精密播种机种子运动调控方法研究进展
张鹏飞 李景宇 张思豪 刁培松 王文君

摘要:精密播种技术是农业机械化生产的重要组成部分,也是规模化种植实现节本增效的重要手段。对种子的运动行为的精准调控,是精密播种技术的核心,也是改善单粒精播质量的关键。从播种机种子运动各环节角度,在充种清种、导种输种、投种落地三个阶段的种子运动调控以及后续触土部件对种子位置的影响等方面,综述单粒精播机械中种子运动调控方法的国内外研究现状和进展。从排种器、导种输种装置、种子落地时的弹跳滚动、后续触土部件等方面指出精密播种过程中存在的应着重解决的技术问题,并针对以上技术问题结合我国的生产现状对今后精密播种机种子运动调控方法发展趋势作展望,指出了精密排种技术、导种输种技术、种子落地防弹跳技术、覆土镇压技术的具体发展建议,为精密播种技术研究及装备创新设计和应用推广提供参考。
关键词:精密播种;单粒率;种子运动;调控方法
中图分类号:S223.2
文献标识码:A
文章编号:2095-5553 (2023) 04-0122-07
Abstract: Precision planting technology is an important part of agricultural mechanization production, and also an important means of saving cost and increasing profits in large-scale farm production. Accurate control of seed motion is the core of precision planting technology and the key to improve the quality of single-seed precision planting. From the perspective of seed motion stages in precision seeding operation, the overall situation of seed motion control method of the single-seed precision planter was discussed, and the main technical problems in precision seeding operation were pointed out. In view of the above technical problems and combined with the current production situation of China, the future development trend of precision planting technology is forecasted. Specific suggestions are given in terms of precision seeding technology, seed guide technology, seed bouncing inhibition technology, and soil covering and compaction technology. The research provides reference for innovation design and application promotion of precision planter.
Keywords: precision planting; single-seed rate; seed motion; control method
0 引言
现代农业向着高精度、高效率的方向发展,尤其是农业的基础—种植业,对先进高效农业生产技术有着更为迫切的需求[1],如精密播种技术、高效耕整地技术、精准植保技术、低损收获技术等[2-5],其中精密播种技术作为大田农业生产技术的起点,已成为现代农业中农作物生长发育和丰产丰收的重要保障。
精密播种是指在根据农艺要求,将确定数量的种子按照固定的行距、粒距和深度播入土壤并准确定位的过程[6],其主要目的是提高粒距、行距均匀性及播深一致性,为种子创造均匀一致的生长环境[7-9],降低由于株距不一致造成的相邻植株对空间、营养物质、光照等资源的过度竞争,节约种子、减少间苗用工、提高产量。其中精量排种系统是实现高速精密播种的基础。
精量排种系统是由充种箱体至种沟土壤的整个过程中提供种子运移和自由度约束的系列串联装置,包括单粒精量排种、种子平稳运移、种子准确定位等关键技术和装置[10-14],其目标是对种子的运动行为进行精准控制,是单粒精密播种技术装备的核心。在整个精量排种系统中,种子的运动贯穿于从充种到落地的各个环节。因此,对精量排种系统各环节的种子运动行为进行有效调控是改善单粒精播质量的关键。
精密播種机械作业过程中,种子一般经历充种清种、导种输种、投种落地三个阶段,每个阶段中的种子运动均会对最终的播种精度产生影响。国内外关于高速精密播种机的种子运动特性研究也主要集中在这三个方面。除此之外,后续触土部件的作业过程也会影响土壤中种子的位置。
本文的目的是从充种清种、导种输种、投种落地三个阶段的种子运动调控以及后续触土部件对种子位置的影响等方面,综述单粒精播机械中种子运动调控方法的国内外研究现状和进展,指出精密播种过程中普遍存在的应着重解决的技术问题,并结合我国的生产现状对今后的精密播种发展趋势作展望。
1 精密播种机种子运动调控方法国内外研究进展
1.1 充种清种阶段的种子运动调控方法
充种清种是利用精量排种器将种子群体化为连续均匀的单粒种子,提高充种率和单粒率。国内外研究人员对机械式和气力式精量排种器进行了大量研究。针对机械式排种器,通过分析排种器内种子的运动规律,优化排种盘[15-16]、取种部件[17-19]、清种装置[20-21]等结构,改善其排种性能;运用高速摄像技术探索机械振动对取种、携种、清种过程的影响规律[22-23]。针对气力式排种器,采用气流扰动种群的方法,改善种群空间状态与气流结构[24-25];采用正压气流充种方式[26],并结合电力驱动方式[27],改善高速作业稳定性;采用机械和气力相结合的排种方式[28],实现种子的稳定吸附和单粒率;采用正负压双作用排种器,负压吸种和正压卸种相结合,或负压吸种和机械卸种机构相结合[29],保证小粒种子吸种和卸种稳定性。目前在充种清种方面的研究主要是通过优化排种器结构或采用多种原理组合形式,改善种子在取种、携种、清种、卸种过程中的运动,以适应高速作业需求,保证单粒率。不同排种方式的技术总结和对比如表1所示。
相比于机械式排种器,气力式排种器在单粒精播作业过程中优势明显,作业速度高、种子损伤小、排种性能可靠,因此气力式排种器被广泛应用在要求大型高速作业的规模化农场中。
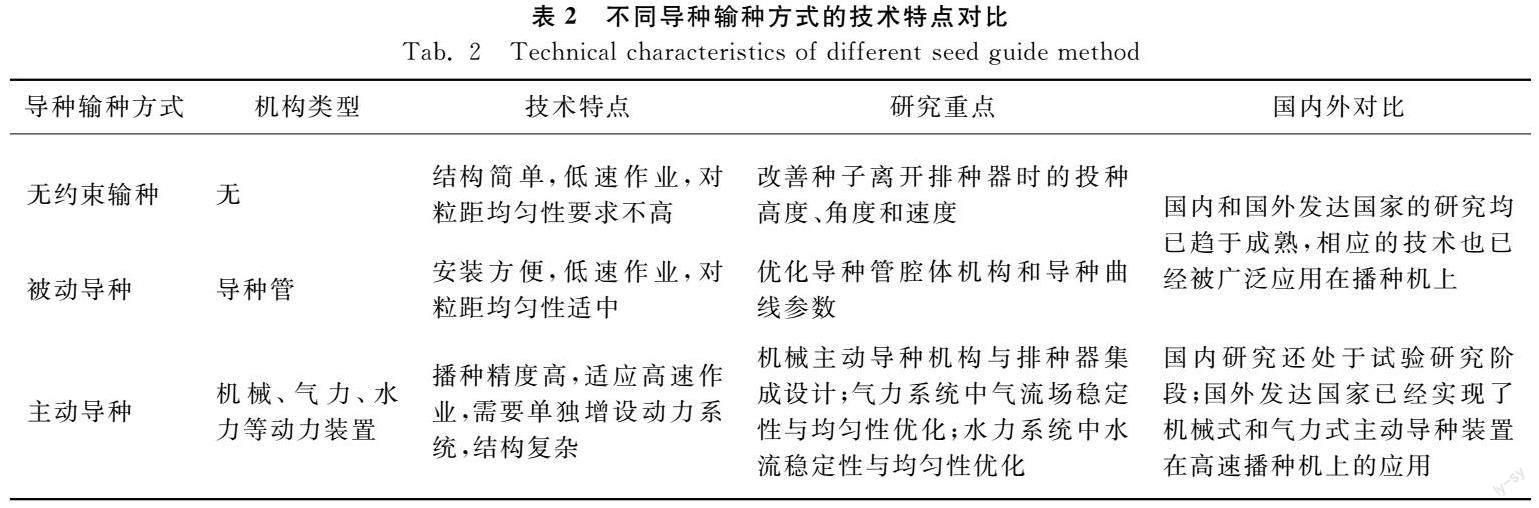
1.2 导种输种阶段的种子运动调控方法
导种输种是对离开排种器的种子通过自身重力、被动约束或主动约束等方式引导至种沟的过程,主要分为无约束输种、被动导种和主动导种三种方式。无约束输种是指种子离开排种器后,只受到重力和惯性力的作用而没有其他的约束,相关研究主要集中在改善种子离开排种器时的投种高度、投种角度和投种速度上[30-31]。被动导种是利用导种管使种子按照相对固定的轨迹运动,研究主要集中在通过优化导种管腔体机构和导种曲线参数[32-34],提高导种均匀性和稳定性。主动导种分为机械、气力、水力三种输送方式强制种子保存有序状态,其中,机械输送方式采用柔性导种带[35]、毛刷式导种部件[36]、输送带式导种部件[37]、V型凹槽拨轮式导种部件[38]等主动运移机构,减少种子输送过程中的无序碰撞;气力输送方式通过优化气送风压工作参数[39]和导种部件、集排器[40]、导流涡轮[41]等结构参数,提高种子流的均匀性;水力输送方式采用电磁控制[42]、水泵驱动[43]、凸轮推抵[44]等方式控制水流压力,减小种子和管壁的碰撞。目前国外发达国家技术已经非常成熟,拥有先进的气力式主动导种输种系统,播种粒距一致性高,作业可达20 km/h,并得到推广应用。然而,国内播种机的主动导种输种系统还处于研究试验阶段,目前仍普遍采用被动导种方式(导种管),播种速度为6~8 km/h,速度和精度都有待提升。不同导种输种方式的技术总结和对比如表2所示。
随着作业速度的提高,无约束导种和被动导种的方式由于无法很好地解决种子离开排种器时的运动稳定性和种子在导种管中无序碰撞问题,研究人员逐渐将研究重点逐步转向主动导种方式。另外,主动投种方式还可以通过降低投种速度和高度,间接降低种子落地后的弹跳和滚动,提高单粒播种精度。
1.3 投种落地阶段的种子运动调控方法
投种落地是种子从离开导种输种装置开始到静止在种沟某个位置的整个运动过程。而研究种子与土壤碰撞瞬间的运动特性是消除种子落地弹跳和滚动的基础。国内外研究人员对种子与土壤碰撞关系进行了部分探索,如通过分析种子离开排种器的运动轨迹,找到碰撞速度和角度、土壤表面特性、种子类型对弹跳高度和位移的影响规律[45];通过测量土壤物理特性,建立了大豆种子与土壤颗粒的EDEM模型,分析大豆种子与土壤碰撞过程中的瞬间速度、受力情况[46];通过分析种沟形貌、土壤类型和土壤含水率等因素对种子落地弹跳位移影响规律,建立了种子弹跳的力学模型[47]。关于种子与种沟土壤碰撞后产生弹跳的研究主要集中在测量种子弹跳高度、位移及建立力学和仿真模型上,并没有针对如何控制种子的弹跳进行深入研究,也没有提出对应的控制方法。
为实现对种子落地弹跳和滚动的限制,国外研究人员普遍采取了种子落地弹跳后的补救措施,主要是通过在导种输种机构的后方增设压种装置,如拖带式压种舌、刚性压种轮、橡胶压种轮[48]等,减少种子落地碰撞后产生的弹跳和滚动。国内研究人员借鉴国外研究成果,也采取类似的方法降低种子落地弹跳[49]。这些方法目前在大型高速精密播种机械,特别是气力式播种机械上应用普遍。
然而,这类种子落地弹跳后的补救措施,只能在一定程度上减少种子落地后的弹跳和滚动范围,并不能从根本上消除种子的弹跳和滚动。另外,压种舌或压种轮等被动压种装置虽然可以增加种子土壤的充分接触,但也会造成种子位置的二次移动和种子损伤。
1.4 后续触土部件对种子位置影响的研究进展
种子落入种沟后,为保证种子土壤的充分接触,通常还需要压种、覆土、镇压等工序,在该过程中,土壤与种子的相对位置也会产生一定的变化。国内外研究人员针对后续工作部件对种子位置的影响进行了相关研究,主要集中在通过试验或仿真,优化部件结构和工作参数,减小种子的位移,如针对不同土壤类型和种子类型,选用不同的压种装置,以减小种子损伤和种子的移动[48];通过对覆土过程中土流与种子运动状态的仿真分析,优化覆土器的结构和工作参数,减小覆土过程中的种子位移量[50];通过建立镇压装置与土壤、种子作用的离散元模型,分析镇压作业时土壤和种子的流动过程,找到了镇压装置对种子位置的影响规律[51]。
随着触土部件结构的成熟和针对不同作物的专用部件的开发,触土部件对种子位置的影响越来越小,相关的研究也逐渐減少。
2 存在问题
1) 高速高效是现代农业的发展方向,而气力式排种器在规模化种植大型机具和高速作业中的优势非常明显,因此近年来气力式排种方式得到了快速发展和广泛应用。然而,目前我国的气力式排种器在高速作业条件下的播种单粒率和稳定性还不能满足要求,随着作业速度的提高,排种盘转速也会相应地增加,由于充种时型孔处气流力作用时间缩短、离心力增大,清种时种子与清种部件接触时间短、动量大,导致充种和清种性能下降,尤其在14 km/h以上的高速作业条件下,会严重影响播种单粒率和稳定性。另外,气力式排种方式的快速发展,并不意味着机械式排种方式将被气力式排种方式取代,我国现有的耕地政策以及复杂的地形特点,尤其是丘陵山区机械化需求日益增加,决定了小型低速播种作业机具的长期需求,而机械式排种器在小型播种机具和低速作业中的优势不可替代,因此未来机械式和气力式两种排种方式会长期并存发展。然而,丘陵山区的复杂作业条件,如大斜坡、振动严重等,对机械排种性能也有显著影响。
2) 主动导种输种装置是实现高速播种作业条件下种子稳定运移的关键,发达国家针对主动导种输种装置进行了系统研究,匹配特定的排种器进行作业,因此,主动导种输种装置与不同排种器适应性相对较差。相比之下,近年来我国的主动导种输种技术和装置虽然已经进行了一些相关研究并取得了一定进展,还处于模仿和试验阶段,目前还没有成熟的主动导种输种装置广泛应用在高速播种机上,也没有深入研究主动导种输种过程中的种子相对位置变异过程。另外,现有的工作也主要集中在机械式导种输种装置的研究上,对气流和水流导种输种过程的研究很少。
3) 种子离开导种输种机构,脱离约束并自由下落,会与种沟土壤发生碰撞而产生无规则的弹跳,最终使种子落地位置失去控制,抵消充种排种、导种输种、播深控制等机构的作用。随着播种作业速度的进一步提高,这一问题也更加凸显。目前对投种落地阶段相关技术的研究相对滞后,关于种子落地弹跳行为的控制方法主要有两种:(1)投种前的主动控制,通过主动导种装置实现近地投种,降低投种高度和速度,减少落地碰撞能量进而降低种子落地弹跳位移;(2)种子落地彈跳后的补救措施,通过在导种管后方增设压种装置实现对种子落地弹跳后的强制按压,降低种子弹跳范围,在土壤含水率高的情况下该方法作业效果较差,此外被动压种装置虽然可以增加种子土壤的充分接触,但也会造成种子位置的二次移动和种子损伤。现有这两种方法在一定程度上降低了种子落地后弹跳滚动的运动范围,属于通过间接方式来抑制种子落地后的弹跳滚动,但不能从根本上克服落地碰撞瞬间的种子弹跳问题。
4) 对于一般播种机来说,排种器后面还需要安装一系列的触土部件,如压种装置、覆土装置、镇压装置等,已完成整个播种作业过程。在设计和改进播种机械后续触土部件时,研究人员主要考虑其本身作业效果,如压种装置作业后的种子土壤充分接触情况、覆土装置作业后的覆土厚度一致性、镇压装置作业后的土壤坚实度等,很少有研究将触土部件作业过程中对种子位置变异的影响作为设计和改进触土部件的依据。这些触土部件作业过程中,会带动种子周围土壤流动,而土壤的流动会带动种子位置的变异,进而改变种子相对位置,降低粒距一致性。
3 展望
1) 随着高速高效农业的发展,气力式排种器将得到更加广泛的应用,而机械式排种器在小型播种机具和低速作业中的优势不可替代,因此未来机械式和气力式两种排种方式会长期并存发展。针对气力式排种器,重点应该放在14 km/h以上的高速作业条件下提高充种、清种和携种的稳定性。针对机械式排种器,其结构和种类繁多,结合我国现有的耕地政策以及复杂的地形特点,尤其是丘陵山地,研究适应于不同作物和不同种植模式的排种器,将农机农艺相融合,提高排种器在复杂地形(如斜坡倾角大、地表起伏大)条件下的作业质量。同时,不同作物排种器的通用性也是未来的研究重点。
2) 与发达国家相比,我国的主动导种输种技术和装置几乎没有成熟的主动导种输种技术应用在播种机上,为适应高速高效作业需求,国内科研人员应加快主动导种输种技术的实用性研究及推广应用,提高单粒播种的速度和精度。另外,导种输种技术和装置不能在播种机上完成独立工作,必须与相应的排种器配合使用。因此,针对不同区域、不同作物、不同种植模式,进一步开展导种输种装置与排种器的集成化设计,提高导种质量和效率。
3) 现有对精量排种系统的研究主要集中在充种排种、导种输种等装置的结构与控制方法方面,对投种落地阶段相关技术的研究相对滞后,仅仅采用简单的被动压种装置,能在一定程度上降低种子弹跳范围,但也会造成种子位置的二次移动和种子损伤。未来应从种子与种沟土壤的碰撞行为入手,寻求落地碰撞瞬间直接抑制种子弹跳的新方法。通过研究种子与土壤碰撞后弹跳和滚动的直接原因,改变种子土壤接触瞬间的碰撞条件或环境,直接消除或抑制落地碰撞瞬间抑制种子弹跳。
4) 对单粒精播种子位置变异的研究还是主要集中在前三个方面,而后续触土部件对种子位置变异的影响少有考虑,很容易被忽略,因此,在设计和改进压种装置、覆土装置、镇压装置等播种机后续触土部件时,除了考虑本身作业效果外,还需关注触土部件作业过程中由于土壤流动对种子位置变异的影响,将其作为后续触土部件设计和改进的一个重要指标,尽量减小由后续触土部件作业造成的种子位置的变异。
参 考 文 献
[1] Yost M A, Kitchen N R, Sudduth K A, et al. A long-term precision agriculture system sustains grain profitability [J]. Precision Agriculture, 2019, 20(6): 1177-1198.
[2] Mikula K, Izydorczyk G, Skrzypczak D, et al. Controlled release micronutrient fertilizers for precision agriculture—A review [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 712: 136365.
[3] OBrien P, Daigh A. Tillage practices alter the surface energy balance—A review [J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 2019, 195: 104354.
[4] Zhao Y S, Gong L, Huang Y X, et al. A review of key techniques of vision-based control for harvesting robot [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2016, 127: 311-323.
[5] Kusumastuti R D, Van Donk D P, Teunter R. Crop-related harvesting and processing planning:A review [J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2016, 174: 76-92.
[6] Kireev I M, Koval Z M. Study of the distribution of seeds using a pneumatic precision drill assembly [J]. Machinery and Equipment for Rural Area, 2019, (6): 12-17.
[7] Nielse S K, Munkholm L J, Lamande M, et al. Seed drill depth control system for precision seeding [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 144: 174-180.
[8] Zhao Z, Li Y M, Chen J, et al. Numerical analysis and laboratory testing of seed spacing uniformity performance for vacuum-cylinder precision seeder [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2010, 106(4): 344-351.
[9] Yang L, Yan B X, Yu Y M, et al. Global overview of research progress and development of precision maize planters [J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2016, 9(1): 9-26.
[10] Jin X, Li Q W, Zhao K X, et al. Development and test of an electric precision seeder for small-size vegetable seeds [J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2019, 12(2): 75-81.
[11] 苑嚴伟, 白慧娟, 方宪法, 等. 玉米播种与测控技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(9): 1-18.
Yuan Yanwei, Bai Huijuan, Fang Xianfa, et al. Research progress on maize seeding and its measurement and control technology [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(9): 1-18.
[12] 杨丽, 颜丙新, 张东兴, 等. 玉米精密播种技术研究进展[J]. 农业机械学报, 2016, 47(11): 38-48.
Yang Li, Yan Bingxin, Zhang Dongxing, et al. Research progress on precision planting technology of maize [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(11): 38-48.
[13] He X T, Ding Y Q, Zhang D X, et al. Development of a variable-rate seeding control system for corn planters Part I: Design and laboratory experiment [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2019, 162: 318-327.
[14] Yin X, Noguchi N, Yang T X, et al. Development and evaluation of a low-cost precision seeding control system for a corn drill [J]. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 2018, 11(5): 95-99.
[15] Robert J O, Scott R M, Steven G, et al. Evaluation of a mechanical seed planter for transplanting Zostera marina (eelgrass) seeds [J]. Aquatic Botany, 2009, 90(3): 204-208.
[16] 都鑫, 刘彩玲, 姜萌, 等. 自扰动内充型孔轮式玉米精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(13): 23-34.
Du Xin, Liu Cailing, Jiang Meng, et al. Design and experiment of self-disturbance inner-filling cell wheel maize precision seed-metering device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(13): 23-34.
[17] 王金武, 唐汉, 王金峰, 等. 指夹式玉米精量排种器导种投送运移机理分析与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2017, 48(1): 29-37, 46.
Wang Jinwu, Tang Han, Wang Jinfeng, et al. Analysis and experiment of guiding and dropping migratory mechanism on pickup finger precision seed metering device for corn [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(1): 29-37, 46.
[18] 赖庆辉, 贾广鑫, 苏微, 等. 凸包异形孔窝眼轮式人参精密排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(7): 60-71.
Lai Qinghui, Jia Guangxin, Su Wei, et al. Design and test of ginseng precision special-hole type seed-metering device with convex hull [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(7): 60-71.
[19] 侯加林, 王后新, 牛子孺, 等. 大蒜取种装置取种清种性能离散元模拟与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(24): 48-57.
Hou Jialin, Wang Houxin, Niu Ziru, et al. Discrete element simulation and experiment of picking and clearing performance of garlic seed-picking device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(24): 48-57.
[20] Khwantri S, Choochart C, Khanita K, et al. Effect of metering device arrangement to discharge consistency of sugarcane billet planter [J]. Engineering in Agriculture Environment & Food, 2018, 11(3): 139-144.
[21] 杨薇, 方宪法, 李建东,等. 种腔自净型气吸式玉米小区精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(6): 64-73.
Yang Wei, Fang Xianfa, Li Jiandong, et al. Design and experiment of air-suction precision seed meter with self-clearing seed chamber for corn plot test [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(6): 64-73.
[22] Cay A, Kocabiyik H, May S. Development of an electro-mechanic control system for seed-metering unit of single seed corn planters Part I: Design and laboratory simulation [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 144: 71-79.
[23] 王奇, 朱龙图, 李名伟, 等. 指夹式玉米免耕精密播种机振动特性及对排种性能的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2019, 35(9): 9-18.
Wang Qi, Zhu Longtu, Li Mingwei, et al. Vibration characteristics of corn no-tillage finger-type precision planter and its effect on seeding performance [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2019, 35(9): 9-18.
[24] 史嵩, 周纪磊, 刘虎, 等. 驱导辅助充种气吸式精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(5): 61-70.
Shi Song, Zhou Jilei, Liu Hu, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic precision seed-metering device with guided assistant seed-filling [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(5): 61-70.
[25] 崔濤, 韩丹丹, 殷小伟, 等. 内充气吹式玉米精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(1): 8-16.
Cui Tao, Han Dandan, Yin Xiaowei, et al. Design and experiment of inside-filling air-blowing maize precision seed metering device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 8-16.
[26] 劉礼阳, 唐兴月, 祝培栩,等. 水稻气压滚筒式集中排种器设计与试验[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2020, 25(12): 122-133.
Liu Liyang, Tang Xingyue, Zhu Peixu, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic cylinder-type centralized seed-metering device for rice [J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2020, 25(12): 122-133.
[27] Arzu Y, Adnan D. Measurement of seed spacing uniformity performance of a precision metering unit as function of the number of holes on vacuum plate[J]. Measurement, 2014, 56: 128-135.
[28] 贾洪雷, 陈玉龙, 赵佳乐, 等. 气吸机械复合式大豆精密排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(4): 75-86, 139.
Jia Honglei, Chen Yulong, Zhao Jiale, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic-mechanical combined precision metering device for soybean [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(4): 75-86, 139.
[29] 丁力, 杨丽, 张东兴, 等. 气吸式排种器卸种机构设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(1): 37-46.
Ding Li, Yang Li, Zhang Dongxing, et al. Design and test of unloading mechanism of air-suction seed metering device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(1): 37-46.
[30] 廖宜涛, 李成良, 廖庆喜, 等. 播种机导种技术与装置研究进展分析[J]. 农业机械学报, 2020, 51(12): 1-14.
Liao Yitao, Li Chengliang, Liao Qingxi, et al.Research progress of seed guiding technology and device of planter [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(12): 1-14.
[31] 李玉环, 杨丽, 张东兴, 等. 气吸式玉米高速精量排种器直线投种过程分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(9): 26-35.
Li Yuhuan, Yang Li, Zhang Dongxing, et al. Analysis and test of linear seeding process of maize high speed precision metering device with air suction [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(9): 26-35.
[32] Carpes D P, Alonco A D, Rossato F P, et al. Effect of different conductor tubes on the longitudinal distribution of corn seeds [J]. Revista Brasileira de Engenharia Agrícola e Ambiental, 2017, 21(9): 657-662.
[33] Kumar R, Raheman H. Detection of flow of seeds in the seed delivery tube and choking of boot of a seed drill [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2018, 153: 266-277.
[34] 刘立晶, 杨慧. 基于Geomagic Design软件的导种管三维逆向工程设计[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(11): 40-45.
Liu Lijing, Yang Hui. 3D reverse engineering design on seed tube based on Geomagic Design software [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(11): 40-45.
[35] Nakarmi A D, Lie T. Within-row spacing sensing of maize plants using 3D computer vision [J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2014, 125: 54-64.
[36] John Deere brochures online [EB/OL]. https://www.deere.com/assets/publications/index.html?id=6f7a8a69#14, 2021-07-20.
[37] Precision planting precision meter [EB/OL]. http://www. precision planting.com/#products/precision meter/, 2021-07-20.
[38] 赵淑红, 陈君执, 王加一, 等. 精量播种机V型凹槽拨轮式导种部件设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(6): 146-158.
Zhao Shuhong, Chen Junzhi, Wang Jiayi, et al. Design and experiment on V-groove dialing round type guiding-seed device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(6): 146-158.
[39] Siemens M, Gayler R. Improving seed spacing uniformity of precision vegetable planters [J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2015, 32(5): 579-587.
[40] 雷小龍, 廖宜涛, 丛锦玲, 等. 油菜小麦兼用气送式直播机集排器参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(12): 16-26.
Lei Xiaolong, Liao Yitao, Cong Jinling, et al. Parameter optimization and experiment of air-assisted centralized seed-metering device of direct seeding machine for rape and wheat [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(12): 16-26.
[41] 高筱钧, 徐杨, 贺小伟, 等. 气送式高速玉米精量排种器导流涡轮设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2019, 50(11): 42-52.
Gao Xiaojun, Xu Yang, He Xiaowei, et al. Design and experiment of diversion turbine of air-assisted high speed maize precision seed metering device [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(11): 42-52.
[42] 周福君, 王文明, 官晓东. 电磁控制式压力水流导种机构[P]. 中国专利: ZL201810082814.2, 2018-07-13.
[43] 贾洪雷, 陈玉龙, 王佳旭, 等. 一种水力精确投种系统[P]. 中国专利: ZL201610263437.3, 2016-09-07.
[44] 罗海峰, 杨丽华. 水力推送式精密排种装置[P]. 中国专利: ZL201610623476.X, 2016-12-07.
[45] Ahsan Z, Dankowicz H. Optimal scheduling and sequencing for large-scale seeding operations [J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2019, 163: 1-9.
[46] Xu T Y, Yu J Q, Yu Y J, et al. A modelling and verification approach for soybean seed particles using the discrete element method [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2018, 29(12): 3274-3290.
[47] Wang W J, Jia H L, Diao P S. Effects of strip till planter on soil physical properties and maize (Zea mays L.) growth in Northeast China [J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2021, 67(1): 1-14.
[48] Kubik F. Amazone ED2 drill for an accurate seeding of sugar beets, corn, sunflowers, legminous plants and other cultivations [J]. Listy Cukrovarnické a Rˇeparˇské, 2003, 119(1): 12.
[49] 贾洪雷, 姚鹏飞, 袁洪方, 等. 种沟碎土镇压器[P]. 中国专利: ZL201510296582.7, 2017-01-18.
[50] 李丽艳. 前后分置圆盘式覆土器的试验研究与仿真分析[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2017.
[51] 徐天月. 精密播种单体及其关键部件工作过程的试验研究与仿真分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.

