Immune responses of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 functions as a novel biomarker in gastric cancer
Ze-Xuan Fang,Yan-Yu Hou,Zheng Wu,Bing-Xuan Wu,Yu Deng,Hua-Tao Wu,Jing Liu
Abstract BACKGROUND Immune cells play an important role in regulating the behavior of tumor cells.According to emerging evidence,six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (STEAP4) performs a crucial part in tumor microenvironmental immune response and tumorigenesis,and serves as the potential target for cellular and antibody immunotherapy.However,the immunotherapeutic role of STEAP4 in gastric cancer (GC) remains unclear.AIM To investigate the expression of STEAP4 in GC and its relationship with immune infiltrating cells,and explore the potential value of STEAP4 as an immune prognostic indicator in GC.METHODS The expression level of STEAP4 was characterized by immunohistochemistry in tumors and adjacent non-cancerous samples in 96 GC patients.Tumor Immune Estimation Resource was used to study the correlation between STEAP4 and tumor immune infiltration level and immune infiltration gene signature.R package was used to analyze the relationship between STEAP4 expression and immune and stromal scores in GC (GSE62254) by the ESTIMATE algorithm,and Kaplan-Meier Plotter and Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis were applied to analyze the effect of STEAP4 on clinical prognosis.RESULTS Immunohistochemistry analysis showed that STEAP4 expression was higher in GC tissues than in adjacent tissues,and STEAP4 expression was positively correlated with the clinical stage of GC.In GC,the expression of STEAP4 was positively correlated with the infiltration levels of B cells,CD4+T cells,macrophages,neutrophils,and dendritic cells.The expression level of STEAP4 was strongly correlated with most of the immune markers.In addition,STEAP4 expression was inversely correlated with tumor purity,but correlated with stromal score (r=0.43,P < 0.001),immune score (r=0.29,P < 0.001) and estimate score (r=0.39,P < 0.001).Moreover,stromal,immune,and estimate scores were higher in the STEAP4 high expression group,whereas tumor purity was higher in the STEAP4 Low expression group.The relationship between STEAP4 expression and prognosis of patients with GC was further investigated,and the results showed that high STEAP4 expression was associated with poor overall survival and disease-free survival.In addition,Kaplan-Meier Plotter showed that high expression of STEAP4 was significantly correlated with poor survival of patients with GC.CONCLUSION The current findings suggest an oncogenic role for STEAP4 in GC,with significantly high levels being associated with poor prognosis.Investigation of the GC tumor microenvironment suggests the potential function of STEAP4 is connected with the infiltration of diverse immune cells,which may contribute to the regulation of the tumor microenvironment.In conclusion,STEAP4 may serve as a potential therapeutic target for GC to improve the immune infiltration,as well as serve as a prognostic biomarker for judging the prognosis and immune infiltration status of GC.
Key Words: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4;Gastric cancer;Immune infiltration;Prognosis;Biomarker
INTRODUCTION
Gastric cancer (GC),the fifth most common malignant tumor,is the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide[1,2].Although the overall survival (OS) of GC patients has improved with standardized extended (D2)lymphadenectomy and the implementation of chemotherapy and targeted therapy,its survival rate is still less than 30%[3,4].However,recent studies have shown that immune-involved mechanisms play a certain critical role in gastric tumors,and immunotherapy is considered a promising strategy for the therapeutics of gastric tumors[5].In addition,Zhangetal[6] found that tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes can affect the prognosis and efficacy of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in GC patients.Therefore,there is an urgent need to elucidate the mechanism of tumor-immune interaction in GC,and to identify novel prognostic targets for immunotherapy.
Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (STEAP4) consists of an N-terminal oxidoreductase domain and a six-helix transmembrane domain,serving as a transmembrane protein involved in metal reductase transport of copper and iron[7,8].It is reported that high expression of STEAP4 is correlated with the pathogenesis of cancer and metabolic diseases[9-11].STEAP4 is not only involved in the occurrence and development of breast cancer[12,13],but is also related to the inflammatory response of colon cancer[14].It is also found that STEAP4 is highly expressed in prostate cancer tissues,serving as a promising prognostic indicator[15].Nevertheless,the effect of STEAP4 in GC development and the mechanisms involved remain unclear.
In this study,the expression of STEAP4 and its correlation with the prognosis of GC patients are comprehensively analyzed.Moreover,the relevance between STEAP4 and different tumor-infiltrating immune cells and immune cell markers is also examined to clarify the essential role of STEAP4 in GC and provide a potential relationship and mechanism between STEAP4 and tumor-immune interactions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patient information and ethics statement
Tissue array (XT17-037,OUTDO,China) recruited total 96 cases of GC,including 84 pairs of GC tissues and corresponding adjacent tissues,and 12 extra GC samples.This investigation of STEAP4 in GC was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shantou University Medical College.
Immunohistochemical staining
The protocol for immunohistochemical staining was conducted as described previously[16].The primary antibody used was anti-STEAP4 antibody in 1:400 diluent (Proteintech 11944-AP).The sections were visualized and evaluated independently under a bright-field microscope (PerkinElmer Vectra,United States) by two investigators with no prior knowledge of the patient information.The evaluation of STEAP4 expression was based on the sum of the scores from the staining intensities (0-3 indicating colorless,light yellow,brown and dark) and the percentage of positive cells (0-4 for 0%,1% to 25%,26% to 50%,51% to 74%,and 76% to 100%),and the patients were divided into two groups based on the sum score results[17].
STEAP4 mRNA expression in GC
Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/index.html),an interactive network from TCGA and GTEx projects was used to further analyze the expression level of STEAP4,in TCGA expression data,in different clinical stages of GC[18].The survival information of GC patients was also evaluated based on STEAP4 expression in the GEPIA datasets.
Relationship between STEAP4 and infiltrating immune cells in GC
Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) (https://cistrome.shinyapps.io/timer/) is an online dataset for systematic analysis of immune infiltration in various types of cancer[19].The correlation between STEAP4 level and the abundance of infiltrating immune cells was analyzed using gene modules in the database.In addition,the correlation between STEAP4 level and biomarkers of tumor-infiltrating immune cells was also investigated,with scatterplots and Spearman’s value for estimated statistical signifcance.Gene markers of tumor-infiltrating immune cells included CD8+T cells,CD4+T cells,B cells,monocytes,TAMs,M1 macrophages,M2 macrophages,neutrophils,natural killer cells (NK),dendritic cells(DCs),T-helper 1 (Th1) cells,T-helper 2 (Th2) cells,and follicle-helper T (Tfh) cells,T-helper 17 (Th17) cells,Tregs and exhausted T cells[20-22].
Expression of infiltrating immune cells in GC
The “ESTIMATE” algorithm of R package was used to calculate the immune score and stromal score of the GSE62254 dataset (n=300),which was helpful for the evaluation of immune and stromal constitute in tumors.The immune and stromal scores were also calculated by STEAP4 expression in immune and stromal cells in GC.
The prognostic value of STEAP4 in GC
Kaplan-Meier Plotter (http://kmplot.com/analysis/) was applied to analyze the correlation between STEAP4 and survival rate of GC[23].Hazard ratios (HRs) and log-rankPvalues for 95% confidence intervals were calculated simultaneously.
Statistical and survival analysis
SPSS software was used forχ2or Fisher’s exact probability tests to analyze the relationship of STEAP4 level and clinic information of GC patients.To investigate the prognosis of GC patients,the Kaplan-Meier survival curve was conducted,along with log-rank test.Differences were achieved withP< 0.05.
RESULTS
STEAP4 is highly expressed in GC compared with adjacent normal tissues
To investigate the expression profiling of STEAP4 in GC tissues,cancerous tissues and adjacent normal tissues were obtained from GC patients.Representative images of STEAP4 expression are shown in Figure 1.Based on the quantitation of STEAP4 expression levels in GC,a significantly high level of STEAP4 in GC tissues was found,compared with corresponding adjacent normal tissues (P=0.0056) (Table 1).
A high level of STEAP4 tends to contribute to GC progression
The expression level of STEAP4 in 96 GC patients was further analyzed with their clinicopathological parameters(Table 2).Although no statistical significance was found between the expression level of STEAP4 and the clinicopathologic parameters,including age of diagnosis,gender,lymph node status,vascular invasion and clinical stage (P> 0.05),the proportion of patients with high STEAP4 expression tended to increase with the progression of pathological stage,and high STEAP4 expression tended to be associated with lymph node metastasis and vascular invasion,indicating the potential contribution of STEAP4 to the progression of GC.The GEPIA database,regarding mRNA expression,was usedto verify the relationship of STEAP4 with clinical stage of GC.Interestingly,there was no significant difference in the expression of STEAP4 between 4 different clinical stages.However,an increased expression of STEAP4 was found in Stage III and Stage IV,compared with Stage I and Stage II,predicting the potential promoting role of STEAP4 in GC(Figure 2).

Table 1 Comparison of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 levels between gastric cancer and adjacent normal tissues

Table 2 Correlation between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 expression and clinicopathological parameters in gastric cancer patients
STEAP4 is positively correlated with the extent of immune infiltration in GC

Figure 1 Representative images of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 expression in patients with gastric cancer. A:Low expression of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (STEAP4);B: High expression of STEAP4.
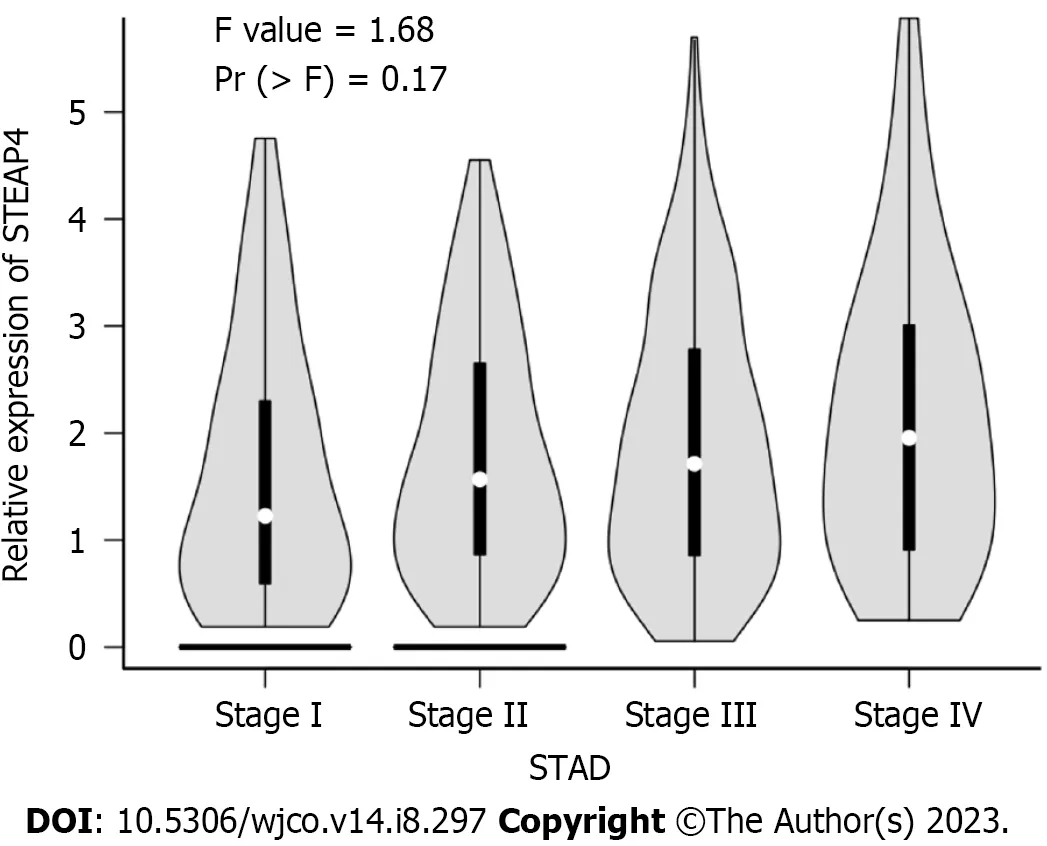
Figure 2 Relationship between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 level and clinical stage of gastric cancer patients.STAD: Stomach adenocarcinoma;STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4.
Considering that tumor purity is an important factor affecting immune infiltration of clinical tumor samples analyzed by genomic approaches[24],it is of interest to investigate the tumor microenvironment-related immune infiltration with STEAP4 levels.Interestingly,STEAP4 expression levels were found to be associated with higher immune infiltration in GC.The level of STEAP4 expression was positively associated with that of immune-infiltrating cells,including B cells,CD4+T cells,neutrophils,macrophages and dendritic cells (Figure 3).
External verification confirms the positive correlation of STEAP4 with immune infiltration in GC
External verification was conducted on the GSE62254 dataset,with 300 GC samples,using the ESTIMATE algorithm in R software.Based on the features,stromal and immune scores were generated to reflect the proportion of stroma and immune cells,respectively,and single sample gene set enrichment analysis was used to combine the two to measure tumor purity.In Figure 4A-D,it is revealed that STEAP4 expression was inversely correlated with tumor purity and stromal score (r=0.43,P< 0.001),immune score (r=0.29,P< 0.001) and ESTIMATE score (r=0.39,P< 0.001).In addition,stromal,immune,and estimate scores all increased with high STEAP4 expression (Figure 4F-H),whereas tumor purity was accompanied by low STEAP4 expression (Figure 4E).
Correlation analysis between STEAP4 expression and immunomarker sets
Due to the positive correlation between STEAP4 and immune infiltration was found in GC,further investigation was conducted to uncover the role of STEAP4 in the development of GC,and specify the subtype of immune cells associated with STEAP4.Diverse immunomarker sets were analyzed in TIMER database to verify the relationship of STEAP4 level with immune-infiltrating cells.After adjustment for purity,STEAP4 expression levels were significantly correlated with most of the immune marker sets of various immune cells and different T cells (Table 3).
Interestingly,the expression levels of gene markers for B cells,monocytes,TAMs,M1 and M2 macrophages and other immune cells were correlated with the expression of STEAP4.Specifically,it was found that the expression level of CD19,B cell CD79A,CD86,monocyte CD115,TAM CCL2 and IL-10,M1 macrophage IRF5 and PTGS2,and M2 macrophage CD163,VSIG4,and MS4A4A were significantly correlated with STEAP4 expression (P< 0.01) (Table 3,Figure 5),suggesting a function of STEAP4 in regulating the infiltration of macrophages during the progression of GC.

Table 3 Correlation analysis between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 and the immunomarkers in gastric cancer
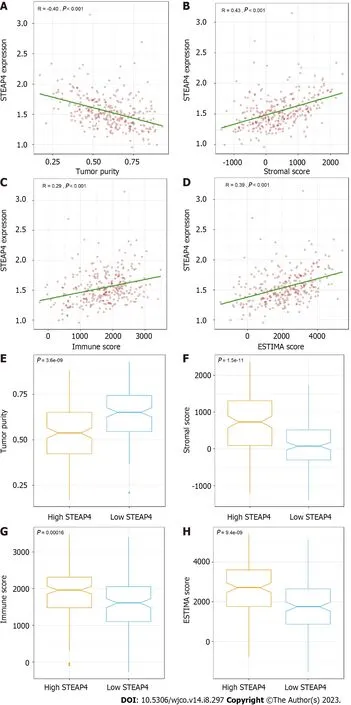
Figure 4 Stromal and immune scores in relation to six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 in gastric cancer. A: Tumor purity;B: Stromal score;C: Immune score;D: ESTIMATE score;E: Tumor purity was higher in the six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (STEAP4) low expression group;F-H: Stromal score,immune score and ESTIMATE score were higher in the STEAP4 high expression group.STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4.

Figure 5 Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 expression correlates with macrophage infiltration in stomach adenocarcinoma (n=415). A-D: Scatter plots of associations between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 and gene markers,including CD86,CSF1R of monocytes (A);CCL2,CD68,and IL10 of TAMs (B);IRF5,PTGS2 of M1 macrophages (C);and CD163,VSIG4,and MS4A4A of M2 macrophages (D).STAD: Stomach adenocarcinoma;TAM: Tumor-associated macrophage;STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4.

Figure 6 The close relationship between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 and dendritic cell and Treg cell infiltration. Scatter plots of associations between six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 and markers,including HLA-DPB1,CD1C,NRP1,and ITGAX of dendritic cells (A);and STAT5B,TGFB1 of Tregs (B).DC: Dendritic cell;Treg: Regulatory T cell;STEAP4: Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4.
DCs promote tumor metastasis by increasing the activity of Treg cells and decreasing the activity of CD8+T cells[25].Here,high expression of STEAP4 was correlated with a high degree of DC infiltration,and DC markers such as HLADPB1,CD1C,NRP1 and ITGAX were also significantly correlated with STEAP4 expression (P< 0.01).In addition,STEAP4 was positively correlated with,that is STAT5B and TGFB1,biomarkers of Treg cells (Table 3,Figure 6),indicating a close relationship between STEAP4 and DC and Treg cell infiltration.However,whether STEAP4 can also mediate DC and tumor metastasis needs further research.
High expression of STEAP4 predicts poor prognosis in patients with GC
Based on the increased level of STEAP4 expression in GC,the prognostic value of STEAP4 was also evaluated on survival rate by using GEPIA database.It is worth noting that the expression of STEAP4 affects prognosis in all GC patients,and patients with high expression of STEAP4 have poor OS (P=0.0015) and disease-free survival (DFS) (P=0.059) (Figure 7A and B).
For immunohistochemical staining of STEAP4,it is showed that STEAP4 expression was not significantly correlated with OS.Although the difference did not meet statistical criteria (P> 0.05),high expression of STEAP4 tended to predict shorter OS in patients with GC,suggesting that STEAP4 protein levels could be used as a predictor of survival in patients with GC (Figure 7C).For further investigation,the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database was also applied to evaluate the prognostic signature of STEAP4.Interestingly,poor prognosis [OS: HR=1.25,95%CI: 1.05-1.48,P=0.01;post-progression survival (PPS): HR=1.8,95%CI: 1.44-2.25,P=1.5e-07;first progression (FP): HR=1.38,95%CI: 1.11-1.70,P=0.003] was correlated with higher STEAP4 expression,suggesting that the level of STEAP4 influences the prognosis of GC patients(Figure 7D-F).
DISCUSSION
It is accepted that STEAP4 is an inflammatory metal reductase to catalyze the reduction of copper and iron,and the oxidation of NADPH.It has been shown that STEAP4 expression can promote the uptake of iron and copper,which can only be transported in reduced form through the cell membrane to exert their effects[9,14,26].Liaoetal[9] recently reported higher levels of cellular copper can enhance and maintain the activation of NF-κB,which leads to the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines,and Zhaoetal[27] found STEAP4-mediated chemokine and cytokine induction enhances recruitment and activation of immune cells.As an important type of malignancy in gastrointestinal tract,GC is significantly associated with inflammatory and immune infiltration,both of which interact with the tumor microenvironment[28].However,the regulatory factors in GC are not well characterized regarding inflammatory and immune infiltration.
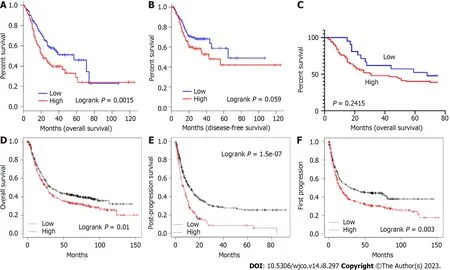
Figure 7 High expression of six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 tends to be associated with poor prognosis in the patients of gastric cancer. A and B: Survival curves of overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival in the Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis database (n=384);C: Survival curves of OS in the tissue chip (n=96);D-F: Survival curves of OS (D),post-progression survival (E),and first progression (F) in the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database (n=875,n=498,and n=640).OS: Overall survival;DFS: Disease-free survival;PPS: Post-progression survival;FP: First progression.
Here,current research focused on STEAP4,a reductase related to oxidation,and its role in the progression of GC.We found that changes in STEAP4 expression levels are associated with the prognosis of GC,predicting poor prognosis of GC patients.Interestingly,high STEAP4 expression had a tendency to promote lymph node metastasis and vascular invasion,proposing STEAP4 as a predictor of tumor metastasis.In addition,we also show that in GC,the level of immune infiltration and multiple immune marker sets are correlated with STEAP4 expression level,and STEAP4 expression is positively correlated with stromal cells and immune cells of the tumor microenvironment.Thus,studies demonstrating the potential role of STEAP4 in tumor immunology and its use as a cancer biomarker provide insight.
In current investigation,we used a GC tissue microarray to determine the expression level of STEAP4 in GC and its adjacent tissues,and prognosis.Based on the immunohistochemical analysis,STEAP4 is highly expressed in GC compared with normal tissues,and is associated with poor prognosis.Although there was a significant correlation between STEAP4 expression and clinicopathological parameters,patients with high STEAP4 expression tended to have a higher pathological stage,lymph node metastasis and vascular invasion.Analysis of the GC cohort in TCGA showed that increased expression of STEP4 is associated with higher clinical stage.Furthermore,analysis of data from GEPIA and Kaplan-Meier Plotter revealed that high levels of STEAP4 expression are associated with high hazard ratios of OS,DFS,PPS,and FP.Together,these findings suggest that STEAP4 may be a prognostic biomarker in GC.
Another important aspect of this study is that STEAP4 expression correlates with different levels of immune infiltration in GC.Our results show a moderate to strong positive correlation between the infiltration levels of M1/M2 macrophages and DCs with STEAP4 expression levels in GC,implicating a potential regulatory function of STEAP4 in tumorassociated macrophage infiltration.Moreover,there is a significant correlation between STEAP4 expression and the regulation of several markers of helper T cells (Trf,Th17,and Treg),and it is known that the recruitment of regulatory T cells (Tregs) is another mechanism of immunosuppression[29].Tumor cells secrete chemokines to attract Tregs and promote tumor angiogenesis[30],indicating that STEAP4 is a potential source for regulating T cell function in GC.
In addition,ESTIMATE algorithm analysis showed that high STEAP4 expression is positively correlated with stromal cells and immune cells.Interestingly,cancer develops in a complex tissue environment,and they rely on this environment for continuous growth,invasion and metastasis.Studies have shown that under the influence of carcinogenic factors,various cells in the tumor microenvironment undergo metabolic changes,which creates favorable conditions for the occurrence and development of tumors[31].Not only immune cells,but also other stromal cells constituting the TME are also involved through metabolic reprogramming.Metabolites of stromal cells and immune cells not only serve as nutrient reservoirs to provide energy sources for tumor growth,but also act as messengers to transmit intercellular signals and participate in a variety of tumor-promoting signaling pathways[32].This may be due to the recruitment of tumor-mediated immune cells by various chemokines secreted by tumor cells through activation of relevant signals in the TME[33].Therefore,these results reveal that STEAP4 is specifically associated with immune-infiltrating cells,suggesting that STEAP4 plays a role in immune escape in the microenvironment of GC.
CONCLUSION
The present study found that STEAP4 is a cancer-promoting factor in GC and can be used as a prognostic indicator in GC patients.GC patients with high expression of STEAP4 have a shorter survival time,and may play an important role in immune cell infiltration in GC patients,as well as serve as a prognostic biomarker.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 4 (STEAP4),a transmembrane protein involved in metal reductase transport of copper and iron,has been reported as a potential target for cellular and antibody immunotherapy.
Research motivation
Few studies on STEAP4 in gastric cancer (GC),which may play a role in the immune response to the occurrence and development of GC.
Research objectives
The expression of STEAP4 in GC tissues and its correlation with the level of tumor immune infiltration were comprehensively analyzed and to explore the potential immune effect of STEAP4 in GC.
Research methods
The protein expression level,clinicopathological parameters and prognosis of STEAP4 in tumor and adjacent tissues of GC patients were detected by immunohistochemistry.An online database was used to study the correlation between STEAP4 and the level of tumor immunoinfiltration and the characteristics of immunoinfiltration genes.The relationship between STEAP4 expression and immune and stromal scores in the GC was analyzed by ESTIMATE algorithm.
Research results
Immunohistochemistry analysis showed that STEAP4 was highly expressed in GC and was positively correlated with the clinical stage of GC.The infiltration levels of immune cells such as B cells,CD4+T cells,macrophages,neutrophils and dendritic cells were positively correlated with STEAP4.The expression level of STEAP4 was strongly correlated with most of the immune markers.In addition,the ESTIMATED algorithm analysis showed that the stromal,immune and estimated scores were higher in the group with high expression of STEAP4,while the tumor purity was higher in the STEAP4 Low expression group.The relationship between STEAP4 expression and prognosis of GC patients was further studied,and the results showed that high STEAP4 expression had shorter overall survival and disease-free survival.Moreover,Kaplan-Meier Plotter showed that high expression of STEAP4 was associated with poor survival in patients with GC.
Research conclusions
STEAP4 is indicated as a potential immune indicator of GC,targeting STEAP4 may provide a new therapeutic method for GC patients.
Research perspectives
The comprehensive analysis of STEAP4 function in GC still needs to explore the mechanism by which STEAP4 plays an immune role in GC.
FOOTNOTES
Author contributions:Liu J and Fang ZX designed the research study;Fang ZX performed the research;Fang ZX,Hou YY,Wu Z,Wu BX,Deng Y,and Wu HT analyzed the research and wrote the manuscript;Liu J revised the manuscript critically;and all authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Supported bythe National Natural Science Foundation of China,No.82273457 and No.81 501539;Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation,No.2023A1515012762 and No.2021A1515 012180;Special Grant for Key Area Programs of Guangdong Department of Education,No.2021ZDZX2040;and Science and Technology Special Project of Guangdong Province,No.210715216902829.
Institutional review board statement:The current study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shantou University Medical College (Approval No.SUMC-2022-075).
Informed consent statement:The informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee because our experiment was conducted on commercial microarray.
Conflict-of-interest statement:All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Data sharing statement:No additional data are available.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORCID number:Ze-Xuan Fang 0000-0002-6100-9012;Yan-Yu Hou 0000-0002-4249-8770;Zheng Wu 0000-0002-1393-7586;Bing-Xuan Wu 0000-0002-1212-7936;Yu Deng 0000-0002-0950-6169;Hua-Tao Wu 0000-0002-1640-6094;Jing Liu 0000-0002-7483-4572.
S-Editor:Chen YL
L-Editor:A
P-Editor:Zhang XD

