Interleukins in liver disease treatment
Ming Yang,Chun-Ye Zhang
Abstract Cytokines play pleiotropic roles in human health and disease by regulating both innate and adaptive immune responses.Interleukins (ILs),a large group of cytokines,can be divided into seven families,including IL-1,IL-2,IL-6,IL-8,IL-10,IL-12,and IL-17 families.Here,we review the functions of ILs in the pathogenesis and resolution of liver diseases,such as liver inflammation (e.g.,IL-35),alcoholrelated liver disease (e.g.,IL-11),non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (e.g.,IL-22),liver fibrosis (e.g.,Il-17a),and liver cancer (e.g.,IL-8).Overall,IL-1 family members are implicated in liver inflammation induced by different etiologies,such as alcohol consumption,high-fat diet,and hepatitis viruses.IL-2 family members mainly regulate T lymphocyte and NK cell proliferation and activation,and the differentiation of T cells.IL-6 family cytokines play important roles in acute phase response in liver infection,liver regeneration,and metabolic regulation,as well as lymphocyte activation.IL-8,also known as CXCL8,is activated in chronic liver diseases,which is associated with the accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages.IL-10 family members contribute key roles to liver immune tolerance and immunosuppression in liver disease.IL-12 family cytokines influence T-cell differentiation and play an essential role in autoimmune liver disease.IL-17 subfamilies contribute to infection defense,liver inflammation,and Th17 cell differentiation.ILs interact with different type I and type II cytokine receptors to regulate intracellular signaling pathways that mediate their functions.However,most clinical studies are only performed to evaluate IL-mediated therapies on alcohol and hepatitis virus infection-induced hepatitis.More pre-clinical and clinical studies are required to evaluate IL-mediated monotherapy and synergistic therapies.
Key Words: Interleukins;Family members;Liver disease;Treatment;Clinical trials
INTRODUCTION
Cytokines coordinate both innate and adaptive immune responses,and they display pleiotropic roles in healthy and disease conditions[1].Interleukins (ILs),a large group of cytokines,play important roles in immune cell growth,differentiation,and activation,as well as other tissue-resident cells by interacting with their receptors[2].Acute and chronic liver diseases are characterized by liver inflammation and cell death[3,4],which are commonly associated with infiltration of different immune cells and activation of hepatic parenchymal cells to secrete ILs[5,6].ILs as a major type of cytokines are involved in the pathogenesis and resolution of liver diseases,such as liver inflammation (e.g.,IL-35)[7],alcohol-related liver disease (e.g.,IL-11)[8],non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (e.g.,IL-22)[9],liver fibrosis (e.g.,Il-17a)[10],and liver cancer (e.g.,IL-8)[11].
Herein,we review the members of IL families and their functions in liver disease.Especially,we summarize the current findings for liver disease treatment by targeting different ILs in clinical trials.
INTERLEUKIN FAMILIES
Interleukins can be divided into seven families (Table 1),including IL-1 family[12,13],IL-2 family[14,15],IL-6 family[16,17],IL-8 family[18,19],IL-10 family[20,21],IL-12 family[22,23],and IL-17 family[24,25].All the families of interleukins are involved in the liver disease.For example,IL-1 family cytokines are implicated in liver inflammation induced by different etiologies[26,27],such as alcohol consumption,high-fat diet,and hepatitis viruses.IL-2 family members mainly regulate T lymphocyte and NK cell proliferation and activation,and the differentiation of T cells[28-30].IL-6 family cytokines play important roles in acute phase response in liver infection,liver regeneration,and metabolic regulation,as well as lymphocyte activation[31,32].IL-8,also known as CXCL8,is activated in chronic liver diseases,which is associated with the accumulation of neutrophils and macrophages[33,34].IL-10 family members contribute key roles to liver immune tolerance and immunosuppression in liver disease[35,36].IL-12 family cytokines influence T-cell differentiation and play an essential role in autoimmune liver disease[37,38].IL-17 subfamilies contribute to infection defense,liver inflammation,and Th17 cell differentiation[39,40].Commonly,several IL families function together in each liver disease,contributing to liver disease progression and resolution.Therefore,targeting interleukins provides therapeutic strategies for liver disease.

Table 1 Interleukin families in liver diseases
INTERLEUKIN RECEPTORS
Cytokines such as interleukin family members can bind their receptors to activate intracellular signaling pathways (e.g.,Janus kinase/signal transduction and transcription activation or JAK/STAT signaling pathway) to regulate cell biological functions.Cytokine receptors are mainly classified into two classes,type 1 and type 2 receptors.Most receptors of IL family members belong to type 1 receptors (Table 2),such as IL-2 and IL-6,and IL-10 and IL-10 family cytokine (e.g.,IL-19) receptors belong to type 2 receptors[41,42],while IL-1 family member receptors have both type 1 and type 2 receptors[12].Type 1 cytokine receptors have a conserved Trp-Ser-X-Trp-Ser (WSXWS) motif at their C-terminals and four conserved cysteine residues at their N-terminals,and they can interact with cytokines with four-helical bundle motifs[43].Most type 2 cytokine receptors are heterodimers (Table 2),and their intracellular domains are linked by a Janus kinase which can activate the STAT signaling pathway[44].

Table 2 Interleukins and their receptors
IL-MEDIATED THERAPIES IN CLINICAL TRIALS
Given the important roles of ILs in liver diseases,many clinical trials are undergoing to evaluate their direct and synergistic functions in liver disease treatment.The cases (Table 3) were reviewed from the website https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on December 3,2023).To date,most studies have been performed to evaluate IL-mediated therapies on alcohol and hepatitis virus infection-induced hepatitis.
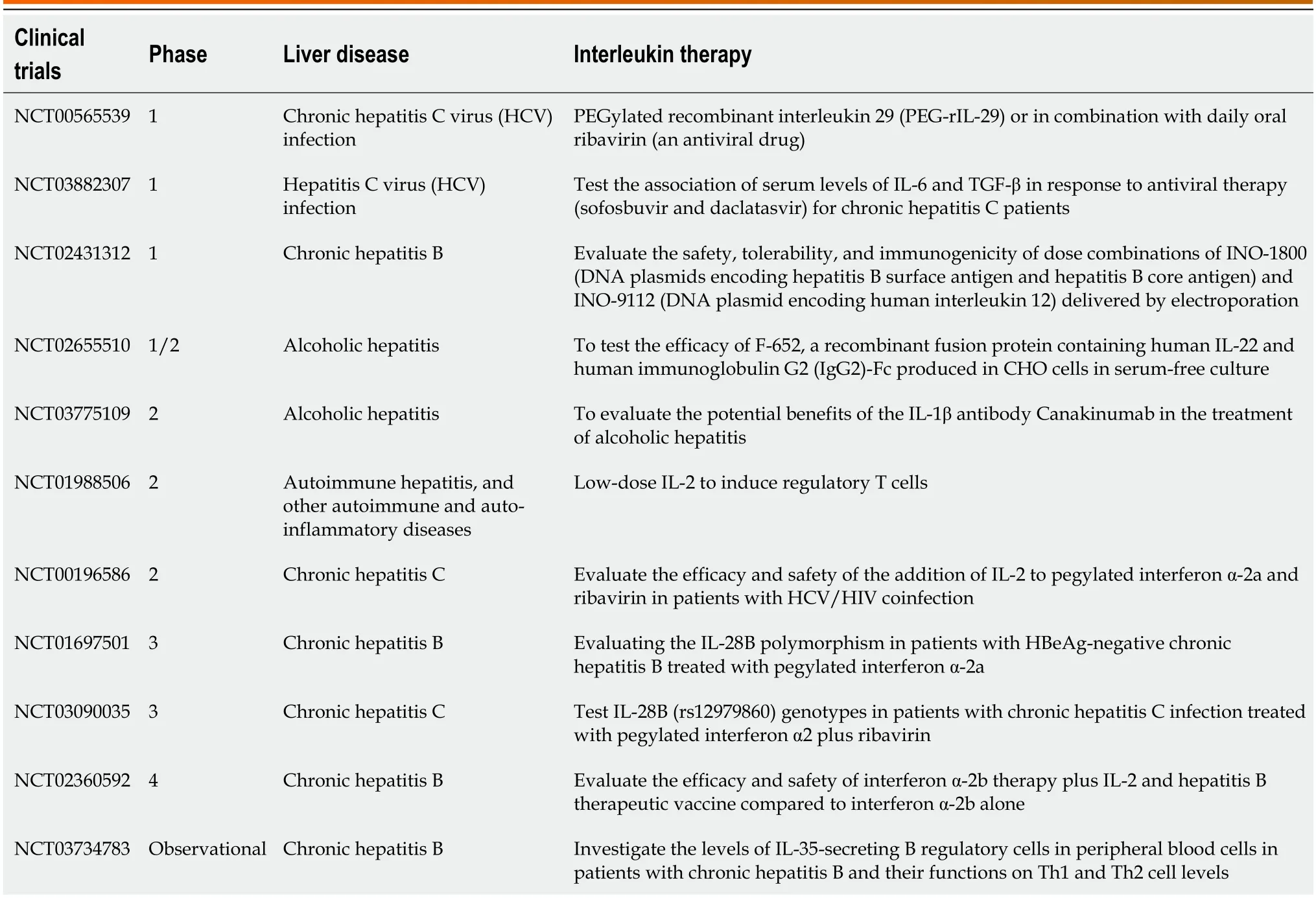
Table 3 Interleukin-mediated therapies in liver disease
CONCLUSION
In summary,all seven families of ILs play pivotal roles in liver homeostasis and pathogenesis by regulating both innate and adaptive immune responses.However,current studies mainly focus on evaluating the roles of ILs in alcohol and hepatitis virus infection-induced hepatitis.Pre-clinical and clinical evaluations of IL effects in different chronic liver diseases should be further studied by testing the efficacy of interleukin monotherapy or synergistic effects with other therapies.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Yang M and Zhang CY designed,collected data,wrote,revised,and finalized the manuscript,contributed equally,and shared the first authorship.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:United States
ORCID number:Ming Yang 0000-0002-4895-5864;Chun-Ye Zhang 0000-0003-2567-029X.
S-Editor:Liu JH
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Cai YX
 World Journal of Hepatology2024年2期
World Journal of Hepatology2024年2期
- World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Changes in the etiology of liver cirrhosis and the corresponding management strategies
- Advancements in autoimmune hepatitis management: Perspectives for future guidelines
- Non-invasive assessment of esophageal varices: Status of today
- Insights into skullcap herb-induced liver injury
- Can rifaximin for hepatic encephalopathy be discontinued during broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment?
- New markers of fibrosis in hepatitis C: A step towards the Holy Grail?
