CRRT联合血浆置换救治高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者的疗效分析
程炯炯 李琳琳 赵浩东 胡志旭 陈卫东 王兴宇
摘要:目的 探討连续性肾脏替代治疗(CRRT)联合血浆置换(PE)救治高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者的疗效及其影响因素。方法 109例高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者根据治疗方法分为CRRT组51例和CRRT联合PE组(联合组)58例,比较2组疗效、症状消失时间和预后情况;计算联合组患者治疗72 h三酰甘油(TG)下降程度,根据TG下降程度(取60%为界限),分为高效(TG下降>60%)组37例和低效(TG下降≤60%)组21例,采用多元线性回归模型分析影响CRRT联合PE疗效的因素。结果 联合组治疗72 h后总胆固醇(TC)、TG、淀粉酶(AMY)、C反应蛋白(CRP)及降钙素原(PCT)水平低于CRRT组(P<0.05);联合组腹痛、发热和恶心呕吐症状消失时间、机械通气时间和ICU住院时间短于CRRT组(P<0.05)。高效组治疗前TC和TG水平高于低效组,发病至PE开始时间短于低效组(P<0.05);多元线性回归分析显示,CRRT联合PE的TG下降程度=33.591+1.010×治疗前TC+2.088×治疗前TG-0.443×发病至PE开始时间。结论 CRRT联合PE可有效减轻患者症状,有利于疾病转归,其疗效与患者治疗前TC、TG水平和发病至PE开始时间有关。
关键词:急性出血性胰腺炎;高脂血症;连续性肾替代疗法;血浆置换;线性模型
中图分类号:R576文献标志码:ADOI:10.11958/20221994
Curative effect of CRRT combined with plasma exchange in the treatment of hyperlipidemic severe acute pancreatitis
CHENG Jiongjiong, LI Linlin, ZHAO Haodong, HU Zhixu, CHEN Weidong, WANG Xingyu
Department of Emergency Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230001, China
Corresponding Author E-mail: wang_wxy@126.com
Abstract: Objective To analyze the curative effect of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) combined with plasma exchange (PE) in patients with severe acute pancreatitis of hyperlipidemia. Methods According to different treatment methods, 109 patients with severe acute pancreatitis of hyperlipidemia were divided into the CRRT group (51 cases) and the combination group (CRRT combined with PE, 58 cases). The curative effect, disappearance time of symptoms and complications were compared between the two groups. The decline degree of triglyceride (TG) was calculated in the combination group after 72 h treatment. According to the decline degree of TG (60% as the limit), patients were divided into the high efficiency group (>60%, 37 cases) and the low efficiency group (≤60%, 21 cases). The influencing factors on the curative effect of CRRT combined with PE were analyzed by multivariate linear regression model. Results After 72 h of treatment, levels of total cholesterol (TC), TG, amylase (AMY), C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) were lower in the combination group than those of the CRRT group (P < 0.05). The disappearance time of symptoms (abdominal pain, fever, nausea and vomiting), mechanical ventilation time and stay time in ICU were shorter in the combination group than those of the CRRT group (P < 0.05). Before treatment, levels of TC and TG were higher in the high efficiency group than those of the low efficiency group, while interval from onset to PE was shorter than that in the low efficiency group (P < 0.05). The results of multivariate linear regression analysis showed that the regression equation:TG decline =33.591+1.010×(TC before treatment)+2.088×(TG before treatment)-0.443×(interval from onset to PE). Conclusion CRRT combined with PE can effectively relieve symptoms, which is conducive to disease outcomes. The curative effect is related to TC and TG levels before treatment and the interval from onset to PE.
Key words: pancreatitis, acute hemorrhagic; hyperlipidemias; continuous renal replacement therapy; plasma exchange; linear models
急性胰腺炎是常见的急腹症,轻症患者以胰腺组织水肿为主,病情具有自限性,而重症患者病情凶险,易继发多种并发症,严重威胁患者生命安全[1]。造成急性胰腺炎的病因复杂,其中高脂血症是第二大病因,伴发者病情也更为严重[2]。国际改善全球肾脏病预后组织(KDIGO)、急性透析质量倡议工作组(ADQI)推荐连续性肾脏替代治疗(continuous renal replacement therapy,CRRT)能够清除重症急性胰腺炎患者体内炎症介质和内毒素,恢复机体免疫稳态,改善预后[3]。研究發现,患者体内三酰甘油(TG)水平越高,急性胰腺炎病情越危急[4]。血浆置换(plasma exchange,PE)可在数小时内迅速降低高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者的TG水平,延缓病情进展[5]。目前,对于PE的研究多侧重于治疗方案探讨[6-7],但美国血液分离学会认为PE治疗应考虑个体差异,尤其是高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者[8]。基于此,本研究回顾性收集高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者临床资料,探讨CRRT联合PE对患者治疗效果及预后的影响,为临床提供参考。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
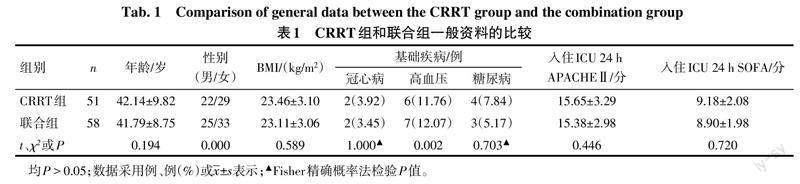
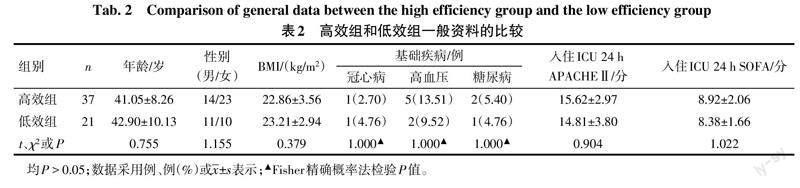
选取2018年6月—2022年6月于安徽医科大学第一附属医院治疗的高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者109例。纳入标准:符合《2016年中国成人血脂异常防治指南》中高脂血症和《急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2014)》中重症急性胰腺炎的诊断标准;临床资料完整。排除标准:胰腺癌、胆石症、手术创伤等其他因素引起的重症急性胰腺炎;伴有严重的凝血功能障碍;处于妊娠或哺乳期。根据治疗方法不同将患者分为CRRT组51例和CRRT联合PE组(联合组)58例。参照文献[9-10]取TG下降60%为阈值,将治疗72 h后联合组患者分为高效(TG下降>60%)组37例和低效(TG下降≤60%)组21例。CRRT组与联合组、高效组与低效组的年龄、性别、体质量指数(BMI)、基础疾病、入住ICU 24 h急性生理与慢性健康状况评分Ⅱ(acute physiol-ogy and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ,APACHEⅡ)、序贯器官衰竭估计评分(sequential organ failure assessment,SOFA)比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表1、2。
1.2 治疗方法
所有入组患者均行生命体征监护,禁食3 d,并予以抗感染、抑酸抑酶、营养支持等常规治疗。CRRT组治疗采用瑞典金宝百特连续性血液净化设备Prismaflex,模式选定血液透析滤过,滤器为M150,设置参数:血流速150 mL/min,置换流速1 000~1 500 mL/h,治疗剂量35 mL/(kg·h),持续治疗24 h,置换液购自上海华源长富药业集团,动态监测滤器和动脉血血钙水平,4%枸橼酸钠和5%氯化钙用量。联合组CRRT治疗方法同CRRT组,PE治疗采用瑞典金宝百特连续性血液净化设备Prismaflex,滤器为Prismaflex血浆分离器,模式选定为PE,管路预先抗凝处理,凝血功能异常时作无肝素化处理,设置参数:血流速80 mL/min,置换流速1 000~1 500 mL/h,血浆置换量参照文献[11],置换时间120~180 min。
1.3 观察指标
1.3.1 一般资料
收集患者年龄,性别,BMI,基础疾病(冠心病、高血压、糖尿病),入住ICU 24 h内APACHEⅡ和SOFA,发病至PE开始时间等资料,其中APACHEⅡ、SOFA越高表明病情越重。
1.3.2 生化指标
记录患者治疗前、治疗72 h后血常规[白细胞计数(WBC)、血小板计数(PLT)、红细胞比容(HCT)],血脂指标[总胆固醇(TC)、TG],淀粉酶(AMY)及炎性指标[C反应蛋白(CRP)、降钙素原(PCT)]水平。
1.3.3 疗效及预后情况
以2组患者治疗72 h后TG下降程度反映疗效,TG下降程度=(治疗前TG-治疗72 h后TG)/治疗前TG×100%。治疗期间记录患者腹痛、发热和恶心呕吐等症状消失时间,预后情况包括机械通气时间、ICU住院时间以及治疗1周内复发率(治疗后再次出现急性发作的持续性腹上区剧烈疼痛)、病死率。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 25.0软件进行数据分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示,组内治疗前后比较采用配对t检验,组间比较采用独立样本t检验;计数资料以例(%)表示,组间比较采用χ2或Fisher精确概率法;采用多元线性回归模型分析影响CRRT联合PE疗效的因素,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
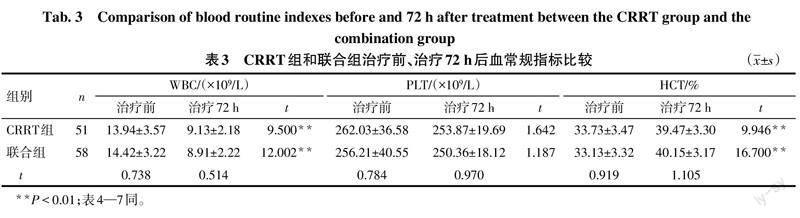
2.1 CRRT组和联合组治疗前后生化指标比较
2组患者治疗72 h后WBC、TC、TG、AMY、CRP以及PCT水平较治疗前下降,HCT水平较治疗前升高(P<0.01)。联合组患者治疗72 h后TC、TG、AMY、CRP以及PCT水平低于CRRT组(P<0.01),见表3—5。
2.2 CRRT组和联合组疗效及预后情况比较
联合组TG下降程度高于CRRT组,腹痛、发热和恶心呕吐症状消失时间、机械通气时间和ICU住院时间短于CRRT组(P<0.05),但2组复发率和病死率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表6。
2.3 高效组和低效组治疗前生化指标及发病至PE开始时间的比较
高效组治疗前TC和TG水平高于低效组,发病至PE开始时间短于低效组(P<0.05);但2组治疗前WBC、PLT、HCT、AMY、CRP及PCT水平比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),见表7。
2.4 CRRT联合PE疗效的影响因素分析
以TG下降程度为因变量,治疗前TC和TG水平以及发病至PE开始时间为自变量,多元线性回归模型分析显示模型的拟合优度较好(R2=0.807),模型差异有统计学意义(F=75.099,P<0.01),见表8。
3 讨论
高脂血症患者体内TG水平升高会提高血液黏稠度,引起胰腺组织内局部循环障碍,且胰腺内及胰周大量的TG水解产物脂肪酸可以活化胰酶,直接导致胰腺细胞缺血坏死和体内炎症反应爆发,损害胰腺组织功能[12-13]。有研究认为,TG水平控制在5.65 mmol/L以下可延缓急性胰腺炎病情加重[14]。因此,除了阻断全身炎症反应,早期积极调节血脂水平也至关重要。
肝素、降脂药等是临床常用的降脂方法,但往往需要数日才能将血脂恢复正常。PE也是血液净化治疗的一种模式,可将高浓度血脂血浆替换为新鲜血浆,再结合红细胞等成分输回患者体内,可快速降低TG水平,减少TG对胰腺的持续损伤[15-16]。本研究发现,相较于单纯采用CRRT治疗,CRRT联合PE可有效降低患者血清TC、TG、AMY、CRP及PCT水平,减轻患者腹痛、发热和恶心呕吐症状,有利于疾病转归,但两种方法复发率和病死率差异无统计学意义,这与Chen等[17]研究结果一致。分析其原因可能为:相较于单纯CRRT,CRRT联合PE不仅可以持续清除炎症介质,还可积极控制TG水平;当患者血脂水平得到控制后,治疗重心应转移至控制炎症反应、调节容量状态,CRRT可改善患者循环状态,减少PE过程中产生的过敏反应,进一步强化了治疗效果。吴世浪[18]研究显示,早期血浆置换可有效降低高脂血症性急性胰腺炎患者近期(28 d)死亡和远期(12个月)复发风险。与本研究不符,考虑与本研究随访时间(治疗1周)短有关,后续将延长随访时间深入观察。
相关研究表明,治疗前TC、TG和HCT水平及发病至PE开始时间等均会影响血液净化治疗效果[19]。本研究结果亦显示,以治疗72 h后TG下降程度反映疗效,多元线性回归分析发现治疗前TC、TG水平和发病至PE开始时间是影响CRRT联合PE疗效的重要因素。考虑机制为随着病程进展,胰腺内微循环紊乱的持续和大量炎性因子、游离脂质颗粒,仅凭CRRT难以清除,尽早行PE治疗可清除游离脂质颗粒和部分炎性因子,缓解治疗压力。因此,患者基础血脂状态是影响CRRT联合PE疗效的重要因素,发病早期行PE治疗,联合器官功能支持,有助于提高疗效。值得注意的是,PE治疗过程中需要输注大量血浆,可能有发热、过敏等不良事件发生风险,临床应用还需综合考虑治疗费用、血管建立、感染等因素。
综上所述,CRRT联合PE可有效减轻高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者症状,有利于疾病转归,其疗效与治疗前TC、TG水平和发病至PE开始时间有关。
参考文献
[1] VALVERDE-L?PEZ F,MART?NEZ-CARA J G,REDONDO-CEREZO E. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Med Clin(Barc),2022,158(11):556-563. doi:10.1016/j.medcli.2021.12.012.
[2] WANG Y H,XU Z H,ZHOU Y H,et al. The clinical characteristic of biliary-hyperlipidemic etiologically complex type of acute pancreatitis:a retrospective study from a tertiary center in China[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2021,25(3):1462-1471. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202102_24854.
[3] 魏甜甜,张凌,付平. 急性肾损伤肾脏替代治疗的KDIGO与ADQI指南解读[J]. 西部医学,2019,32(1):175-179,184. WEI T T,ZHANG L,FU P. Comparative interpretation of ADQI and KDIGO guidelines for renal replacement therapy in patients with acute kidney injury[J]. Med J West China,2019,32(1):175-179,184.
[4] 陈美如,张丽贤,张莉. 低分子肝素聯合奥曲肽对高脂血症性急性胰腺炎的治疗效果及对患者血脂的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2021,41(24):5547-5551. CHEN M R,ZHANG L X,ZHANG L. Curative effect of low molecular weight heparin combined with octreotide on hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis and its influences on blood lipid[J]. Chin J Gerontol,2021,41(24):5547-5551. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2021.24.021.
[5] ZHENG C B,ZHENG Z H,ZHENG Y P. Therapeutic plasma exchange for hyperlipidemic pancreatitis:current evidence and unmet needs[J]. World J Clin Cases,2021,9(21):5794-5803. doi:10.12998/wjcc.v9.i21.5794.
[6] FOGLIA M J,PELLETIER J H,BAYIR H,et al. Tandem therapeutic plasma exchange reduces continuous renal replacement therapy downtime[J]. Blood Purif,2022,51(6):523-530. doi:10.1159/000518348.
[7] 黎晓磊,孔耀中,肖观清,等. 日间连续性血液净化联合血浆置换治疗非胆源性重症急性胰腺炎的疗效分析[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2019,35(9):670-675. LI X L,KONG Y Z,XIAO G Q,et al. Therapeutic effect of daytime continuous blood purification combined with plasma exchange on non-biliary severe acute pancreatitis [J]. Chin J Nephrol,2019,35(9):670-675. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-7097.2019.09.005.
[8] SCHWARTZ J,PADMANABHAN A,AQUI N,et al. Guidelines on the use of therapeutic apheresis in clinical practice-evidence-based approach from the writing committee of the American society for apheresis:the seventh special issue[J]. J Clin Apher,2016,31(3):149-162. doi:10.1002/jca.21470.
[9] KANDEMIR A,CO?KUN A,YAVA?O?LU ?,et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange for hypertriglyceridemia induced acut pancreatitis: the 33 cases experience from a tertiary reference center in Turkey[J]. Turk J Gastroentero,2018,29(6):676-683. doi:10.5152/tjg.2018.17627.
[10] FEI F,BOSHELL N,WILLIAMS LA 3rd. Predictability and efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange for hypertriglyceridemia induced acute pancreatitis[J]. Transfus Apher Sci,2020,59(2):102699. doi:10.1016/j.transci.2019.102699.
[11] STEFANUTTI C,DI GIACOMO S,VIVENZIO A,et al. Therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with severe hypertriglyceridemia:a multicenter study[J]. Artif Organs,2009,33(12):1096-1102. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1594.2009.00810.x.
[12] 王亚平,赵振,唐莉,等. 血管内皮细胞生长因子诱导自噬致高脂血症性急性胰腺炎大鼠胰腺組织细胞炎症损伤[J]. 生理学报,2022,74(2):225-236. WANG Y P,ZHAO Z,TANG L,et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces inflammatory injury of pancreatic tissue by activating autophagy in hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis rats[J]. Acta Physio Sin,2022,74(2):225-236. doi:10.13294/j.aps.2022.0011.
[13] WU Z,WANG X,JIANG X. Study on the mechanism of probucol nanosuspension on hyperlipidemic pancreatitis and regulation of blood lipid function[J]. J Nanosci Nanotechnol,2021,21(2):1286-1292. doi:10.1166/jnn.2021.18663.
[14] 杨丹丹,刘川,陈昱璨,等. 入院48小时内血清甘油三酯水平对急性胰腺炎并发症的影响[J]. 中华消化杂志,2021,41(10):692-698. YANG D D,LIU C,CHEN Y C,et al. Effects of serum triglyceride level within 48 hours after hospitalization on the complications of acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Dig,2021,41(10):692-698. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn311367-20200522-00342-1.
[15] GUBENSEK J. Potential differences between double-filtration plasmapheresis and therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of acute hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Apher,2021,36(1):223-224. doi:10.1002/jca.21843.
[16] TAN S Y T,TEH S P,KAUSHIK M,et al. Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis in pregnancy:case review on the role of therapeutic plasma exchange[J]. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep,2021,2021:21-0017. doi:10.1530/EDM-21-0017.
[17] CHEN Z,HUANG X,ZHANG M,et al. Rapid reduction in triglyceride levels by therapeutic plasma exchange in patients with hypertriglyceridemic pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Apher,2022,37(1):82-90. doi:10.1002/jca.21954.
[18] 吳世浪. 早期血浆置换对高脂血症性急性胰腺炎患者疗效、预后和远期复发的影响[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗,2019,24(2):186-189. WU S L. Effect of early plasma exchange on efficacy,prognosis and long-term recurrence in patients with hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis [J]. Mod Dig Interv,2019,24(2):186-189. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2019.02.021.
[19] 李梦蝶,许明,史新格,等. 早期血液灌流联合连续性静脉-静脉血液滤过治疗高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎的临床效果观察[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志,2021,28(6):662-667. LI M D,XU M,SHI X G,et al. Clinical observation of early hemoperfusion combined with continuous venous-venous hemofiltration on severe acute pancreatitis with hyperlipidemia [J]. Chin J Integr Tradit Western Med Intensive Crit Care,2021,28(6):662-667. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2021.06.004.
(2022-12-02收稿 2023-04-11修回)
(本文编辑 陆荣展)

