名词复数讲堂
杨 静
一、构成方法及读音规则
1. 一般情况加-s:清辅音后读/s/,浊辅音和元音后读/z/。例如:
map—mapsboy—boysgirl—girlspen—pensbag—bagscar—cars
2. 以s, sh, ch, x等结尾加-es, 读/iz/。例如:
bus—buseswatch—watchesbox—boxesbrush—brushes
3. 以辅音字母+y结尾,变y为i再加es, 读/z/。例如:
baby—babiescity—citiescountry—countries
但以y结尾的专有名词,或元音字母+y 结尾的名词变复数时,直接加s即可。例如:
two Marysthe Henrysmonkey—monkeysholiday—holidays
4. 以o结尾的名词,变复数时:
a. 加s。如: photo—photospiano—pianosradio—radioszoo—zoos
b. 加es。如: potato—potatoestomato—tomatoes
c. 上述a和b两种方法均可。如: zero—zeros/zeroes
5. 以f或fe结尾的名词变复数时:
a. 加s。如: belief—beliefsroof—roofssafe—safesgulf—gulfs;
b. 去f/fe加ves。如: half—halvesknife—knivesleaf—leaveswolf—wolveswife—wiveslife—livesthief—thieves;
c. 上述a和b两种方法均可。例如: handkerchief—handkerchiefs/handkerchieves
二、名词复数的不规则变化
1. child—childrenfoot—feettooth—teethmouse—miceman—menwoman—women
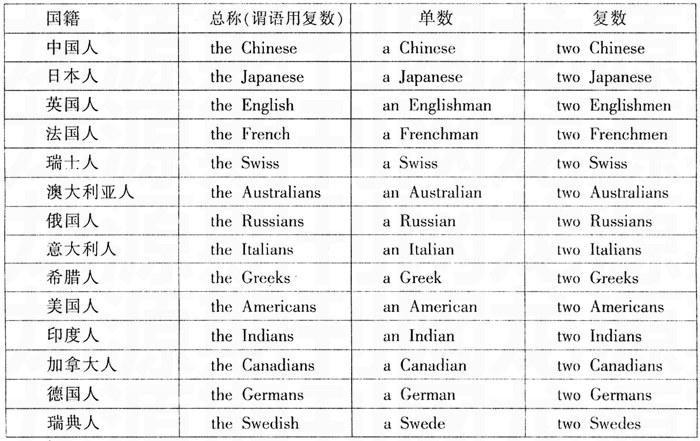
注意:由一个词加man或woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men和-women,如an Englishman, two Englishmen。但German不是合成词,故复数形式为Germans; Bowman是姓,其复数是the Bowmans。
2. 单复数同形,如deer, sheep, fish, Chinese, Japanese, li, jin, yuan, two li, three mu, four jin等。但除人民币的元、角、分外,美元、英镑、法郎等都有复数形式。如:a dollar—two dollars; a meter—two meters。
3. 集体名词,以单数形式出现,但实为复数。如: people, police, cattle 等本身就是复数,不能说 a people, a police, a cattle,但可以说a person, a policeman, a head of cattle。
4. 以s结尾,仍为单数的名词,如:
a. maths, politics, physics等学科名词,一般是不可数名词,为单数。
b. news 为不可数名词。
c. the United States, the United Nations 应视为单数。例如:
The United Nations was organized in 1945. 联合国是1945年组建起来的。
d. 以复数形式出现的书名,剧名,报纸,杂志名,也可视为单数。例如:
The Arabian Nights is a very interesting story-book.
《一千零一夜》是一本非常有趣的故事书。
5. 表示由两部分构成的东西,如:glasses(眼镜), trousers, clothes等,若表达具体数目,要借助数量词pair(对,双); suit(套)等,如: a pair of glasses; two pairs of trousers等。
6. 另外还有一些名词,其复数形式有时可表示特别意思,如:goods货物, waters水域,fishes(各种)鱼。
三、不可数名词量的表示
1. 物质名词
a. 当物质名词转化为个体名词时为可数。例如:
Cake is a kind of food. 蛋糕是一种食物。(不可数)
These cakes are sweet. 这些蛋糕很好吃。(可数)
b. 当物质名词表示该物质的种类时,可数。例如:
This factory produces steel. 这个工厂生产钢。(不可数)
We need various steels. 我们需要不同的钢。(可数)
c. 当物质名词表示份数时,可数。例如:
Our country is famous for tea. 我国因茶叶而闻名。(不可数)
Two teas, please. 请来两杯茶。(可数)
2. 抽象名词表示具体的事例时也可数。例如:
four freedoms 四大自由 the four modernizations四个现代化
物质名词和抽象名词可以借助单位词表一定的数量,如a glass of water; a piece of advice; a pile of coal; a flash of lightening; a burst of laughter
四、定语名词的复数
名词作定语一般用单数,但也有以下例外。
1. 用复数作定语。例如:
sports meeting 运动会 students reading-room 学生阅览室
talks table 谈判桌 the foreign languages department 外语系
2. man, woman, gentleman等作定语时,其单复数以所修饰的名词的单复数而定。例如:
men workers women teachers gentlemen officials
3. 有些以s结尾的名词,作定语时,s保留。例如:
goods train(货车) arms produce 武器生产
customs papers 海关文件 clothes brush 衣刷
4. 数词+名词作定语时,这个名词一般保留单数形式。例如:
two-dozen eggs 两打鸡蛋 a ten-mile walk 十英里路
two-hundred trees 两百棵树 a five-year plan 一个五年计划
五、不同国籍人的单复数