Study on regulating mechanisms of oxocrebanine obtained from Stephania hainanensis H.S.Lo et Y.Tsoong on microtubule sites and tubulin in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
XIAO Di, YAN Cai-feng, YU Jing-han, XU Sheng-jiang, WANG Xian-zheng, WANG Zheng-wen✉
1.College of Pharmacy, Harbin University of Commerce, Harbin 150076, China
2.Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Hainan Cancer Hospital, Haikou 570000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To determine the destructive ability of oxocrebanine, an anti-breast cancer active compound obtained from Stephania hainanensis H.S.Lo et Y.Tsoong, on microtubule network, and investigate the effect of oxocrebanine on microtubule network homeostasis at both molecular and cellular levels.Methods: the EBI site competition method and molecular docking method were used to determine the occupation of the microtubule site of oxocrebanine.Western Blot was used to detect the effect of oxocrebanine on microtubuleassociated proteins including STAT3, PAK1, CAMK4, and PKA.Results: The results of EBI site competition assay showed that the binding of EBI to β-Tubulin covalent fusions produced adducts that appeared in regions of lower molecular weight than β-tubulin (ctrl 2).Molecular docking results showed that oxocrebanine could occupy the colchicine site of microtubule proteins.As revealed by Western Blot, the expression of STAT3 protein was decreased after MCF-7 cells have been treated with low, medium, and high concentration of oxocrebanine or the positive drug taxol for 48 h (P<0.01).The expression levels of PAK1 and Camk4 proteins aslo showed significant reductions (P<0.05, or P<0.01).Oxocrebanine also decreased the PKA protein in MCF-7 cells compared to the control group (P<0.01).Conclusions: Oxocrebanine,a ligand that binds at the colchicine site of tubulin, perturbs tubulin polymerization and causes mitosis in MCF-7 cells, thus leading to MCF-7 cell death.Oxocrebanine may promote microtubule dynamics through stathmin by inhibiting the expression levels of STAT3, PAK1,Camk4, and PKA proteins in MCF-7 cells.Oxocrebanine interfers with spindle formation, and ultimately causes mitotic catastrophe in MCF-7 cells.
1.Introduction
Stephania hainanensisH.S.Lo et Y.Tsoong is a genus of Stephania, also known as Jinbuchangensis and mountain turtle.It is a kind of overgrown lianas, which is unique to Hainan.It was found in crevices, cliffs, semi-shady piles of rubble or in the bush by a stream on Hainan Island[1].Stephania hainanensisbe used as traditional medicine, tuber medicine of Hainan Li nationality.Bitter taste, cold, small poison.It has the functions of clearing heat and detoxifying, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory,blocking malaria and relieving pain.Mainly contains isoquinoline alkaloids, aporphine alkaloids, protoberberine alkaloids, morphine alkaloids, etc.These alkaloids have anti-tumor, anti-oxidation, anticonvulsant and anti-platelet agglutination, and are used to treat cancer, injury, and inflammation[2,3].The apophenoid alkaloids ofStephania hainanensiswere determined in the previous stage--monomer compound oxocrebanine(The structural formula is shown in Figure 1).It has anti-breast cancer activity and its sensitive cell line is MCF-7 cell with IC50 of 16.66 µmol/L[4].Microtubules are cylindrical structures composed of α and β-tubulin heterodimers.By inhibiting the polymerization of tubulin or blocking the depolymerization of microtubules, the microtubule dynamic balance is interfered, and the normal function of microtubules is hindered, resulting in cell death.Colchicine was the first identified tubulin disrupting agent[5].At present, most tumor blood vessel blocking agents that have entered clinical trials are microtubule inhibitors, and most of them are compounds that act on colchicine sites[6].Stathmin is a microtubule unstable protein that binds to α, β-tubulin heterodimers and regulates microtubule motility.STAT3 binds to Stathmin in the carboxyl terminal region, and Stathmin is the direct target for STAT3 to maintain microtubule morphology.Overexpression of STAT3 antagonizes the microtubule depolymerization activity of Sathmin[7].
Previous studies have found that as a dual inhibitor of topoisomerase and tubulin, Stephania hainanensis oxocrebanine can interfere with the microtubule structure and homeostasis of MCF-7 cells at the same time[8].In this paper, the effect of oxocrebanine on microtubule network of MCF-7 cells was further observed, and the mechanism of action of oxocrebanine on microtubule network was discussed through the action sites and signaling pathways.At the microscopic level, the mechanism of promoting microtubule depolymerization was further determined by detecting the effect of oxocrebanine on microtubule regulatory proteins.
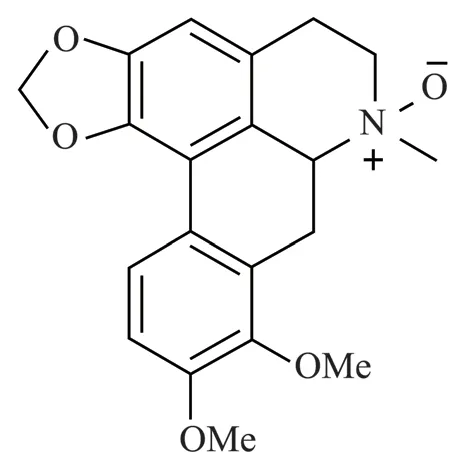
Fig 1 The structural formula of oxocrebanine in Stephania hainanensis H.S.Lo et Y.Tsoong
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Human breast cancer MCF-7 cells were provided by the Drug Engineering Technology Research Center of Harbin University of Commerce; Oxocrebanine(98%).Provided by Hainan Medical College, paclitaxel was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co., LTD(Article No.B21695),Colchicine was purchased from Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.,LTD(Article No.ST1173), EBI (2-iodo-iV-[2-[2-[2-[2- iodoacetyl]ethyl] acetamide)purchased from Boorson Biological Group Limited(BA09167173),DMSO was purchased from Tianjin Fuyu Fine Chemical Co., LTD (Article No.20200605),RPMI-1640 medium was purchased from Dalian Meilun Biotechnology Co.,LTD(Article No.MA0215-Nov-17H),Trypsin was purchased from Sigma Pharmaceuticals(Article No.20200603),Fetal bovine serum was purchased from Guangzhou Xiangbo Biotechnology Co.,LTD(Article No.20201013);Electrophoresis apparatus (Model:DYY-7C),Vertical electrophoretic transfer slot (Model: DYCZ-40D)Purchased from Beijing 61 Biotechnology Co., LTD,The gel imaging system was purchased from GE (Article No.ImageQuant LAS500).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 The competitive microtubule sites of oxocrebanine were determined by EBI competition method
Oxocrebanine was administered at 8.33 µmol/L, 16.66 µmol/L,33.32 µmol/L, and the final concentration of colchicine was 6.8µmol/L.After treating MCF-7 cells for 48 h, the cells were incubated with EBI (100 µmol/L) for 2 h.In the blank control group, the same volume of RPMI 1640 medium was added to each well, cells were collected, RIPA lysate was added for 30 min and centrifuged at 4℃ at 12 000 r/min for 15 min to extract proteins.Protein samples were added to the low, middle and high dose groups with EBI, then transferred to PVDF membrane by 10% sodium dodecyl sulphatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, closed in 5% skim milk for 60 min, and incubated with antibody.
2.2.2 Molecular docking
Molecular docking was studied by using molecular simulation software AutoDock.The tubulin crystal structure was downloaded from the PDB database (PDB: 1SA0).AutoDock is used to process the crystal structure, including extraction of ligands, removal of water molecules, hydrogenation, addition of partial charge and minimization of energy.At the same time, the structure diagram of oxocrebanine was drawn by ChemDraw software, and the threedimensional structure of the compound to be tested was constructed by PyMOL software, and the conformation library was generated after minimizing energy.Select the default docking parameters to pair the compound to the defined docking point.
2.2.3 The expression of STAT3, PAK1, CAMK4 and PKA were determined by Western Blot
Oxocrebanine was administered at 8.33 µmol/L, 16.66 µmol/L,33.32 µmol/L, and colchicine at 6.8 µmol/L.Protein was extracted from MCF-7 cells after 48 h treatment.The protein samples were transferred to PVDF membrane by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and closed in 5% skim milk for 60 min.Rabbit anti-human STAT3, PAK1, CAMK4 and PKA antibodies were added, respectively, and incubated at 4 ℃ overnight.TBST was washed 3 times, secondary antibody was added and incubated at room temperature for 60 min.TBST was washed 3 times and ECL luminescent reagent was added for development.
2.2.4 Statistical analysis
SPSS for Windows 21.0 software was used to analyze the data.Multivariate mean comparisons between groups were performed using One-Way ANOVA and LSD multiple comparison analysis.P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.Result
3.1 Effects of oxocrebanine on microtubule sites
The EBI competition test was used to determine whether oxocrebanine acts on the colchicine site of tubulin.As shown in Figure 2, the adduct produced by covalent fusion of EBI and β-tubulin appears in the region with smaller molecular weight(ctrl2), and the adduct bands disappear with the increasing concentration of oxocrebanine.The situation of high concentration group was the same as that of colchicine control group.
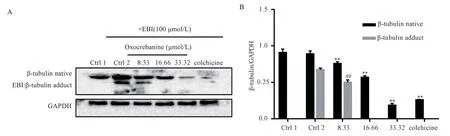
Fig 2 EBI assay verified that oxocrebanine targeted colchicine sites
Tab 1 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of β-tubulin in MCF-7 cells(n=3, ±s)
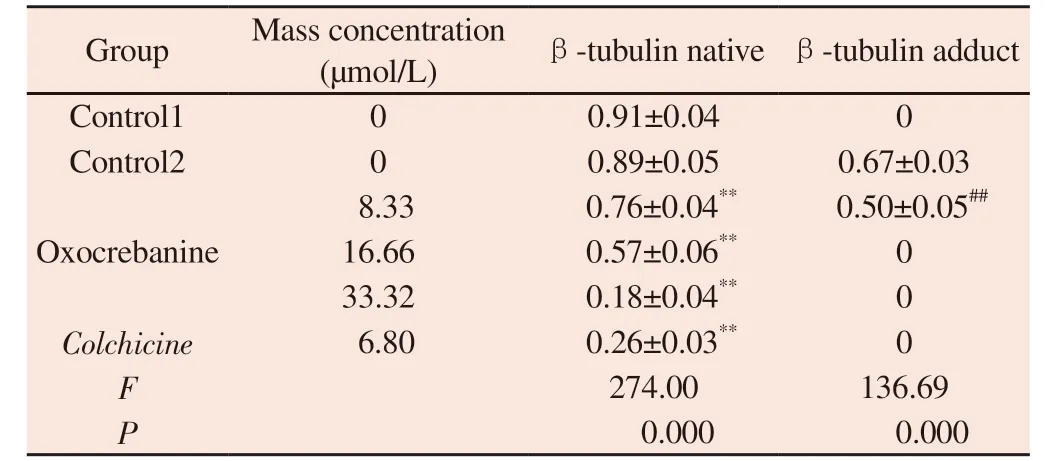
Tab 1 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of β-tubulin in MCF-7 cells(n=3, ±s)
Note: Compared with blank control group 1,**P<0.01 Compared with blank control group 2,##P<0.01
Group Mass concentration(µmol/L) β-tubulin native β-tubulin adduct Control1 0 0.91±0.04 0 Control2 0 0.89±0.05 0.67±0.03 8.33 0.76±0.04** 0.50±0.05##16.66 0.57±0.06** 0 33.32 0.18±0.04** 0 Colchicine 6.80 0.26±0.03** 0 F 274.00 136.69 P 0.000 0.000 Oxocrebanine
3.2 Molecular docking experiment results
It is speculated that oxocrebanine targets microtubules by binding to tubulin.Therefore, AutoDock software was used to study the fusion and connection of oxocrebanine and tubulin (PDB: 1SA0), so as to better evaluate the fusion mode of oxocrebanine and tubulin.The results showed that oxocrebanine could occupy the colchicine site of tubulins.As shown in Figure 3, oxocrebanine could form hydrophobic effects with Lys-254, Leu-255, Cys-241 and Leu-248 residues.The methylene dioxy group in oxocrebanine forms a hydrogen bond with Asn-258.This also suggests that oxocrebanine may be an inhibitor of tubulin binding.
3.3 Effects of oxocrebanine on microtubule key proteins in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
3.3.1 Effects of oxocrebanine on microtubule regulatory protein STAT3 in MCF-7 cells
The experimental results are shown in Figure 4 and Table 2.The protein gray value of STAT3 showed a dose-dependent decreasing trend (P< 0.01), indicating that the expression of STAT3 protein in MCF-7 cells decreased after 48 h of oxocrebanine administration.After 6.80 µmol/L Taxol treatment, STAT3 expression in MCF-7 cells was also significantly decreased (P< 0.01).
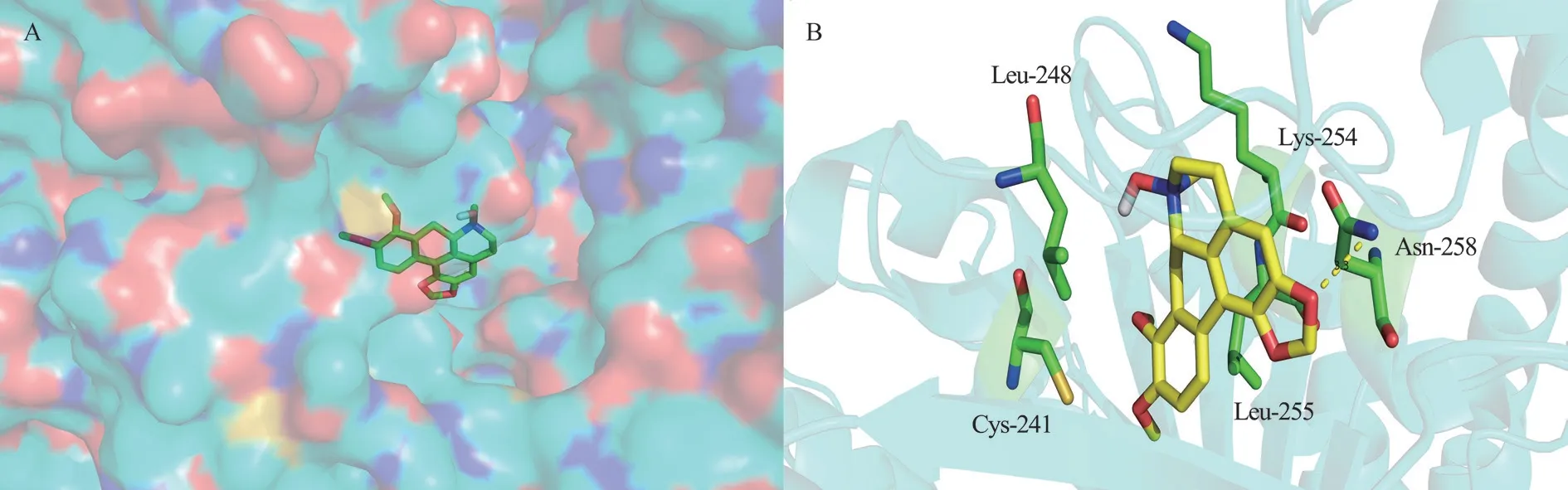
Fig 3 Structure diagram of oxocrebanine ; the binding sites of oxocrebanine and β-tubulin
Tab 2 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of STAT3 in MCF-7 cells(n=3,±s)

Tab 2 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of STAT3 in MCF-7 cells(n=3,±s)
Note: Compared with blank control group ,**P<0.01
Group Mass concentration(µmol/L) STAT3 Control 0 1.13±0.04 Taxol 6.80 0.69±0.02**8.33 0.93±0.03**16.66 0.71±0.04**33.32 0.56±0.05**F 102.84 P 0.000 Oxocrebanine
Tab 3 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of PAK1and CAMK4 in MCF-7 cells (n=3, ±s)
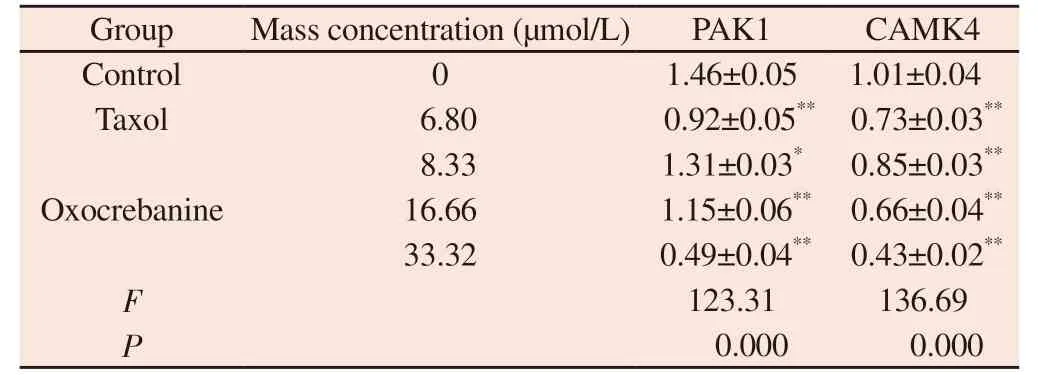
Tab 3 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of PAK1and CAMK4 in MCF-7 cells (n=3, ±s)
Note: Compared with blank control group ,**P<0.01
Group Mass concentration (µmol/L) PAK1 CAMK4 Control 0 1.46±0.05 1.01±0.04 Taxol 6.80 0.92±0.05** 0.73±0.03**8.33 1.31±0.03* 0.85±0.03**16.66 1.15±0.06** 0.66±0.04**33.32 0.49±0.04** 0.43±0.02**F 123.31 136.69 P 0.000 0.000 Oxocrebanine
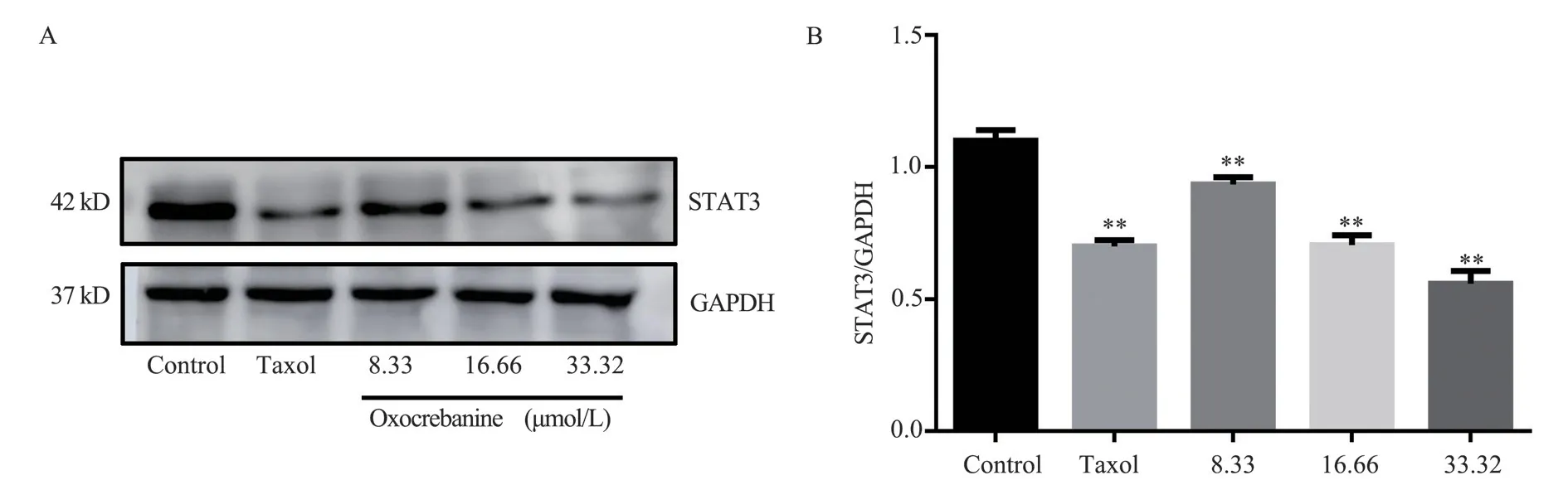
Fig 4 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of STAT3 in MCF-7 cells
3.3.2 Effects of oxocrebanine on Stathmin-regulated proteins PAK1 and CAMK4 in MCF-7 cells
The experimental results are shown in FIG.5, FIG.6 and Table 3.Oxocrebanine treated cells with 16.66 µmol/L and 33.32 µmol/L for 48 h, the expression level of PAK1 protein in the cells decreased significantly (P< The expression level of PAK1 protein also decreased in 8.33 µmol/L dose group (P< 0.05).The expression level of CAMK4 protein decreased significantly in all dose groups(P< 0.01).After 6.80 µmol/L Taxol treatment, PAK1 and CAMK4 protein expressions in MCF-7 cells were also significantly decreased(P< 0.01).
3.3.3 Effect of oxocrebanine on Stathmin-regulated protein PKA in MCF-7 cells
The experimental results, as shown in Figure 7 and Table 4, showed that different doses of oxocrebanine (8.33 µmol/L, 16.66 µmol/L,33.32 µmol/L) could reduce the expression level of PKA protein in MCF-7 cells for 48 h (P< 0.01).PKA protein expression in Taxol group also showed the same decreasing trend (P< 0.01).
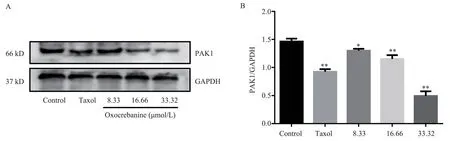
Fig 5 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of PAK1 in MCF-7 cells
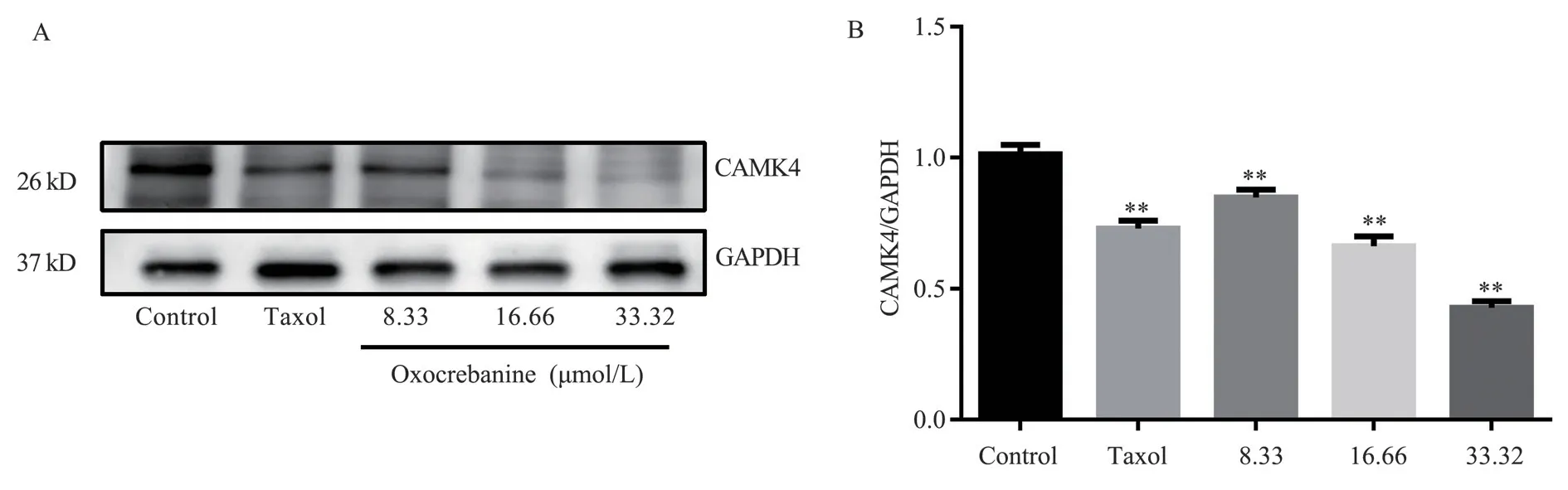
Fig 6 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of CAMK4 in MCF-7 cells
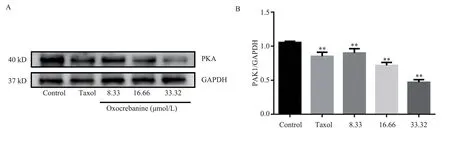
Fig 7 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of PKA in MCF-7 cells
Tab 4 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of PKA in MCF-7 cells (n=3,±s)
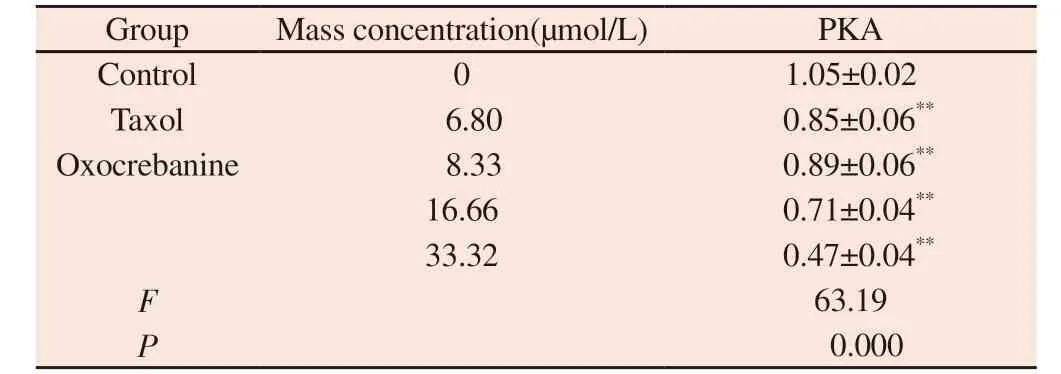
Tab 4 Effect of oxocrebanine on the expression level of PKA in MCF-7 cells (n=3,±s)
Note: Compared with blank control group ,**P<0.01
Group Mass concentration(µmol/L) PKA Control 0 1.05±0.02 Taxol 6.80 0.85±0.06**Oxocrebanine 8.33 0.89±0.06**16.66 0.71±0.04**33.32 0.47±0.04**F 63.19 P 0.000
4.Discussion
Stephania hainanensisis a commonly used drug in the clinic for the treatment of breast cancer (mammary carbuncle) in local hospitals[1].In our previous experiments, oxocrebanine, an active monomer compound against breast cancer, was discovered, which has a dual inhibitory effect on tubulin and topoisomerase.In this paper, the microtubule regulatory mechanism of the mitotic disaster of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells caused by oxocrebanine oxide was deeply studied.
Microtubules have important biological functions, such as involvement in chromosome separation, intracellular transport and maintenance of cell morphology[9].Microtubules are composed of non-covalent tubulin heterodimers (α-tubulin and β-tubulin), which play an important role in key cellular events, especially in mitosis,so microtubules become an important target for anticancer drug design[10].Microtubule targeting drugs are essential chemotherapy drugs for various types of cancer, and microtubule disrupting drugs such as paclitaxel, vincristine and vincristine can treat a variety of cancers clinically.Microtubule destructors (such as vinblasine)usually bind to tubulin at the vinca alkaloid site, while colchicine exerts its biological effects at the intersubunit interface of tubulin dimers[11].The colchicine binding site is located at the junction of the α and β subunits of the microtubule, adjacent to the GTP binding site on the α subunit.Some scholars believe that colchicine binds to β microtubulin, causing the original straight conformation bending,and forming steric hindration between colchicine and α microtubulin,thus affecting microtubule polymerization[12,13].oxocrebanine, as a novel microtubule inhibitor, can selectively regulate the activity of tubulin, resulting in significant cytotoxicity to MCF-7 cells, while less cytotoxicity to normal cells[14-17].Molecular docking results further demonstrated that oxykerbanx binds to tubulin.As a result,oxykerbanine binds to the tubulin colchicine site and disrupts tubulin polymerization, leading to mitosis of MCF-7 cells, resulting in MCF-7 cell death.
EBI reagent is a special structuring agent, which is crosslinked with residues of Cys239 and Cys354 of β-tubulin.On this basis,the transfer rate of β-tubulin adducts is significantly higher than that of β-tubulin itself, and bands of β-Tubulin-ebi adducts are formed in the parts of which the relative molecular weight is small.When tubulin inhibitors occupy the colchicine site, the production of β-tubulin adducts is inhibited[18].However, MCF-7 cells were treated with oxocrebanine or colchicine, and then added with EBI reagent, the formation of β-tubulin-EBI adducts was inhibited,indicating that oxocrebanine interacts with colchicine sites of tubulin.As the concentration of oxocrebanine increased, the adduct bands no longer appeared, indicating that the higher the concentration of oxocrebanine, the closer the binding to the colchicine site of tubulin,the easier it was to strengthen the microtubule motility.
Stathmin inhibits tubulin by binding to tubulin dimers, and the microtubule instability of Stathmin can be turned off by cell surface receptor kinase cascade and cyclin-dependent kinase.Cell stimulation can activate STAT family members through tyrosine phosphorylation, inducing dimerization, and translocation of activated STAT3 from cytoplasm to nucleus, mediating transcription of many STAT3 response genes.STAT3 is frequently overexpressed in cancer and is considered to be a key factor in cancer progression as a transcription factor for growth promoting and anti-apoptotic genes[19].Since oxocrebanine can act on the colchicine site of tubulin and enhance microtubule motility, it is speculated that oxocrebanine may exert its tubule inhibition through promoting microtubule depolymerization factor.
It has been reported that STAT3 can regulate microtubule function by binding to the end of Stathmin, and overexpression of Stathmin has no significant effect on the activity of STAT3, but increased expression of STAT3 can antagonize the depolymerization activity of microtubules induced by non-phosphorylated Stathmin[20].oxocrebanine can increase the activity of Stathmin and accelerate the process of microtubule depolymerization by blocking the accumulation of STAT3 and inhibiting its activity.By regulating the levels of PAK1, PKA and CAMK4 proteins, Stathmin activation pathway is promoted to disrupt the microtubule network, resulting in mitotic arrest.STMN1 serine sites can be phosphorylated by PAK1,CAMK4 and PKA proteins.Among them, the change of Stathmin expression level affects the activation of RhoA/ROCK pathway,and then regulates the change of microtubule.oxocrebanine can promote Stathmin, a key factor of microtubule motility, by inhibiting the expression levels of STAT3, PAK1, CAMK4 and PKA proteins in MCF-7 cells, and promote microtubule depolymerization by regulating microtubule-related proteins, thus preventing spindle formation and ultimately causing mitotic disaster in MCF-7 cells.
Authors’ contribution
The experiment was completed by Xiao Di, the article was written by Yan Caifeng, and the data were statistically analyzed by Yu Jinghan.Xu Shengjiang, Wang Xianzheng and Wang Zhengwen conducted the final review of the manuscript.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年15期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年15期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Progress in diagnosis and treatment of invasive aspergillosis after liver transplantation
- An overview of the mechanism of acupuncture and moxibustion in treating depression comorbidities insomnia
- The significance of SREBP1 expression in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Efficacy and safety of Revlimid combined with Rituximab in the treatment of follicular lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- Study on the mechanism of Fuzi in the treatment of allergic rhinitis based on network pharmacology and experimental validation
- Effect of acupuncture on acupoint "Yingxiang-Hegu" on Th1, Th2 cytokines and T-bet/GATA-3 of allergic rhinitis rats
