Screening for proteins interacting with DND1 by yeast two-hybrid system
Zhang Jing,Li Shundong ,Zhang Yong ,Yang Zhi ,Peng Xiaoning
(1.Department of Clinic Medicine,Medical College,Hunan Normal University,Changsha 410006,China;2.Department of Internal Medicine,the Third Hospital of Changsha,Changsha 410005,China)
Dnd1 protein is an evolutionary conserved RNA binding protein and required for primordial germ cell(PGC)survival in zebrafish and mammals[1-3].Dnd1 transcripts are upregulated in primordial germ cells after E7.25 and expressed in adult testes and heart in mouse;Dnd1 transcripts were significantly decreased in embryonal germ(EG)cells and tumours from 129-Ter/Ter males[3-5].DND1 is the first protein with an RNA recognition motif(RRM)that is directly implicated as a heritable cause of spontaneous tumourigenesis,in 129 inbred mice.A point mutation in Dnd1 that introduces a stop codon result in truncated DND1,which give rise to PGC deficiency,and TGCT development[3].
The mechanism as to how the loss of Dnd1 leads to primordial germ cell death or tumor development is unknown.The identification of Dnd1 targets is important to determine the underlying molecular mecha-nisms.It has been found Dnd1 protein specifically interacts with apolipoprotein B mRNA editingenzyme-catalytic polypeptide3 (APOBEC3)in mammalian cells and mouse gonads[6];Dnd1 increases expression of particular proteins essential for PGC development,such as nanos homolog 1(NANOS1)and tudor domain containing 7 (TDRD7),through binding to the NANOS1 and TDRD7 mRNAs and preventing miR-430-mediated inhibition of their expression in germ cells.DND1 also up-regulates the tumor suppressors p27 and large tumor suppressor,homolog 2 (LATS2)by binding to their mRNAs and preventing miR-221-or miR-372-mediated inhibition of their expression[7].It is likely that DND1 regulates its targets through a miRNA-mediated pathway,and that loss of DND1 deregulates miRNA activity and can be responsible for defects in germ cell survival and tumor formation.Recent studies on DND1 also revealed that mouse DND1 localizes to the cytoplasm or the nucleus depending on the mammalian cell type by GFP-fusion protein localization approach[4].DND1 is not only necessary for maintaining viability of germ cells,but also has other important cellular functions in different tissues and cell types during development.
To further understand DND1 cellular functions,we utilized yeast two-hybrid approarch to screen the 10.5 day mouse embryo library with Dnd1 coding sequence.We identified Jun,Actinin alpha 1(Actn1),Nuclear Receptor Bingding Protein(NrBP1)and Chloride Channels 2 (Clcn2)as protein partners of DND1.This work will have important implication for our further understanding of Dnd1 function and the molecular mechanism of tumourigenesis of TGCT.
1 Materials and methods
Yeast two hybridization The Yeast two-hybrid system (ProQuest TM Two-Hybrid System)and 10.5 d mouse embryo cDNA library we used were products of GibcoBRL Company.The entire ORF of Dnd1 was amplified by PCR and in-frame cloned into the pDBLeu vector resulting in pDBLeu-Dnd1,which was confirmed by sequencing.The MaV203 yeast strain was transformed with the pDBLeu-Dnd1 using the lithium acetate-based method as described in the GIBCO/BRL protocol.Toxicity of the plasmid DBLeu-Dnd1 to yeast strain MaV203 was tested by comparing the color,shape,and growth status between MaV203-pDBLeu and MaV203-pDBLeu-Dnd1 cells in nutritional deficiencies circumstance.The positive yeast strain B,C,D provided by Yeast two-hybrid system were streaked on the SC-Leu-Try-His yeast culture plates contained different 3AT concentration,and the optimal concentration of 3AT for the screening was determined according to the growth state and the number of colonies of yeast cells.
Screening was carried out as its protocol and previously described[8-9].To verify the true proteinprotein interaction and exclude false positives,the plasmids of positive colonies were cotransformed into MaV203 cells with pDBLeu-Dnd1.Then the yeast cells were spread on SC-Leu-Try plate and covered with X-gal to test the specificity of interaction.After the positive colonies were sequenced,the sequences were analyzed by online tools of Bioinformatic Harvester of the European Center for Biotechnology Information(http://harvester.embl.de/).
2 Results
After screening approximately 2.0×106transformants,we obtained 8 positive clones.We confirmed the eight preyed plasmids interacted with pDBLeu-Dnd1 once again in yeast.Subsequently,we isolated and sequenced the eight plasmids(sequensing primer provided by ProQuest TM Two-Hybrid System).Through bioinformaic analysis,we found four proteins interact with Dnd1,which were Jun,Actinin alpha 1,Nuclear Receptor Binding Protein 1 and Chloride Channels 2.The data are presented in Table 1.
3 Discussion
The study of protein interaction is an important way in the understanding of gene function.For its simple,sensitive,and high-performance features,Yeast two-Hybrid system has been widely used in various fields,such as cell signal transduction and cell cycle regulation,gene transcription and translation regulation,and so on.In this study,we succeeded in constructing the bait plasmid pDBLeu-Dnd1,and we confirmed the pDBLeu-Dnd1 had not autonomous LacZ activation and toxicity to yeast,thus we can exclude the false positive and negative interaction well in the course of screening.After three rounds of screening,it not only greatly reduce thefalse positive,but also in favor of the latter the library plasmid isolation and amplification.We obtained eight true positive clones by the facts that the positive plasmids have no auto activation of transcription of Lac z and interact with bait plasmid pDBLeu-Dnd1 in yeast once again.Through sequencing and bioinformaic analysis of the eight isolated library plasmids,we found four proteins,which were Jun,Actinin alpha 1,Nuclear Receptor Bingding Protein and Chloride Channels 2 interact with DND1.
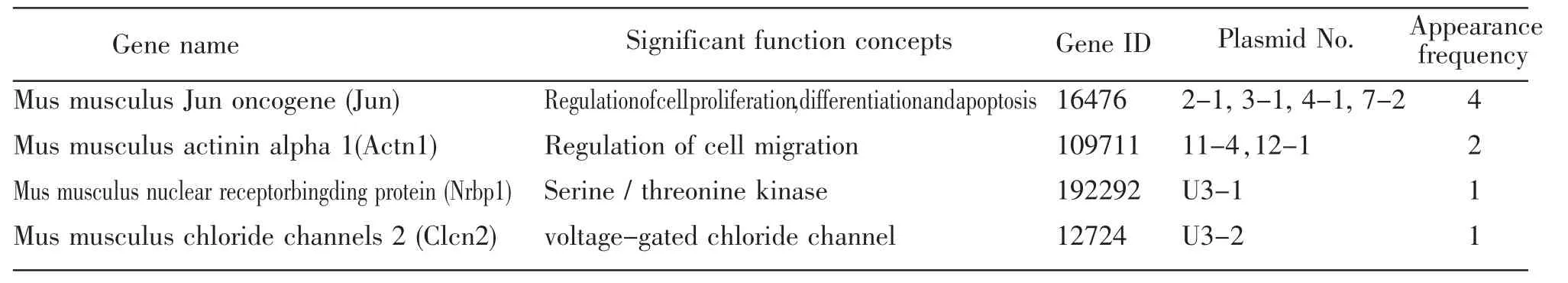
Table1.Sequence analysis of eight positive clones interacting with DND1
It is interesting that the Jun oncoprotein is a major component of the transcription factor complex AP-1,which regulates the expression of multiple genes essential for cell proliferation,differentiation and apoptosis.Constitutive activation of endogenous AP-1 is required for tumor formation in avian and mammalian cell transformation systems,and also occurs in human tumor cells suggesting that AP-1 plays an important role in human oncogenesis[10-14],so DND1 may participate in multiple cellular activities through interact with JUN.and DND1-JUN interaction has also important potential function of TGCT pathogenesis and PGC biology.Jun protein mainly expresses in cytoplasm of primary spermatocyte,secondary spermatocyte,and spermatocyte,are also found in the nucleus of expression[15].JUN involved in transcription regulation of genes related proliferation and differentiation in germ cells[16,17].DND1 maybe act as a negative factor of AP-1 regulated gene,and regulates transcription or expression of these genes with other positive factor in germ cells.If Dnd1 gene mutation or deletion,thereby weaken such a regulation and further lead to germ cells over proliferation and the transformation of cancer cells,which result in testicular germ cell tumors occur at last.
Actn1 protein belongs to the blood protein super-family members and plays an important role in the cell migration[18-20].DND1-Actn1 interaction has important potential function of TGCT pathogenesis and PGC biology.For Ter strains of mice,Dnd1 inactivation may affect normal primordial germ cells migration to reproductive ridge,on the one hand,causing a large number of germ cells lost,on the other hand,leading to the occurrence of the tumor maybe resulted from a small amount of germ cells survive in a large number growth factor.
NrBP1 is a serine/threonine kinase[21].NrBP1 interacts with Jab1,and inhibit the Jab1-mediated phosphorylation[22],thereby inhibiting c-Jun and AP-1 activation.Therefore,we speculate DND1 involved in gene transcription and cell transformation process also through its interaction with NrBP1 and Jab1.
Clcn2 is a kind of voltage-gated chloride channel-type structure[23].Clcn2-/-knockout mice studies have shown that loss of function Clcn2 gene will lead to the destruction of the testes and abnormal retinal development[24,25].We can deduce that DND1 regulate concentration of ions inside and outside cells through interacts with Clcn2 to maintain normal cell activity.When Dnd1 gene mutation or inactivation,which result in abnormal PGC development and disease,such as TGCT.
In summary,we speculate DND1 might through direct interaction with Jun proteins,or with NrBP indirectly inhibit c-Jun and AP-1 transcription activity to involve in regulation of cell proliferation;DND1 interact with Actn1 to involve in regulation of cell migration process;and DND1 interact with Clcn2 to involve in the control of PGC development by regulation of ion concentration in PGC.Considering all of these results and related papers,it would appear that DND1 is involved in the process of cell proliferation,migration and transformation and has important potential function of TGCT pathogenesis and PGC biology.
In conclusion,we demonstrated that Dnd1,which is the first RNA-binding protein known direct-ly implicated as a heritable cause of spontaneous tumor genesis,also interacts specifically with Jun,Actinin alpha 1,Nuclear Receptor Bingding Protein and Chloride Channels 2 in yeast.In the next experiments we will use immunoprecipitation,GST pulldown and intracellular co-localization methods to verify interactions between DND1 and Jun protein,Actn1,Nrbp1 and Clcn2 in vivo and in vitro,and study their role in the PGC development and tumourigenesis of testicular germ cell tumour.
[1]Horvay K,Clauben M,Katzer M,et al.Xenopus dead end mRNA is a localized maternal determinant that serves a conserved function in germ cell development[J].Dev Biol,2006,291(1):1-11.
[2]Weidinger G,Stebler J,Slanchev K,et al.Dead end,a novel vertebrate germ plasm component,is required for zebrafish primordial germ cell migration and survival[J].Curr Biol,2003,13(16):1429-1434.
[3]Youngren KK,Coveney D,Peng X,et al.The Ter mutation in the dead end gene causes germ cell loss and testicular germ cell tumours[J].Nature,2005,435(7040):360-364.
[4]Bhattacharya C,Aggarwal S,Zhu R,et al.The mouse dead-end gene isoform alpha is necessary for germ cell and embryonic viability [J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2007,355(1):194-199.
[5]Yabuta Y,Kurimoto K,Ohinata Y,et al.Gene expression dynamics during germline specification in mice identified by quantitative single-cell gene expression profiling[J].Biol Reprod,2006,75(5):705-716.
[6]Bhattacharya C,Aggarwal S,Kumar M,et al.Mouse apolipoprotein B editing complex 3 (APOBEC3)is expressed in germ cells and interacts with Dead-end(DND1)[J].PLOS One,2008,3(5):e2315.
[7]Kedde M,Strasser MJ,Boldajipour B,et al.RNA-binding protein Dnd1 inhibits microRNA access to target mRNA[J].Cell,2007,131(7):1273-1286.
[8]Ketting RF.A dead end for microRNAs.Cell,2007,131(7):1226-1227.
[9]Ding XF,Zhou JL,Zhong YL,et al.GAS41 interacts with transcription factor AP-2β and stimulates AP-2β?-mediated transactivation [J].Nucleic Acid Res,2006,34(9):2570-2578.
[10]Hartl M,Bader AG,Bister K.Molecular targets of the oncogenic transcription factor jun[J].Curr Cancer Drug Targets,2003,3(1):41-55.
[11]Peter K Vogt.Jun,the oncoprotein[J].Oncogene,2001,20(19):2365-2377.
[12]Hans van Dam,Marc Castellazz.Distinct roles of Jun:Fosand Jun:ATF dimers in oncogenesis[J].Oncogene,2001,20(19):2453-2464.
[13]Behrens A,Haigh J,Mechta-Grigoriou F,et al.Impaired intervertebral disc formation in the absence of Jun[J].Development,2003,130(1):103-109.
[14]Yu Z,Guo R,Ge Y,et al.Gene expression profiles in different stages of mouse spermatogenic cells during spermatogenesis[J].Biol Reprod,2003,69(1):37-47.
[15]Wolfes H,Kogawa K,Millette CF,et a1.Specific expression of nuclear proto-oncogenes before entry into meiotic prophase of spermatogenesis[J].Science,1989,245(4919):740-743.
[16]Chieffi P,Angelinl F,Pierantoni R.Proto-oncogene activity in the testis of the lizard,Podarcis s.sicula,during the annual reproductive cycle[J].Gen Comp Endocrinol,1997,108(2):173-181.
[17]Shalini S,Bansal MP.Role of selenium in spermatogenesis:differential expression of c jun and c fos in tubular cells of mice testis[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2006,292(1-2):27-38.
[18]Brachmann RK,Vidal M,Boeke JD.Dominant-negative p53 mutations selected in yeast hit cancer hot spots[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1996,93(9):4091-4095.
[19]Baldini G,Martelli AM,Tabellini G,et al.Rabphilin localizes with the cell actin cytoskeleton and stimulates association of granules with F-actin cross-linked by{alpha}-actinin[J].J Biol Chem,2005,280(41):34974-34984.
[20]Dhavan R,Greer PL,Morabito MA,et al.The cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activators p35 and p39 interact with the alpha-subunit of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and alpha-actinin-1 in a calcium-dependent manner[J].J Neurosci,2002,22(18):7879-7891.
[21]De Langhe S,Haataja L,Senadheera D,et al.Interaction of the small GTPase Rac3 with NRBP,a protein with a kinase-homology domain [J].Int J Mol Med,2002,9(5):451-459.
[22]Lim R,Winteringham LN,Williams JH,et al.MADM,a novel adaptor protein that mediates phosphorylation of the 14-3-3 binding site of myeloid leukemia factor 1[J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(43):40997-41008.
[23]Haug K,Warnstedt M,Alekov AK,et al.Mutations in CLCN2 encoding a voltage-gated chloride channel are associated with idiopathic generalized epilepsies [J].Nat Genet,2003,33(4):527-532.
[24]Nehrke K,Arreola J,Nguyen HV,et al.Loss of hyperpolarization-activated Cl(-)current in salivary acinar cells from Clcn2 knockout mice [J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(26):23604-23611.
[25]Bosl MR,Stein V,Hubner C,et al.Male germ cells and photoreceptors,both dependent on close cell-cell interactions,degenerate upon ClC-2 Cl(-)channel disruption[J].EMBO J,2001,20(6):1289-1299.

