Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of medicinal plant Gynostemma pentaphyllum
Yibo Wang,Yi’an Shi,Guanyi Zhao,Shuo Wang,Ying Li,Yu Chen
School of Life Science and Biopharmaceutic, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract Gynostemma pentaphyllum (G.pentaphyllum) is a traditional medicinal plant with medicinal and economic value.With in-depth research on the chemical compositions and pharmacological effects,the applications of G.pentaphyllum have been expanded.G.pentaphyllum has the effects of clearing heat and detoxification,relieving cough and phlegm,nourishing heart,tranquilizing nerves,and can be used to treat gastroenteritis,tracheitis,pharyngitis,hyperlipidemia,and arteriosclerosis.It can also be used to alleviate symptoms such as migraines,insufficient sleep,and white hair.In recent years,G.pentaphyllum has also been used for clinical adjuvant treatment of various cancers.In this study,the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects on G.pentaphyllum in recent years were reviewed.This review could provide reference for further development and utilization of G.pentaphyllum.
Keywords: Gynostemma pentaphyllum;chemical composition;pharmacological effect
1 Introduction
Gynostemma pentaphyllum(G.pentaphyllum)is the whole grass ofCucurbitaceaeplantG.pentaphyllum,and it was firstly recorded in the Ming dynasty’s “Disaster relief materia medica”.In the Compendium of Materia Medica,it was mentioned as a herbal medicine under the name of “Black Drum Zi”.G.pentaphyllumis clinically used to treat cough,phlegm and asthma,senile chronic tracheitis,infectious hepatitis and fatigue.It has become a research hotspot for scholars as an immune enhancer similar to ginseng in recent years.G.pentaphyllumcontains saponins,polysaccharides,flavonoids,amino acids,plant proteins,sterols,pigments,organic acids,cellulose,chlorophyll,and trace elements.Modern pharmaceutical research shows that saponins are the main active ingredients ofG.pentaphyllum[1,2].
With the improvement of modern chemical analysis technology and pharmacological activity evaluation method,progress has been made in the research ofG.pentaphyllum.In this study,the chemical constituents and pharmacological effects ofG.pentaphyllumwere reviewed in order to provide reference for further research and development ofG.pentaphyllum.
2 Chemical constituents
With the rapid development of chromatographic separation technology,more and more components have been isolated fromG.pentaphyllum,such as saponins,sterols,polysaccharides,flavonoids,organic acids and trace elements.
2.1 Saponins
Up to now,142 saponins have been isolated fromG.pentaphyllum,and their specific structures are shown in Fig.1 [3-33].
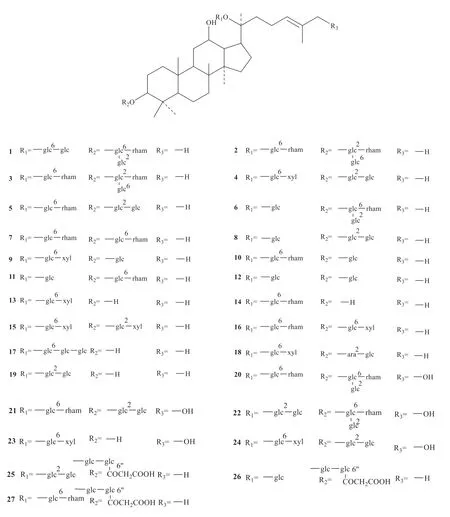
Fig.1 Structures of saponins isolated from G.pentaphyllum

Continued fig.1
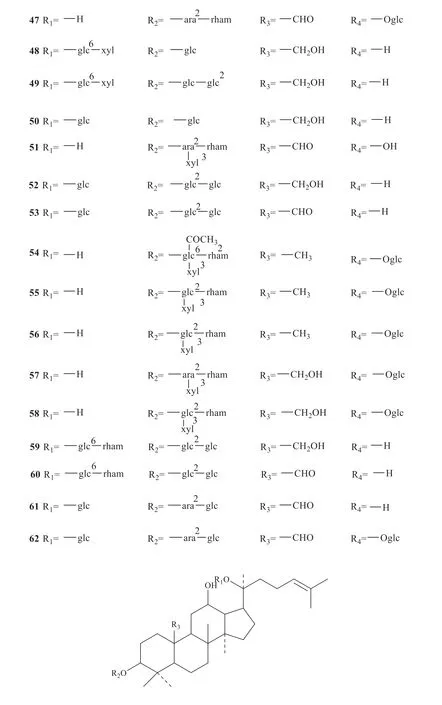
Continued fig.1
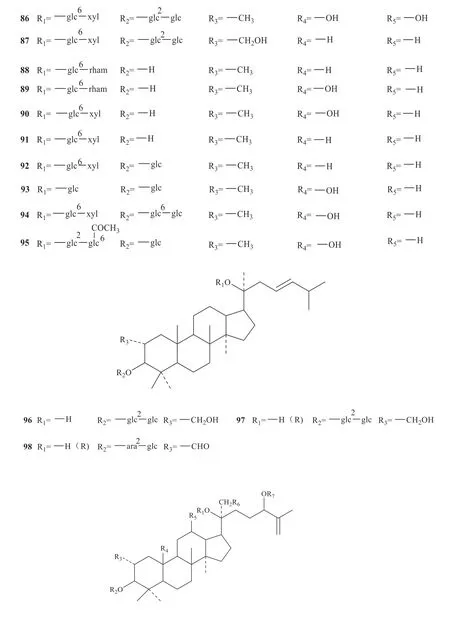
Continued fig.1
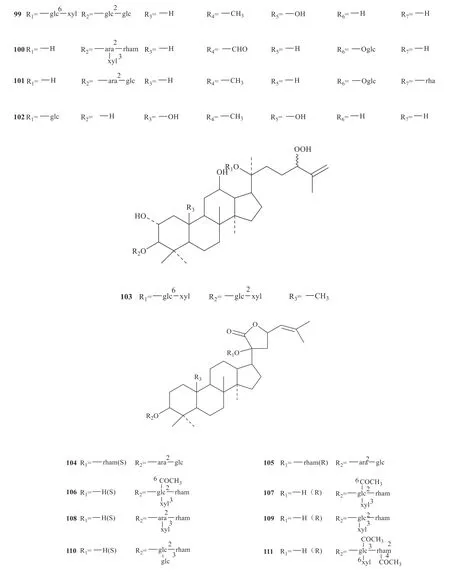
Continued fig.1
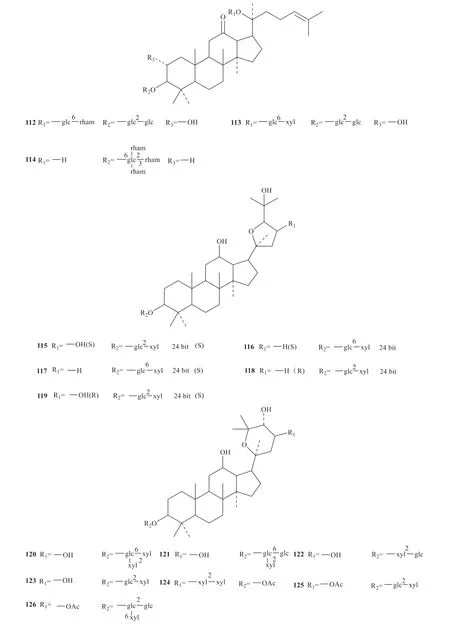
Continued fig.1
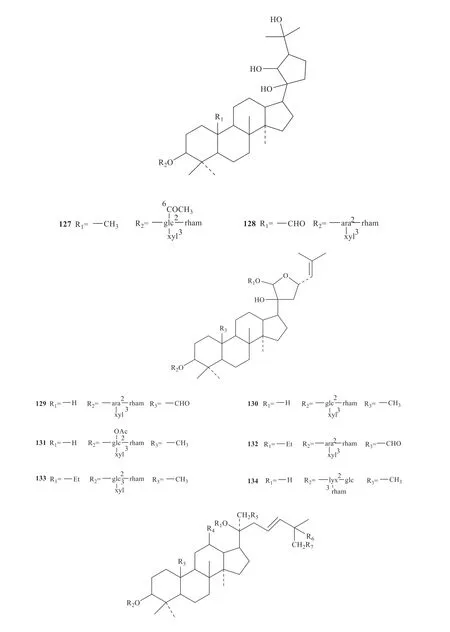
Continued fig.1
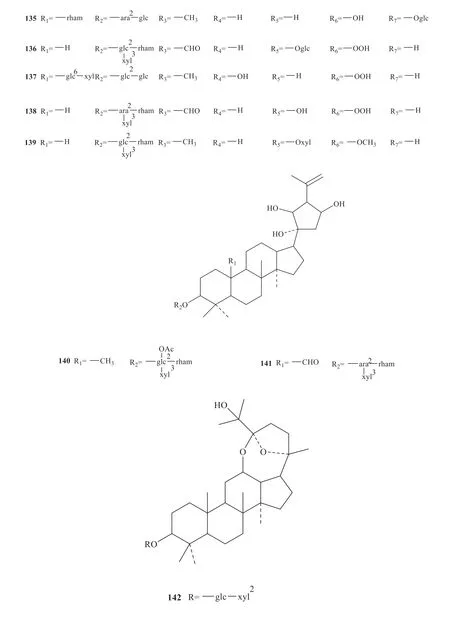
Continued fig.1
2.2 Sterols
18 sterols have been successively isolated fromG.pentaphyllum,whose structural formulas are shown in Fig.2 [34-42].
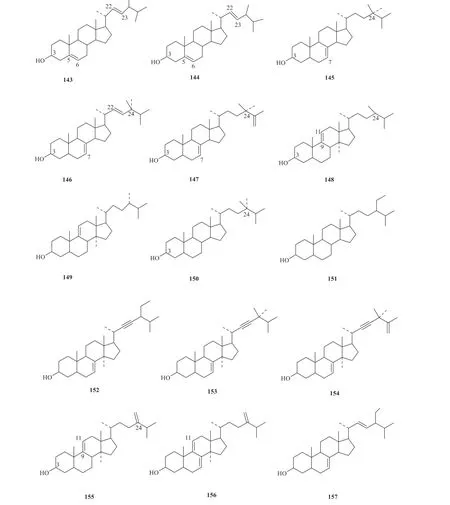
Fig.2 Structures of sterols isolated from G.pentaphyllum
2.3 Polysaccharide compounds
Polysaccharide compounds are abundant inG.pentaphyllum,and have attracted increasing attention in recent years.GPP-S (184) can be isolated and purified fromG.pentaphyllum.The molar ratio of polysaccharide components,namely rhamnose(161),xylose (162),arabinose (163),galactose(164),and glucose (165) is 1:1.75:3.72:7.82:19.49.The structural formulas of polysaccharide (166)and monosaccharide compounds are shown in Fig.3.
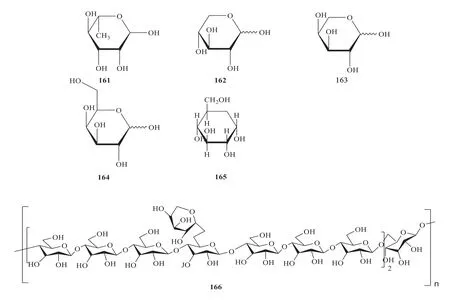
Fig.3 Structures of polysaccharides and monosaccharides in G.pentaphyllum
2.4 Amino acids
G.pentaphyllumcontains many amino acids,such as leucine (167),lysine (168),methionine(169),isoleucine (170),and phenylalanine (171).The structures of amino acids are shown in Fig.4.
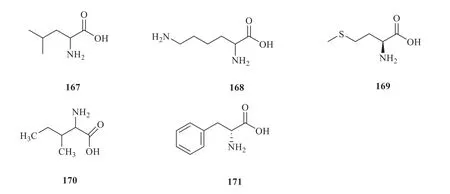
Fig.4 Structures of amino acids isolated from G.pentaphyllum
2.5 Trace elements
G.pentaphyllumcontains a large number of trace elements,and these trace elements are necessary for the human body.Calcium,phosphorus,potassium,natrium and magnesium are five essential macroelements.Boron,magnesium,and manganese have obvious anti-cancer activity [43].
2.6 Vitamins
Vitamins include water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins.G.pentaphyllumcontains water-soluble vitamins B1(172),B2(173),B6(174) and C (175),and fat soluble vitamins D3(176) and E (177),shown in Fig.5,among which the content of fat soluble vitamin E is the highest [44].
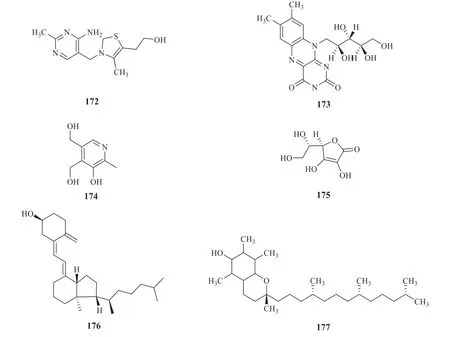
Fig.5 Structures of vitamins isolated from G.pentaphyllum
3 Pharmacological activities
3.1 Anti-tumor mechanism
G.pentaphyllumsaponins have obvious antitumor effect,inhibiting the growth and reproduction of tumor cells.The mechanism is shown in Fig.6.
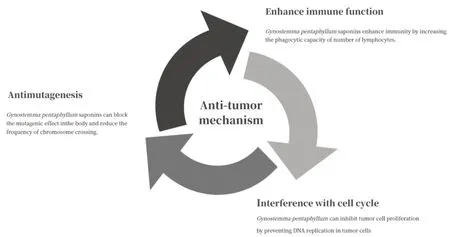
Fig.6 Anti-tumor mechanism of G.pentaphyllum
3.1.1 Antimutagenesis
G.pentaphyllumsaponins inhibit the growth of tumor cells by blocking the mutagenic effects of certain mutagens in the body [45].Song et al.studied the antimutagenic effect ofG.pentaphyllumsaponins with cyclophosphamide as a mutagen in the laboratory.With the cross frequency of chromosomes as the evaluation index,it was found thatG.pentaphyllumsaponins significantly reduced the cross frequency of chromosomes to 5.995%,indicating thatG.pentaphyllumsaponins had significant antimutagenic effect [46].
3.1.2 Interference with cell cycle
Han et al.concluded through relevant research that the saponin component ofG.pentaphyllummacrolignin B could block the G0/G1 phase of human hepatoma HepG2 cells,prevent the transition of HepG2 to S phase,inhibit DNA replication,and achieve the purpose of anti-tumor [47].The treatment ofG.pentaphyllumsaponins isolated fromG.pentaphyllumon human prostate cell PC-3 showed that the saponins ofG.pentaphyllummacrolignin B caused cell cycle arrest in S phase and G2/M phase by regulating the expression of cell cyclin [48].
3.1.3 Enhancement of immune function
G.pentaphyllumsaponins can enhance the phagocytosis of mouse peritoneal macrophages,increase the number of lymphocytes,increase the NK activity of mouse natural killer cell and the production and activity of serum hemolysin,improve the ability of splenocyte to secrete antibodies.Liu et al.injected saponins into the peritoneum of mice transplanted with Lewis lung cancer cells,and found that the immune response function of mice was enhanced,indicating that saponins have significant anti-tumor effects.
3.2 Hepatoprotective effect
The liver bears many important functions of the body and is also the main organ for biotransformation of exogenous compounds.This unique vascular layout and the secretion,synthesis,and metabolic functions of the liver determine that it is the main target of toxic effects [49].The reason whyG.pentaphyllumpolysaccharide has a protective effect on carbon tetrachloride and alcoholic liver injury is thatG.pentaphyllumpolysaccharide has anti-lipid peroxidation effect,and it can directly capture and eliminate free radicals,reduce the attack of free radicals on lipid membrane and mitochondrial membrane,and stabilize the membrane structure of cells to protect the liver.Wang et al.found thatG.pentaphyllumpolysaccharide had a good scavenging effect on superoxide free radicals,hydroxyl free radicals,and other free radicals.Its antioxidant effect is comparable to that of vitamin C,further confirming our speculation on the mechanism ofG.pentaphyllumpolysaccharide against alcoholic liver injury [50].
3.3 Hypolipidemic effect
Li et al.randomly divided 48 patients with hyperlipidemia into the original dose group and the increased dose group.All of them tookG.pentaphyllumtotal glycosides capsules,one capsule each time for the original dose group,and four capsules each time for the increased dose group.The results showed that the effective rate in the increased dose group was significantly higher than that in the original dose group.Moreover,serum TC,TG and other indicators decreased more in the increased dose group,suggesting that the hypoglycemic effect ofG.pentaphyllumis dose dependent.The results show thatG.pentaphyllumnot only reduces blood lipids,but also alleviates accompanying symptoms [51].
3.4 Protective effect on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease
Animal experiments showed that total saponins ofG.pentaphyllumhad extensive protective effects on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems [52].It had protective function on myocardial ischemia and cardiac systolic function in rats [53,54],and could resist the damage of oxygen free radicals to the heart,protect the integrity of myocardial cell membrane,and improve the myocardial diastolic function in acute myocardial ischemia [55,56].
3.5 Protective effect on ischemic brain tissue
Chi et al.used the first embolization method to prepare the middle artery fragment hypoperfusion(MCAO/R) model in rats,and measured the contents of Malondialdehyde (MAD),nitric oxide (NO),total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) and Catalase (CAT)activity in brain homogenate [57].The results show thatG.pentaphyllumpreparationG.pentaphyllumpill protects brain tissue with obvious cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury,and protects brain through antioxidant mechanism [58].
3.6 Protective effects on myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury
Total flavonoids ofG.pentaphyllumcan affect the content of Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and cTnI in myocardial culture medium and free Ca2+in myocardial cells of hypoxia injury group.After the intervention ofG.pentaphyllumflavone (TFG),the content of cTnI in LDH induced cell culture medium and the concentration of intracellular free Ca2+TFG decreased significantly.TFG has protective effect on hypoxic cardiomyocytes,and its mechanism may be related to reducing calcium overload of cardiomyocytes [59].
3.7 Antithrombotic and platelet aggregation inhibiting function
G.pentaphyllumsaponins can inhibit experimental cerebral thrombosis in rats,extracorporeal arterial thrombosis and acute pulmonary thrombosis in mice.Zhang et al.found thatG.pentaphylluminhibited thrombosis in rats,and prolonged coagulation time,prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time [60].
4 Conclusion
G.pentaphyllumhas been a traditional Chinese medicine since ancient times.With the development of modern research,more and more in-depth research has been made on the chemical composition and pharmacological effects ofG.pentaphyllum.It mainly contains saponins,sterols,polysaccharides,flavonoids and other chemical components.At the same time,it has been proved to have anti-tumor,lipid-lowering,liver protective effects,cardiovascular protection,and ischemic brain tissue protective activity.However,the pharmacological research onG.pentaphyllummainly focuses on saponins,polysaccharides and other related substances,giving less attention to the pharmacological activities of sterols and flavonoids.With the improvement and innovation of related analytical instruments and test methods,the pharmacological activities ofG.pentaphyllumwill have great development propects.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China(81973284) and Scientific Research Foundation of the Education Department of Liaoning Province(LJKZ0944).
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.

