An Overview of Government-Market Relationships: Evolving Perceptions,Role of the Market, and Government Functions
Li Xiang and Tang Yong
Sichuan University
Abstract: Building a high-level socialist market economy is conducive to giving full play to the market’s decisive role in resource allocations and bringing the government into better play.Correctly handling the market and the government relationships has been a central issue in China’s economic structural reform.Giving a comprehensive review and summary of the research findings achieved by the theoretical and academic circles in China,we generalize the evolution and working mechanisms of China’s socialist market economy system, following the developing trajectory and logic of relevant literature, focusing on the three aspects of evolving perceptions,the role of the market, and the functions of the government.Based on our literature overview, we also induced and extracted the basic conclusions and evolutionary features of relevant research and made suggestions for the future direction of theoretical research regarding China’s socialist market economy.
Keywords: socialist market economy system, evolving perceptions, the role of the market, government functions
The theory of a socialist market economy is a major theoretical innovation in adapting Marxist political economy to Chinese conditions.It has guided our economic development and is an important foundation for achieving social harmony, safeguarding fairness and justice,maintaining long-term and steady economic development, and bringing prosperity to all (Jiang& Li, 2019).Since its reform and opening up was launched, China, in light of its actual national conditions and development stage, has creatively proposed to develop a market economy under socialist conditions and has established a vibrant socialist market economy system, which has led to the liberation and rapid development of productive forces (Li et al., 2022).In this process,the Chinese academic circle has conducted extensive research on the relationships between the government and the market which is the core issue of a socialist market economy, and which has yielded numerous results.
Evolving Perceptions of the Government-Market Relationships: Views by Authors of Marxist Classics
To deeply understand the relationships between the government and the market, one must explain, from the perspective of the development history of Marxism, why it is historically inevitable that socialism would be integrated with a market economy and ascertain the inherent law from theoretical arguments.In the historical process of socialist revolution and construction,authors of Marxist classics have developed views on the government-market relation that are consistent but each with distinctive features, and have drawn many conclusions that can guide our actions with sustaining relevance.
Interpretations of Relevant Perceptions by Marx and Engels
The development history of market socialism is an indispensable and critical part of the world history of socialist thought.In economic development, productive forces must be matched with the relations of production.Marx and Engels both discussed the roles of, and the relationships between the market and the government in their books, correspondences, and remarks, which have laid the foundation for their theoretical system of a socialist market economy and provided the sources, from which socialist countries can develop their theories of a socialist market economy.This research has paved the way for theoretical innovations in government-market relationships.
Marx and Engels’ views on market-government relationships can be generalized into four points.
First, in capitalist production relationships, all actions by economic entities are decided by the market, which regulates and determines the production, exchange, supply, and demand of goods and serves as the medium for realizing value.The essence of exchange reflects the market relationships.Marx and Engels’ theories of the market are contained in their comprehensive analysis of goods, currency, value, capital, and many other factors, as well as in their criticalreflection on the laws governing the development of capitalism.
Second, the market is “the sum total of all the mutual relationships of commodity-owners.”The exchange takes place in the market, which is the physical space for circulation—one defining feature of the market.When the seller and the buyer exchange their commodities in the market,their economic relationships are reflected through the relationships between their commodities, so the market is a sum total of the exchange relations—this is another defining feature of the market.
Third, Marx and Engels’ insight into the market is also conveyed in their remarks regarding the cycle and turnover of capital and the reproduction and circulation of total social capital.The market plays an unusually active part in regulating social reproduction, regulating production and circulation, and distribution among various sectors of the national economy.
Fourth, their market theories have two dimensions—time and space.The former is manifested in the existence and realization of time during the circulation of commodities and the historical process of social development under a certain production relationship.At the same time, the latter is reflected in the spatial occupation of the capital, the spatial unity of the market, and the spatial variation caused by limitations.
Academic research in China on Marx and Engels’ remarks on the market and the government focuses on the following three aspects, laying a solid foundation for theoretical innovations in the government-market relationships.
The first focus is on Marx and Engels’ remarks about the role of the market.In theory,theoretical studies generally hold that the market is where the exchange of commodities takes place, and the consistency between the price and the value of a commodity depends on the planning by commodity producers or the socialist country (Liu, 1992).Marx’s thoughts laid the theoretical foundation for effective management under a socialist market economy.As a way of common human activity and exchange, the commodity economy is matched with a social relationship characterized by human independence based on dependence on things.It is both a denial of human dependence in an economy and a historical stage that cannot be avoided on the way to individuality (Wang, 1995).A market economy emerges when the market engages in the activities of a commodity economy comprehensively, both in breadth and depth.
Marx and Engels revealed the historical trend that a commodity economy would perish eventually and the objective law that a product economy would replace it.Their theories of the market can be summarized into five points: the market is essentially a social and historical concept; the market exists as a physical form of a commodity economy and a market economy; the market structure reflects the scale, structure, and layout of a commodity economy and a market economy; the market functions to enable the operation of a commodity economy and a market economy; and the history of market theories is a comment on theories created by preceding scholars (Song, 2016).Marx and Engels also defined the government-market relationships as the relationships between the country and the market, whose nature is decided by that of the country and the ownership (Liu, 2020).
In practice, when developing a market, we should focus on fostering market entities, improving the market system and mechanisms, and establishing a proper order, with considerations for eight aspects—origin, types, radius, capacities, operating mechanisms, roles and operating patterns of the market, and limitations of the market mechanisms (Ding, 1993).In the broad sense, a market economy is the product of social divisions of work, the existence of the latter ensuring the former.Moreover, when integrated with public ownership, a market economy would take on public characteristics (Zhuo, 1998).In a market economy, the distribution of interests and allocation of resources are both regulated by value, and China’s reform efforts to build a market economy will create conditions for that (Zhang, 2004).
The second focus is on Marx and Engels’ remarks regarding the functions of the government.Research in this area generally stresses the Marxist view on government functions—the political function aimed at control and the administrative function aimed at economic and social development (Tian, 1984).Some researchers have questioned the inappropriate elements in this view, arguing that the traditional class theory regarding government functions is no longer suitable for the changed reality and that government functions should adapt according to the tasks and situations in different periods.Other researchers have held that “dichotomy” remains the fundamental principle for defining and transforming government functions (Rong, 1986).
As “dichotomy” is on the macro level and current discussions on the “transformation of government functions” are becoming increasingly specific, Marx and Engels’ theories have rarely been applied in research on government functions.Some researchers have instead drawn nourishment from other theoretical findings to enrich the theories of government functions in a socialist market economy.We must think about the goals of the country and the nation,adhering to the Marxist position and the methodology of historical materialism, and balance“what ought to be” and “what is.” We should not only consider what kind of model is needed but,more importantly, transcend the government-market dichotomy (Hu, 2005).What role does the government play in a market economy? According to Marx, the division of interests necessitates the role of the country or government, whose functions tend to expand with economic and social development and whose role must involve economic development to promote it (Shi, 2014).The Marxist theory of government functions features people-oriented values and twofold contents.Regarding the relationships between the government and society, it emphasizes the decisive effect of civil society.It advocates optimizing the government’s economic functions and scientifically allocating the duties among state organs.
The third focus is on Marx and Engels’ remarks regarding the allocation of resources.Marx explained the allocation of resources with the concept of social labor—resource allocation is an objective requirement of social production and a general law governing social and economic development.Social production requires that all social labor be proportionally allocated among different productive sectors across society (Wang, 1995).Marx and Engels assumed that a commodity economy would not be repelled in the early stage of socialism and proved that animportant reason for the emergence, development, and existence of a commodity exchange was the emergence and development of the social division of labor and private ownership.In the early stage of socialism, when economic entities of various forms coexist, the best way to form economic connections is through a commodity currency.
The Marxist theories of resource allocation encompass a wide range of contents, such as the theory of the regulating mechanisms, the approach to resource allocations, the composition of production factors, the circulation of production factors as industrial capital, the relationships between microeconomic activities and macroeconomic operations, the laws governing macroeconomic operations, and the effect of business on resource allocations in society.These theories are characterized by the unity between the description of economic phenomena and analysis of their essence, between the study of the approach of resource allocations and the way of social production, between analysis of the aggregate and the structure, and between analysis of value and substance (Wang, 2004).As productive relationships are the factor that directly decides the socioeconomic operation, organization, and structure, Marxist political economics analyzing the productive relationships is significant in that it reveals the laws governing economic activities.Given the means of connections and the nature of social labor, there are three resource allocation approaches—direct allocation, market-based allocation, and planned allocation.The socialist economy is still a commodity economy (Guo & Kang, 2017).
Interpretation of Relevant Perceptions in Chinese Theoretical Circles
Correctly understanding and handling the relationships between socialism and a market economy is an important reason why China’s reform and opening up has achieved great success.While developing the basic principles of Marxism, the Chinese theoretical circles have formed a series of consistent views and ideas and have come to many convincing conclusions that can guide our actions.We searched “socialist market economy” on the CNKI platform, which returned 26,066 articles collected in the overview of Chinese periodicals compiled by Peking University Press and in CSSCI through November 1, 2022, involving twelve research levels.Their research mainly involves topics relevant to the market economy, commodity economy, distribution according to work, credit system, macro regulation, labor, social equity, and related others (Figure 1).This section will elaborate on how the Chinese theoretical circle understands the governmentmarket relationships in two parts—the evolving perception during reform and opening up and the new era of the socialist modernization drive, and the evolving perception in the new era of socialism with Chinese characteristics.A systemic review is also made of relevant perceptions and remarks.
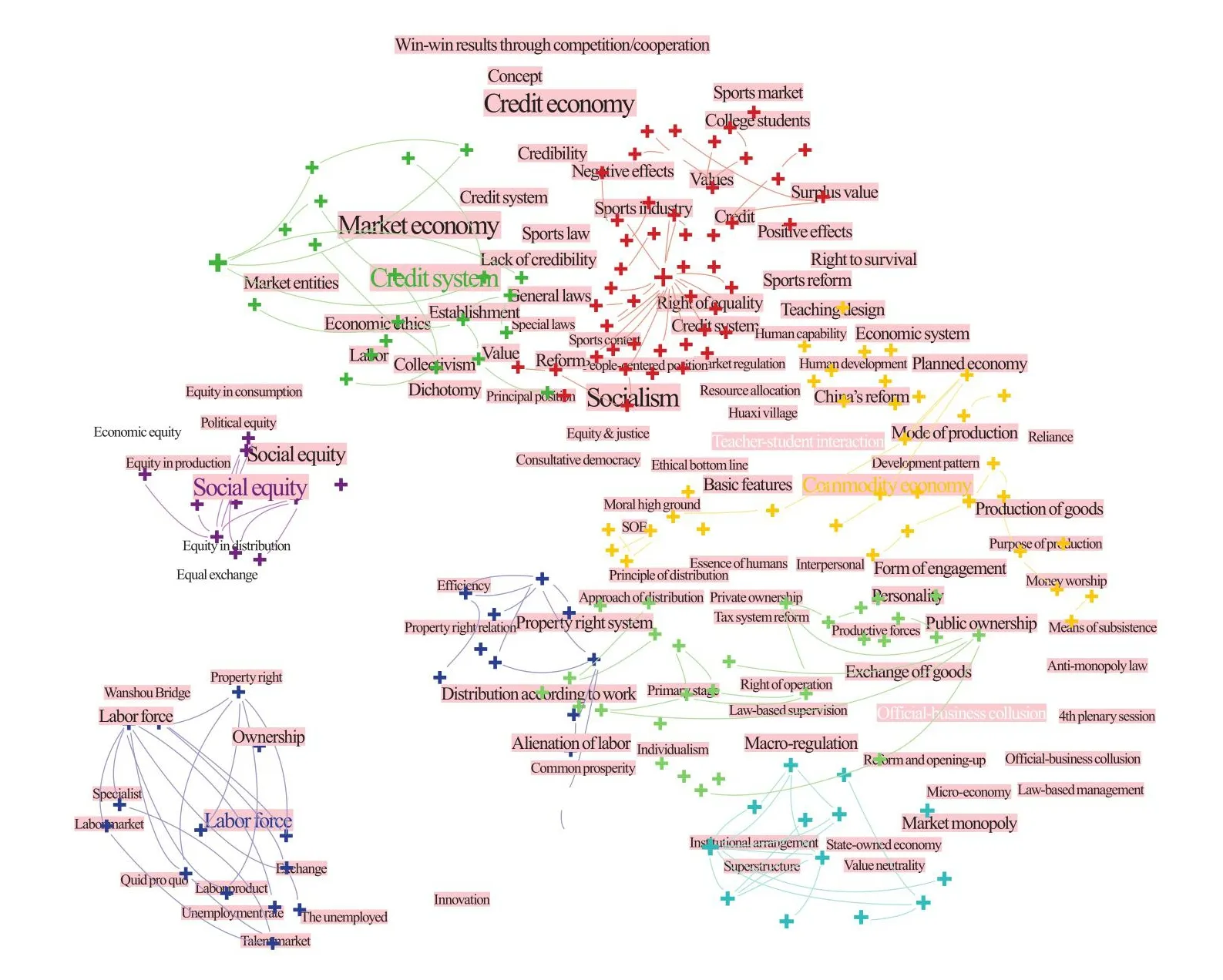
Figure 1 A citespace clustergram of high-frequency keywords in the study of socialist market economy Source of diagram: Citespace v6.1.2
Evolving Perceptions During Reform and Opening Up and the New Era of the Socialist Modernization Drive
Regarding the evolution of policies, Deng Xiaoping theoretically elaborated on the market economy.“It is wrong to maintain that a market economy exists only in capitalist societies andthat there is only one type of ‘capitalist’ market economy…We cannot say that a market economy exists only under capitalism.A market economy was in its embryonic stages as early as feudalist societies.We can surely develop it under socialism.”①Selected Works of Deng Xiaoping (Vol.II) (Beijing: People’s Publishing House, 1994), 236.His remarks emancipated people’s minds,introduced the idea that socialism and a market economy were not necessarily independent of each other, and promoted the development of socialist market economy theories.
The sixth plenary session of the 11th CPC Central Committee proposed to take a planned economy as the main approach and assist it with market regulations, and following the idea that we must develop the economy by respecting and taking advantage of the value laws became a consensus across society.The third plenary session of the 12th CPC Central Committee decided to develop a planned commodity economy, which broke away from the traditional perception that a planned economy and a commodity economy were independent of each other.It pointed out that a planned economy meant a planned commodity economy based on public ownership,and the full development of a commodity economy was an unavoidable stage in socioeconomic development (Jiang, 1998).The 13th CPC National Congress clarified that the system of a socialistplanned commodity economy should be one in which planning and the market are integrated in unity.①Collection of Important Literature Since the 13th CPC National Congress (Vol.I) (Beijing: People’s Publishing House, 1991), 26.The third plenary session of the 13th CPC Central Committee adopted the guidelines for improving the economic environment, defining the economic order, and comprehensively deepening the reform.The fourth plenary session determined the goals of the reform to establish a socialist market economy and its basic framework,②Brief History of the Communist Party of China (Beijing: People’s Publishing House, Party History Publishing House, 2021), 529.and the seventh plenary session announced the decision to establish an economic mechanism in which the planned economy and the market regulations functioned in coordination.
The 14th CPC National Congress officially affirmed that the goal of the economic system reform in China is to establish a socialist market economy,③Memorabilia of the Communist Party of China in the Past 100 Years (Beijing: People’s Publishing House, 2021), 139.which indicated our deepened understanding of the government-market relationships.The 15th CPC National Congress decided to let the market play a basic role in the allocation of resources under macro regulation and defined more clearly the market’s and the government’s functions.The fifth plenary session of the 15th CPC Central Committee declared that a socialist market economy had been primarily established in China.The 16th CPC National Congress proposed to give greater play to the market’s basic role in the allocation of resources.④Collection of Important Literature Since the 18th CPC National Congress (Vol.I) (Beijing: Central Party Literature Press, 2014), 499.The third plenary session of the 16th CPC Central Committee passed theDecisions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Some Issues Concerning the Improvement of the Socialist Market Economy, indicating that the reform had gone beyond the economic domain.The 17th CPC National Congress vowed to make institutional arrangements to give better play to the market’s basic role in the allocation of resources.
Evolving Perception in the New Era of Socialism With Chinese Characteristics
In terms of policy evolution, since the 18th CPC National Congress, Xi Jinping, general secretary of the CPC Central Committee has attached great importance to the relationships between the government and the market and formed a series of important theories that suit China’s national conditions and the context of the times.The 18th CPC National Congress pointed out, “We should leverage to a greater extent and in a wider scope the basic role of the market in allocating resources,” and the third plenary session of the 18th CPC Central Committee replaced the market’s “basic role” with a “decisive role,” a change of epochal significance.The 19th CPC National Congress stressed that we must see that the market plays the decisive role in resource allocations and the government plays its role better, while the 20th CPC National Congress placed“continue reforms to develop the socialist market economy” in a prominent position.In the new era of building a modern socialist country in all respects, achieving good government-market relationships means we must properly answer the following question, “Does the market or the government play the decisive role in resource allocation?” We should truly let the market playthe decisive role in resource allocation①Xi Jinping: The Governance of China (Vol.IV) (Beijing: Foreign Languages Press, 2022), 168.and transform the pattern of economic development and government functions.
Overview of Academic Literature on the Role of the Market
The socialist market economy is neither an imitation of the Western capitalist market economy nor a simple addition of socialism to a market economy.Rather, it is a systematic restructuring and reorganization of the mechanisms and institutions and a new road of development blazed by China through reform and opening up.Better government-market relationships and a clearer understanding of the market’s role under a socialist market economy are of great importance for comprehensively deepening the reform and building a strong modern socialist country in all respects.At present, Chinese scholars are of four views regarding the market’s role in a socialist market economy—it plays a decisive role, a neutral role, an instrumental role, and a microscopic role.
The Market Plays the Decisive Role
The core issue in the economic system reform is properly handling the relationships between the government and the market.Since the 18th CPC National Congress, more attention has been paid to respecting market laws and better exerting the government’s role in reforming the economic system.The academic circle has also gained a deeper understanding of the market’s decisive role in resource allocations.
The market deciding the allocation of resources is a general law in a market economy and an institutional requirement for realizing economic growth in modern times.The market’s autonomous regulation of price and production and the effect of free competition provide the most efficient and vibrant mechanisms for economic operation and means of resource allocation.Wu Jinlian (2014) emphasized five conditions for the market to play a decisive role—unity, openness,competition, order, and a market system.Zhang Zeyi (2014) demonstrated the market’s “decisive role” in industrial restructuring, as stated in theCapital, on three dimensions—the market competition is the decisive force in industrial restructuring, division of labor and coordination promote the upgrade from manufacturing to modern mechanized industry, and industrial and technological upgrade results from the technological progress of numerous competing enterprises.Clearly, admitting and leveraging the market’s decisive role in resource allocation is inevitable,given the basic laws of a market economy, and imperative to give better play to the government’s role.Having the market play a decisive role in resource allocation is essential to minimize the government’s effect while strengthening the market’s effect (Qiao, 2014).
Generally, resource allocation is defined as the combination of the three factors of labor;specifically, it means how the means of production and labor are combined in different societies,reflecting each society’s nature (Wang, 2015).Economically, reforming the planned economic system is to improve its low efficiency; philosophically, the reform reflects the flaw of empirical philosophy, which upholds objectivism, of seeing the world as a permanent, unchanging entity.The essence of Marxist philosophy is practical, and the perception that the market plays a decisive role embodies a practical philosophy’s core spirit and requirements (Li, 2016).The perception of the market’s role has evolved through three shifts—from total denial to admitting its auxiliary,from an auxiliary role to a primary role, and from a primary role to a decisive role.With the change of times and conditions, the market has assumed an ever more important position and effect—from the stage of survival to the stage of development, from the prominence of investment to the prominence of consumption, and from focusing on traditional industries to focusing on Internet Plus development (Su, 2016).It is with its deepening understanding that the academic circle has gradually recognized the market’s decisive role in the allocation of resources, and this indicates that we must take the initiative while observing the laws of value.
The Market Plays a Neutral Role
TheModern Chinese Dictionarydefines “neutrality” as a property that is neither acid nor alkaline, different fromYinorYang, and irrelevant to praise or criticism—it is an intermediate where confrontation, opposition, or repulsion does not exist.The academic circle has three types of views on whether the market is neutral under a socialist market economy.
Some researchers believe the market is neutral but do not deny its special social attributes.The concept of a market economy is below the concept of productive forces but above the concept of productive relationships.The development from the commonness of a market economy to the neutrality of a market economy reflects a deepened understanding of this concept.To understand the market’s neutrality, we must consider four aspects: (a) Defining the nature of a market economy; (b) Apprehending the structure of the basic contradiction in the economic domain with the three factors of social production; (c) Discussing the intermediary role of a market economy in the contradiction between productive forces and production relationships based on its intermediary position; and (d) Revealing the source of strength for emancipating and developing productive forces and perfecting socialist production relationships based on the intermediary position of a market economy (Yang, 1994).Moreover, Deng Xiaping’s talks during his tour in southern China established, on a theoretical level, the new viewpoint of “neutral planning” and “neutral market,”which paved the way for recognizing the market’s primary role in resource allocation (Gu, 1994).Regarding the market as neutral does not deny the special properties of the capitalist market.The“market” is just a community of economic exchanges.Its neutrality and instrumentality imply the possibility of a “socialist market” (Di, 2005).
Other researchers take the market as a dialectical unity of commonness and peculiarity.The market economy is characterized by its inherent contradictions, which decide that it is amarket-oriented way of allocating resources and regulating economic operations, being capable of selecting the fittest through competition, evaluating value, maximizing interests, and many other things in addition to the functions mentioned above.Wu Shuqing (2004) argued that a market economy should be regarded as a mere method and means of economic organization, and planning, a planned economy, and planned regulation as synonyms of the market, the market economy, and market-based regulation.That would fundamentally emancipate our minds from the old perception of a planned economy and a market economy as representing basic social systems.Some researchers point out that the market is neutral because it is a common economic phenomenon in various social forms with some common features and properties.In the meantime,it is not completely neutral because it always exists in a specific social and historical environment,is always associated with a specific social system, and has its social properties.Therefore, the market is a dialectical unity of commonness and peculiarity (Zhang, 2016).The nature of a planned and market economy depends on which social system they are associated with.The market is a concept of dialectical unity—it is socialist when combined with a socialist system(Zhou, 2020).
Some researchers oppose the “neutrality” theory and hold its basis and purpose to be wrong.According to this group, to say that a market economy is neutral is erroneous in a theoretical expression and misleading in practice.It creates a pattern of research involving one’s subjective will when defining a scope, overlooks the peculiarity of a market economy when associated with a certain social system, and neglects the importance of the basic socialist economic system and its Chinese characteristics (Gu, 1993).In a market economy, the rising capital income and falling labor income are accompanied by a loss of balance in the structure of investment and consumption, which is detrimental to expanding the domestic demand and transforming the economic structure.We must pay enough attention to the role of the market economy.Ownership cannot be “neutral.” To say ownership is neutral negates its connotations and characteristics and contravenes the basic principles of Marxist political economics.That “competition is neutral”does not lead to the conclusion that “ownership is neutral” or “a market economy is neutral” (Jian,2019).
The Market Plays an Instrumental Role
The academic circle has long discussed the instrumentality of the market.In this process, it has moved from the view that “the market economy is essentially instrumental” to the view that“the market is instrumental in every sense.”
On the one hand, the idea of taking the market as an instrument can date back to the comparative economic systems in the 1970s, when Eckstein (1971), Bell (1971), Lindblom(1977), Gregory (1985), and other scholars regarded the market and planning as just an“instrument” and a “means” of resource allocation (Lindblom, 1975).DiQuattro (1975) held that socialism’s basic principles do not contradict a market economy.The development ofcomparative economics and socialist economic theories has led to breakthroughs in marketoriented socialism.Willy Kraus pointed out in hisSocial Market Economythat the core of a market economy is a form of the economic process.It functions as an instrument—being a means of accounting or operation and a flexible coordinating and calculating system.The domestic academic circle has produced a growing body of research supporting this view,which, however, has never been recognized as mainstream.Being an instrument in nature, a market economy needs to be complemented by economic policies adapting to market trends,effective competition, social security systems, and macroeconomic regulation systems (Huang et al., 1998).The common features of a market economy under different social systems attest to its instrumentality, which means economic activities are market-based, enterprises operate independently, macro regulation is indirect, economic order is based on the law, and social security is provided (Zhang, 2011).Both a socialist and a capitalist market economy are modern market economies, so they are both “instrumental,” which refers to market-based economic relations, independent actions of enterprises, indirect macro control, and law-based economic operations (Cao & Ding, 2015).
On the other hand, the market is regarded as “instrumental in every sense.” He Liping(2000) argued that the instrumental functions of a market economy, if being used to express the essential nature of a market economy, fail to reach the true depth.It is simply wrong to understand the nature of a market economy with its externalities of functions and operating mechanisms.That implies the neglect of the inevitability of a market economy and the magnification of man’s subjective behaviors.The socialist market economy both assumes the basic features of a market economy and reflects the nature of the socialist system.In terms of macro control, it is aimed at realizing the interests of the broadest majority of the working people, gives better play to the strengths of planning and the market, and narrows the differences in the factors of distribution, especially of property and knowledge, owned by different groups, through the market approach (Hong, 2015).In Miliband’s instrumentalist theory of the state, his theory of the government-market relationship is not only an“instrumentalist” explanation but also conveys the thinking on the historical destiny of the working class and socialism (Fang, 2019).How the market exerts its role under the socialist economic system has been demonstrated by some researchers from three perspectives—the public ownership of the means of production is the core of a socialist economic system, the generality of a market economy and the conditions for the market to take effect, and how the socialist public ownership guarantees the effectiveness of the market (Zhang, 2021).
The Market Plays a Role on the Micro Level
Scholars who stand for the market’s microscopic role generally believe its decisive role in resource allocation is mainly demonstrated in the microeconomic domain.In contrast, in the macroeconomic domain, the government needs to make up for the market’s defects and flawsthrough macro-regulation and administration.What is most essential about the socialist market economy is that the public sector of the economy, with support from the CPC and the government,dominates the macro-national market.The socialist market relationships restrict the capitalist market relationships and offset capitalist distortion (Ma, 2014).In a market economy, the market is the bond that connects the main economic relations and the various behaviors of transactions.The transactions among market entities trigger the flow of commodities, services, factors of production, and other objects and promote market operations on the micro level (Du, 2014).The allocation of resources aims at equity and efficiency, with the government and the market as the two major approaches, whose coordinated functioning is the only way to optimize the allocation of resources.
At the same time, some scholars analyzed the different levels and domains where the market takes effect on the micro level.The scope in which the market plays its part is decided by six factors—transaction fee, dedicated use of assets, externality, public use of things, cost of internal management, and monopolistic profits.The market system is suitable when the use of assets is barely dedicated, properties are barely for public use, and transactions are small in scale; it is transitional when the dedicated use of assets, public use of properties, and transaction scale are all on a medium level (Luo, 2000).On the micro level, resource allocation occurs among different market entities.Here the laws of value play a “decisive” role through the change of supply, demand, and competition.On the macro level, which refers to the overall balance of supply and demand, the sectoral and regional proportion and structure, the fair distribution of social resources, and so on, government administration is needed to rectify and complement market behaviors (Liu, 2014).The market playing a decisive role means it does not function under government command but decides resource allocations autonomously.That, however, does not mean a free market would bring a high-efficiency allocation (Hong, 2014).The market’s decisive role is only effective in a certain scope, and it is necessary for the government to compensate for its deficiencies by means of macro regulation and administration.Moreover, although the market plays a decisive role, there are other factors at work.In some special areas on the macro level, we cannot rely on the market to regulate resource allocations, as a distorted market of production factors and products would cause misallocations (Yin & Zhang, 2021).
Overview of Academic Literature on Government Functions
In a socialist market economy, the government is more than just an important political organization.It is, at the same time, a key organization of macroeconomic regulations performing such main duties as economic regulation, market supervision, social administration, public service, and administration of state-owned assets.In discharging its duties, the government must take into consideration all entities’ interests and stimulate their initiative.Regarding the government’s functions under a socialist market economy, two views are prevalent in theChinese academic circle today—the government is well-functioning, and the government is complementary.
The Government Is Well-Functioning
The socialist market economy with Chinese characteristics combines a well-functioning government and an effective market.Thanks to this combination, China has made tremendous achievements in such areas as economic and social development, improvement of livelihoods,and enhancement of national strength.The theories of a socialist market economy, breaking away from the framework of the mainstream economics of the West, have revealed, from an economic point of view, the secret to China’s economic miracles and added new materials to the development of the relevant theoretical system (Chen, 2019).
Part of the research findings focus on how to build a “well-functioning government” and how this government promotes economic growth.It is generally believed that under an advanced socialist market economy, the combination of an effective market and a well-functioning government will, at a higher starting point, on a higher level and guided by higher goals, further improve the economic institution as a foundation for achieving great national rejuvenation (Ren& Zhao, 2021).Some scholars have studied how a well-functioning government affects economic development in the following dimensions—development strategy, industrial and trade policy,market system, public investment and construction, and others.The government adopts policies to change the development environment and consequently upgrade the use and development of relevant factors (Hu et al., 2011).A well-functioning government is the basic requirement of a socialist market economy and democracy.We urgently need to change the thinking of the government and the people and promote the integration of government-market relationships and society-citizen relationships to meet public expectations (Shi, 2013).Fostering an effective market requires the correct interference from a responsible government, which should guide the market accordingly based on the country’s comparative advantages (Lin, 2020).
On the other hand, some research findings focus on the importance of a “well-functioning government.” They generally hold that the combination of a responsible government and an effective market demonstrates the institutional strengths of socialism with Chinese characteristics,and the government (playing the core role) and the market (playing a key role) support and complement each other (Wang & Fan, 2021).Most developing countries fail to handle the government-market relationships well when formulating development and transformational policies.Therefore, they have found themselves stuck in the low-income or middle-income trap.In contrast, China has made good use of both the visible and invisible hands in its economic development and transformation and succeeded in coordinating the market’s and government’s roles and having them promote each other (Lin, 2017).Although a well-functioning government has an active role in guiding the entrepreneurs’ behaviors and allocating their resources, it finally needs an effective market to take effect.As a result, the market mechanisms and governmentadministration can achieve common advancement through complementarity.When the public sector is the mainstay of the economy, a well-functioning government is needed to conduct effective operations and management of public assets to maintain and increase their value.
The Government Is Complementary
Some researchers argue that the government is not a “night watcher” in a socialist market economy but should make up for market malfunctions and overcome the market’s defects.To do that, the government needs to perform its economic functions.Market malfunctions are manifested in five ways—monopolistic malfunction, external effect, provision of public goods,unemployment, inflation, economic imbalance, and income distribution.To address them, the government should fully increase social equity by harnessing unemployment, inflation, and economic imbalance (Peng, 2011).Market defects are a generalization that refers to all kinds of situations when the market cannot effectively play its role in allocating resources, distributing income, and stabilizing the economy—in other words—when the market mechanisms cause the misallocation of resources or the waste of productive factors (Zhang & Jia, 2003).These defects make appropriate government interference indispensable for the market economy to establish and operate properly.That means the government needs to set reasonable goals for macro-regulations,select the right way, scientifically define its economic duties, and determine the basic approaches to performing those duties (Liu & Xu, 2008).The theory of a socialist market economy integrates socialism as a social system with a market economy as a mechanism of resource allocation.This combination gives birth to new institutional strengths, makes up for market defects, and improves government functions.
Summary and Outlook
As the academic research on government-market relationships goes deeper and relevant practices continue to progress and innovate under theoretical guidance, the research findings on these relationships have continued to evolve.There are numerous categories of research in this field.Researchers, considering China’s national conditions and the requirements of the times,have creatively developed a theoretical system for a socialist market economy with Chinese characteristics.More importantly, they have cumulated valuable experience in the exploratory efforts of theoretical applications, institutional developments, and deepened reforms.The main purpose of giving a literature overview of the government-market relationships is to guide our policymaking and reforms in the future based on drawing on international practices.
Summary of the Research on Government-Market Relationships
The theory of a socialist market economy is an important component of the socialist system with Chinese characteristics.Proper handling of the relationships between the government andthe market is the centerline of the economic system reform in the primary stage of socialism.Academic research on government-market relationships has yielded many results with three characteristics.
First, they adhere to the people-centered position and promote deepening understanding.Whether the government-market relationships are handled well concerns the future direction of reform and development and the immediate interests of the people.As we adapt the Marxist theories to the market and the government in a Chinese context, the theoretical and academic circles, always respecting the people’s principal position, have conducted great explorations and practices for building the socialist market economy through reform.In general, policy evolution and the evolution of mainstream perceptions have been kept basically in step.
On the theoretical level, Western scholars’ research on government-market relationships mostly stays on the superficial level of economic operations.The theory of a socialist market economy with Chinese characteristics is built under the guidance of Marxist theories and based on outstanding traditional Chinese culture and the reasonable substances of Western economics.In the academic circle, the understanding of government-market relationships has been continuously deepened—although neither the government nor the market is replaceable, they both have their limitations.In future research, efforts should be made to unveil the nature and the operating pattern of economic systems in the new development pattern.
On a realistic level, as the construction of socialism with Chinese characteristics unfolds in-depth, arguments exist on various issues, such as the definition of government-market relationships, its dominant connotations, measurements, and other details.However, despite the divergences, all parties have consistently stressed the importance of strengthening comprehensive regulation and meeting the people’s expectations for a better life.
Second, they uphold the scientific and rational attitude and represent significant theoretical breakthroughs.The Marxist theory of the market and the government creatively reveals the laws governing the development of human society.It is the guideline that tells us how to grasp the essential relationships between the government and the market.Socialist political economics with Chinese characteristics is the theoretical achievement of adapting Marxist political economics to Chinese realities.In the new development stage, it is manifested in the harmony and unity between the government and the market.The academic circle has always looked at the Marxist theory of the market and the government with a scientific and rational attitude.With the progress of socialist reforms, its understanding of what a socialist market economy means has deepened,and its policy interpretations, explorations, and research have made epochal innovations.Most scholars have agreed upon the government-market relationships in the primary stage of socialism.We should give full play to the market’s decisive role in resource allocation on the one hand and let the government better play its role on the other.There is no fundamental conflict between this and a socialist market economy with Chinese characteristics.While adhering to the basic principles of Marxism, we must creatively apply them in light of our actual national conditions, tomake the government-market relationships more efficient and sustainable with higher quality.
Third, they commit to innovation while carrying forward what has worked in the past and actively cope with problems and challenges.The change of times has injected the concept of a socialist market economy with richer and evolving contents.The reform of the governmentmarket relationships has largely stimulated the people’s initiative of production and promoted the advancement of productive forces and the adjustment of productive relations.It consists of the theoretical development of a socialist market economy and has proven itself through the historical achievements that China has made in economic and social development.As our reforms continue to deepen, the scholars, in view of the new development stage, have consistently and actively discussed the direction, effect, and means of adjusting the government-market relationships.Our economic development practices have revealed a spate of major problems, such as the unsatisfactory quality and efficacy of development, low levels of independent innovation, and lukewarm development of the real economy.The scholars believe that the fundamental way to address these problems is to apply the theoretical essence of socialist political economics with Chinese characteristics by coordinating the market’s decisive role in resource allocations, and the government better plays its role.The research findings by Chinese academia represented breakthroughs in the theories of socialist political economics with Chinese characteristics and paved the way for exploring the government-market relationships under socialism with Chinese characteristics.
Future Studies of Government-Market Relationships
To further the supply-side structural reforms and the establishment of a modern market economy, we need to, having summarized and reviewed the evolution of government-market relationships, accelerate adjusting these relationships and blaze a road of economic system reform with Chinese characteristics and styles that ensure the coordinated development of the government and the market.The massive amount of academic research on government-market relationships has made the reforms more in-depth, thorough, and realistic.We must be fully aware that reform cannot be accomplished overnight.It requires strenuous efforts to tackle the problems in various aspects of the economic system and to keep seeking new thoughts and solutions based on China’s conditions.
To begin with, we should build a symbiotic and coordinated relationship between the government and the market and advance relevant studies in depth for tangible results.Its evolution since the launch of reform and opening up shows that the government-market relationship has transformed from contradiction to unity and will continue to reach a higher level of unity to achieve “symbiotic coordination” at an early date.To support future research on this relationships,we must make great efforts to collect basic data and conduct surveys, create a database, and find new methods and angles of research.
At the same time, we should uphold the “people first” development philosophy and increaseresearch on the transformation of government functions.The government should play a better rather than a bigger role.This means that where the market fails or where it is unable to solve a problem.The government should transform its functions and proactively step in.It should actively transform itself into a service-oriented government and strengthen and improve its functions in social administration and public services.We must keep a close eye on the dynamic development of government functions.In developing a socialist market economy, our most important experience is adhering to the socialist direction, which will ensure the government serves all the people and the public interests, and guarantees its role of guiding and rectifying the market.While conducting academic research, we should always integrate dialectical materialism and historical materialism and look at the government-market relationships in a dialectical light.We should stick to the market’s decisive role in resource allocations and improve the market mechanisms while giving better play to the government.
Furthermore, we should jump out of stereotyped thinking and advance the establishment of a modern economic system.Establishing the modern economic system is an important decision made by the CPC Central Committee considering the new requirements in the new era to achieve the second centenary goal.It is the foundation that underpins the modernization of other domains.In general, letting the market fully play its decisive role in resource allocations while having the government better play its role is an effective approach to comprehensively deepening the reform.For one thing, government-market relationships are the core issue in the reform of the economic system, and the reform of the economic system is an inherent requirement for building a modern economic system.Keeping in mind the roles of the market and the government, researchers should focus on the comprehensive reform of the government-market relationship, which bears on all the other aspects and domains, and promote the establishment of a modern economic system faster.For another, a thorough study of the synergy between the government (the visible hand)and the market (the invisible hand) will help resolve major problems that emerge in establishing a modern economic system.It will fully activate and unleash the inherent strengths of socialism and advance the establishment of a modern economic system with high-level research findings.
 Contemporary Social Sciences2023年3期
Contemporary Social Sciences2023年3期
- Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- Application of Blank Symbols in Japanese Architecture and Indoor Designs
- Flavor Amidst Plainness: An Examination of the Subjectivity of the“People’s Films” From the Perspective of Classical Aesthetics
- Considerations for Restriction on the Right of Rescission in Case of Obviously Minor Breaches
- Research on Yang Xiong from a Calligraphic Perspective
- An Investigation Into the Needs and Challenges of County-Level Family Education Guidance Services and Corresponding Improvement Measures
- A Comparative Study on Achievements in Negative Nominal Interest Rates Published in Literature in English and Chinese
