Relationship between the Alignment of a Non-Mydriatic Fundus Camera,Anterior Chamber Depth and Axial Length
Yin Guo, Yaqin Zhang, Liang Xu*, Yaxing Wang, Yingnan Ma, Xin Wang, Jost B.Jonas
1.Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology,Beijing Tongren Hospital and Capital Medical University,Beijing 100005, China
2.Department of Ophthalmology,Faculty of Clinical Medicine Mannheim,University of Heidelberg,Mannheim 08222,Germany


Materials and methods

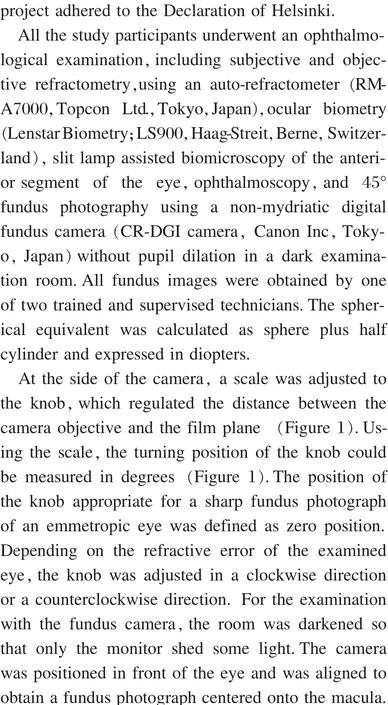

Figure 1 Photograph of the adjustment knob at the site of the fundus camera
Statistical analysis

Results
Discussion


Figure 2 Scattergram showing the correlation between the position of the adjustment knob for focusing of the fundus image in the fundus camera and the refractive error of the examined eye(P<0.001;correlation coefficient r=-0.77);Refractive Error (Diopters)=-0.22 x Position of the adjustment knob of the fundus camera (Degree)-1.16.


Figure 3 Scattergram showing the correlation between the position of the adjustment knob for focusing of the fundus image in the fundus camera and the axial length of the examined eye(P<0.001; correlation coefficient r= 0.65); Axial Length(mm)=0.08 x Position of the adjustment knob of the fundus camera (Degree) +23.90.
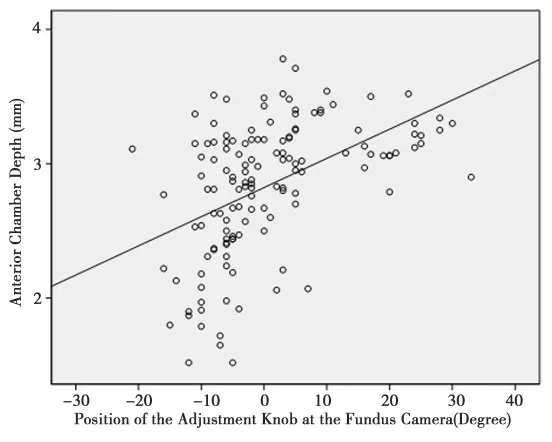
Figure 4 Scattergram showing the correlation between the position of the adjustment knob for focusing of the fundus image in the fundus camera and the anterior chamber depth of the examined eye(P<0.001; correlation coefficient r=0.48);Anterior Chamber Depth.(mm)=0.022 x Position of the ad justment knob of the fundus camera (Degree) +2.82.


- 眼科学报的其它文章
- New Applications of Femtosecond Laser in Cataract Surgery
- Late-onset Lens Particle Glaucoma as a Consequence of Posterior Capsule Rupture after Pars Plana Vitrectomy
- Eyelid Basal Cell Carcinoma Arising on the Site of a Congenital Port Wine Hemangioma
- Comparison of Corneal Thickness of Young People with Middle and High Myopia between Shantou and Zhengzhou
- Efficacy of Cytidine-5′-diphosp-bocholine Combined with Compound Anisodine in the Treatment of Early Optic Nerve Contusion
- Efficacy of Removing Dislocated Lens using Intravitreal Phacoemulsification

