Mobile Cloud for Personalized Any-Media Services
Bhumip Khasnabish
(Standards Development and Industry Relations,ZTE USA Inc.,Morristown,NJ,07960,USA)
Abstract In this paper,we define mobile cloud computing and describe how it can be used for delivering advanced any-media services to both nomadic and mobile users.We focus on service delivery that is localized and personalized and suggest that virtualization and tighter cross-layer communication allows for convergence and seamless transition of services.These are also creating new and never-before seen ways of developing and delivering personalized any-media services.We discuss current paradigms for implementing cloud-based any-media services that generate revenue.Future research topics and requirements for evolving network and service elements are also discussed.
Keyw ords mobile cloud;virtualization;cross-layer communications;any-media service;personalized services;localized services
1 Cloud Computing and Networking
A chieving better quality,cheaper,and faster any-media communication is not a dream anymore.Virtualization and tight cross-layer communication means any computing or communication solution can be established and used on demand.The beauty of this approach is that no significant capex1Capex is the capital expenditure associated with acquiring fixed assets such as computing equipment,equipment rooms and real estate,networks,and plants.These are necessary infrustructure for running a business.or opex2Opex is the operational expenditure of a business.This is the amount of money spent on running costs such as salaries and benefits;maintenance of systems,network,and equipment;and upgrades.is incurred.
In cloud computing,there is no need to develop and own physical infrastructure because virtualized computing and communications elements such as virtual machines(computer systems)and network elements can be rented from a cloud service provider.This can be done through open-network application programming interfaces(APIs)or service APIs as long as the data centers3A data center is a collection of computing,communications,storage,application,and service resources that can be offered to internal and external customers through open APIs.Data centers are commonly installed on racks in a building with raised floors.They may also be stored in a secure trailer that has adequate communication bandwidth,ventilation,and power supply.of the cloud service provider can be accessed over the Internet.Further details about cloud-based systems and services can be found in[1]-[3].
With cloud computing,virtualization can be used to develop next-generation any-media services[4].Cloud networks can deliver these services to nomadic or mobile users through virtualization and tight cross-layer communications[4].
Anomadic user moves from one location to another,but their device is in a fixed location.Therefore,they may be serviced by a different data center at a different time.When a service or session is initiated,it is hosted in the same data center for the duration of the session until the location changes.
Amobile user moves with their device from one location to another without service interruption.Consequently,a mobile user may initiate a session or service in one data center and then move to a neighboring data center during the same session.This is commonly done with a service handover or stitched session through specialized border gateways.
Increasingly,data-center network elements are capable of converting traditional four-layer TCP/IPInternet into a three-layer data-center network(Fig.1).These data-center network elements support virtualized routing and switching,which allows traditional network and transport-layer functions to be mixed and matched.In this way,virtual machines can be seamlessly moved from one rack to another(distant)rack.
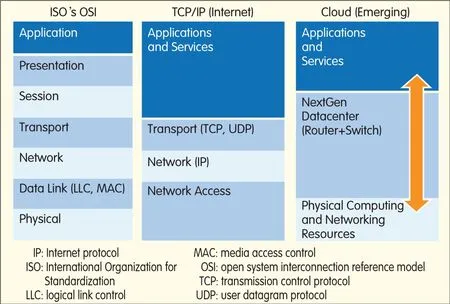
▲Figure 1.Evolution of computer networking model,from seven-layer to three-layer system.
Load balancing and service continuity can be achieved at minimalcost.Table 1 shows emerging networking and services paradigms.Cloud computing and networking supports the emerging paradigm.Fig.2 shows the new network model.This is expected to be where seamless innovation in applications and services willoccur.Fig.3 shows how the cloud-based ecosystem will be used for continuous development of services.Creating cloud-based services is similar to piecing together a puzzle together;one best solution always exists.

▼Table 1.Emerging networking and service paradigms.Cloud computing and networking supports the emerging paradigm.
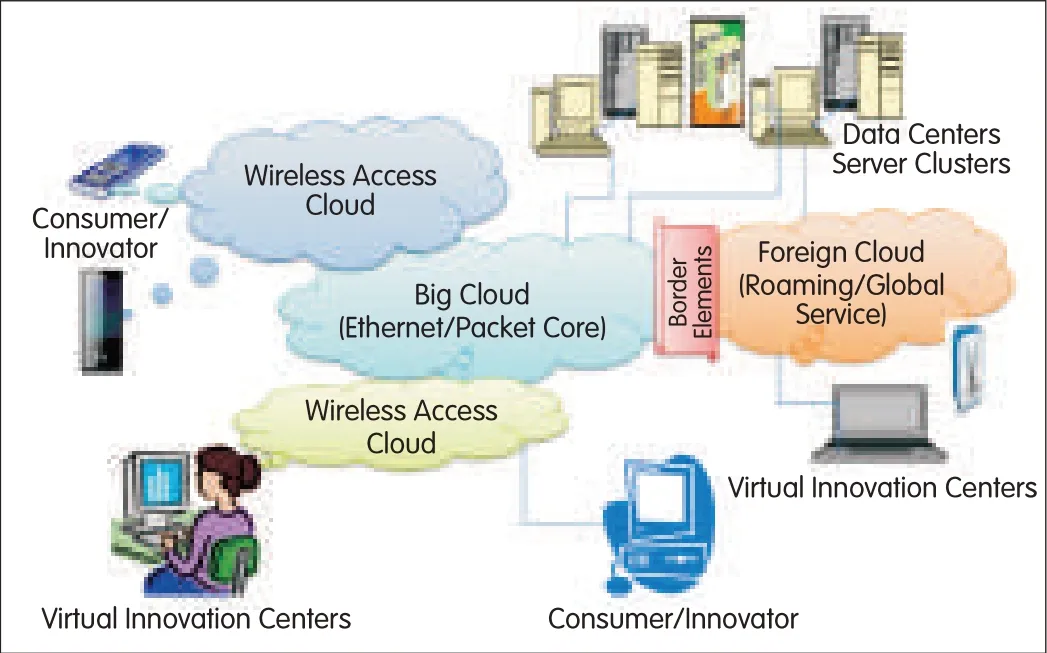
▲Figure 2.The new network is a playground for seamless innovation.
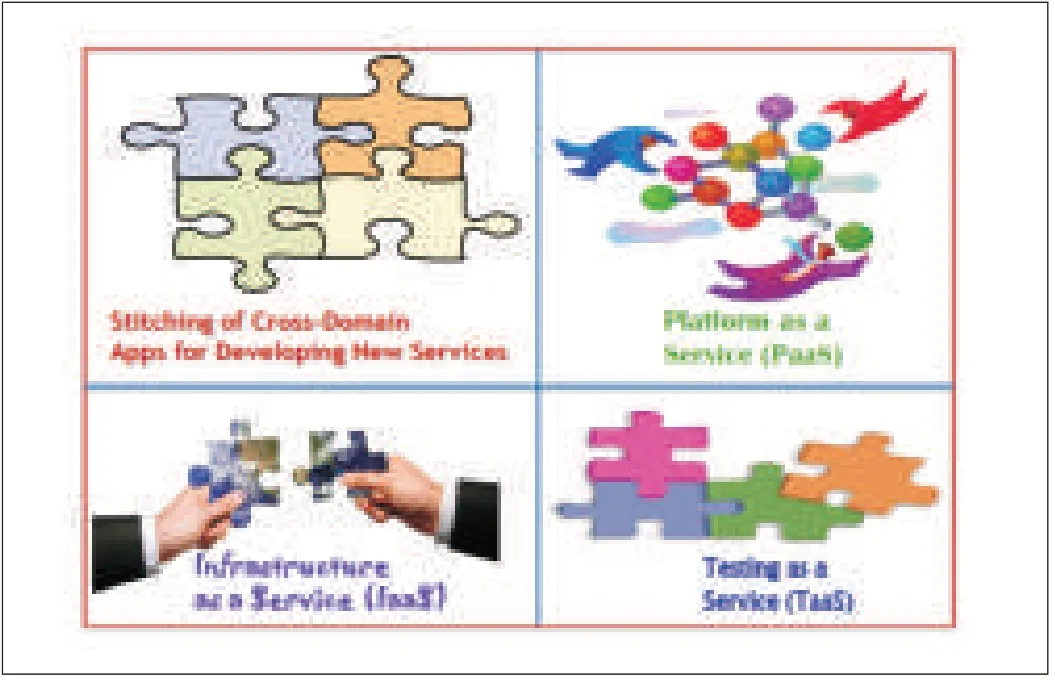
▲Figure 3.An ecosystem for continuous developmentand innovation.
Cloud computing,networking,and service management(including grid computing)have recently emerged as viable computing and networking tools.These tools can be used to reduce infrastructure deployment and service management costs without sacrificing QoSand QoE[5].
At the heart of cloud computing is virtualized computing and networking resources.The self-organizing nature of the interconnections between these resources is similar to neural networks in the human brain.
However,the methods,mechanisms,and tools used to expose resources and their APIs for the purpose of developing XaaSare stillad-hoc and proprietary.Security,privacy,and multitenancy requirements add another dimension to the already-complex set of cloud management problems.
2 Why Mobile Cloud is Different
Mobile cloud refers to seamless delivery of cloud-based applications and services to clients with mobile or nomadic devices.With innovative mash-up of data,interface,service,and content as well as normalization of APIs,mobile cloud can seamlessly deliver real-time session and transaction-oriented services.
Mobile cloud delivers services from Internet and social networking platforms to clients.Such platforms include Google,Yahoo,Microsoft/Skype,and Facebook.Traditional and virtual network service providers such as ATamp;T,British Telecom,China Telecom,Deutsche Telekom,and France Telecom-Orange can offer these services.
Media-based sessions and calling-in to share virtual space will become commonplace.Dynamic sharing of computing,communications,and display resources between hand-held devices and networked servers will give rise to user experience beyond expectations.This trend will be equally applicable to the ICTand entertainment industries[4]-[6].Mobile cloud is a new service-delivery paradigm currently being fleshed out at industry events and summits[7].
3 The Potential of Mobile Cloud
Mobile cloud is the best way of providing personalized services.Gathering information from mobile clients,devices,and ecosystems and effectively using this information to provide necessary,low-cost,customized services is a winning proposal.Policies can be steered in real-time,and gathered data can be micromined for charging purposes.This provides localized intelligence and allows services to be rapidly customized.Providing accurate,personalized real-time recommendations and assistance through any-media devices will strengthen customer loyalty and improve UE.
4 A Sample of Modern Mobile Cloud Services
This section gives a summary of emerging mobile cloud services.Both transaction-and session-oriented services are discussed.
4.1 Personalized Spam Filter for SMS
In addition to keywords and flow rate,individual preferences can be the basis for dynamically setting and modifying spam filters.These filters can be based on personal profile,location,quality,or connection bandwidth.These services use micro data-mining as wellas minidatabases with virtual agents embedded in mobile clients.
4.2 On-demand Security for Transaction and Session
Mobile devices and clients are inherently vulnerable to impersonation and security threats.Mobile cloud immediately detects any impersonation or attack and mitigates these by allowing suitable agents to be embedded in mobile devices.An acceptable level of security during a transaction or session can be maintained by an independent,localized,trusted third-party platform.
4.3 Automated and Personalized Emergency Service
This service can be delivered through an embedded,local authorized proxy server.With appropriate agents and customer profiles,a mobile device can provide various personalized emergency services.Authenticating the mobile device and determining exact location are very important for such services,and mobile cloud is best suited for this purpose.
4.4 Automated Mobile Device Portability
This implies that hand-held clients and devices are seamlessly portable between carriers.No hardware—for example,SIM cards—need to be changed.The goalis to support dynamic provisioning and activation of devices and services.Also,billing and settlement for interservice providers can occur almost in real-time through intelligent service delivery.
5 Emerging Personalized Mobile Cloud Services
5.1 Mobile Transaction and Streaming Media Ecosystem
Mobile cloud can be used in health,banking,games,and entertainment where culture and location are important factors.For example,the Mc Donald's menu in Bangalore is different to that in Boston.A ubiquitous mobile service within a device may be able to sense location and act on behalf of the user if it is programmed to do so.Wearable devices can communicate with mobile devices so that important health and environment information can be relayed to a central location and assistance can be organized.
5.2 Services that Require Dynamic Creation and Restructuring of User Groups
A mobile cloud network can be used for vehicular communications and entertainment.It can also be used for health monitoring.
5.3 Mobile Cloud that Offers Context-Aware Media Adaptation and Communications
This service can be used for energy saving,signaling,and processing in display and bandwidth management.QoEis not sacrificed;however,a broker or proxy agent may be needed to ensure QoE.
5.4 Instant Access to Up-to-Date Information Using Mobile Cloud
Database information,such as profile and personal information,automatically migrate from the home cloud to the user's current location.Secure and efficient mechanisms are needed to move personaldatabases and caches from one location to another in order to provide the same UE.Maintaining privacy and data integrity is of the utmost importance.
5.5 Cloud-Broker-Based Ubiquitous Access to Any-Media Services
Any-media services are delivered to devices anywhere in the world.Both private and public mobile cloud domains may be used for delivering services.To successfully deliver services,mobile devices must be capable of dynamically adjusting the required service and security profiles according to the service and the openness of the domain from where the resources are being borrowed.
5.6 Any-Media Content Downloading From Anywhere
Movies,video clips,and e-books are downloaded to a device from anywhere in the world,irrespective of the service or network access provider.
5.7 Location-Based Real-Time Maps and Traffic Update
This service is very similar to a navigation service provided over a mobile device.However,the device uses information about current location and personal habits and preferences to recommend direction-related services.
5.8 Seamless Tracking of Goods and Services
Goods can be seamlessly tracked throughout the transportation cycle.
5.9 Network-based Assisted Living
The mobile device intelligently and adaptively monitors the health requirments and location of the person carrying the device.It is sensitive to the requirements of the carrier and should support their computing and communications needs.
5.10 Location-Aware Mobile Wallet
This is equivalent to a near-field electronic-wallet service except that electronic cash is automatically converted to local currency through a banking service proxy.
5.11 Media Adaptation for Any-Media Cloud Services
Mobile cloud services often deliver audio,video,and graphics to a variety of devices.The media may be encoded in a format that cannot be rendered or displayed on the device.Therefore,virtualized resource-based transcoding may be required for any-media-based services.
▲Figure 4.Main elements of a CRF.
5.12 Virtualization of Clients and Services
Mobile cloud services sometimes require features and functions that are not easy to implement on the handset.Using virtualization and other embeddable features,it is possible to instantiate(emulate)advanced features and functions required by the service[8],[9].These features may include 3D image viewing or multiparty video gaming.
5.13 Platforms for Mobile Cloud Services
Some platforms for mobile cloud services support virtualization and seamless mobility of virtual resources.These resources can be mobilized(according to specified arrangements)from one domain to another irrespective of physical location or ownership.Mobility can be triggered by proximity of the client,device,or user.It can also be triggered by malfunctioning or overload of the service delivery platform(SDP)[6].
5.14 Incorporating Intelligence in Mobile Cloud Clients and Platforms
Using virtualization,intelligence can be incorporated into both mobile devices and platforms.A cloud-based mobile device can dynamically invoke cloud-host-based features to provide enriched audio,video,and gaming.Similarly,mobile SDPs can support normalization of APIs and invoke resources needed for enhancing UEon demand.
5.15 Innovative Business Models Using Mobile Clouds
Virtualization-enabled clients,SDPs,and associated components provide the agility and flexibility needed for innovation in the mobile cloud ecosystem.
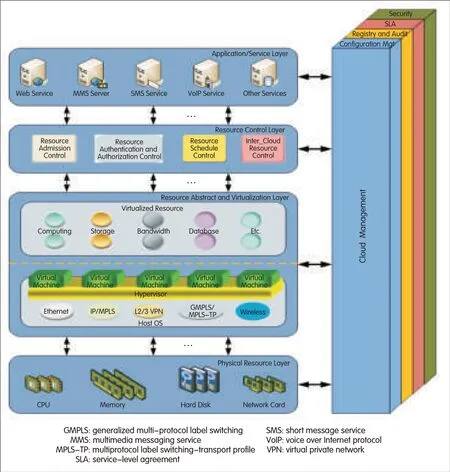
6 ACloud Reference Framework
The cloud reference framework(CRF)consists of four horizontal layers and one stacked vertical layer(Fig.4).The four horizontal layers are 1)application/service layer,2)resource control layer,3)resource abstraction and virtualization layer,and 4)physical resources layer.The stacked verticallayer is used for configuration management,registry,logging and auditing,security management,and service-level agreement(SLA)management.The CRFcan be used to install cloud-based services(Fig.5).It can also be used to describe the virtual resource management(VRM)(Fig.6).Details about this CRF and its application can be found in[10].
7 Converging IT and Networking Services
Such mentioned demands are the driving force behind convergence.Converged applications include map,picture,RBT,and video search.They also include e-ticket purchasing and mobile payment,bookings,banking,SMS-based weather forecast,hospital registering,calendar reminders,mobile stock trading,and marketplace recommendations.Converged applications willcause an explosion in the number of devices that can support rich-media services and content over the mobile Internet.
Although such devices willhave different sizes,shapes,and forms,they may run on the same operating system and virtual clients but have different features and functions.These features and functions may change many times throughout a day based on the applications and services they are supporting.
Fig.8(a)shows how three-dimensional images and augmented-reality-based services can be delivered to the same hand-held device using network-based capability to a virtual client.Fig.8(b)shows how adding,moving,changing,and updating can be easily facilitated when a virtual client is available in a hand-held device.Further details on virtualized clients and their use in a cloud environment can be found in[8],[9],[11],and[12].
Telecom and IToperators(including ISPs and content delivery companies)are able to benefit from the new paradigm of convergence when delivering rich-media services with cloud-based infrastructures(as shown in Fig.9).Hand-held device manufacturers need to support virtualized clients and cognitive access to networks and services(as shown in Fig.2).Wireline and wireless telecom operators must support cognitive access to content and services regardless of the home network where the device originally registered for the service.This may require service-specific,policy-based interconnection with foreign networks and cloud data centers for the duration of a session.Privacy and security of everyone involved must not be compromised.
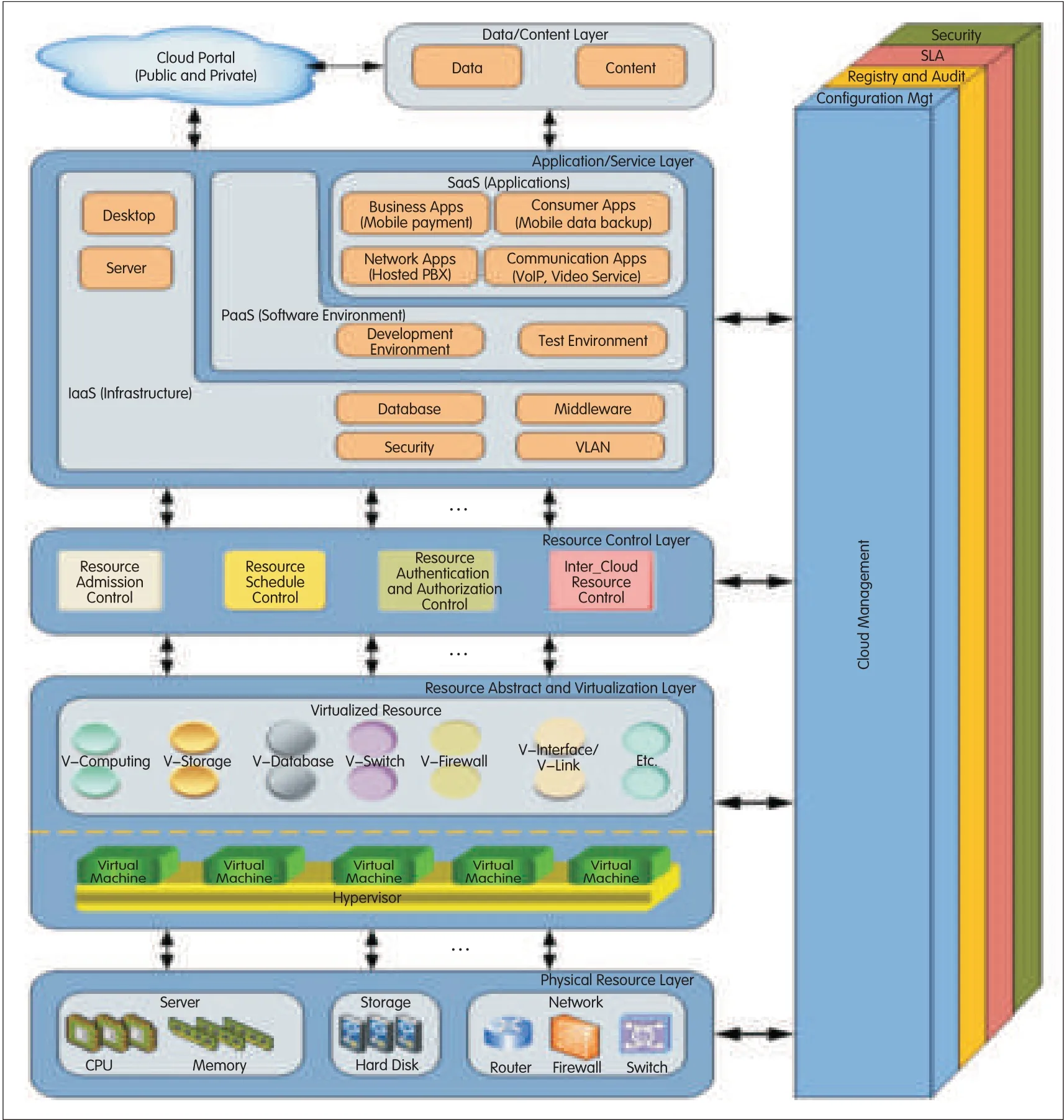
▲Figure 5.CRFfor describing service instantiation.
8 Role of the Service Development Platform
Although devices come in the form of televisions,laptops,tablets,or mobile phones,they may use similar virtual clients with application-specific features and functions.The service may be hosted through an SDPto a service-specific application store
Application developers,however,want to develop applications for use in all devices and platforms.Therefore,a toolkit is needed that can provide an appropriate level of normalization and customization.Fig.11 shows one such model.Unified network APIs,such as Parlay Xand OMA RESTful,are desirable.Application and service developers also want seamless access to important information about subscribers and users,for example,a verifiable address,location,and age.They also want identification,billing,and charging information about the subscribed service.Subscriber and service information can be used for unified messaging and session control,service discovery and delivery,and seamless migration of service from device to device as the user moves.Fig.11 shows how developers can use open web-based APIs for customizing standard services offered by various service providers[4],[5],[13],and[14].

▲Figure 6.CRFfor VRM.
9 SDP and Cloud Storage Creates an Intelligent Application Store
SDPalone cannot seamlessly deliver all of desired applications and services across different access networks and devices.A variety of gateways,interconnecting devices,storage,and business process development and maintenance elements are required(Fig.12).
It was a depressed6 minister and his wife who attended a benefit auction7 for the church youth group that afternoon. One of the items put of for bid was an old gold-and-ivory-colored lace tablecloth8, nearly fifteen feet long.
Fig.12 shows a business strategy and processes.Policy-based network operation and management needs to be implemented in order to generate direct and indirect revenue from mobile app stores.
These can be coupled with an interconnected multidomain service overlay network so that services can be dynamically created using service components from different domains.This coupling also allows for dynamic allocation of computing,networking,and service resources across wired,wireless,private,and public domains to create unified and seamless UE.These resources can be offered by intelligent applications and service stores(Fig.13),and this is what self-organizing and cloud-based systems(SOCS)and networks are expected to deliver[6],[14].SOCSnetworks can also dynamically reconfigure networked platforms and devices in order to deliver customer-desired content and services with required security and QoS,irrespective of the location and ownership of the content and features.
An innovative business model needs high-quality and agile partners as wellas excellent system and service integration.It also needs to be based on standard platforms that can be rapidly customized so that content and services from any provider can be abundantly and consistently supplied[6],[14].
10 Conclusion and Future Research Topics
Mobile cloud is about to transform the ICTand entertainment industries and create the ultimate UE.The effect of this transformation will be that device and equipment manufacturers,application and service developers,system integrators,and network and service operators will have to adapt rapidly to new business models.An infrastructure business model based on CAPEXand OPEXwill disappear as will the line between wired and wireless services.Sharing of content,infrastructure,applications,and other resources will be widespread.Commoditization will trigger innovation in business models,services,and devices and will enable anyone with a broadband-capable device to provide anyservice to anyone,irrespective of location.However,the following issues need to be addressed before this can become a reality:
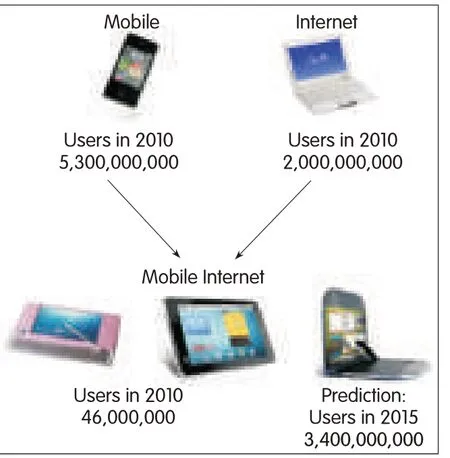
Figure 7.▶Market potentialfo mobile Internetdevicesand services will be enormous in the nea future
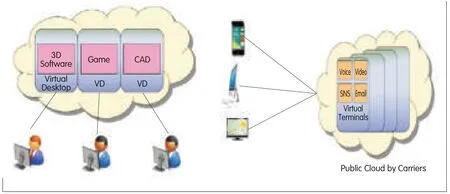
▲Figure 8.Examples of XaaS.(a)3Dgame,augumented reality,or CADsoftware as a service based on virtual desktop infrastructure.(b)Terminal hosting for seamless access to services using any device from anywhere(seamless add,move,change,and update).
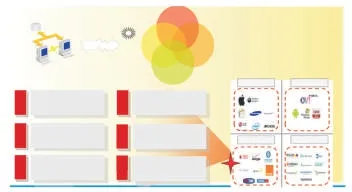

▲Figure 10.SDPand application store is a“factory behind store”model.
•virtualization of clients,desktops,applications,services,and databases for delivering customized UEfor any service(convergence is the objective)
•mobility management in cloud,that is,in distributed shared network and resource environments
•APIs for developing and delivering services seamlessly over public,private,and hybrid mobile clouds(including support for single sign-on,unification of profiles,and service mash-ups)
•development of agile mobile cloud ecosystems
•visualization and dynamic provision of computing and communications resources,including automatic debugging and diagnosis
•cloud service logging and monitoring,including auditing and verification
•soft and hard privacy and security for cloud-based services
•privacy protection and on-demand security in open networked environments
•service continuity,automated software and hardware updates,and disaster recovery
•affordable and useful services,environmentally friendly evolution of networks and services
•regulatory compliance in a borderless world
•instant detection of violation of intellectual property rights
•protection of intellectual property rights
•policy management in a mobile cloud environment
•adaptive protocols for resources and service management in multidomain mobile cloud environments
•service-and content-specific addressability,networking extensions,service quality and experience agreement(SQEA)•risk-tolerance,risk-sharing,and mean-time to failure and repair management for mobile clouds
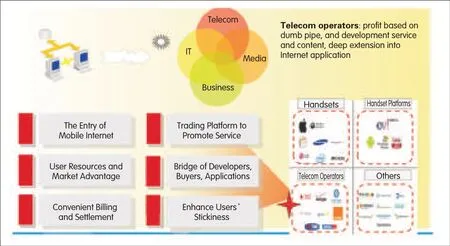
▲Figure 9.Industry convergence and competition between telecommunications,IT,and media,companies.
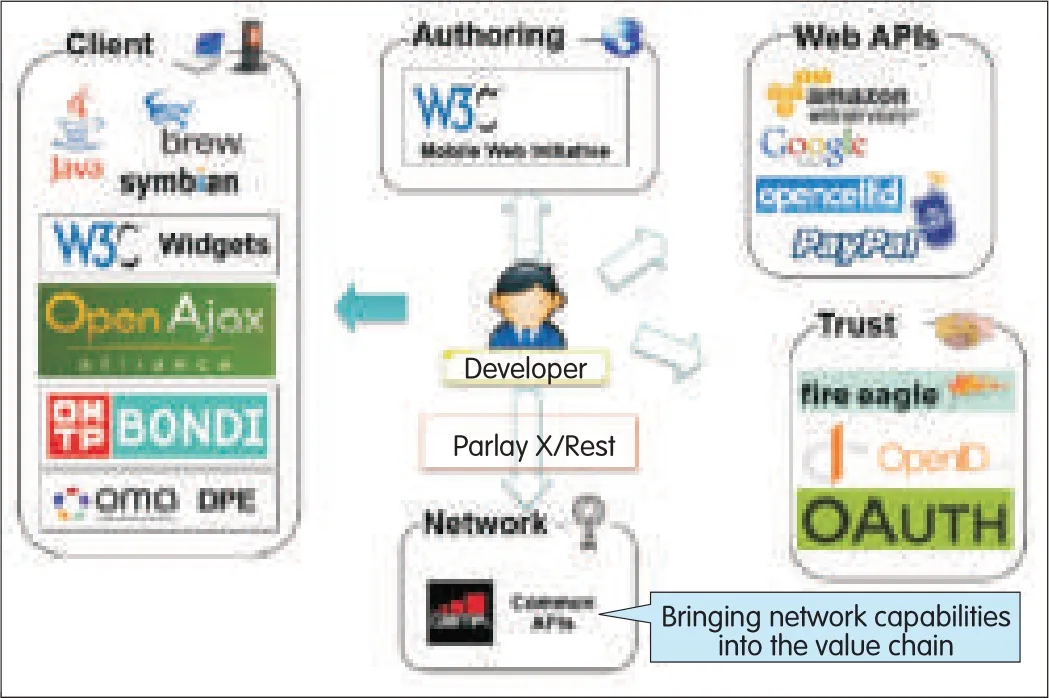
▲Figure 11.Developers want to develop an application once only for ubiquitous deployment.This requires unified network APIs such asParlay X,and OMARESTfulinterfaces.
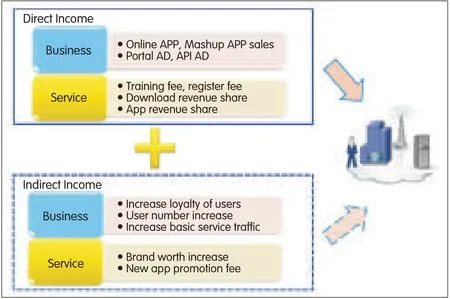
▲Figure 12.Business plus service constitutes a profit model.
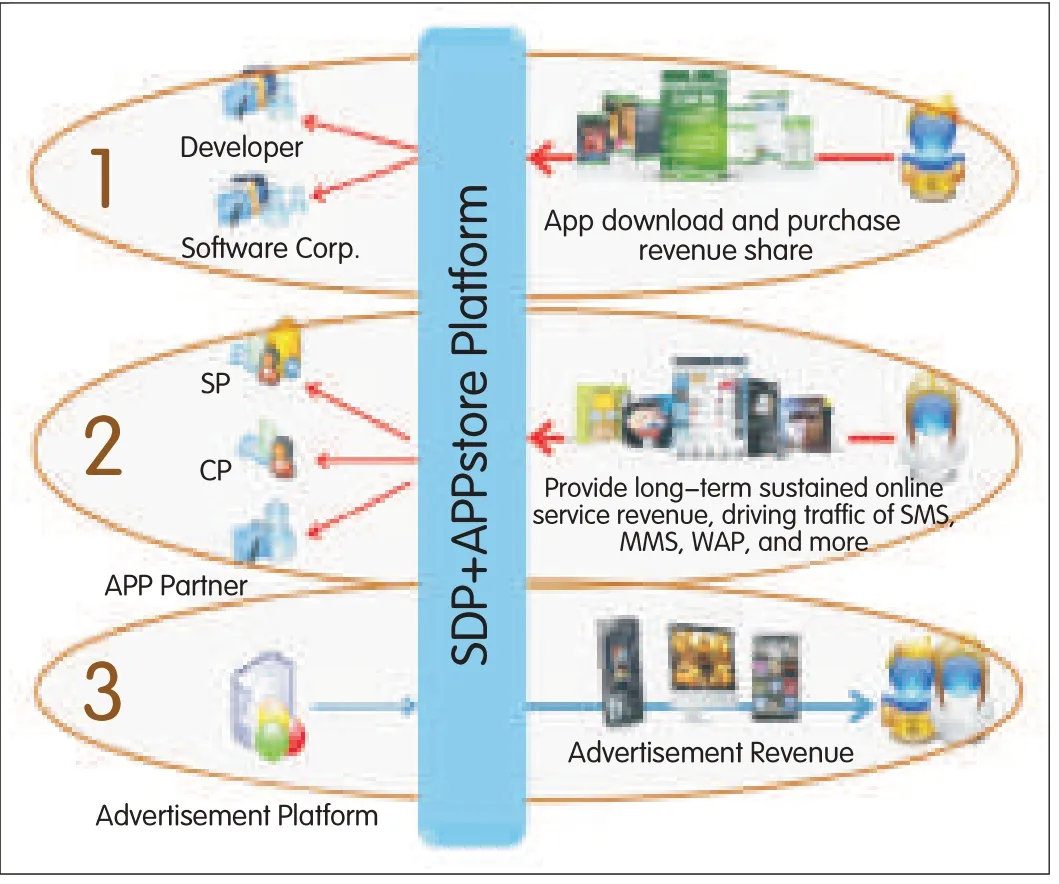
▲Figure 13.SDPwith an intelligentapplication store is an innovative business model.
•mobile cloud service and infrastructure management
Additional details about these and related topics can be found in[10].
Acknowledgements
This paper is based on my Distinguished Lecture on XaaS given at IEEERegion 1 Innovation Day(May 17,2011).An earlier version of this paper was also presented at Communic Asia 2011 during the mobile VASstrategy session on 22 June,2011.Iam grateful to the ZTEiVASProduct and Marketing Team for helping me put the slides together for the presentation.In particular,Meng Yu,Hu Jie,Chu JunSheng and Liang Liang have provided many contributions and drafts that have assisted me in my work with standards development organizations in the areas of virtualization,data center operation,and general clouds.Isincerely thank all of them.
- ZTE Communications的其它文章
- Introduction to ZTECommunications
- ZTEWins Contract to Provide LTEWireless Uifi Set to UNE
- ZTEPartners with KPNGroup Belgium to Deploy Packet-Switched Core Network
- Multiple-Constraint-Aware RWA Algorithms Based on a Comprehensive Evaluation Model:Usein Wavelength-Switched Optical Networks
- Open Augmented Reality Standards:Current Activities in Standards-Development Organizations
- Field Transmission of 100Gand Beyond:Multiple Baud Ratesand Mixed Line Rates Using Nyquist-WDMTechnology

