Determination of Ten Kinds of Alpha-2 Agonists Residues in Animal Derived Food by UHPLC-Triple Quadrupole/Composite Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry
Fang LI, Xuemei LI, Xiangang LI, Sining LIU, Sha LIU, Ying WANG
Integrated Technical Service Center of Donggang Customs, Donggang 118300, China
Abstract [Objectives] The paper was to establish an ultra high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/linear ion trap complex mass spectrometry for the determination of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists in animal derived food. [Methods] The samples were extracted with sodium carbonate buffer solution and ethyl acetate, and analyzed by mass spectrometry after solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography separation. [Results] Ten kinds of α2-receptor agonists showed a good linear relationship in the range of 1-100 μg/mL, with the average recovery of over 69% and the relative standard deviation less than 8.32%. The detection limit of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists was up to 1 μg/kg. [Conclusions] The method has good selectivity and strong anti-interference ability, and can meet the requirements of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists residues in animal derived food.
Key words Animal derived food; α2-receptor agonist; Solid-phase extraction; Ultra-high performance liquid phase-triple quadrupole/linear ion trap composite mass spectrometry
1 Introduction
Alpha-2 receptor agonists have many effects on humans, and some of these drugs have specific affinity for α2-receptors and can be used to treat human hypertension[1]; some α2-receptor agonists are specific to shock, analgesia, anti-anxiety, anti-sympathia and mild respiratory depression[2]; some are used to enhance animal growth and improve ketone body tissue[3]; some can be used to treat diseases such as increased skeletal muscle tone, myospasm and myotonia caused by brain and spinal cord injury, cerebral hemorrhage, encephalitis and multiple sclerosis[4]; others are neurostimulants, which can excite the feeding center and cause hunger, thus making the animal gain weight and promoting food intake[5]. α2-receptor agonists have been used as a new type of drugs that can promote growth and increase lean meat rate. The use of such drugs is also gradually attracting attention, and there is a trend of illegal use in the feed industry. The previous research on such drugs is more reflected in the field of medicine, and there are relatively few research reports in the field of animal food. The lack of detection standards for this type of drug in animal derived foods is likely to constitute a blind spot in food safety monitoring[6]. Hence, it is of great significance to study the detection methods of α2-receptor agonist drugs in the field of food.
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS)[7-8]and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)[9]are the major existing methods for the detection of α2-receptor agonists. LC/MS has been widely used in drug residue detection because of its better anti-interference ability and higher sensitivity than HPLC. In this test, ultra high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole/composite linear ion trap mass spectrometry was adopted. This method established a rapid quantitative method for the determination of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists residues in animal derived foods by combining the advantages of conventional tandem quadrupole and time-of-flight mass spectrometry, and presetting multiple reaction monitoring (MRM), information dependent acquisition (IDA) and enhanced product ion (EPI) advanced collection mode, which can more efficiently remove matrix interference and exclude false positives. The method has been gradually applied to various fields with good application effects, and can be applied to the detection of α2-receptor agonists residues in animal derived foods.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1Reagents. Sodium carbonate (analytically pure), Kermel; sodium bicarbonate (analytically pure), Kermel; formic acid (chromatographically pure), Merck (USA); acetonitrile (chromatographically pure), Merck (USA); methanol (analytically pure), Kermel; ammonia (analytically pure), Kermel; ethyl acetate (chromatographically pure), Merck (USA); MCX (mixed cation exchange column) solid phase extraction column, 60 mg/3 mL, Waters (USA).
2.1.2Instruments and equipments. 4500 Triple quadrupole/composite linear ion trap mass spectrometer, AB SCIEX (USA); LC-30AD high performance liquid chromatograph, Shimadzu (Japan); ultrapure water machine, Sartorius (Germany); E-916 parallel evaporator, Buchi (Switzerland); solid phase extraction device, Agilent (USA).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1Sample pretreatment. The samples were commercially available chicken and pork; 2 g samples were loaded into a centrifuge tube, then added with 5 mL of 1 mol/L sodium bicarbonate solution -1 mol/L sodium bicarbonate solution (9+1) by shaking, and added with 10 mL of ethyl acetate to fully shake and extract for 5 min. After centrifuged at 8 000 r/min for 5 min, the supernatant was transferred to a parallel evaporation bottle, and the lower solution was extracted again with 10 mL of ethyl acetate. Two extracts were merged and dried by parallel steaming at 55 ℃, and 4.0 mL of formic acid-acetonitrile was added to dissolve the residue for later purification.
2.2.2Sample purification. The MCX solid phase extraction column was successively activated with 3 mL of methanol and 3 mL of water. The extracting solution was passed through the activated solid phase extraction column and completely discarded, and the column was eluted with 3 mL of water and 3 mL of methanol. Afterwards, the solid phase extraction column was drained under air and eluted with 3 mL of 5% ammonia/methanol water. The eluent was collected in a glass test tube and blow-dried with nitrogen at 55 ℃. The residue was dissolved in 1 mL of 0.2% formic acid-acetonitrile solution (8+2), filtered, and tested.
2.2.3Chromatographic condition. Column: HILIC Plus, 2.1 mm×100 mm, 3.5 μm; mobile phase A: 0.1% formic acid water, mobile phase B: acetonitrile; flow rate: 0.4 mL/min; column temperature: 35 ℃; injection volume: 10 μL. The elution gradient is shown in Table 1.
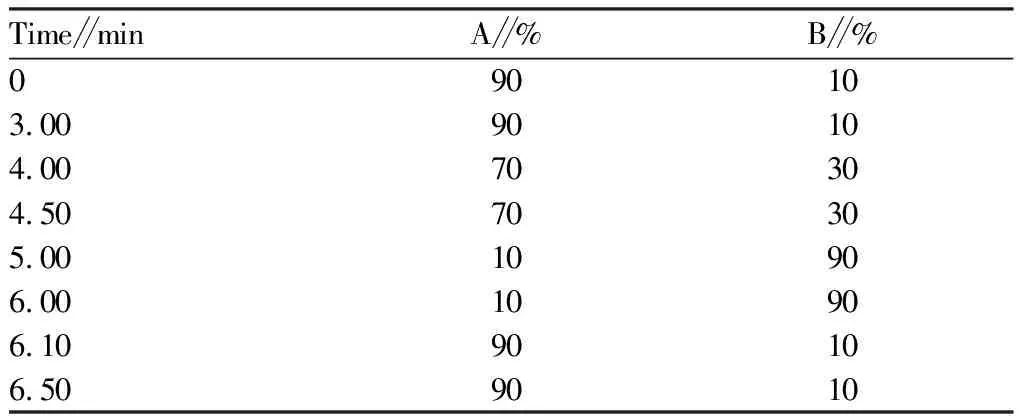
Table 1 Mobile phase gradient elution
2.2.4MS conditions. Electrospray ionization (ESI), positive ion scanning; scanning mode: multiple reaction monitoring-information-dependent acquisition-enhanced product ion (RM-IDA-EPI). The characteristic ions are shown in Table 2. Curtain gas (CUR), 25 psi; ion source gas 1 (GS1), 55 psi; ion source gas 2 (GS2), 55 psi; ion spray voltage (IS), 5 500 V; collision gas (CAD), high; temperature (TEM), 550 ℃; IDA conditional trigger threshold: 5 000 cps. The mass parameters of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists are shown in Table 2.
2.2.5Formulation of standard curve. The blank sample matrix was selected for simultaneous pre-treatment, and the blank sample extract was used as the solvent to prepare the standard working liquid with the concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0, 100.0 μg/L, respectively. The standard curve of the corresponding matrix was plotted.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Optimization of sample extractionSince ethyl acetate is used as the extraction solvent for most α2-receptor agonists, sodium carbonate buffer and ethyl acetate were selected for liquid-liquid stratification in this test, and α2-receptor agonists in samples were extracted by ethyl acetate. The experimental results showed that the method could effectively extract α2-receptor agonists from animal derived food, with a recovery rate of over 69%.

Table 2 Mass parameters of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists
3.2 Optimization of chromatographic conditionsIn this test, Agilent SB-Aq (100 mm×2.1 mm, 2.1 μm) column, HILIC Plus (2.1 mm×100 mm, 3.5 μm) column, SB-Aq (2.1 mm×50 mm, 2.7 μm) column were attempted. By comparing the mass spectra, it was found that most compounds from SB-Aq (100 mm×2.1 mm, 2.1 μm) and SB-Aq (2.1 mm×50 mm, 2.7 μm) columns had double peaks or double peak tips, with high baseline noise, which reduced the sensitivity. The mass spectrum obtained from HILIC Plus (2.1 mm×100 mm, 3.5 μm) chromatographic column had sharper peak, with lower baseline noise, which improved the sensitivity. Therefore, HILIC Plus (2.1 mm×100 mm, 3.5 μm) chromatographic column was selected in this test. The chromatographic diagram of each target object is shown in Fig.1.
3.3 Choice of internal standard method and external standard methodIn this test, we compared internal standard method and external standard method. D4-clonidine,2H3-medetomidine and D6-xylazine were selected in internal standard method. Considering the quantitative results, the recoveries obtained by internal standard method and external standard method were basically the same. Taking chicken as an example, the recoveries obtained by internal standard method and external standard method are shown in Table 3. Considering the qualitative results, the MRM-IDA-EPI collection mode was selected in this test, which could collect all secondary fragment information of the target compound and establish the information spectrum database of the target compound. This technology further compared all the daughter ion information, conducted qualitative analysis through IDA collection mode, and performed quantitative analysis through MRM collection mode. On the basis of MRM, the secondary daughter ions of positive samples were analyzed and confirmed, and the quantitative and qualitative data were obtained simultaneously after one sample injection, to search and confirm the spectral database and rule out false positive results. Compared with MRM mode, it had stronger selectivity and improved qualitative ability. Compared to the internal standard method, the external standard method is more economical and practical, and ensures the qualitative accuracy as well as the quantitative accuracy.
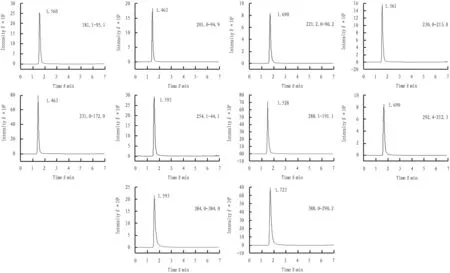
Note: a. Rilmenidine; b. Medetomidine; c. Xylazine; d. Clonidine; e. Guanabenz; f. Tizanidine; g. Cyproheptadine; h. Brimonidine; i. Prazosin; j. Terazosin.
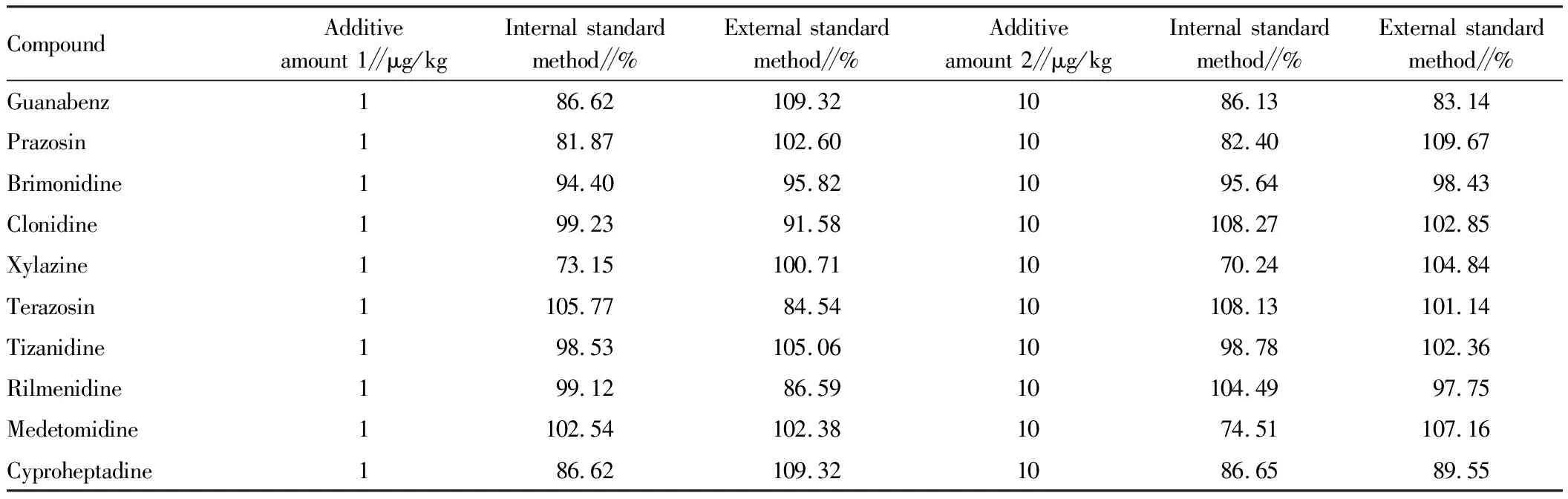
Table 3 Comparison of recoveries of ten kinds of α2-receptor agonists in chicken by internal standard method and external standard method
3.4 Selection of solid phase extraction columnIn this test, three kinds of solid phase extraction columns (Waters MCX solid phase extraction column 60 mg/3 mL, Waters MCX solid phase extraction column 200 mg/6 mL and Agilent PCX solid phase extraction column 60 mg/3 mL) were selected to compare the recoveries of chicken and pork with additive amounts of 1 and 10 μg/kg. The recovery rate of PCX solid phase extraction column was relatively low, while that of two MCX specifications was basically the same. Considering the economic property, the Waters MCX solid phase extraction column 60 mg/3 mL was selected in this test. The recoveries of three solid phase extraction columns are shown in Table 4.
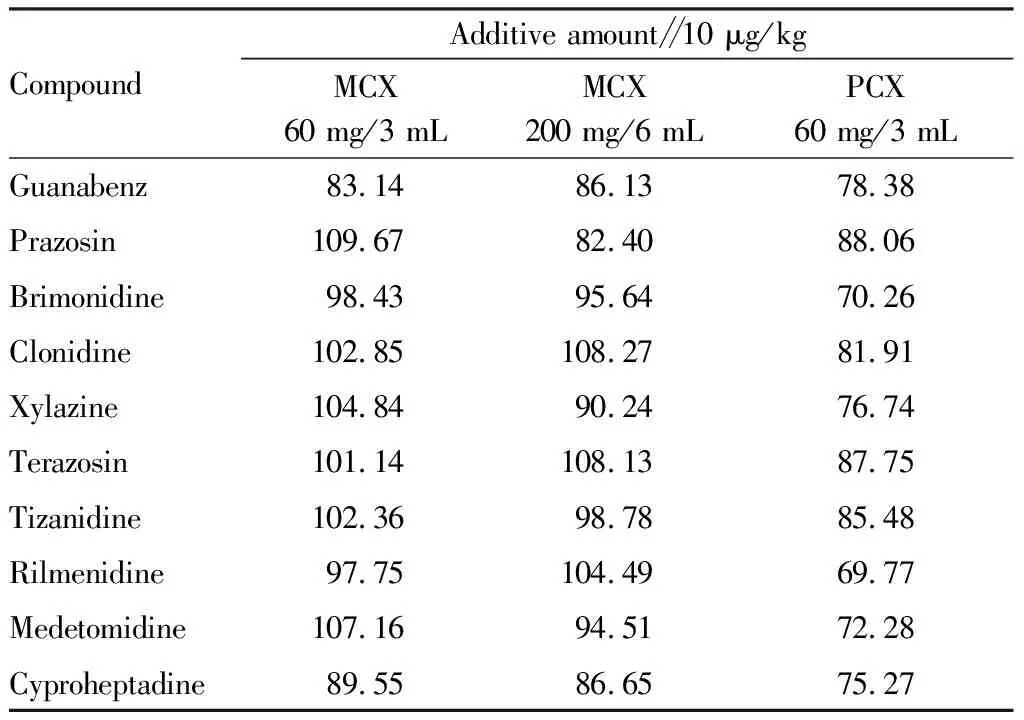
Table 4 Comparison of recoveries of three solid phase extraction columns %
3.5 Standard curveThe mixed standard working liquid was determined by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/linear ion trap complex mass spectrometry. Ten kinds of α2-receptor agonists showed good linear relationship in the range of 0.5-100 μg/L. The linear equations and correlation coefficients are shown in Table 5. As shown in Table 5, the correlation coefficients of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists were all greater than 0.992 in the range of 0.5-100 μg/L.
3.6 Precision and recoveryIn this test, chicken and pork were selected as test objects, and the standard test was carried out according to the conditions determined by the experimental method. When the additive amount was 0.5 μg/kg, although the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists was greater than 3, it was difficult to make qualitative judgment due to large noise. When the additive amount was 1 μg/kg, the method could better qualitatively analyze the samples, with good recovery and stability. The experimental results showed that the recovery of the method was greater than 69%. Repeatability tests were performed 6 times for each concentration. The results showed that the relative standard deviation of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists in animal derived foods determined by this method was less than 8.32%, and the test had good accuracy and precision. The recoveries and precision of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists are displayed in Table 6.
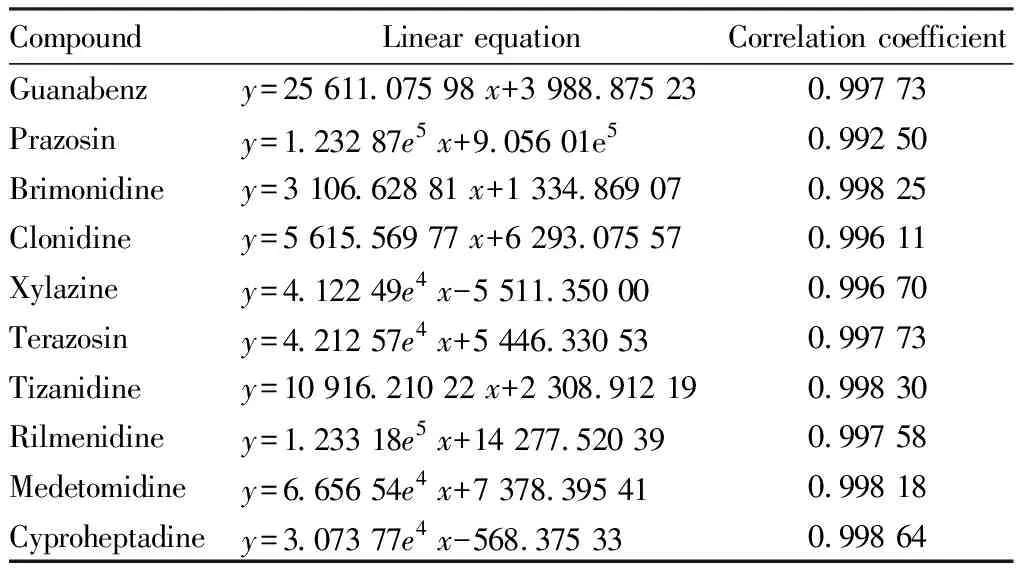
Table 5 Regressions and correlation coefficients of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists
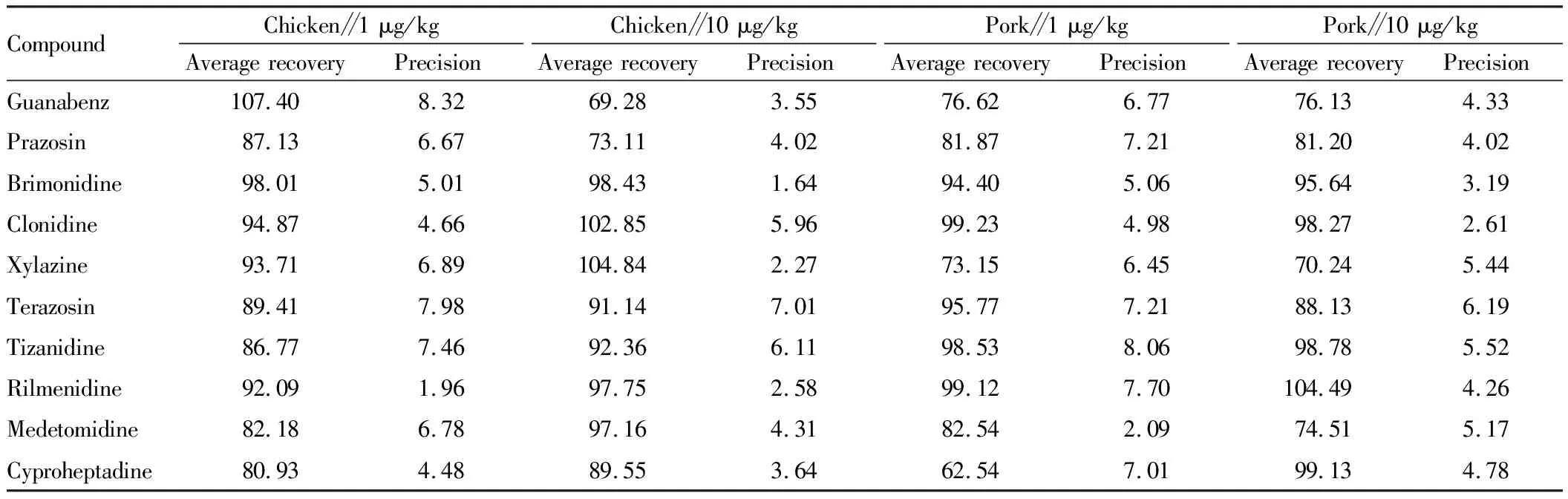
Table 6 Recoveries and precision of 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists (n=6, %)
4 Conclusions
In this test, an ultra high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/linear ion trap complex mass spectrometry was established to determine 10 kinds of α2-receptor agonists in animal derived food. This method has the advantages of high sensitivity of conventional tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry and full scanning accuracy and qualitativeness of time-of-flight mass spectrometry. By conducting standard test on chicken and pork samples, it is found that the method has good accuracy, high precision and more accurate qualitative ability, with the detection limit up to 1 μg/kg, and has certain practical application.
- 植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Comprehensive Prevention and Control Technology of Vegetable Diseases and Pests in Shandong Province
- Technical Points of Green Prevention and Control Technology of Major Diseases and Pests in Lixian Rhubarb (Rheum palmatum L.)
- Risk Analysis of Passalora sequoiae Invasion to China with Imported Coniferous Wood
- Investigation and Analysis of Main Diseases of Landscape Plants in the Main Urban Area of Lu’an City
- Effects of Low Temperature Stress on Germination and Physiological Characteristics of Different Sweet Maize Varieties
- Research on Blended Teaching Mode: A Case Study of Floristry

