SM4抗差分功耗分析轻量级门限实现
蒲金伟,高倾健,郑欣,徐迎晖
SM4抗差分功耗分析轻量级门限实现
蒲金伟,高倾健,郑欣*,徐迎晖
(广东工业大学 自动化学院,广州 510006)( ∗ 通信作者电子邮箱xinzheng9209@gmail.com)
针对SM4门限实现(TI)面积大、随机数消耗多的问题,提出一种SM4门限实现的改进方案。在满足门限实现理论的情况下,对S盒非线性求逆进行了无随机共享,并引入面向域的乘法掩码方案,将S盒随机数消耗减少至12 bit;基于流水线思想,设计了新的8 bit数据位宽的SM4串行体系结构,复用门限S盒,并优化SM4线性函数,使SM4门限实现面积更加紧凑,仅6 513 GE,相较于128 bit数据位宽的SM4门限实现方案,所提方案的面积减小了63.7%以上,并且更好地权衡了速度和面积。经侧信道检验,所提出的改进方案具备抗一阶差分功耗分析(DPA)能力。
SM4;差分功耗分析;门限实现;S盒;非线性求逆;无随机共享;面向域的乘法掩码方案
0 引言
SM4算法[1]是我国国家密码管理局于2012年3月公布的第一个完全自主设计的商用对称加密算法,是主要用于无线局域网和可信计算系统的专用分组密码算法,在不同场景下对数据加密保护,目前在金融交易、物联网、通信等领域被广泛应用。因此SM4安全性的研究对我国密码学发展、社会经济发展、信息安全等具有重要意义。
美国密码学家Kocher[2]在20世纪90年代末首次提出了侧信道分析(Side Channel Analysis, SCA),并成功对一些主流加密算法进行了攻击,SCA成为加密算法实现的最大的安全威胁之一。在密码学领域为击败SCA而开发的众多对策中,Nikova等[3]和Bilgin等[4]提出的基于门限实现的对策无疑是当今最流行的对策,该对策基于秘密共享的思想,使用多个随机变量作用于一个中间值,即使在探针攻击[3]的情况下,依然能保证安全性,并且具备抗差分功耗分析(Differential Power Analysis, DPA)的能力。自2006年以来,门限实现被广泛应用于应用于高级加密标准(Advanced Encryption Standard,AES)、PRINCE、数据加密标准(Data Encryption Standard, DES)等国际加密算法中,有效降低了加密算法在侧信道攻击中的脆弱性,但针对SM4的门限实现方案较少。2007年,Liu等[5]给出了SM4算法S盒的代数表达式,奠定了SM4算法的研究基础;2014年,Liang等[6]利用正则基在复合域中实现求逆,提出了更紧凑的S盒;2018年,李新超等[7-8]构造秘密共享函数代替仿射变换,提出了两种基于门限实现的SM4 S盒结构,并具备抗一阶、抗二阶DPA的能力,但并未在实际应用中进行侧信道安全分析;2022年,武小年等[9]基于多项式基设计了面积更紧凑的门限SM4方案,具备抗一阶DPA能力。就目前来说,现有文献主要关注SM4 S盒的门限实现设计方案,但S盒门限实现仍存在整体实现硬件开销大、随机数使用多等缺点。此外门限SM4均采用128 bit数据位宽的结构,存在S盒门限实现面积增大导致SM4整体实现面积显著增加的缺点,在门限AES实现中,均采用8 bit数据位宽的串行结构以克服上述缺点。
本文基于正则基S盒结构,对复合域求逆均匀共享进行优化实现,并引入面向域掩码(Domain Oriented Masking, DOM)方案,设计更紧凑、随机数更少的SM4门限S盒;基于8 bit数据位宽的串行SM4以及门限S盒结构,提出SM4轮函数中线性函数的优化实现,设计了新的基于流水线设计的门限SM4结构,正确实现SM4加密运算;相较于文献[7-9]采用的128 bit数据位宽的门限SM4,本文结构中门限S盒的数量仅为1,有效避免了门限S盒面积较大导致整体SM4面积大幅增加的问题,具有更好的时间-面积积(Area-Time Product, ATP)性能指标。仿真结果表明,本文设计的SM4硬件结构面积更加紧凑,所需随机数更少,在一阶DPA下具备安全性。
1 预备知识
1.1 门限实现理论

性质1 正确性(Correctness)。异或所有共享分量值等于未共享变量值。

1.2 正则基求逆
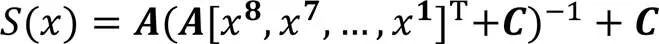
其中:为仿射矩阵;表示输入的第 bit;为行向量。
在复合域进行S盒计算时,需要先进行前仿射、同构映射运算,在设计中,两个运算进行合并可提高计算效率,定义线性运算LM如下:
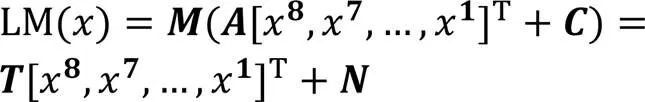
在S盒复合域计算末尾,会进行逆同构映射、仿射运算,同样采用合并的方法进行实现,定义线性运算ILM如下:

2 S盒门限实现方案
图1描述了本文采用的复合域分解的S盒,根据各函数的线性和非线性,将它划分为了5个部分,并且采用2输入共享方案,由性质2可知,可以抵御一阶DPA。接下来以一种分阶段的方式来介绍门限S盒设计,其中每个阶段由流水线寄存器进行分隔。完整的门限S盒如图2所示。

图 2 SM4 S盒门限实现结构



其中:



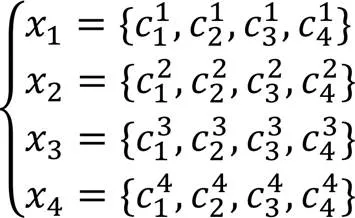

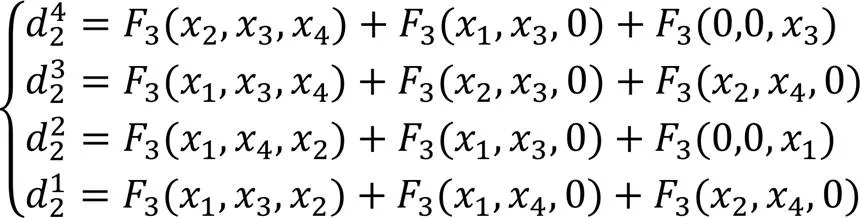
算法1 检验掩蔽均匀性。
输出 True,False。
end For
end For
Return False
end if
end For
end For
Return True
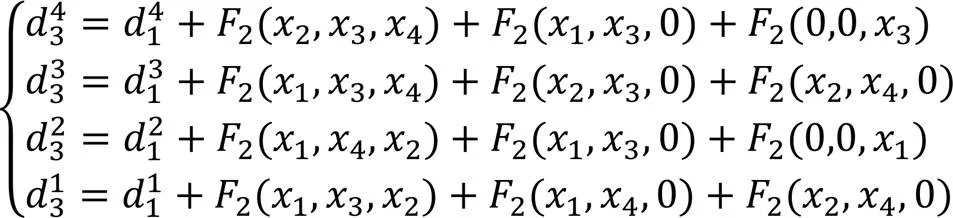
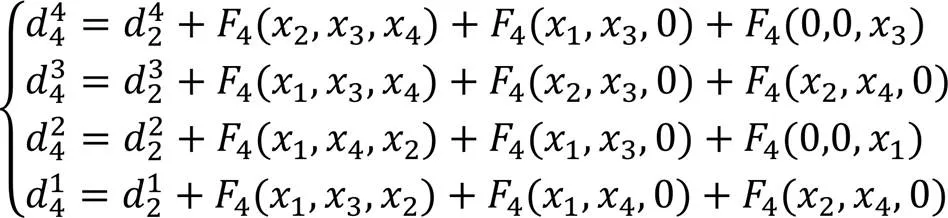


(19)
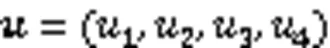

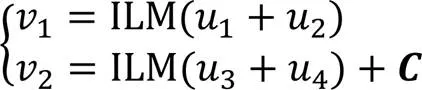
3 SM4线性函数优化设计






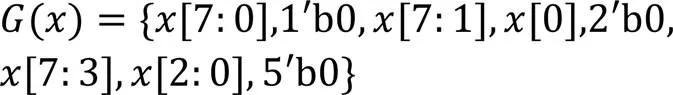
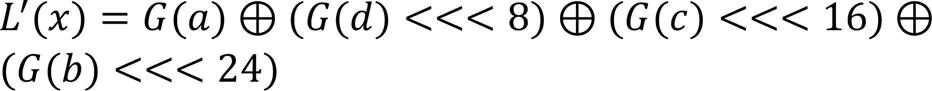
4 SM4门限实现电路结构
4.1 整体结构
文献[3-4]中所设计的门限AES电路结构,均采用8 bit数据位宽的串行AES结构,例化一个门限S盒模块,按行逐字节加载明文和密钥,进而避免门限S盒面积过大导致整体AES面积大幅增加。本文结合文献[3,15]的方法,并考虑SM4以及门限S盒的整体硬件结构,设计了基于门限S盒实现的SM4加密电路结构,如图5所示。采用串行实现来进行轮操作和密钥调度,总体结构包括2个状态寄存器,1个密钥寄存器、1个门限S盒、1个伪随机数生成模块。在数据路径上8 bit和128 bit数据位宽,128 bit数据位宽仅用于加密开始前后的明文共享、密钥、密文共享的读写。

图5 SM4门限实现串行体系结构
4.2 状态寄存器



图6 SM4状态寄存器
4.3 密钥寄存器


5 安全性分析与验证
5.1 安全性分析
为了对SM4门限实现的安全性进行评估,本设计在SPARTAN-6 XC6SLX9 型号芯片的FPGA开发板中进行实现,使用PICO 3206D数字示波器采集电路加密时的实际功耗曲线,采样频率为250 MHz。在本设计中采用伪随机数发生器(Pseudo-Random Number Generator,PRNG)为门限S盒提供随机数,因此分别采集关闭PRNG和开启PRNG的1万条功耗曲线进行安全性对比,图8展示了门限SM4加密前4轮的功耗曲线,可以观察到由于PRNG的使用,图8(b)的功耗略高于图8(a)。
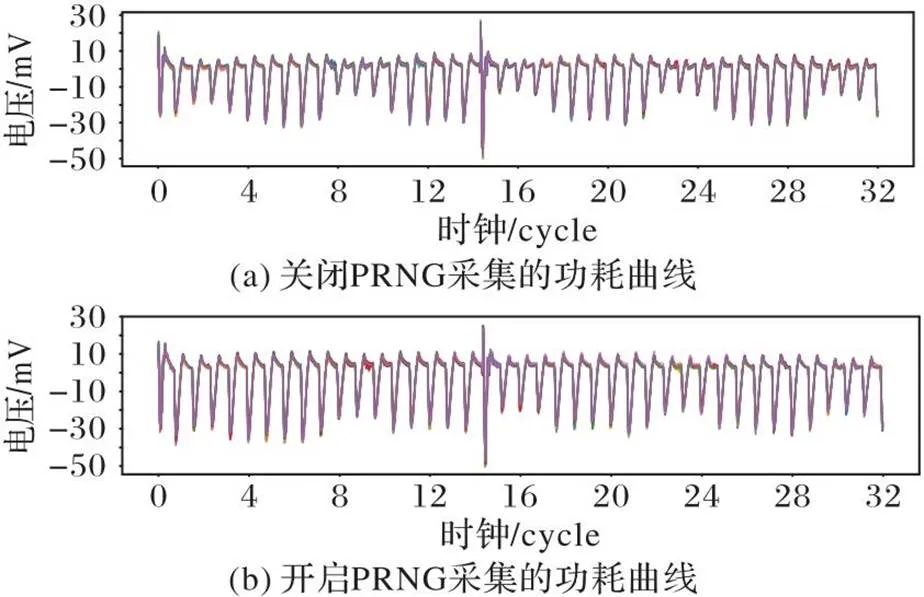
图8 关闭与开启PRNG的功耗曲线
首先,采用相关能量分析(Correlation Power Analysis, CPA)[17]方法对无保护和有保护的1万条SM4第一轮加密功耗曲线进行安全性分析。选择对SM4第1字节密钥进行攻击,攻击结果如图9所示。图9(a)可以看出存在1个密钥猜测值的相关系数远大于其他密钥猜测值,表明无保护的SM4第1字节密钥被成功攻击,这是由于门限S盒每个阶段不满足均匀性从而导致了信息泄露。从图9(b)可以看出所有密钥猜测值的相关系数无明显差异,表明有保护的门限SM4则无法通过CPA获取密钥。

图9 关闭与开启PRNG的CPA结果
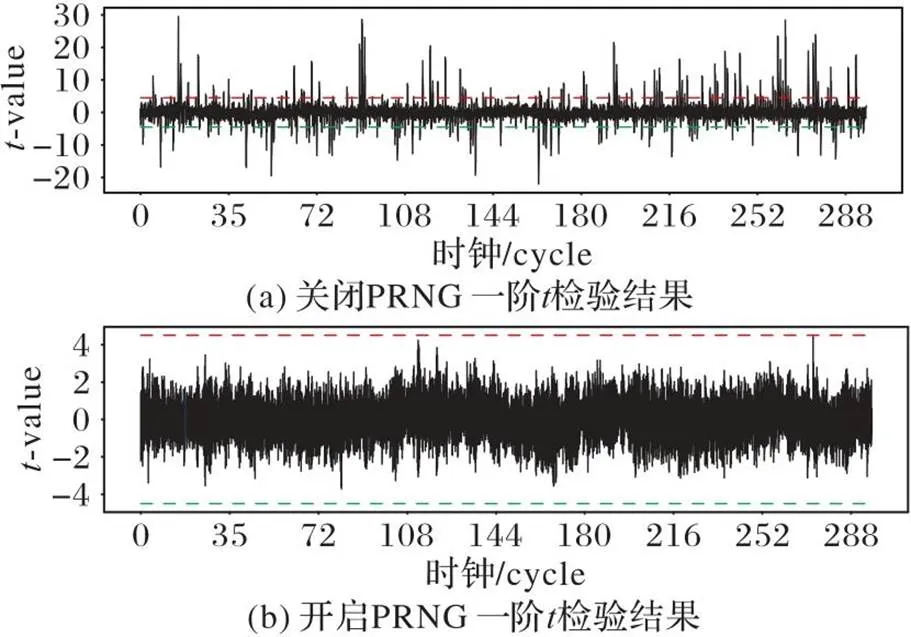
图10 关闭与开启PRNG的一阶检验结果
5.2 性能对比
使用Verilog语言实现本文基于门限实现的SM4方案,并在Xilinx ISE Design Suite上对方案的正确性进行仿真验证,使用Synopsys Design Compiler工具以及SMIC 55 nm工艺库进行逻辑综合,与现有的一些掩码方案对比如表1所示。

表1 SM4门限实现设计比较
由表1可知在相同条件下,与文献[7-9]采用128 bit数据位宽实现的门限SM4相比,本文方案面积减小约63.7%~75.7%,门限S盒消耗的随机掩码数量仅为12 bit,远低于文献[7-8]方案中S盒的随机掩码消耗数量,但SM4门限实现完成整个加密过程所需时钟数增加了52.1%~82.5%。此外,本文采用ATP指标对不同门限SM4方案进行对比。假设时钟频率均为50 MHz,文献[7-9]方案的ATP指标分别为89.60、84.40、59.86,本文ATP指标为38.00,更好地权衡了面积和性能。本文也给出了门限SM4各模块的面积,如表2所示。因此,本文8 bit数据位宽的门限SM4具有更好的性能,面积更加紧凑,门限S盒所需随机数更少。

表2 SM4门限实现模块面积
6 结语
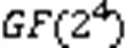
目前SCA手段不断更新,如高阶探针攻击、DPA。因而,具备抵御高阶SCA能力的密码算法实现研究依旧是一个研究重点。本文采用2共享方案,因此仅能抵御一阶DPA,能够抵御高阶DPA的SM4算法实现是下一阶段的研究工作所重点追求的目标。
[1] Office of State Commercial Cipher Administration. Block cipher for WLAN products — SMS4 [EB/OL]. [2022-03-21]. http://www.oscca.gov.cn/UpFile/2006021016423197990.pdf.
[2] KOCHER P C. Timing attacks on implementations of Diffie-Hellman, RSA, DSS, and other systems[C]// Proceedings of the 1996 Annual International Cryptology Conference, LNCS 1109. Cham: Springer, 1996: 104-113.
[3] NIKOVA S, RECHBERGER C, RIJMEN V. Threshold implementations against side-channel attacks and glitches[C]// Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Information and Communications Security, LNCS 4307. Cham: Springer, 2006: 529-545.
[4] BILGIN B, GIERLICHS B, NIKOVA S, et al. Trade-offs for threshold implementations illustrated on AES[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2015, 34(7): 1188-1200.
[5] LIU F, JI W, HU L, et al. Analysis of the SMS4 block cipher[C]// Proceedings of the 2007 Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, LNCS 4586. Berlin: Springer, 2007: 158-170.
[6] LIANG H, WU L J, ZHANG X M, et al. Design of a masked S-box for SM4 based on composite field[C]// Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security. Piscataway: IEEE, 2014: 387-391.
[7] 李新超,钟卫东,张帅伟,等.一种基于门限实现的SM4算法S盒实现方案[J].计算机工程与应用,2018,54(17):83-88. (LI X C, ZHONG W D, ZHANG S W, et al. New S-box of SM4 based on threshold implementation [J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2018, 54(17): 83-88.)
[8] 李新超,钟卫东,张帅伟,等.一种SM4算法S盒的门限实现方案[J].密码学报,2018,5(6):641-650.(LI X C, ZHONG W D, ZHANG S W, et al. A new threshold implementation of the S-box in SM4[J]. Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2018, 5(6): 641-650.)
[9] 武小年,李金林,潘晟,等.SM4算法门限掩码方案设计与实现[J].计算机应用研究,2022,39(2):572-576.(WU X N, LI J L, PAN S, et al. Threshold masking schema design and implementation on SM4 algorithm[J]. Application Research of Computers.2022,39(2): 572-576.)
[10] NIKOVA S, RIJMEN V, SCHLAFFER M. Secure hardware implementation of nonlinear functions in the presence of glitches[J]. Journal of Cryptology, 2011, 24(2): 292-321.
[11] BILGIN B, GIERLICHS B, NIKOVA S, et al. A more efficient AES threshold implementation[C]// Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Cryptology in Africa, LNCS 8469. Cham: Springer, 2014: 267-284.
[12] DE CNUDDE T, REPARAZ O, BILGIN B, et al. Masking AES with+1 shares in hardware[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, LNCS 9813. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 194-212.
[13] WEI M, SUN S W, WEI Z H, et al. A small first-order DPA resistant AES implementation with no fresh randomness [J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(6): No.169102.
[14] GROSS H, MANGARD S, KORAK T. Domain-oriented masking: compact masked hardware implementations with arbitrary protection order [C]// Proceedings of the 2016 ACM Workshop on Theory of Implementation Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 3.
[15] SHANG M, ZHANG Q L, LIU Z B, et al. An ultra-compact hardware implementation of SMS4[C]// Proceedings of the 2014 IIAI 3rd International Conference on Advanced Applied Informatics. Piscataway: IEEE, 2014:86-90.
[16] 郑朝霞,资义纯,吴旭峰,等.SMS4算法串行化设计及其轻量级电路实现[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(2):61-64.(ZHENG Z X, ZI Y C, WU X F, et al. Serialized design of SMS4 and lightweight implement[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2016, 44(2): 61-64.)
[17] BRIER E, CLAVIER C, OLIVIER F. Correlation power analysis with a leakage model [C]// Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, LNCS 3156. Berlin: Springer, 2004: 16-29.
[18] ROY D B, BHASIN S, PATRANABIS S, et al. Testing of side-channel leakage of cryptographic intellectual properties: metrics and evaluations[M]// Hardware IP Security and Trust. Cham: Springer, 2017: 99-131.
SM4 resistant differential power analysis lightweight threshold implementation
PU Jinwei, GAO Qingjian, ZHENG Xin*, XU Yinghui
(,,510006,)
Aiming at the problems of large area and large consumption of fresh randomness in Threshold Implementation (TI) of SM4, an improved threshold implementation scheme of SM4 was proposed. In the case of satisfying the threshold implementation theory, the operation of S-box nonlinear inversion was shared with no fresh randomness, and a domain-oriented multiplication mask scheme was introduced to reduce the fresh randomness consumption of S-box to 12 bits. Based on the idea of the pipeline, a new SM4 serial architecture with 8-bit data width was designed. The threshold implementation of S-box was reused, and the linear function of SM4 was optimized to make the area of threshold implementation of SM4 more compact, only 6 513 GE. In comparison with the TI scheme of SM4 with 128-bit data width, the area of the proposed scheme is reduced by more than 63.7%, and there is a better trade-off between speed and area. The side-channel experimental results show that the proposed scheme has the capability of anti-first-order Differential Power Analysis (DPA).
SM4; Differential Power Analysis (DPA); Threshold Implementation (TI); S-box; nonlinear inversion; shared with no fresh randomness; domain-oriented multiplication mask scheme
1001-9081(2023)11-3490-07
10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022101579
2022⁃10⁃24;
2022⁃12⁃29;
广东省基础与应用基础研究基金资助项目(2021A1515110777)。
蒲金伟(1998—),男,重庆人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:密码算法侧信道防护; 高倾健(1997—),男,广东普宁人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:密码算法侧信道防护; 郑欣(1993—),女,湖北咸宁人,博士,主要研究方向:SoC设计、软硬件协同设计、图神经网络; 徐迎晖(1977—),男,湖南长沙人,副教授,博士,主要研究方向:信息安全、嵌入式系统、多媒体信号处理。
TP309.2
A
2023⁃01⁃03。
This work is partially supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515110777).
PU Jinwei, born in 1998, M. S. candidate. His research interests include cryptographic algorithm side-channel protection.
GAO Qingjian, born in 1997, M. S. candidate. His research interests include cryptographic algorithm side-channel protection.
ZHENG Xin, born in 1993, Ph. D. Her research interests include SoC (System on Chip) design, software and hardware co-design, graph neural network.
XU Yinghui, born in 1977, Ph. D., associate professor. His research interests include information security, embedded systems, multimedia signal processing.

