2012,25(1):55-62.
[15]TIEKINK E R T.Antimony and bismuth compounds in oncology[J].Crit Rev Oncol Hemat,2002,42(3):217-224.
[16]ZHONG G Q,GUO Y C,CHEN Y R,et al.Synthesis and crystal structure of the complex of thioglycollic acid and trivalent antimony ion[J].Acta Chim Sinica,2001,59(10):1599-1603.
[18]WENKIN M,TOUILLAUX R,DEVILLERS M.Bismuth derivatives of 2,3-dicarboxypyrazine and 3,5-dicarboxypyrazole as precursors for bismuth oxide based materials[J].New J Chem,1998,22(9):973-976.
[19]ALLAN J R,PATON A D.Thermal and electrical studies on pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid compounds of manganese(Ⅱ),cobalt(Ⅱ),nickel(Ⅱ),copper(Ⅱ)and zinc(Ⅱ)[J].Thermochim Acta,1988,124:345-357.
[20]ZHONG G Q,SHEN J,JIANG Q Y,et al.Synthesis,characterization and thermal decomposition of SbⅢ-M-SbⅢtype trinuclear complexes of ethylenediamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetate(M:Co(Ⅱ),La(Ⅲ),Nd(Ⅲ),Dy(Ⅲ))[J].Therm Anal Calor,2008,92(2):607-616.
[21]WANG X M,LI H B,LIU H P.et al.The interaction of methylthymol blue-Er(Ⅲ)complexes with herring sperm DNA[J].J Nat Sci Hunan Normal Univ,2006,29(2):61-64.
[22]KUMAR R S,ARUNACHALAM S.Synthesis,characterization and DNA binding studies of a polymer-cobalt(Ⅲ)complex containing the 2,2'-bipyridyl ligand[J].Polyhedron,2006,25(16):3113-3117.
[23]JIANG Q Y,DENG H Q,ZHONG G Q,et al.Sm(Ⅲ)-Bi(Ⅲ)heterometallic complexes with aminopolycarboxylate ligand:structure,thermal stability and spectral property[J].Chin J Chem,2011,29(12):2637-2642.
[24]LI Y W,TAO Y,HU T L.Synthesis,structure,and photoluminescence of Zn(Ⅱ)and Cd(Ⅱ)coordination complexes constructed by structurally related 5,6-substituted pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylate ligands[J].Solid State Sci,2012,14(8):1117-1125.
[25]LI X M,JI J Y,NIU Y L,et al.Synthesis,crystal structure and fluorescent property of zinc coordination polymer assembled by pyrazine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid and bis(imidazol)ligands[J].Chin J InorgChem,2012,28(8):1712-1716.

