Morphological variation patterns and taxonomy of Medicago sativa complex
YANG Hai-jun,CUI Da-fang,2,LI Fei-fei,FANG Ying
(1.Center of Ex perimental Teaching for Common Basic Courses,South China Agricultural University,Guangdong Guangzhou 510642,China;2.College of Forestry,South China Agricultural University,Guangdong Guangzhou 510642,China;3.College of Life Sciences,South China Ag ricultural University,Guangdong Guangzhou 510642,China)
Lots ofMedicagospecies are rich in nutrition and are widely used in animal husbandry.Annual species,Medicago lupulina,has wider distribution and more nutrition than perennial species such asMedicago sativain China[1],but the biological production of the latter is larger than the former.In addition,the varieties ofM.sativafrom different sources have different self-compatibility[2],therefore identification of chineseMedicagogermplasm will contribute to forage breeding,pasture building and the development of animal husbandry in Northwest China.
At present,the genusMedicagois still a problematic genus of Leguminosae despite that lots of research have been done on its taxonomy[3-6].Reviewing the taxonomic history,it is distinct that the reason for having no widely recognized taxonomic opinion about the genus is not only intergrading withTrigonellabut also containing many complexes in itself.M.sativacomplex is the most important resource because of its utilization as forage and other uses.Species of the complex are mainly distributed in the area from Central Asia to Northwest China,due to inter-fertility,more and more variants occur.Between 1919 and 1950,there were more than 40 species described as separate species belonging toM.sativacomplex by taxonomists in Russia[3],but Lubenetz[7]and Cuiet al[8]indicated most of the species should be identifiedas some different ecological types or formas.GenerallyM.sativacomplex may be grouped into 3 types:yellow-flowered with uncoiled pods,purple-flowered with highly spirally coiled pods and intermediates between the first two cases.Lesins and Lesins[3]analysed thatM.sativa,M.f alcataandM.glutinosawere the basic species of the complex,and all of other taxa of hybrid origin should be brought intoM.×variaorM.media.Small and Brookes[9]took the complex as a single comprehensive species,M.sativa,and downgraded many species to subspecies.For example,they downgradedM.f alcatatoM.sativasubsp.falcata.Small[10]studied the relationship between the morphological differentiation and the ploidy,and found that yellow-flowered plants with different ploidy exhibited substantially overlapping morphological variation,while in the same instance purple-flowered plants might be separable from morphology.Hence,classification based only on flower color become incredible.Small[11]studied the taxonomy of the complex making use of the characters of pod's trichomes,and separatedM.sativasubsp.falcatavar.viscosafrom the yellow-flowered type.Recently,Pecettiet al[12]studied the phenotypic variation mainly based on morpho-physiological traits and considered it was necessary to use all of the available characters.
The objective of the present study is to observe the range of morphological variations and to evaluate the taxonomic value of morphological characters ofM.sativacomplex.A large number of quantitative and qualitative data were obtained fromMedicagoaccessions to be operated in order to clarify the relationships of several taxa in the complex.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 MaterialsThis study was conducted on 125 herbarium specimens(Table 1)from Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography,Chinese Academy of Science(XJBI),Xinjiang Agricultural University(XJA),Grassland Research Institute of XJAAS(XAG),Xinjiang Normal University(XJNM),Shihezi University(SHI)and South China Agricultural University(CANT).
1.2 MethodsTotal 39 characters relating to leaf,flower and pod were selected and observed(Table 2),and the coding strategy of character referred to Xu[13].Qualitative characters were scored with ordinal number and quantitative characters were measured with ruler or using computer image technique.Regarding computer image technique,the process was as following:1)laying a leaf on the glass platform of scanner;2)setting the important parameters of software(the values of the parameters unchanged in the course of the study)and scanning the leaf to get its image;3)using the measure tool of image software(Adobe Photoshop)to get data.The morphological data matrix was standardized and a multivariate analysis based on both Principal Component Analysis(PCA)and Cluster Analysis(CA)was carried out.In CA,the similarity matrix was calculated using the average taxonomic distance,Unweighted Pair-Group Method Using Arithmetic Average(UPGMA)was used to cluster analysis.In PCA,the similarity matrix was based on the product-moment correlation.From this correlation matrix,eigenvalue and eigenvector matrices were obtained.The multivariate analysis was carried out with the software package NTSYS-pc[14].
2 Results
The morphological diversity ofM.sativacomplex was well reflected by the data listed in Table 2.A-mong all the quantitative characters,M.sativa(Sat)had the largest proportion of maximum measurements and accounted for 75%,whileM.f alcata(Fal)had the largest proportion of minimum measurements and accounted for 50%.The ratio of the other 5 taxa ranged between 0 to 32.14%.This information indicated that some distinct morphological intergradations existed among the seven taxa.
The leaves of the seven groups inM.sativacomplex were similar to each other,and it was difficult to identify them accurately only depending on the characteristics of leaves.The distribution of individual
plant on the coordinate system defined by the length and the width of leaflet was showed in Fig.1.It was obvious that these plants intermixed together.
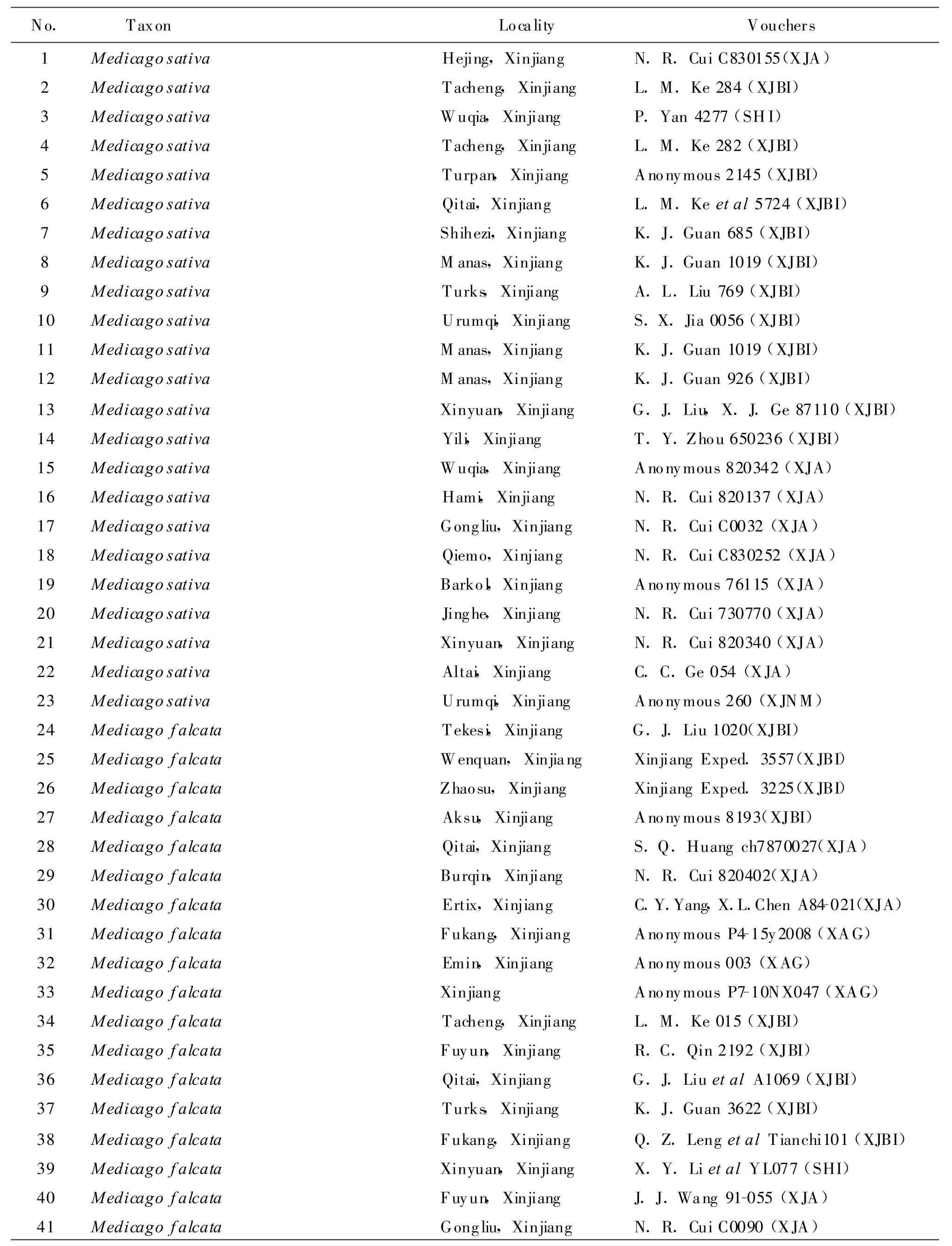
Table 1 Source of vouchers specimens
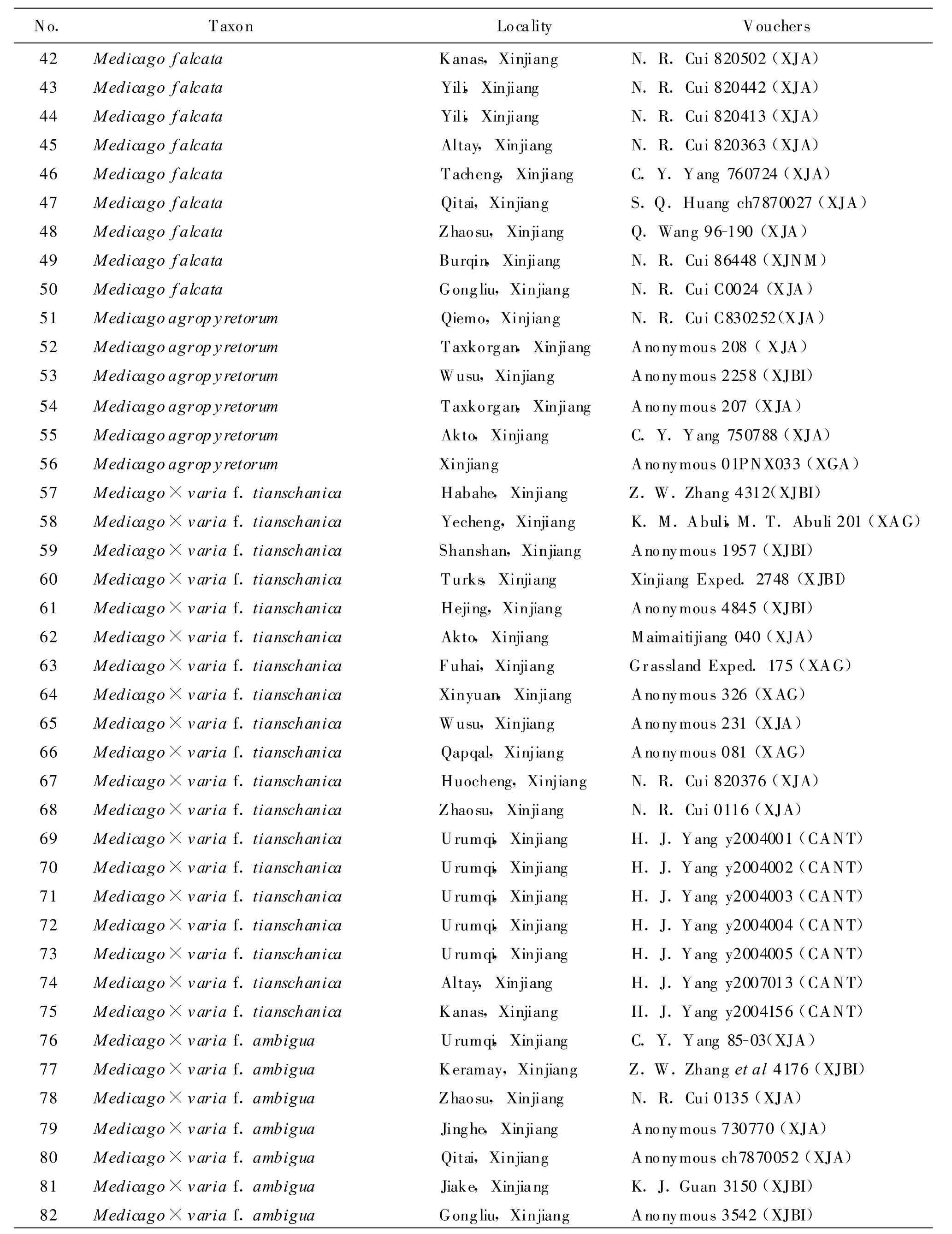
Continuous Table 1
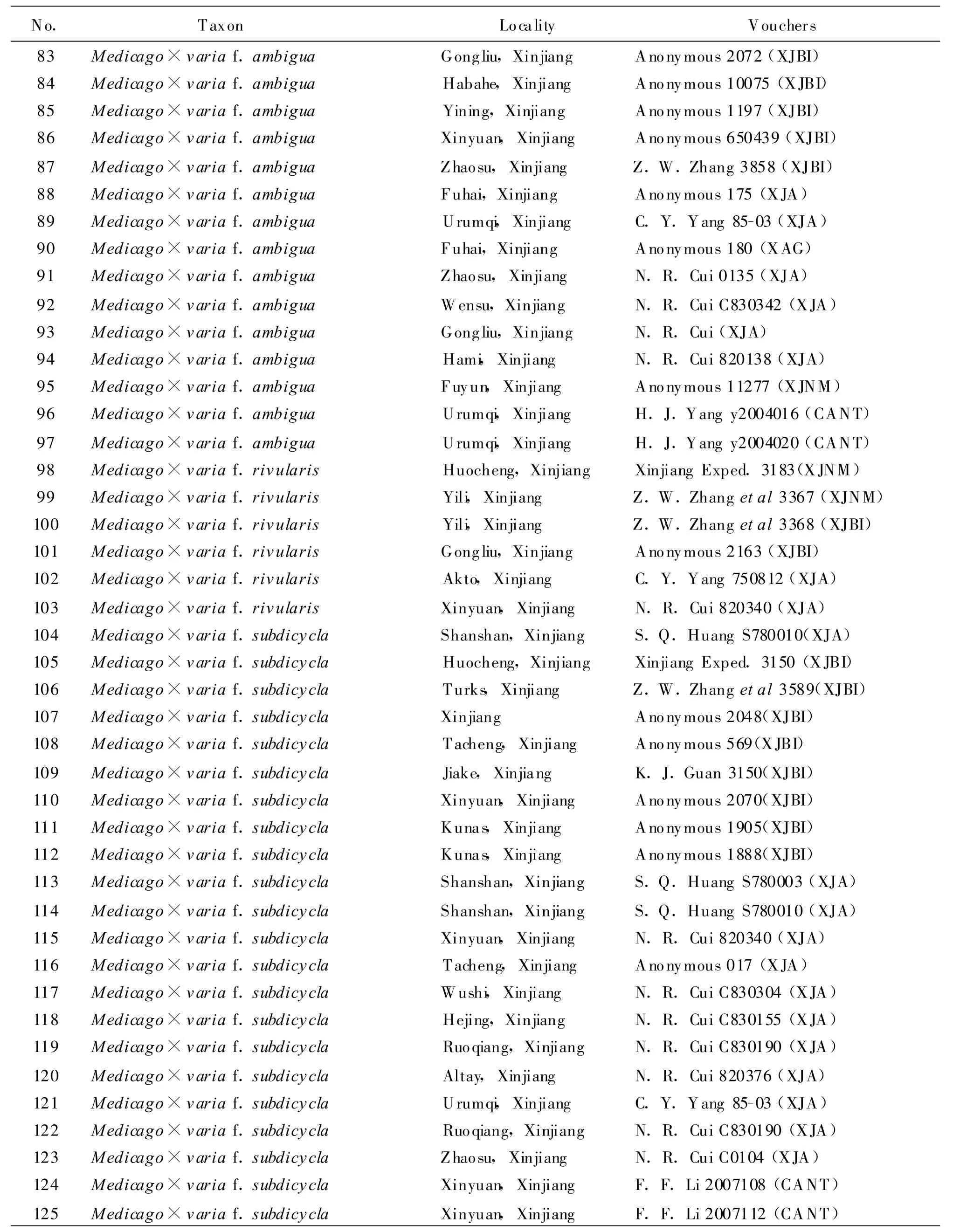
Continuous Table 1
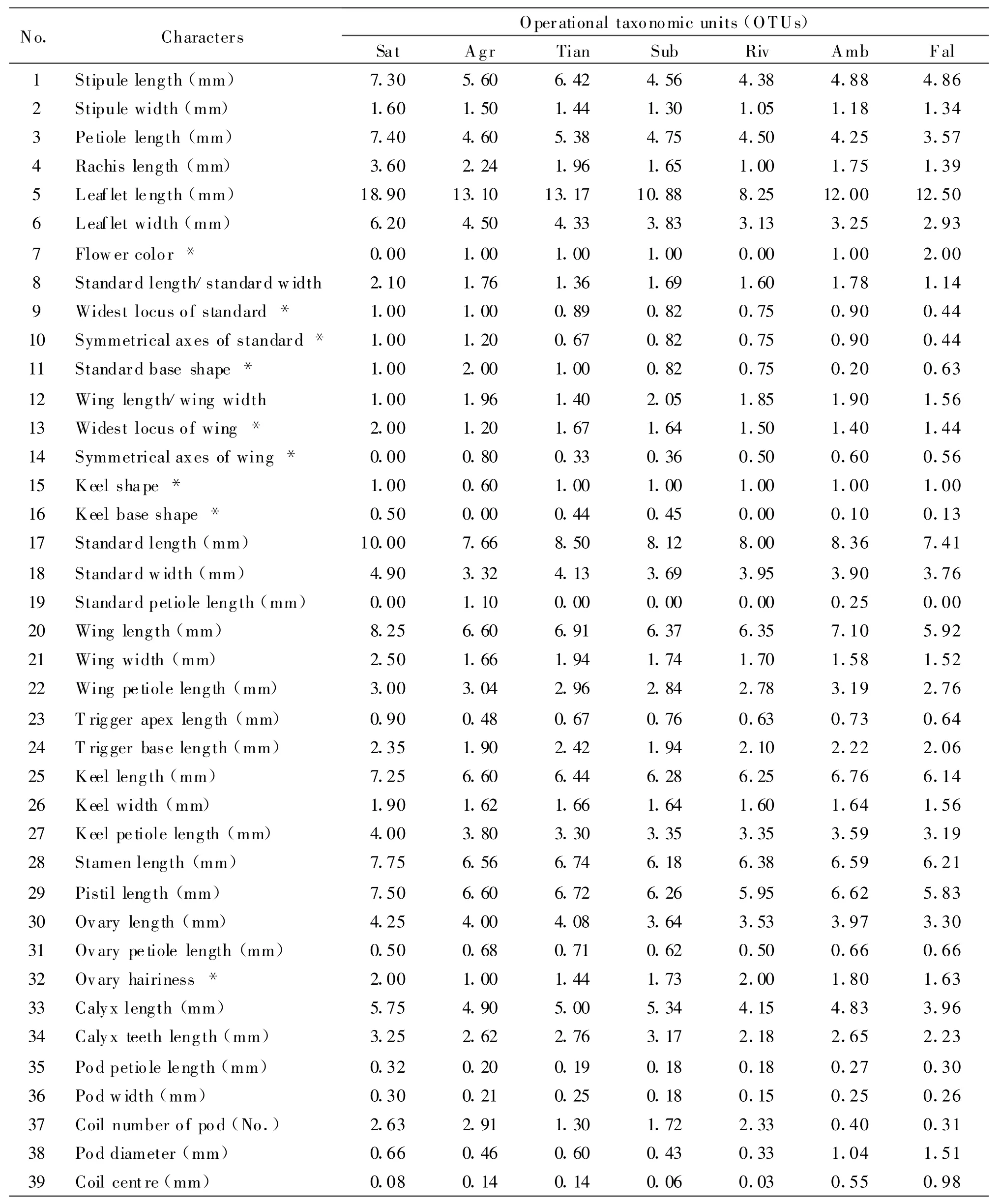
Table 2 The value of characters of the 7 taxa as circumscribed in this research
The flower ofM.sativacomplex includes pedicel,calyx,corolla,stamens and a pistil.The corolla is typically papilionaceous,consisting of a standard,two wings and two keels which fused together.The standard is longer than other 4 petals,but more variable in size at the range of 0.55 to 0.95 cm.Generally,in the taxonomy ofMedicago,the length of flower was an important character.Analyzing the overlapping in size among the seven groups,an approximate normal distribution curve which suggests that taking the length of the standard as a taxonomic character might not be eligibly,or the complex might be a species,can be got(Fig.2).
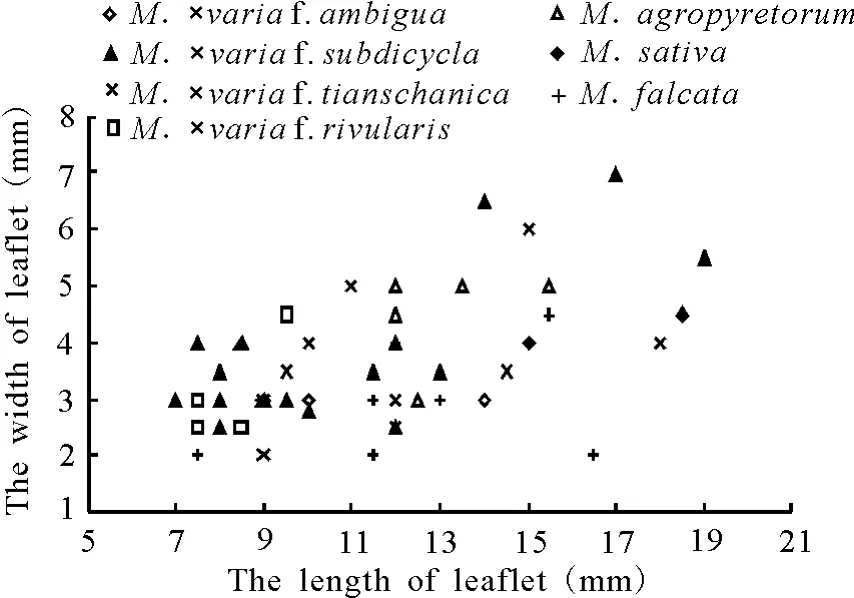
Fig.1 Two-dimensional distribution based on width and length of middle leaflets
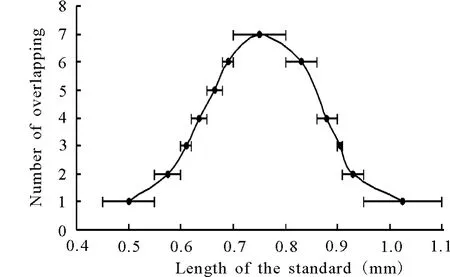
Fig.2 The overlapping status of flower length in M.sativa complex
There are two types of pods ofMedicagoin morphology.One is almost straight to sickle-shaped,such as the pods ofM.f alcata,M.×variaf.ambigua;and the other is spiral varying from 3/4 of a coil to several coils which occurs in most species.The pods ofM.agropyretorumhave most coils with smaller diameter like a cylinder,but there are fewer coils and bigger diameter in other intermediate taxa.However,sickle-shaped pods are likewise presented inTrigonella,so it is always confused to identify the two genera.
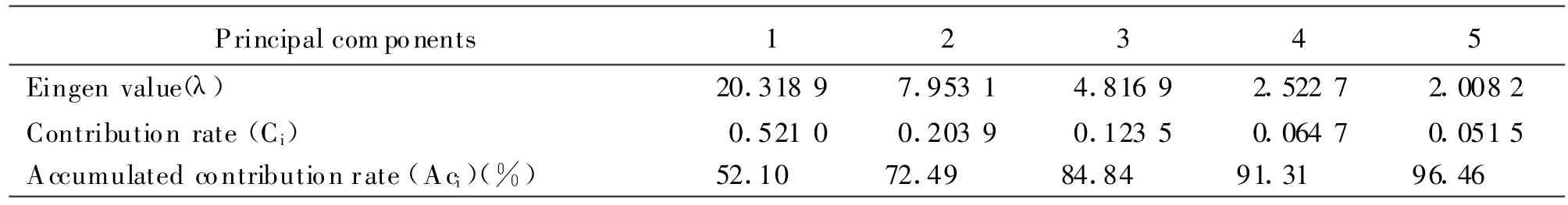
Table 3 The principal component analysis of morphological characters
The principal component analysis showed that the first two principal components(PC)were in total up to 72.49%,and might reflect the main character of the complex(T able 3).PC1 had the higher loadings for the characters standing for the size of flower and leaf,such as keel width(0.987 4),petiole length(0.974 3),wing length(0.963 7),standard length(0.962 0),stamen length(0.959 5),pistil length(0.957 7),wing width(0.954 8),leaflet width(0.938 8)and rachis length(0.935 9).PC2 had the higher loadings for the characters which were keel shape(-0.934 8),standard petiole length(0.930 0),standard base shape(0.817 6)and symmetrical axes of standard(0.816 5).According to these characters,the length of flower may be an important identification feature for the taxa ofM.sativacomplex,but asshown in Fig.2,the overlapping of flower length so obviously reduce its value of classification.Taking into the lower contribution rate of PC1(Aci=52.10%),the flower pattern ofM.sativacomplex is undergoing evolutionary transformation.While the evolution has not yet stabilized and causes the eigenvalue of characters to close to each other and reduces the contribution rate of PC1.Relatively the variation of flower length is deepened than others and becomes the major aspect in PC1,thus the length of flower,the length of petiole,the width of leaflet,the length of rachis and the shape of pod are valuable for taxonomy of the complex.The plot was established on the first two PCs(Fig.3).Long distance was found between Sat,Fal and Agr,whereas,Amb,Riv,Sub and Tian congregated closely,and then the seven taxa were divided into four groups,including three single groups and one compound group(M).
Taking the distance coefficient d2=1.090 1 for the classification criteria,the dendrogram may be divided into four clusters.Cluster A,B and D only contain one taxa respectively.Sat is a polar variant ofM.sativacomplex and rare in the wild environment now.Fal is the other polar variant of the complex and very common in the field.Cluster C is constitutive of four taxa which usually are considered as the components ofM.×varia.Generally Agr is pointed as a hybrid and merged intoM.×variatoo.
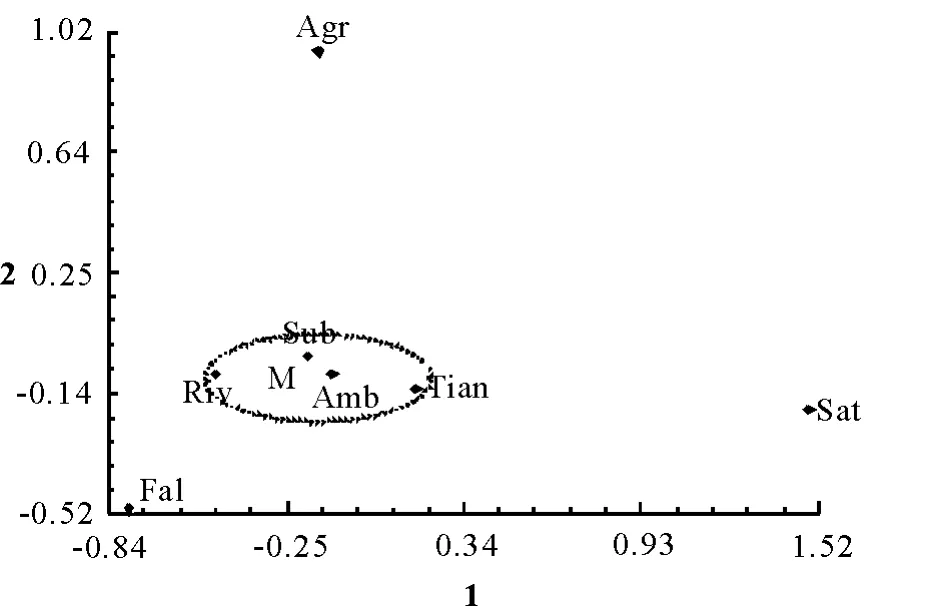
Fig.3 The results of principal component analysis(PCA)
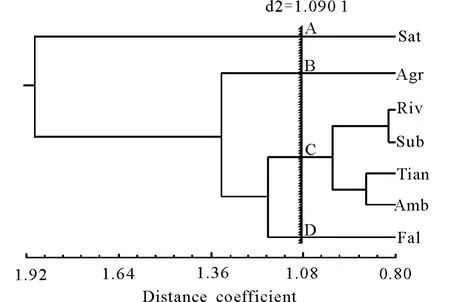
Fig.4 The results of cluster analysis(CA)
3 Discussion
Although some excellent studies aboutM.sativacomplex have been carried out for many years,there are still taxonomic problems about it because it is a complicated group.Leaves are more similar and the shapes of leaflet vary from elliptic to cuneate within a species and they overlap in size.For the complex,the taxonomic value of leaf is inappreciable.Flower and pod are very important characters to identify taxa in the complex.From PCA,flower is in the course of differentiation and tends to be bigger or smaller respectively.The various colors of flower are between yellow and purple controlled pigments.
The morphologic studies with PCA and CA suggested thatM.sativacomplex should be divided into four taxa,viz.M.sativa,M.f alcata,M.agropyretorumandM.×varia.M.sativais approved widely as a separate species,andM.falcatais also taken as a species by Lesins and Lesins[3],Cuiet al[8],Wei and Huang[15].However,some people considered it to be right as a subspecies ofM.sativa[5].Lesins and Gillies[16]indicated the distinct differences not only in morphology but also in pigments betweenM.sativaandM.f alcata.Cuiet al[8]observed the arm ratio of chromosomes and the number of satellite chromosomes ofM.sativawere less than those ofM.f alcata.Calderiniet al[17]also found the locus in situ hybridization ofM.f alcatawere different fromM.sativa.On the other side,Bauchan and Hossian[18-19]an-alyzed the C-banded and N-banded karyotypes of diploid alfalfa and found the chromosomes ofM.f alcatahad only centromeric bands and was different fromM.sativasubsp.caerulea.Cluster andysis showed Fal and Sat respectively assigned to two clusters,and their dissimilarity(d=2.320 9)was the biggest one,and PCA got the same result.Therefore,it was suggested thatM.f alcatashould be treated as a separate species in the present research.
Since there are no strict reproductive isolation,M.sativamay easily hybridize withM.f alcataand produce many viable offsprings which are denominated withM.×varia.Amb,Riv,Sub and Tian are all the components of their offspring[3].PCA and CA showed that the four taxa were clustered together and exhibited some similar characters such as comparative small flowers and pods.Amb has two steady characters viz.blue-purple flower and sickle-shaped pod and is taken as the most typical intergradations ofM.f alcataandM.sativa.Cuiet al[8]found the karyotype of Amb was very different from that ofM.f alcata,but similar toM.sativa,and Amb is considered as a forma ofM.×varianamedM.×variaf.ambigua.The latter three taxa are all with coiled pods,but their flower color was greatly varied.The flowers and the pods of Tian are both bigger than those of Riv and Sub notably,moreover its plants always grow erectly with more high stature,so it is easy to be distinguished from Riv and Sub.Tian was described as a separate species by Vassilczenko[20],but Lubenetz[7]deemed its hybrid origin and rejected it as being merely ecological-geographical variation ofM.sativa.Wu[21]hybridizedM.sativatoM.falcataand obtained some plants which very like Tian since F2generation.We believed that it would help to understand the hybrid origin of Tian.In fact,Lesins and Lesins[3]had narrated the problem of Tian,but provided no affirmatory view.Cuiet al[8]also disapproved of the opinion of Vassilczenko and merged it intoM.×variaas another forma.The results of PCA and CA also supported that Tian should not be a species.However,Riv and Sub are similarly to each other in some way,they are dwarfish and slender,and in the size of flower and pod are similar too.They were primarily clustered together at the lowest distance coefficient(d=0.821 5),and the two taxa had a similar tendency.Moreover,the pollen morphology also showed that Riv was very similar with Sub[8].Based on all the credible results,the four taxa Amb,Riv,Sub and Tian had more similarities rather than differences and should be taken as the members ofM.×varia.Thus,the present research suggested that they were not species but the formas ofM.×varia.
Arg has 3-4 close coils with almost no opening in the centre and blue-purple color flowers,the diameter of its pod and the length of its flower are distinct smaller than those ofM.sativa.Arg was considered as a speciesM.agropyretorum[20]or a formaM.×variaf.agropyretorum[8].Arg was placed in a more independent position by PCA and CA,which denoted that there was a greater difference between Arg and other taxa,so the study approved the opinion of Vassilczenko who took it as a species namedM.agropyretorum.
[1]Feng Y Q,Cao Z Z.Study on the nutrition quality of wild germplasm ofMedicago lupulina[J].Pratacultural Science,2009,26(10):80-84.
[2]Lv L Y,Wei Z W,Zhao Y,etal.A study of self-compatibility and pollinations and separation of offspring traits of alfalfa[J].Pratacultural Science,2009,26(4):33-36.
[3]Lesins K A,Lesins I.GenusMedicago(Leguminosae):a taxogenetic study[M].Hague:Dr.W.Junk Publishers,1979.
[4]Small E.A numerical analysis of major groupings inMedicagoemploying traditionally used characters[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1981,59:1553-1577.
[5]Small E,Jomphe M.A synopsis of the genusMedicago(Leguminosae)[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1989,67:3260-3294.
[6]Small E,Brookes B,Lassen P.Circumscription of the genusMedicago(Leguminosae)by seed characters[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1990,68:613-629.
[7]Lubenetz P A.Lucerne-Medicago[J].Bulletin of Applied Botany,of Genetics and Plant-Breeding,1972,47(3):3-68.
[8]Cui D F,Tian Y W,Min J C,et al.Taxonomy of Medicago in Xinjiang,China[J].Advances in Plant Taxonomy in Northwest China,1992(1):43-57.
[9]Small E,Brookes B S.Taxonomic circumscription and identification in theMedicago sativa-falcata(alfalfa)continuum[J].The Economic Botany,1984,38(1):83-96.
[10]Small E.Morphological differentiation inMedicago sativas.l.in relation to ploidy[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1985,63:1747-1752.
[11]Small E.Taxonomy of glandular wild alfalfa(Medicagosativa)[J].Canadian Journal of Botany,1986,64:2125-2129.
[12]Pecetti L,Piano E,Valentini P,et al.Phenotypic variation and germplasm discrimination in lucern(Medicago sativacomplex)as evidenced by multivariate analysis[J].Journal of Genetics&Breeding,1999,53:37-45.
[13]Xu K X.Numerical Taxonomy[M].Beijing:Science Press,1994.
[14]Rohlf F J.NTSYS-pc Numerical Taxonomy and M ultivariate Analysis System,version 1.80[M].New York:Exeter Publication,1990.
[15]Wei Z,Huang Y Z.Leguminosea[A].In:Cui H B.Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae,Vol.42[M].Beijing:Science Press,1998:321.
[16]Lesins K,Gillies C B.Taxonomy and cytogenetics of Medicago[A].In:Hanson C H.Alfalfa Science and Technology[M].Wisconsin:American Society of Agronomy,1972:53-86.
[17]Calderini O,Pupilli F,Cluster P D,et al.Cytological studies of the nucleolus organizing regions in theMedicagocomplex:sativa-coerulea-falcata[J].Genome,1996,39:914-920.
[18]Bauchan G R,Hossain M A.Karyotypic analysis of C-banded chromosomes of diploid alfalfa:Medicago sativassp.caeruleaand ssp.falcataand their hybrid[J].The Journal of Heredity,1997,88(6):533-537.
[19]Bauchan G R,Hossain M A.Karyotypic analysis of N-banded chromosomes of diploid alfalfa:Medicago sativassp.caeruleaand ssp.falcataand their hybrid[J].The Journal of Heredity,1998,89(2):191-193.
[20]Vassilczenko I T.Lucerne-the best forage plant[J].Acta Institute of Botanica Komarovii,1949,1(8):1-240.
[21]Wu Y F.Report of cross breeding betweenMedicago falcataandM.sativa[J].Grassland of China,1979(1):27-33.
