乳腺癌保乳术后加速部分乳腺照射研究进展
张勇乾 综述 王雅棣 审校
早期乳腺癌保乳手术辅以术后放疗的局部复发率和总生存率与全乳腺切除手术相当,而且具有良好的美容效果,已成为早期乳腺癌的标准治疗模式之一[1]。研究显示,保乳手术后加或不加全乳腺放疗(whole breast irradiation,WBI)的局部复发均多发生在原肿瘤切除区周围较小范围内,而同侧乳腺内远离原瘤床区域复发的可能性与对侧乳腺相似[2],提示切口附近是复发的高危区,有必要进行增强照射,而乳腺照射范围可进一步缩小。因此,缩小照射范围、缩短总疗程的加速部分乳腺照射(accelerated partial breast irradiation,APBI)作为保乳术后WBI的替代治疗方法,得到了越来越广泛的认同。本文对近年来APBI相关的技术进展及临床应用研究进行概述。
1 保乳术后WBI的意义
近年来,随人们对美容及生活质量要求的提高,早期乳腺癌采用保留乳房的手术加术后WBI可取得与根治术相同的疗效[3]。常用放射治疗方式为单次剂量2.0 Gy,1次/d总量50 Gy的全乳腺外照射,根据情况给予或不给予瘤床局部加量,与单纯保乳手术相比,放疗使乳腺癌局部复发率显著降低。曾有学者选择局部复发风险较低的患者,行肿瘤切除,不行术后放疗,发现局部复发率高达23%[4],研究显示乳腺癌保乳术后行和未行放疗的10年局部复发率分别为 5.8%vs.23.5%[2],20年为 14.3%vs.39.2%[3]。因此,术后WBI作为提高保乳手术局部控制率、保证保乳治疗整体疗效是不可缺少的治疗手段,已得到广泛认同。另一方面,虽然术后放疗使乳腺癌相关死亡率显著降低,但并未增加总生存率,因为传统的WBI对于心肺等重要器官的损伤较大,增加了远期病死率[3]。而且,WBI治疗需5~6周,患者必须每天往返于医院和居住地之间,甚至有部分早期患者由于距离放疗中心较远,而被迫选择了改良根治术。
2 APBI技术
APBI相对于WBI而言,照射范围局限在原瘤床周围,常采用的分割方式为3.4 Gy/次,总量34 Gy,一般1周内可完成治疗,所以称为加速部分乳腺照射。常用的治疗方式有术中放疗、外照射和近距离放疗三种模式。
2.1 术中放疗
术中放疗一般是于手术中(肿块切除前或后)给予瘤床周围3~12 MV的电子线21 Gy,或50 KV的低剂量X线、距施源器表面1 mm处剂量20 Gy的一次性照射。其优点是瘤床照射准确,对正常组织损伤小,更有助于降低复发和提高美容效果。另外,相比于其他方式的APBI,术中放疗仅需进行一次照射,减少了医师、物理师的工作量及加速器的占用时间。但术中放疗时并无术后病理结果参考,少数患者可能存在治疗不当的问题,而术中放疗需要专用的无菌术中放疗设备及防护设备,且实施者多是外科医生,相对放射生物及物理知识较少,难以达到技术要求,这也限制了此项技术的普及应用。
2.2 外照射
包括电子线外照射、三维适形放疗(three dimensional conformal radiotherapy,3D-CRT)和调强放疗(intensity-modulated radiation therapy,IMRT)等技术,一般4~7 d完成治疗。外照射常用单次剂量为3.4~3.85 Gy,2次/d,共10次。也有采用1次/d 6 Gy,共5次,总剂量30 Gy的方法[5]。照射范围为原瘤床外扩1.5~3 cm。因为外照射是在术后实施的,可以参考完整的病理结果来制定靶区范围和剂量,并可使靶区剂量均匀分布。相比于近距离放疗和术中放疗,外照射由专业的放疗医生和物理师执行,熟知临床肿瘤的生物学特性及放射生物、放射物理的理论,经验丰富,且对靶区的覆盖及均匀性均优于术中和近距离照射。
Rusthoven等[6]指出IMRT对于正常组织的保护要好于3D-CRT。韩国的一项研究对比了传统的3D-CRT、IMRT、螺旋断层调强放疗(helical tomotherapy,TOMO)、质子束放疗(proton beam therapy,PBT)4种放疗方法。认为对于同侧正常乳腺的保护,PBT要优于TOMO、IMRT和3D-CRT。对于同侧肺的平均V20,PBT和IMRT要明显低于3D-CRT和TOMO。对于左侧乳腺癌患者,TOMO对于心脏的照射明显高于3D-CRT、IMRT和PBT[5]。
2.3 近距离治疗
近距离治疗常用的技术有两种:组织间插植和单导管球囊(mammosite)近距离放疗,通过导管置入低剂量率、高剂量率或脉冲式剂量率192Ir同位素。
组织间插植是应用较早的APBI技术,在保乳术后,全身麻醉下,将多根细针或导管穿过瘤床,治疗范围大致是瘤床外扩1~2 cm,总剂量32~34 Gy(高剂量率)或45~55 Gy(低剂量率)。与单导管技术相比,应用较多的导管可以使肿瘤内剂量分布更加均匀,更好地控制皮肤和胸壁的剂量。组织间插植的缺点是实施复杂,对操作者的技术水平要求较高,在乳腺组织较小或肿瘤接近腋窝时不适用,而且实施时需要进行全身麻醉,这就限制了该项技术的推广应用。
mammosite是另一种常用的近距离放疗设备,是一个具有两个内腔的单导管球囊,为目前应用最广泛的球囊设备。置入乳腺后由一个内腔注入盐水和对比剂使球囊膨胀填充原瘤腔,经另一个内腔,在球囊的中心置入一个高剂量率放射源。常用的治疗方法是2次/d,共10次,总剂量34 Gy。mammosite设备简单、易于操作,因此一经推出,便得到了广泛的应用[7]。临床报道mammostie治疗后具有良好的美容效果,美容效果的好坏与是否感染、球囊距皮肤的距离等因素相关[8],当球囊距皮肤距离≥7 mm时,可取得最佳的美容效果和最少的皮肤损伤[9]。
因为mammosite是单导管,其剂量分布不能根据手术腔的变化而变化,也无法调整剂量分布以避开心脏和肺等重要器官,在瘤腔较大、瘤腔不规则或肿瘤接近乳腺边缘时不适用[10],在乳腺较小时,更易出现放射性皮炎等不良反应[11]。目前正在研究组织间插植与球囊相结合的近距离治疗设备,这些设备具有球囊设备单导管插入的优点和组织间插植的剂量学优势,能够更好地调整剂量分布。市场上现有SAVI、Contura等设备[12-13]。
3 APBI的临床应用现状
国内尚未普遍推广APBI技术,只有少数单位进行了很小样本的研究,关于APBI的研究绝大部分来自国外。目前的报道显示了良好的美容效果,局部复发率和总生存率与全乳腺照射无明显差异[14-15]。近年来有相关APBI的部分研究报道见表1。
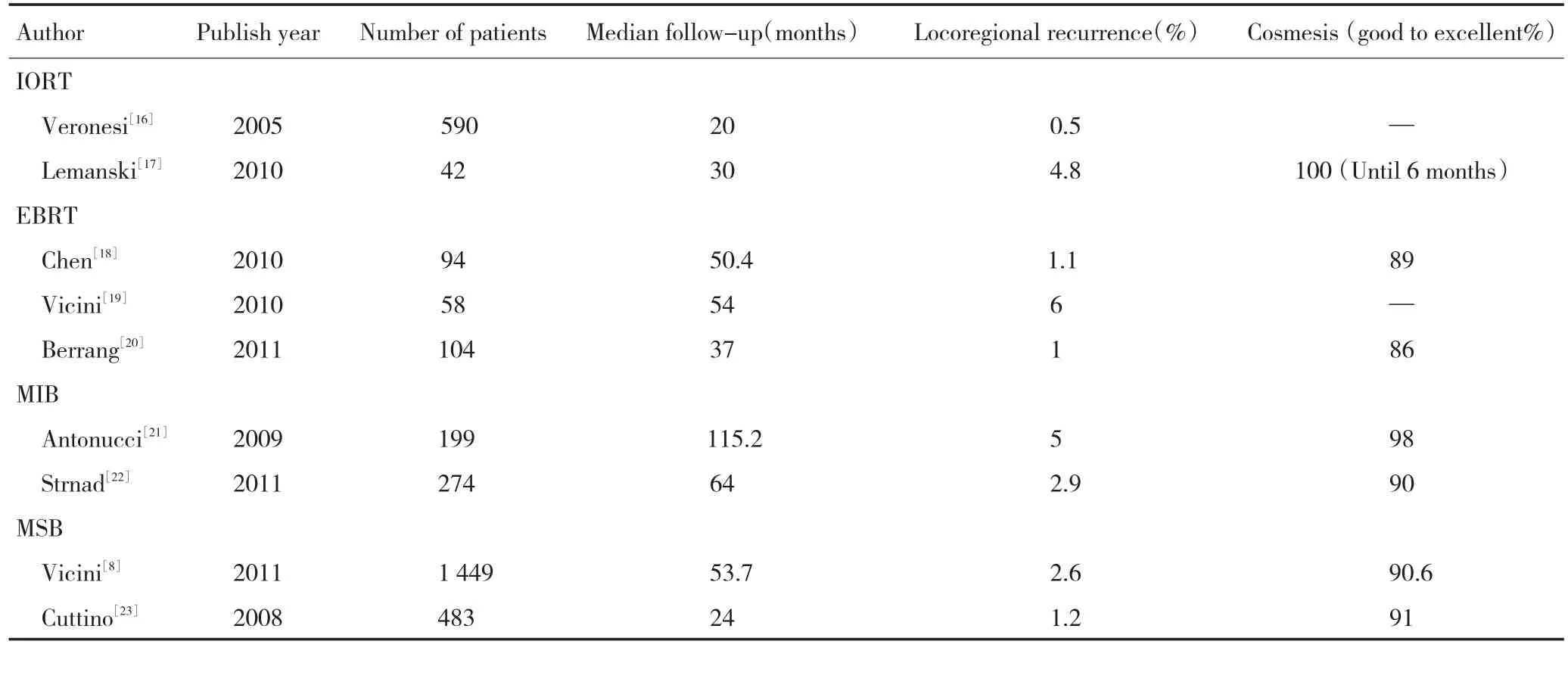
表1 近年研究的APBI报道Table1 Clinical research of accelerated partial breast irradiation in recent years
可见,APBI治疗后局部复发率均≤6%,美容效果优、良的达78%~100%。不良反应各家报道虽不尽一致,但都较小。较常见的不良反应是乳房纤维化,有 30.1%~50%较高的发生率报道[18,22],也有3.2%~11.4%较低发生率的报道[16-17],其他较常见的不良反应有色素沉着和毛细血管扩张,以上不良反应多为症状较轻的1、2级,大部分不需治疗即可自愈。只有少数报道出现3级不良反应,包括乳房纤维化、乳房疼痛、毛细血管扩张等[18-19,22],有人认为较重的不良反应的发生可能与应用全身化疗有关[18]。
4 结论
APBI具有照射体积小,治疗时间短的优势,目前发展很快。但在理论上,APBI也有很多不足之处,比如缩小照射范围可能使乳腺内其余部位隐蔽性病灶剂量不足,导致复发率增加。根据目前有限的报道,疗效与WBI效果相当,然而,尚无足够的临床数据来判断这几种APBI方法的长期疗效。组织间插植是目前随访时间最长的APBI技术,其他方法的随访数据很有限,故保乳手术后的标准治疗仍然是WBI,如果行APBI,则需要进行严格的病例筛选[24]。目前正在进行的一些Ⅲ期临床试验将为评价加速部分乳腺照射提供更可靠的数据。
1 Clarke M,Collins R,Darby S,et al.Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival:an overview of the randomised trials[J].Lancet,2005,366(9503):2087-2106.
2 Veronesi U,Marubini E,Mariani L,et al.Radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery in small breast carcinoma:long-term results of a randomized trial[J].Ann Oncol,2001,12(7):997-1003.
3 Fisher B,Anderson S,Bryant J,et al.Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy,lumpectomy and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer[J].N Engl J Med,2002,347(16):1233-1241.
4 Lim M,Bellon JR,Gelman R,et al.A prospective study of conservative surgery without radiation therapy in select patients with Stage I breast cancer[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2006,65(4):1149-1154.
5 Moon SH,Shin KH,Kim TH,et al.Dosimetric comparison of four differentexternalbeam partialbreastirradiation techniques:Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy,intensity-modulated radiotherapy,helical tomotherapy,and proton beam therapy[J].Radiother Oncol,2009,90(1):66-73.
6 Rusthoven KE,Carter DL,Howell K,et al.Accelerated partial-breast intensity-modulated radiotherapy results in improved dose distribution when compared with three-dimensional treatment-planning techniques[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2008,70(1):296-302.
7 Abbott AM,Habermann EB,Tuttle TM.Trends in the use of implantable accelerated partial breast irradiation therapy for early stage breast cancer in the United States[J].Cancer,2011,117(15):3305-3310.
8 Vicini F,Beitsch P,Quiet C,et al.Five-year analysis of treatment efficacy and cosmesis by the American society of breast surgeons mammosite breast brachytherapy registry trial in patients treated with accelerated partial breast irradiation[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2011,79(3):808-817.
9 Jeruss JS,Vicini FA,Beitsch PD,et al.Initial outcomes for patients treated on the American Society of Breast Surgeons MammoSite clinical trial for ductal carcinoma-in-situ of the breast[J].Ann Surg Oncol,2006,13(7):967-976.
10 Khan AJ,Kirk MC,Mehta PS,et al.A dosimetric comparison of three-dimensional conformal,intensity-modulated radiation therapy,and MammoSite partial-breast irradiation[J].Brachytherapy,2006,5(3):183-188.
11 Vicini FA,Beitsch PD,Quiet CA,et al.First analysis of patient demographics,technical reproducibility,cosmesis,and early toxicity:results of the American Society of Breast Surgeons MammoSite breast brachytherapy trial[J].Cancer,2005,104(6):1138-1148.
12 Gurdalli S,Kuske RR,Quiet CA,et al.Dosimetric performance of Strut-Adjusted Volume Implant:a new single-entry,multi-catheter breast brachytherapy applicator[J].Brachytherapy,2011,10(2):128-135.
13 Tokita KM,Cuttino LW,Vicini FA.Optimal application of the Contura multilumen balloon breast brachytherapy catheter vacuum port to deliver accelerated partial breast irradiation[J].Brachytherapy,2011,10(3):184-189.
14 Polgár C,Fodor J,Major T,et al.Breast-conserving treatment with partial or whole breast irradiation for low-risk invasive breast carcinoma—5-year results of a randomized trial[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2007,69(3):694-702.
15 Shah C,Antonucci JV,Wilkinson JB.Twelve-year clinical outcomes and patterns of failure with accelerated partial breast irradiation versus whole-breast irradiation:Results of a matched-pair analysis[J].Radiother Oncol,2011,100(2):210-214.
16 Veronesi U,Orecchia R,Luini A,et al.Full-dose intraoperative radiotherapy with electrons during breast-conserving surgery:experience with 590 cases[J].Ann Surg,2005,242(1):101-106.
17 Lemanski C,Azria D,Gourgon-Bourgade S,et al.Intraoperative radiotherapy in early-stage breast cancer:results of the montpellier phaseⅡtrial[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2010,76(3):698-703.
18 Chen PY,Wallace M,Mitchell C,et al.Four-year efficacy,cosmesis,and toxicity using three-dimensional conformal external beam radiation therapy to deliver accelerated partial breast irradiation[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2010,76(4):991-997.
19 Vicini F,Winter K,Wong J,et al.Initial efficacy results of RTOG 0319:Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy(3D-CRT)confined to the region of the lumpectomy cavity for stageⅠ/Ⅱbreast carcinoma[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2010,77(4):1120-1127.
20 Berrang TS,Olivotto I,Kim DH,et al.Three-year outcomes of a canadian multicenter study of accelerated partial breast irradiation using conformal radiation therapy[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2011,81(5):1220-1227.
21 Antonucci JV,Wallace M,Goldstein NS,et al.Differences in patterns of failure in patients treated with accelerated partial breast irradiation versus whole-breast irradiation:a matched-pair analysis with 10-year follow-up[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2009,74(2):447-452.
22 Strnad V,Hildebrandt G,Pötter R,et al.Accelerated partial breast irradiation:5-year results of the German-Austrian multicenter phaseⅡtrial using interstitial multicatheter brachytherapy alone after breast-conserving surgery[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2011,80(1):17-24.
23 Cuttino LW,Kesich M,Jenrette JM,et al.Multi-institutional experience using the MammoSite radiation therapy system in the treatment of early-stage breast cancer:2-year results[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2008,71(1):107-114.
24 Smith BD,Arthur DW,Buchholz TA,et al.Accelerated partial breast irradiation consensus statement from the American Society for Radiation Oncology(ASTRO)[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2009,74(4):987-1001.

