circRNA3669 promotes goat endometrial epithelial cells proliferation via miR-26a/RCN2 to activate Pl3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK pathways
Xiaorui Liu ,Jiuzeng Cui ,Mengyao Wei ,Xiaofei Wang ,Yuexia Liu ,Zhongshi Zhu ,Min Zhou,Gui Ba,Langda Suo,Yuxuan Song#,Lei Zhang#
1 Division of Laboratory Safety and Services, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, China
2 College of Animal Science and Technology, Northwest A&F University, Yangling 712100, China
3 Institute of Animal Sciences, Tibet Academy of Agricultural and Animal Husbandry Sciences, Lhasa 850009, China
Abstract The development of receptive endometrium (RE) from pre-receptive endometrium (PE) for successful embryo implantation is a complex dynamic process in which the morphology and physiological states of the endometrial epithelium undergo a series of significant changes,including cell proliferation and apoptosis. However,the molecular mechanisms are not yet fully understood. In this study,a higher circRNA3669 level was observed in PE than in RE of goats. Functional assays revealed that this overexpression promoted the proliferation of goat endometrial epithelial cells (GEECs) by activating the expression of genes related to the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK pathways,thereby inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. Furthermore,circRNA3669 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA(ceRNA) to upregulate Reticulocalbin-2 (RCN2) expression at the post-transcriptional level by interacting with and downregulating miR-26a in GEECs. In addition,RCN2,which is highly expressed in the PE of goats,was found to be regulated by β-estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4). Our results demonstrated that RCN2 also affected the key proteins PI3K,AKT,mTOR,JNK,and P38 in the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK pathways,thereby facilitating GEECs proliferation and suppressing their apoptosis in vitro. Collectively,we constructed a new circRNA3669-miR-26a-RCN2 regulatory network in GEECs,which further provides strong evidence that circRNA could potentially play a crucial regulatory role in the development of RE in goats.
Keywords: circRNA3669,RCN2,miR-26a,goat endometrial epithelial cells (GEECs),proliferation
1.Introduction
Endometrial receptivity is necessary for successful embryo implantation in the reproductive process of domestic animals (Bliteket al.2008;Lessey 2019). The development of pre-receptive endometrium (PE) from receptive endometrium (RE) is a complex dynamic process where the morphology and physiological states of the endometrial epithelium undergo a series of visible changes (Larasati and Ita 2021;Pauleet al.2021). It is an indispensable physiological event to allow the embryo to breach the epithelial barrier and implant into the uterine luminal epithelium owing to the proliferation and apoptosis of endometrial epithelial cells (Galánet al.2006;Boeddeker and Hess 2015;Wang Xet al.2017).Therefore,there is an urgent need to study the molecular regulatory mechanism of the proliferation and apoptosis of goat endometrial epithelial cells (GEECs) during the development of RE in goats.
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are involved in the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression and are crucial in several physiological processes,including the formation of the RE during embryo implantation (Songet al.2015;Wanget al.2016;Wang Yet al.2017;Zhanget al.2020). MicroRNAs(miRNAs),which are an important class of ncRNAs,are major epigenetic regulatory factors in gene regulatory networks (He and Hannon 2004;Ghildiyal and Zamore 2009),and can affect endometrial receptivity by targeting and down-regulating the expression levels of target genes during embryo implantation (Huanget al.2020;Kumaret al.2021). In addition,our previous studies have reported that miR-26a is involved in RE formation and regulates endometrial cell proliferation and apoptosisviathe PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in goats(Zhanget al.2018c).
In recent years,circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been found to act as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs)to sponge miRNAs and decrease their inhibitory effects on target genes,thus regulating gene expression at the post-transcriptional level (Songet al.2021;Zhanget al.2022). Our previous study revealed that circRNAs may play an important regulatory role during the development of RE from PE in the endometrium of goats (Songet al.2019). For example,circ-8073 regulates centrosomal protein of 55 kDa (CEP55) by sponging miR-449a to promote GEECs proliferationviathe PI3K/AKT-mTOR pathway and may participate in the formation of RE during embryo implantation in goats (Liuet al.2018).Thus,it is necessary to investigate the regulatory effects of circRNAs at the post-transcriptional levels of specific functional genes by sponging shared miRNAs in GEECs during RE formation.
This study aimed to explore the functions and effects of circRNA3669 on GEECs proliferation,apoptosis,and PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways,to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms of circRNA3669-miR-26a-RCN2in the development of RE in goats. The results will provide an experimental basis for further studies on GEECs and endometrial development from the pre-receptive to receptive phases in goats.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Sample collection
The endometrium of goats at gestational days 5 (D5,PE) and 15 (D15,RE) was collected from the anterior wall of the uterine cavity (Songet al.2015;Zhanget al.2015). Some of the samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen to extract total RNA,and the others were immediately placed in phosphate-buffered saline(PBS),supplemented with penicillin (100 IU mL–1) and streptomycin (50 mg mL–1),for isolating GEECs.
2.2.Cell culture and treatment
From endometrial samples of goats,primary GEECs were isolated,purified,and cultured,as previously described(Leiet al.2017;Zhanget al.2017a). Overexpression plasmids of circRNA3669 andRCN2were constructed,and the primer sequences are shown in Appendix A. To verify,the entire fragment of circRNA3669 was amplified and cloned into a pMD™19-T vector (TaKaRa,Beijing,China). The restriction fragment of circRNA3669 was obtained by usingKpnI andBamHI restriction sites following double restriction. Furthermore,the digested fragments were cloned into a pcDN2.1(+) (pCD-ciR)vector (Geneseed Biotech,Guangzhou,China) using T4 ligase and buffer H. The whole CDS region fragment ofRCN2(XM_018066370.1) was amplified,connected with A-tail first,and then cloned into a pMD™19-T (TaKaRa,Beijing,China) vector. UsingKpnI andXhoI restriction endonuclease sites,the restriction endonuclease fragments were obtained after double restriction endonuclease. The digested fragment was cloned into a pcDNA3.1(+) vector(Thermo Fisher,Shanghai,China) by T4 ligase.
The miR-26a mimic (negative control,NC),miR-26a inhibitor (NC-inhibitor,NCH),RCN2siRNA (SiRCN2),and circRNA3669 siRNA (SicircRNA3669) were synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai,China). All GEECs were plated at a density of 7.5×105in 6-well plates and were transfected at 50% confluency using Lipofectamine 2000(Invitrogen,Waltham,MA,USA).
2.3.Dual-luciferase reporter assay
To verify the target genes of miR-26a,bioinformatics analysis of miRNA-binding sequences on circRNA3669 andRCN2was performed using Targetscan7.1. In this study,we constructed wild-type and mutatedRCN2-3´UTR or full circRNA3669 psiCHECKTM-2 plasmids for luciferase assays,and the primers are shown in Appendix A. The wild-type (psiCHECK2-WT) and mutated (psiCHECK2-MT) plasmids of the full circRNA3669 psiCHECKTM-2 were co-transfected with miR-26a or NC into GEECs,respectively. After 36 h,the cells were harvested,and the activity of dual luciferase was measured. UsingRenillaluciferase as an internal reference,the detection value ofFireflyluciferase activity was divided by measuring theRenillaluciferase activity,and the relative expression between different samples was compared according to the ratio.
2.4.RNA-FlSH
Complementary probes (RiboBio,Guangzhou,China)targeting the back-splicing junction region were designed to visualize circRNA3669 fluorescencein situ. GEECs were fixed using anin situhybridization fixative. After pre-hybridization,cells were incubated with the labeled circRNA3669 probes in hybridization buffer at 55°C overnight. Laser confocal microscopy (Leica TCS SP8,Leica,Wetzlar,Germany) was used to observe the localization of circRNA3669 in the GEECs.
2.5.RNA extraction and quantitative PCR
Total RNA was extracted using the TRIzol reagent(TaKaRa Biotechnology,Dalian,China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. To quantify the amount of circRNAs,part of the total RNAs was incubated for 15 min at 37°C with or without (mock) 3 U μg–1of RNase R (Epicenter Biotechnologies,Chicago,USA). The RNA purity and concentration were determined by measuring the optical density (OD) at wavelengths of 260 and 280 nm using an Epoch microplate spectrophotometer(BioTek Instruments,Inc.,Winooski,VT,USA). Total RNA(900 ng) was used to convert mRNAs into cDNAs using the PrimeScript RT reagent Kit (TaKaRa Biotechnologies,Dalian,China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
RT-qPCR was performed using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (TaKaRa Biotechnologies,Dalian,China),according to the manufacturer’s instructions,in a 25 μL reaction mixture.β-actingene was used as the reference for mRNAs and U6 for miR-26a. All primers for RT-qPCR are shown in Appendix A. The relative expression levels were calculated using the following equation N=2–ΔΔCt.
2.6.lmmunohistochemistry (lHC) assay
Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression level of the RCN2 protein (10193-2-AP,Proteintech,China) in endometrial tissues on day 5 (D5) and day 15 (D15) after goat pregnancy. IHC images were captured using a fluorescence microscope (DM6B,Leica,Germany) and analyzed as previously described (Zhanget al.2017b) at the Life Science Research Core Services of Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University,China.
2.7.Western blot assay
The GEECs were transfected with NC,NCH,SiRCN2,SicircRNA3669,circRNA3669,or pc3.1-RCN2for 48 h,and the cells were harvested,lysed in RIPA buffer(Solarbio,Beijing,China) supplemented with protease inhibitor (Roche,Mannheim,Germany) and phosphatase inhibitor (Roche,Mannheim,Germany) at 4°C for 30 min,and centrifuged (11,000×g) for 10 min. Soluble proteins in the supernatants were collected,and total protein concentrations were determined using the Bio-Rad DC Protein Assay (Bio-Rad,Hercules,CA,USA),diluted with 100 μL of 4× protein loading buffer (Solarbio,Beijing,China),and boiled for 8 min.
As previously described (Leiet al.2017;Zhanget al.2017a),Western blot analysis was performed in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions,and the primary antibodies are shown in Appendix B. Quantity One (Bio-Rad) was used for quantification,and each experiment was performed in triplicate.
2.8.5-Ethynyl-2´-deoxyuridine (EdU) and Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays
To investigate the effects of circRNA3669 andRCN2on GEECs proliferation,we interfered with or overexpressed circRNA3669 andRCN2in GEECs. The EdU (Ribobio,Guangzhou,China) and CCK-8 assays (ZETA,USA) were used to evaluate the proliferation of GEECs as previously described (Liet al.2017). GEECs were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 2×103cells/well in 100 μL culture medium per well. Each treatment group consisted of six independent replicates.
2.9.Flow cytometry assay
To investigate whether circRNA3669 andRCN2regulate GEECs apoptosis,we used a flow cytometry assay and an Annexin V-FITC PI staining apoptosis assay kit (Liankebio,Hangzhou,China) after overexpression or silencing of circRNA3669 andRCN2in GEECs. According to the manufacturer’s protocol,Annexin-V-positive and PInegative cells were defined as early apoptotic cells,and the late apoptotic cells were defined as Annexin V and PI dual-positive cells.
2.10.Statistical analysis
All data were processed using the SPSS software (version 23.0;SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA). One-way ANOVA and independent-samplet-tests were used to compare differences. Data are presented as the mean±SEM. TheP-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1.circRNA3669 identification and expression pattern in goat endometrium
To understand the role of circRNAs in the development of endometrial receptivity in goats,we screened for differentially expressed circRNA3669 in our published sequencing data (NCBI: GSE85384). The structure of circRNA3669,derived from exon 3 to exon 12 of the Ran-binding protein 9 (RANBP9) gene,is located on chromosome 23 and has a length of 1,246 bp (Fig.1-A).Divergent primers were used to amplify the backspliced junction of circRNA3669 and confirmed using Sanger sequencing (Fig.1-B). Our previous sequencing data revealed that circRNA3669 was remarkably downregulated by approximately 7.4-fold in RE compared to that in PE (Songet al.2019). In this study,the RTqPCR results showed that the circRNA3669 level decreased (P<0.01) in RE (Fig.1-C),which was highly consistent with previous sequencing data. In addition,circRNA3669 was widely expressed in the reproductive tissues of goats,with the highest expression observed in the oviduct (Fig.1-D). To precisely determine the cellular localization of circRNA3669,an RNA-FISH probe was designed to specifically recognize the back-spliced junction of circRNA3669. FISH analysis showed that circRNA3669 was localized in the cytoplasm of GEECs(Fig.1-E).
3.2.circRNA3669 serves as a sponge for miR-26a
In this study,circRNA3669 was predicted to functionally sponge miR-26aviaits predicted binding sites. To validate this,the WT-circRNA3669 and MT-circRNA3669 psiCHECK2 vectors were constructed,details of which are shown in Fig.2-A. The results showed that the luciferase activity of the WT-circRNA3669+miR-26a mimic group decreased (P<0.05),but no change was detected in the MT-circRNA3669+miR-26a mimic group (Fig.2-B).Moreover,the miR-26a inhibitor up-regulated (P<0.01) the expression level of circRNA3669 in GEECs,although the miR-26a mimic had no significant effect (Fig.2-C).
To investigate whether circRNA3669 regulates miR-26a in GEECs,we used RT-qPCR assays after the overexpression or silencing of circRNA3669. Next,the overexpression vector of circRNA3669,was transfected into GEECsin vitro,leading to a nearly 3-fold increase in the level of circRNA3669 (Appendix C),and significant downregulation of the expression level of miR-26a in GEECs,with NC transfection recovering it (P<0.01,Fig.2-D). Knockdown of circRNA3669 (SicircRNA3669)decreased the levels of circRNA3669 (Appendix C),and significantly increased miR-26a levels in GEECs,and NCH transfection recovered it (P<0.01,Fig.2-E).
3.3.circRNA3669 promotes GEECs proliferation by affecting the Pl3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways
We overexpressed and interfered with circRNA3669 to explore its physiological functions in GEECs. The results revealed that the overexpression activates the expression of genes related to the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways (Fig.3-A). However,interference with circRNA3669 had the opposite effect (Fig.3-B).
EdU (Fig.3-C) and CCK-8 assays (Fig.3-D) to determine the proliferation ability of GEECs revealed that overexpression of circRNA3669 significantly increased the proliferation rate of GEECs. However,introduction of SicircRNA3669 exerted the opposite effect on cell proliferation (Fig.3-E and F).
In addition,to explore the effect of miR-26a binding site mutation in circRNA3669 on GEECs proliferation and apoptosis,the mutated circRNA3669 and miR-26a mimic were co-transfected into GEECs. EdU and CCK-8 assays,performed to determine the proliferation ability of GEECs,reported that co-transfection of the mutated circRNA3669 and miR-26a mimic had no effect on the proliferation rate compared to the miR-26a mimic,and flow cytometry assays revealed that co-transfection of the mutated circRNA3669 and miR-26a mimic did not affect GEECs apoptosisinvitro(Appendix D).
3.4.circRNA3669 inhibits GEECs apoptosis
To investigate whether circRNA3669 regulates GEECs apoptosis,we used Western blotting and flow cytometry after the overexpression or silencing of circRNA3669.The results indicated that the overexpression of circRNA3669 increased (P<0.01) the protein levels of Bcl-2 and decreased (P<0.01) those of Bax and caspase3,while interference had the opposite effect (Fig.4-A and B).The apoptosis assay results showed that the introduction of overexpression circRNA3669 decreased (P<0.01)the proportion of apoptotic GEECs (Fig.4-C),whereas SicircRNA3669 increased (P<0.05,Fig.4-D).

Fig. 1 circRNA3669 identification and expression pattern in goat endometrium. A,schematic diagram of circRNA3669 arising from RABNP9 gene. B,the back-splice junction (arrow) of circRNA3669 was identified by Sanger sequencing (bottom). C,the circRNA3669 levels in pre-receptive endometrium (PE) and receptive endometrium (RE) of goats. D,the circRNA3669 levels in various reproduction tissues of goats. E,FISH detection of circRNA3669 in GEECs. The total RNAs were incubated for 15 min at 37°C with 3 U μg–1 of RNase R. The circRNA3669 levels were measured by RT-qPCR and normalized to β-actin. The values are showed as mean±SEM for three individuals. **,P<0.01.
3.5.circRNA3669 regulated RCN2 by sponging miR-26a in GEECs
Targetscan 7.1 and miRanda predicted thatRCN2might be a target gene of miR-26a (Fig.5-A). To validate this prediction,a luciferase reporter gene plasmid containing the wild-type 3´UTR sequence of theRCN2mRNA (WTRCN2) and a plasmid containing the mutated 3´UTR of theRCN2mRNA (MT-RCN2) were constructed based on the psiCHECKTM-2 system (Fig.5-A). The results reported that miR-26a significantly decreased (P<0.01)the luciferase activity of the WT-RCN2-3´UTR than did NC,but exerted no effect on that of the MT-RCN2-3´UTR (Fig.5-B). Furthermore,circRNA3669 and miR-26a co-transfection increased the luciferase activity of the WT-RCN2-3´UTR compare to than that miR-26a,but decreased compare to than that circRNA3669 (Fig.5-C).
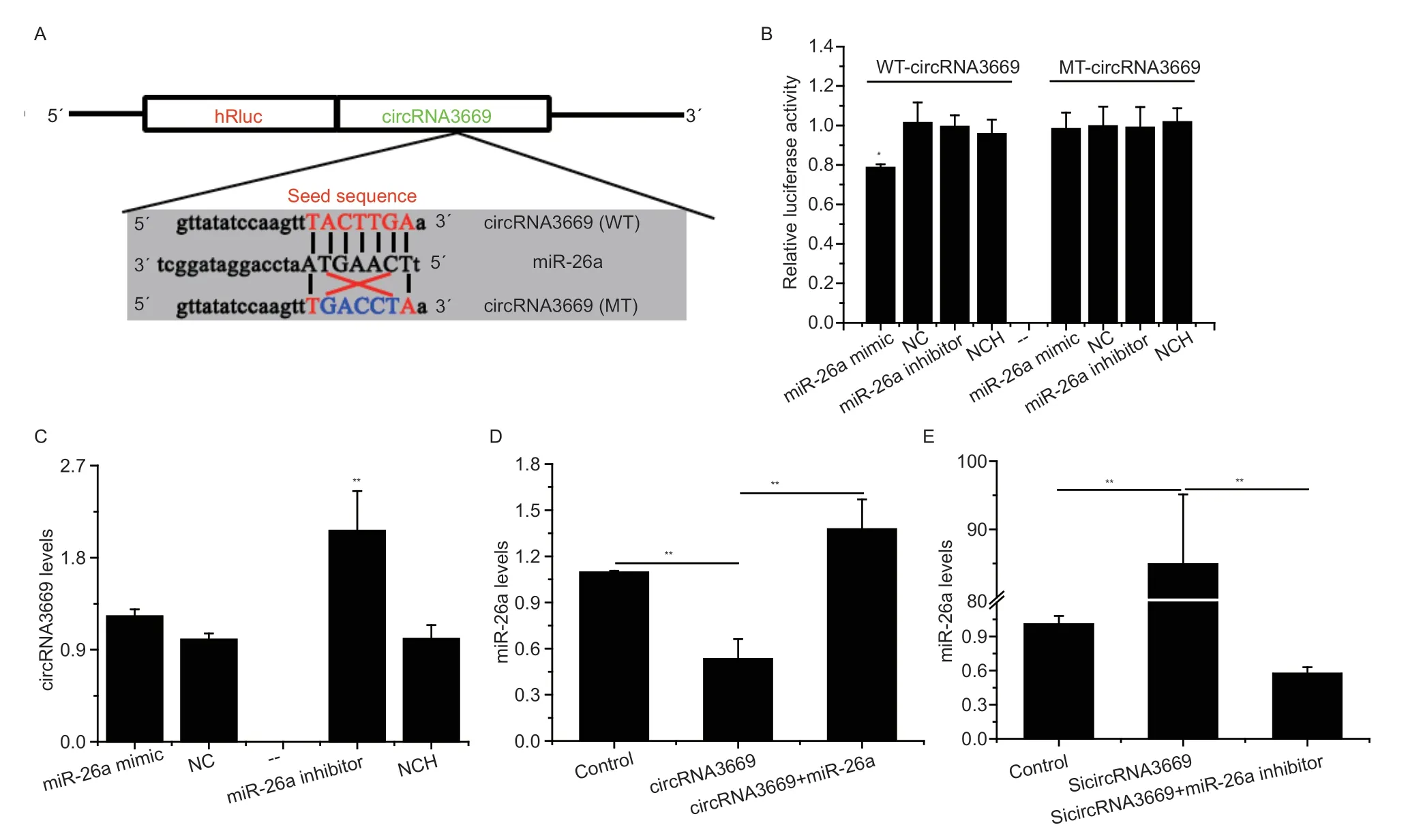
Fig. 2 circRNA3669 serves as a miR-26a sponge in goat endometrial epithelial cells (GEECs). A,schematic diagram illustrating the design of luciferase reporters with the WT-circRNA3669 or the site-specific mutant (MT-circRNA3669). The nucleotides in red represented “seed sequence” of miR-26a,and the mutation nucleotides were in blue. B,luciferase reporter assay of GEECs co-transfected with WT-circRNA3669/MT-circRNA3669 and miR-26a,NC (negative control),miR-26a inhibitor or NC inhibitor(NCH). C,the effect of miR-26a on the circRNA3669 levels in GEECs. D–E,the miR-26a levels in GEECs transfected with overexpression and interference with circRNA3669. The miR-26a levels were measured by stem-loop RT-qPCR and normalized to U6;the circRNA3669 levels were measured by RT-qPCR and normalized to β-actin. The results are represented as mean±SEM for three individuals. *,P<0.05;** P<0.01.
To verify whetherRCN2expression was regulated by miR-26a,we measured mRNA and protein levels in GEECs using RT-qPCR and western blotting,respectively.We observed that miR-26a reducedRCN2mRNA levels(P<0.05,Fig.5-D);and the protein levels of RCN2 were significantly reduced (P<0.01),and the miR-26a inhibitor significantly elevated (P<0.01) RCN2 mRNA and protein levelsinvitro(Fig.5-D-F),revealing that miR-26a targets the 3´UTR ofRCN2specifically and functions as a demotivated mediator.
To investigate whether circRNA3669 could act as a ceRNA to regulateRCN2expression by sponging miR-26a,RCN2mRNA and protein levels were detected in GEECs transfected with circRNA3669 and miR-26a mimic or SicircRNA3669 and miR-26a inhibitors. circRNA3669 downregulated (P<0.01)RCN2mRNA levels (Fig.5-G)but circRNA3669 up-regulated (P<0.05) RCN2 protein levels (Fig.5-I and K). Furthermore,SicircRNA3669 elevated (P<0.01) the mRNA levels ofRCN2(Fig.5-H),whereas RCN2 protein levels were reduced (P<0.05) in GEECs by SicircRNA3669 (Fig.5-J and K). Based on the above results,we concluded that circRNA3669 could function as a ceRNA to regulate the expression levels ofRCN2by sponging miR-26a in GEECsinvitro.
3.6.RCN2 enhanced the GEECs proliferation in vitro
The mRNA levels ofRCN2were higher (P<0.01) in PE than in RE as measured using RT-qPCR (Fig.6-A),and IHC results further demonstrated that RCN2 protein levels were decreased (P<0.01) in RE,particularly in GEECs(Table 1;Fig.6-B). Furthermore,RCN2was widely expressed in the reproductive tissues of goats,with the highest expression level observed in the caruncle,followed by the oviduct,uterus,and uterine horn (Fig.6-C).To investigate the response ofRCN2expression levels to sex hormones in GEECs of PE,β-estradiol (E2) and progesterone (P4) were diluted in the cell medium to different concentrations. In GEECs,the expression level ofRCN2was the highest with 10 ng P4,followed by 5 ng P4 and 100 pg E2+10 ng P4 (Fig.6-D). Thus,we hypothesized that the induction ofRCN2may be a critical event in the development of RE from PE by E2 and P4.
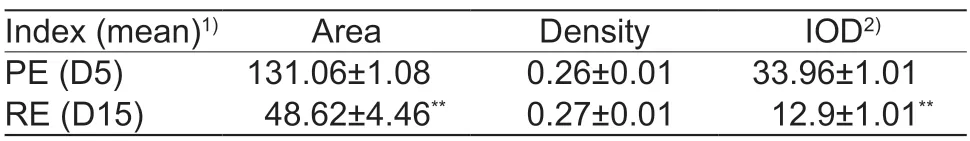
Table 1 The immunohistochemical staining results of RCN2 in uterus of goats
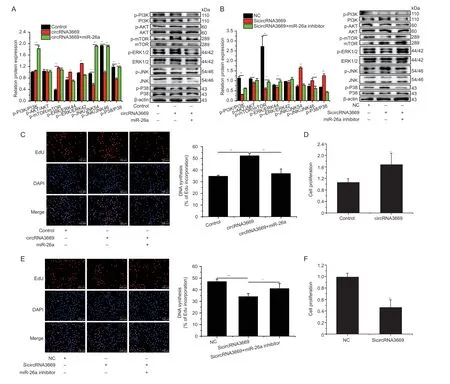
Fig. 3 circRNA3669 promotes GEECs proliferation by affecting the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways. A and B,the expression levels of PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways-related genes were detected by Western blots after overexpression and interference with circRNA3669. C and E,EdU analysis after overexpression and interference with circRNA3669.Scale bars,100 μm. D and F,CCK-8 analysis after overexpression and interference with circRNA3669. The protein levels were measured by Western blot and densitometry was normalized to the β-actin density from the same lane. The results are represented as mean±SEM for three individuals. *,P<0.05,**,P<0.01.
To explore the effect ofRCN2on GEECs proliferation,we overexpressed and interfered withRCN2expression.As shown in Appendix E,overexpressedRCN2significantly increased the mRNA and protein levels ofRCN2,and the knockdown ofRCN2(SiRCN2) reducedRCN2mRNA and protein levels in GEECs. CCK-8 and EdU assays,performed to determine the proliferation ability of GEECs,reported that overexpression ofRCN2increased (P<0.01) the proliferation rate,whereas SiRCN2decreased (P<0.01) its proliferationinvitro(Fig.6-F).
3.7.RCN2 inhibited the apoptosis of GEECs by affecting the Pl3K/AKT-mTOR and JNK/P38 MAPK signaling pathways
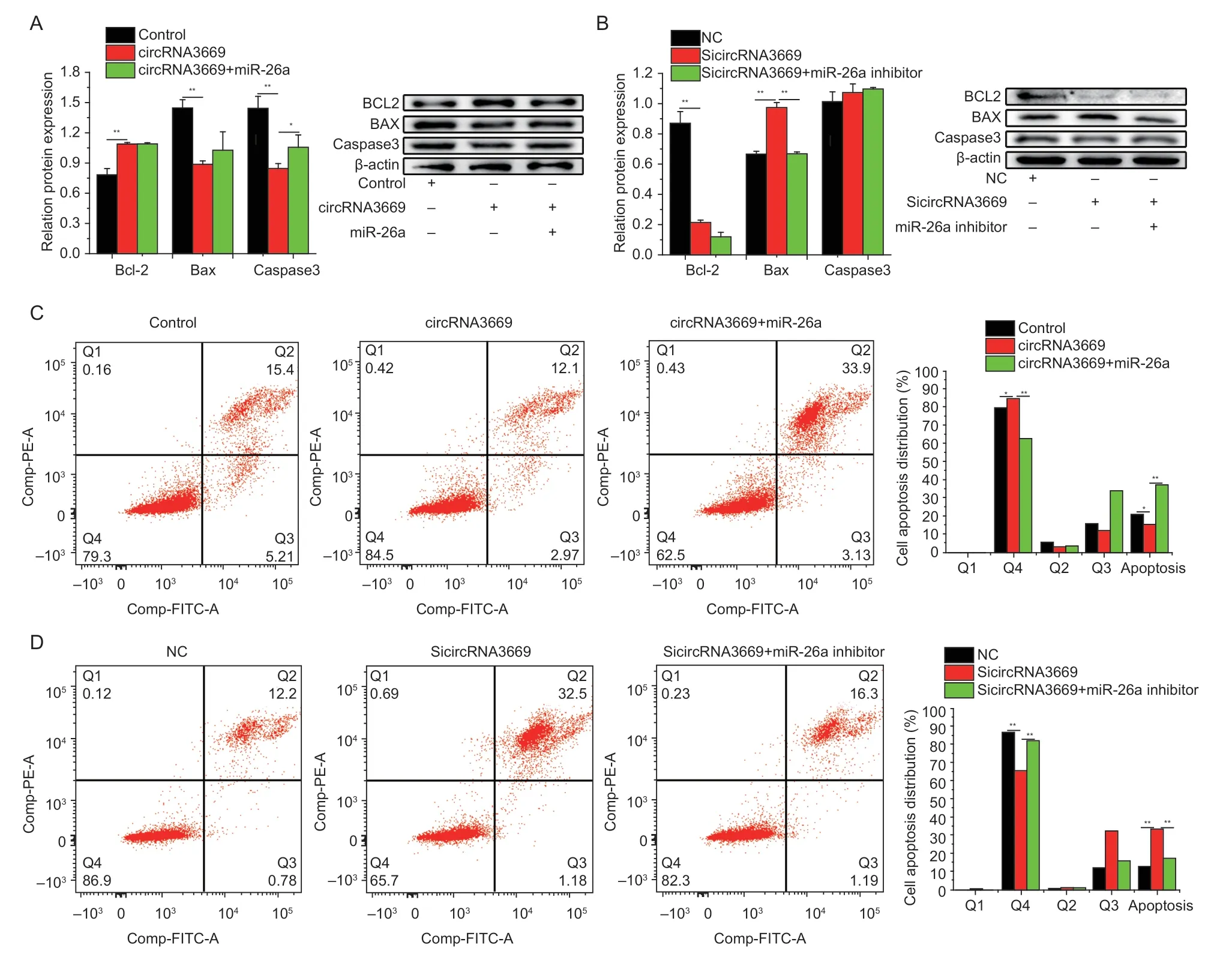
Fig. 4 circRNA3669 inhibits GEECs apoptosis. A and B,the protein levels of Bcl-2,Bax,and caspase3 were detected by Western blot. C and D,cell apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI dual staining followed by flow cytometry after the cells were transfected with overexpression and interference with circRNA3669. The results are represented as mean±SEM for three individuals. *,P<0.05;**,P<0.01.
To investigate whetherRCN2regulates GEECs apoptosis,we used Western blotting and flow cytometry after the overexpression or silencing ofRCN2. The results indicated that overexpression ofRCN2could increase(P<0.01) the protein levels of Bcl-2 and decrease(P<0.01) those of Bax and caspase3,and interference had the opposite effect (Fig.7-A–C). The apoptosis assay showed that the overexpression ofRCN2reduced(P<0.01) the proportion of apoptotic GEECs (Fig.7-D),whereas SiRCN2induced (P<0.01) GEECs apoptosisinvitro(Fig.7-E).
As shown in Fig.7-F and G,Western blotting revealed that overexpression ofRCN2significantly increased the levels of p-PI3K/PI3K (P<0.01),p-AKT/AKT (P<0.01),and p-mTOR/mTOR (P<0.05),and markedly inhibited p-JNK/JNK54 (P<0.01),p-JNK/JNK46 (P<0.05),and p-P38/P38 (P<0.01) levels,whereas the levels of p-ERK/ERKR44 and p-ERK/ERKR42 did not significantly vary.Furthermore,SiRCN2significantly reduced (P<0.01) the levels of p-AKT/AKT and p-mTOR/mTOR and significantly increased (P<0.01) the levels of p-JNK/JNK54,p-JNK/JNK46,and p-P38/P38 in GEECs. However,SiRCN2had no notable suppressive effect on the levels of p-PI3K/PI3K,p-ERK/ERKR44,or p-ERK/ERKR42 in GEECs. As mentioned above,it could be concluded thatRCN2could inhibit GEECs apoptosisviathe PI3K/AKT-mTOR and JNK/P38 MAPK signaling pathwaysinvitro.
4.Discussion
Endometrial receptivity is regulated by complex networks composed of coding and non-coding genes. Following the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics,an increasing number of ncRNAs have been discovered to participate in various cellular physiological processes and play critical roles in epigenetic regulation (Chen and Xue 2016). Recent studies have indicated that circRNAs act as potential regulators of endometrial receptivity at the posttranscriptional level and are expressed in the endometrium(Zhanget al.2018a;Niet al.2021;Zhaoet al.2021).Based on bioinformatic predictions and our previously constructed circRNA library,circRNA3669 was found to be specifically expressed in the pre-receptive PE of goats(Songet al.2019). In this study,the circRNA3669 level decreased in the receptive RE compared to that in the PE,which was highly consistent with previous sequencing data. Therefore,we speculated that circRNA3669 is involved in the development of endometrial receptivity.
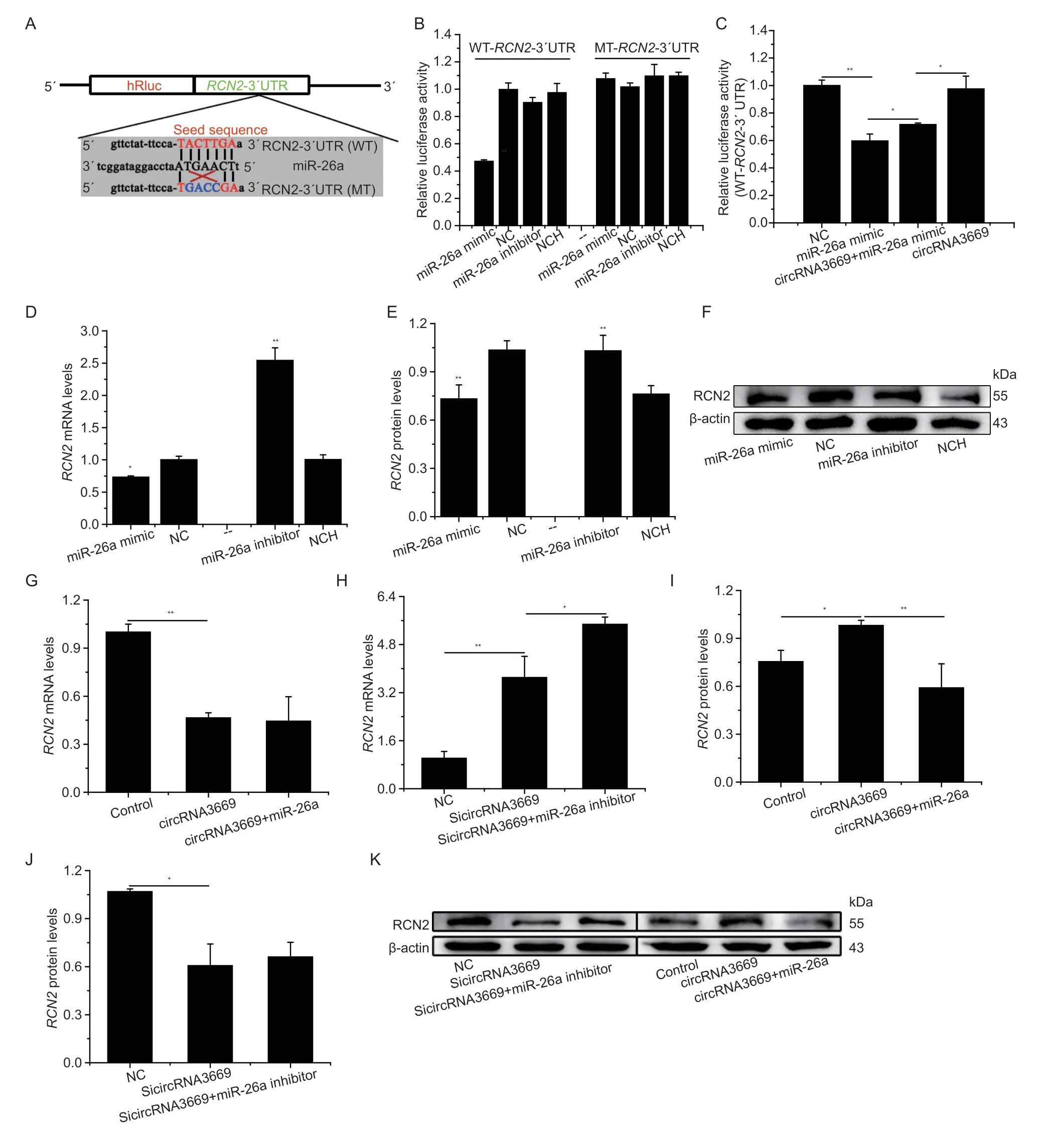
Fig. 5 circRNA3669 regulates RCN2 by sponging miR-26a in GEECs. A,schematic diagram illustrating the design of luciferase reporters with the WT-RCN2-3´UTR (WT-RCN2) and the site-specific mutant RCN2-3´UTR (MT-RCN2). The nucleotides in red represent the “seed sequence” of miR-26a,and the mutated nucleotides were in blue color. B,the RCN2-3´UTR or its mutation luciferase reporter vectors were co-transfected with miR-26a,NC (negative control),miR-26a inhibitor or NC inhibitor into GEECs.C,the RCN2-3´UTR luciferase reporter vectors were co-transfected with miR-26a and circRNA3669 into GEECs. Luciferase assay was performed 36 h after transfection. Results are represented as relative luciferase activity. D,the effect of miR-26a on the RCN2 mRNA levels in GEECs. E and F,miR-26a down-regulated RCN2 protein in GEECs. G and H,the RCN2 mRNA levels in GEECs transfected with overexpression and interference with circRNA3669. I–K,the RCN2 protein levels in GEECs transfected with overexpression and interference with circRNA3669. The mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR and normalized to β-actin;the protein levels were measured by Western blot and densitometry was normalized to the β-actin density from the same lane.The measurements are represented as mean±SEM for three individuals. *,P<0.05;**,P<0.01.

Fig. 6 RCN2 promotes GEECs proliferation in vitro. A,the RCN2 mRNA levels in receptive endometrium (RE) and pre-receptive endometrium (PE). B,the RCN2 protein levels were detected by immunohistochemical (IHC) staining in PE and RE. UC,uterine cavity;LE,luminal epithelium;GE,glandular epithelium;SC,stroma cell. Scale bar was 50 μm. C,the RCN2 levels in various reproduction tissues of goats. D,the effect of E2 and P4 on the RCN2 mRNA levels in GEECs. E and F,CCK-8 analysis after overexpression and interference with RCN2. G,I,H and J,EdU analysis after overexpression and interference with RCN2. H and J,scale bar=100 μm. The mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR and normalized to β-actin. The values are showed as mean±SEM for three individuals. *,P<0.05;**,P<0.01.
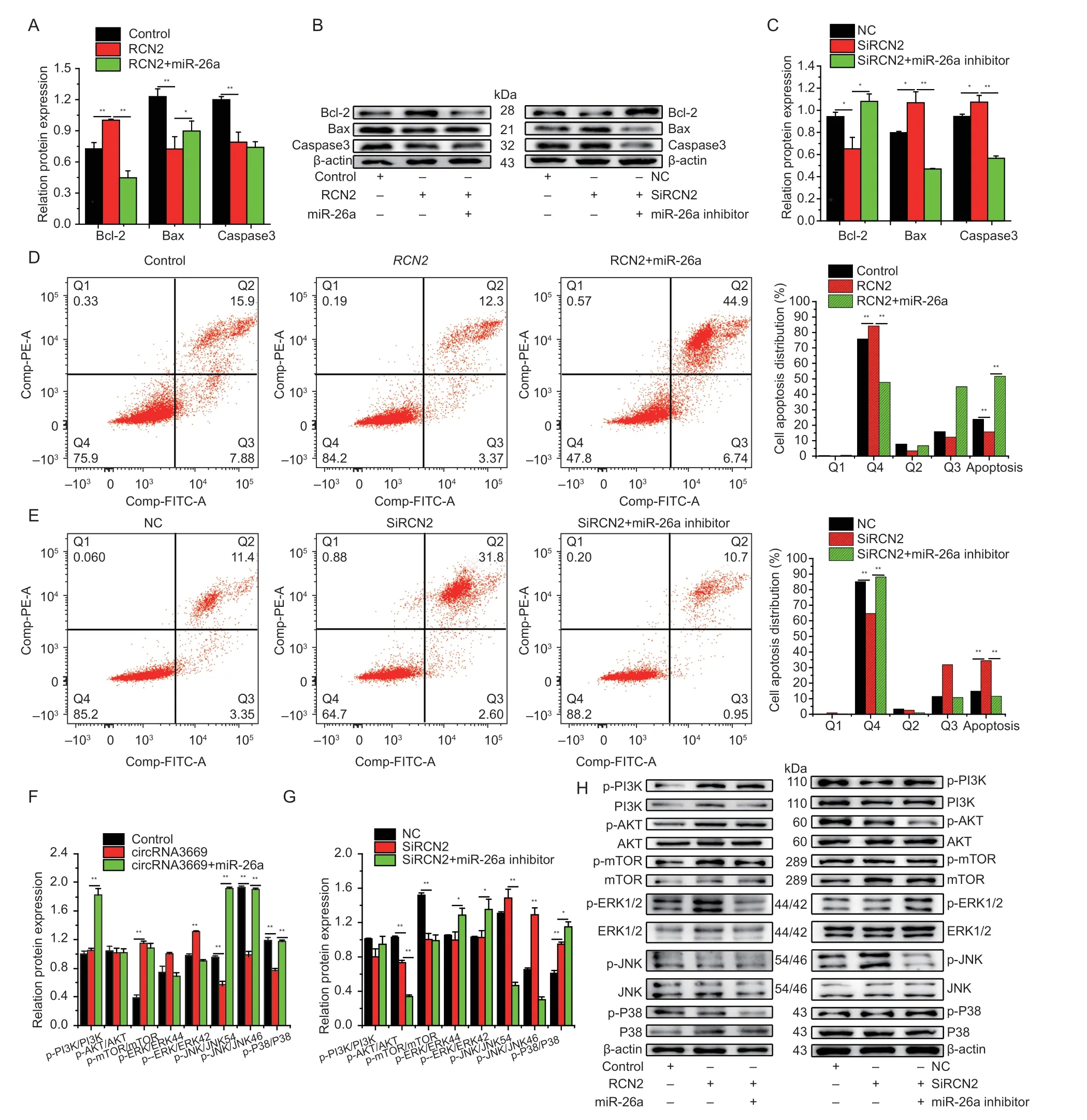
Fig. 7 RCN2 inhibites GEECs apoptosis by affecting the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and JNK/P38 MAPK signaling pathways. A–C,the protein levels of Bcl-2,Bax,and caspase3 were detected by Western blot. D and E,cell apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/PI dual staining followed by flow cytometry after the cells were transfected with overexpression and interference with RCN2.F–H,the expression levels of PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways-related genes were detected by Western blots after overexpression and interference with RCN2. The protein levels were measured by Western blot and densitometry was normalized to the β-actin density from the same lane. The results are represented as mean±SEM for three individuals. *,P<0.05,**,P<0.01.
A circRNA can act as a ceRNA to adsorb miRNA to largely eliminate its regulation of target genes,and plays an important role in gene regulation at post-transcriptional or transcriptional levels (Lin and Chen 2018;Xionget al.2018). It has been reported that circRNA8073 acts as a ceRNA to regulate miR-449a andCEP55and promotes GEECs proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in goats (Liuet al.2018). Additionally,testin (TES) is regulated by circRNA3175/miR182 and inhibits GEECs apoptosis in PE (Zhanget al.2018b). In this study,RNA-FISH localization analysis indicated that circRNA3669 was expressed in the cytoplasm and can act as a ceRNA to up-regulate the protein levels of RCN2 by interacting with miR-26a in GEECs.
Receptive endometrium development undergoes a complex process of fine regulation by multiple factors,which is manifested by morphological and functional changes and involves a delicate interplay between a variety of factors,including hormones (Vennerset al.2006;Yoshinaga 2008;Wilkinsonet al.2021),cytokines(Boomsmaet al.2009;Zhouet al.2021),and growth factors (Singhet al.2011;Tanet al.2020).RCN2is a novel cytokine regulatory factor that encodes a protein of type 4 Bardet-Biedl syndrome,a calcium-binding protein located in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum,also known as calcium-binding protein 2 or endoplasmic reticulum calcium-binding protein 2 (Dinget al.2017;Wang Get al.2017). In this study,RT-qPCR and IHC results revealed that the expression levels ofRCN2were significantly higher in PE than those in RE. This finding suggests thatRCN2may participate in the development of RE in goats.
Under the regulation of E2 and P4,EECs undergo structural and functional changes to establish endometrial receptivity,which is essential for embryo implantation(Zhanget al.2013;Cuiet al.2018). As E2 and P4 levels regularly fluctuate during normal physiological cycles (Renet al.2015),the effects of E2 and P4 on RCN2 expression levels in GEECs were assessed in this study.RCN2was regulated by E2 and P4 in GEECs,but there was no nnotable regularity.
Endometrial cell proliferation and apoptosis are critical for tissue remodeling during the physiological cycles and embryo implantation in numerous mammals (Tranguch and Dey 2014;Leiet al.2017;Zhanget al.2017a). It is an indispensable physiological event for the embryo to breach the epithelial barrier and implant in the uterine luminal epithelium owing to the proliferation and apoptosis of GEECs (Galánet al.2006;Wang Xet al.2017). The PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways are key regulators of cell proliferation,apoptosis,and survival(Dinget al.2021;Jinget al.2022). ERK,JNK,and P38 are three subclasses of the MAPK signaling pathway involved in various physiological processes,such as cell proliferation,development,differentiation,and apoptosis(Liuet al.2017;Zhanet al.2017). In addition,our previous studies discovered that miR-26a is involved in the formation of endometrial receptivity and regulates endometrial cell proliferation and apoptosisviathe PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in goats (Zhanget al.2018c). In this study,we observed that circRNA3669 andRCN2promoted GEECs proliferation by activating the expression of genes related to the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in goats.
In addition,BCL2,BAX,and caspase3 are markers of cell apoptosis (Venkatesan and Sadiq 2017;Wnęket al.2017). BCL2 inhibits apoptosis,and its expression can determine cell proliferation and apoptosis (Conconiet al.2017). BAX belongs to theBCL2gene family and forms a heterodimer with BCL2 to inhibit its function (Conconiet al.2017;Maeset al.2017),and caspase3 is a protease that promotes cell apoptosis (Jameelet al.2010). In this study,our results showed that circRNA3669 andRCN2increased BCL2/BAX levels,but down-regulated caspase3 protein levels in GEECs.
Given these findings,we conclude that circRNA3669 can act as a ceRNA to regulate theRCN2gene by binding to miR-26a and promoting GEECs proliferationviathe PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in goats(Fig.8).
5.Conclusion
In this study,a higher circRNA3669 level was observed in the PE than in the RE of goats. Further results showed that it acted as a ceRNA to regulateRCN2by binding to miR-26a and promoting GEECs proliferationviathe PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK pathwaysinvitro. We identified a new regulatory network of circRNA3669-miR-26a-RCN2in GEECs,thus further provides strong evidence that circRNAs could potentially play a crucial regulatory role in the development of RE in goats.
Acknowledgements
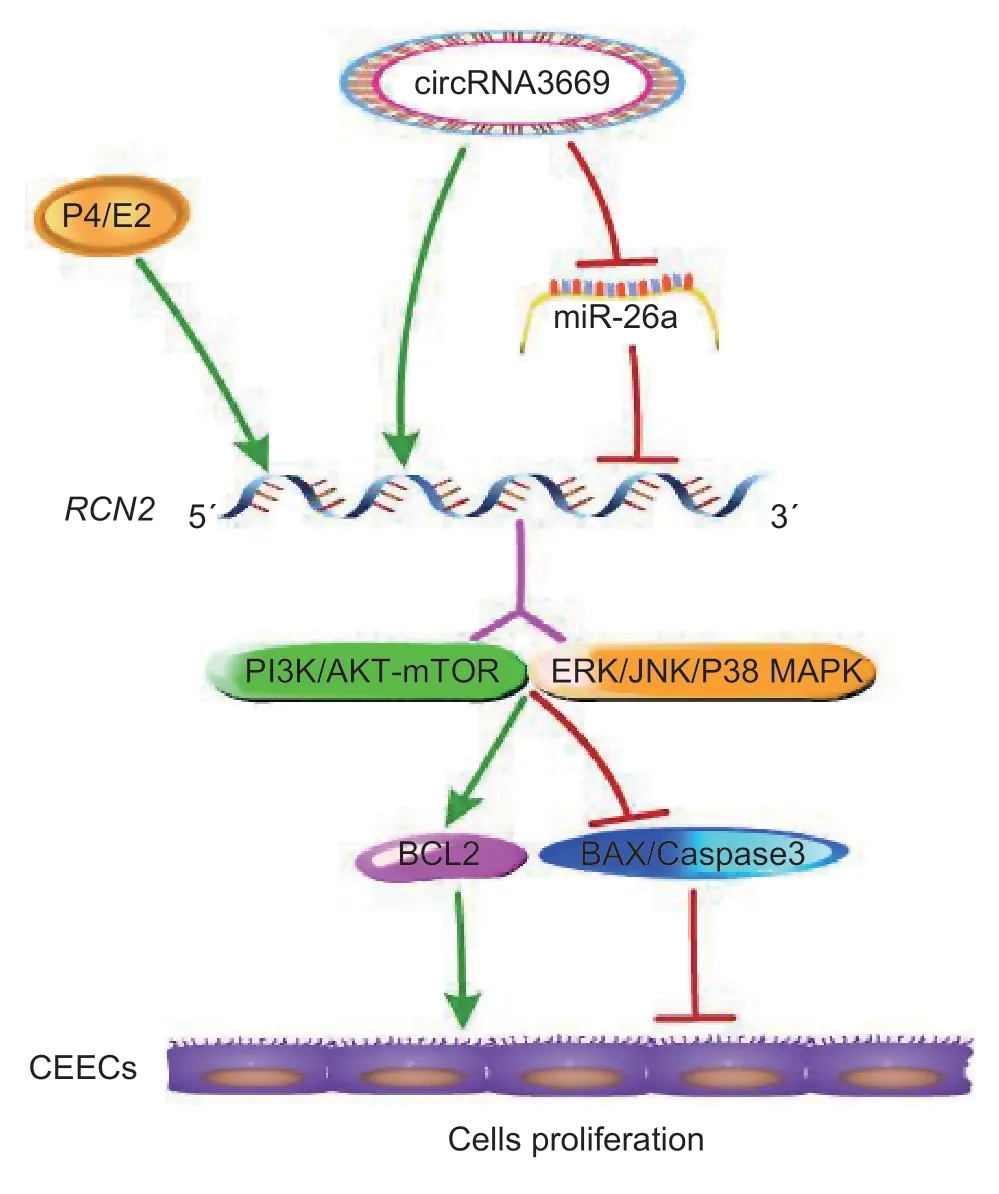
Fig. 8 The schematic cartoon of the molecular mechanism of circRNA3669-miR-26a-RCN2 in the goat endometrium.circRNA3669 acts as a ceRNA to regulate RCN2 gene by bonding to miR-26a and promotes GEECs proliferation via the PI3K/AKT-mTOR and MAPK signaling pathways in goats.
This study was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M653776 and 2020M673516),the Natural Science Basis Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (2023-JC-QN-0181),the Shaanxi Livestock and Poultry Breeding Double-chain Fusion Key Proiect,China (2022GD-TSLD-46-0202),and the Natural Science Fundation of Tibet Autonomous Region,China (XZ202101ZR0063G). The authors would like to acknowledge the Life Science Research Core Services of Northwest A&F University,China,for providing the confocal microscope,flow cytometry and fluorescence microscope.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Review Committee for the Use of Animal Subjects of Northwest A&F University,China approved the animal protocols in this study. All animal experimental procedures were maintained according to the Biosecurity Law of the People’s Republic of China.
Appendicesassociated with this paper are available on https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jia.2023.05.029
 Journal of Integrative Agriculture2024年3期
Journal of Integrative Agriculture2024年3期
- Journal of Integrative Agriculture的其它文章
- Temporal and spatial evolution of global major grain trade patterns
- Does Green Food Certification promote agri-food export quality?Evidence from China
- Lateral root elongation in maize is related to auxin synthesis and transportation mediated by N metabolism under a mixed NO3– and NH4+ supply
- Calcium carbonate promotes the formation and stability of soil macroaggregates in mining areas of China
- Irrigation and nitrogen fertiliser optimisation in protected vegetable fields of northern China: Achieving environmental and agronomic sustainability
- Combining field data and modeling to better understand maize growth response to phosphorus (P) fertilizer application and soil P dynamics in calcareous soils
