Chinese herbal compound Jinsiwei (金思维) improves synaptic plasticity in mice with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease induced by streptozotocin
TIAN Meijing,HE Yannan,ZHENG Mingcui,QIN Gaofeng,GONG Zhuoyan,HUANG Shuaiyang,WANG Pengwen
TIAN Meijing,HE Yannan,ZHENG Mingcui,GONG Zhuoyan,WANG Pengwen,Key Laboratory of Chinese Internal Medicine of Ministry of Education and Beijing,Dongzhimen Hospital,Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100700,China
HUANG Shuaiyang,Department of Respiratory Medicine,the Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100029,China
QIN Gaofeng,Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical College,Shandong 256603,China
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To investigate the efficacy of Jinsiwei (a patented Chinese herbal compound) on learning and memory impairment,the number of synapses and synaptic plasticity-related structural and functional protein expression in mice with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease(SAD) induced by streptozotocin.METHODS: Seventy-five C57/BL6J male mice were intracerebroventricularly injected with streptozotocin to establish the animal model of SAD.Mice were randomly divided into the model group (MG),donepezil group (DG),and the Jinsiwei high,medium,and low-dose groups (JH,JM,JL).Another fifteen C57/BL6J male mice were injected with artificial cerebrospinal fluid as the control group (CG).The intervention groups were intragastrically administrated with corresponding medicine,while the CG and MG were given 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose by gavage.After 3 months,the Morris Water Maze test and step-down passive avoidance test were used to assess the learning and memory ability of mice.Synapses in hippocampal CA1 were observed by transmission electron microscope.Immunohistochemistry and western blotting were used to assess the distribution and expression levels of synaptic plasticity-related structural and functional proteins involving drebrin,cofilin,synapsin(syn),and N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B(NR2B).RESULTS: The Morris Water Maze results showed that the escape latency in the Jinsiwei intervention groups was significantly shorter than that of the MG.Results of the step-down passive-avoidance test showed that the error times in the Jinsiwei intervention groups were significantly reduced compared with the MG.Transmission electron microscope results showed that the number of synapses in hippocampal CA1 was obviously increased in the Jinsiwei intervention groups compared with the MG.Immunohistochemical and western blotting results revealed that the positive cells and expression levels of drebrin,syn,and NR2B were significantly decreased in the MG and meanwhile cofilin significantly increased,while these changes were reversed after the Jinsiwei treatment.CONCLUSIONS: Jinsiwei can alleviate learning and memory impairments in a mouse model of SAD,increase the number of synapses and enhance synaptic plasticity via rescuing the expression of drebrin,syn,and NR2B and inhibiting cofilin expression.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease;streptozotocin;neuronal plasticity;Jinsiwei
1.INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an irreversible,progressive neurodegenerative disease that is characterized by impaired memory and cognitive function.1Typical pathological changes of AD include the aggregation of extracellular β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) forming senile plaques and intracellular hyperphosphorylated tau protein forming neurofibrillary tangles.2Over the past few decades,although several hypotheses about the pathogenesis of AD have been proposed,the mechanisms underlying AD are still uncertain because of its complexity.Worth mentioning is that synaptic plasticity plays a crucial role in the development of AD.For example,neuropathological and morphological studies have found that there is significant synaptic loss in many regions of the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in patients with AD.At the same time,these patients emerge impairments of synaptic structure and function.3As actin-binding proteins,developmentally regulated brain protein (drebrin) and cofilin massively accumulate in dendritic spines,and their dynamic balance plays a vital role in the maturation of dendritic spines and integrity of synaptic structure.4Synapsin (syn) is a calcium-binding protein that is only expressed in neurons and is specifically located in the presynaptic membrane at the synaptic vesicle membrane,controlling the release of transmitters.5As one of the most important subunits of N‐methyl‐D‐aspartic acid receptor (NMDAR),Nmethyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B (NR2B) is crucial for the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP)concerning the formation of memory.6Thus,syn and NR2B together affect synaptic transmission and function.A number of mouse models have been developed to study AD.Streptozotocin (STZ) is a glucosaminenitrosourea compound that comes from soil bacteria.Bilateral intracerebroventricular injection of STZ (ICVSTZ) into the rodent brain has been shown to induce some pathological processes for example neuroinflammation,oxidative stress,synaptic dysfunction,synaptic loss,and biochemical alterations.Thus ICV-STZ is considered to be a valid experimental model reflecting the early pathophysiological changes in sporadic AD (SAD).7,8Overall,this model has been widely used in SAD experimental research worldwide.9Compound Chinese medicine,based on the symptom pattern identification theory,has some unique advantages to mitigate clinical symptoms and delay the long-term course progression of AD.Jinsiwei (金思维),a patented Chinese herbal compound,is composed of Renshen (Radix Ginseng),Roucongrong (Herba Cistanches Deserticolae),Shudihuang (Radix Rehmanniae Praeparata),Yuanzhi (Radix Palygalae),Shichangpu (Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii),Fuling (Poria),Jianghuang (Rhizoma Curcumae Longae),and Danshen(Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae).10According to the therapeutic principles of invigorating kidney Yang and eliminating phlegm,Jinsiwei can improve the symptoms of mild cognitive impairment of patients effectively during clinical treatment,and delay the memory decline of patients with dementia.One randomized comparison clinical trial found that the memory score of patients treating with Jinsiwei was higher than that of the control group at a 1-year follow up.11Meanwhile,given its multi-target and multi-channel effects,Jinsiwei has great potential for the treatment of AD.Our previous studies have confirmed that Jinsiwei largely alleviates learning and memory impairment in animal model of AD through improving cholinergic neurons and oxidative stress damage.12However,understanding of the mechanism underlying the Jinsiwei against synaptic damage is limited.In the current study,we investigated the efficacy of Jinsiwei on synaptic structure-related proteins drebrin and cofilin,and synaptic function-related proteins syn and NR2B,in the STZ-induced mouse model of SAD.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Experimental animals
A total of 90 C57/BL6J male mice age of 3 months and weight of 22-25 g were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co.,Ltd.[Certification SCXK (Beijing) 2016-0006].Mice were bred at a barrier environmental animal laboratory in Dongzhimen Hospital,which is affiliated with Beijing University of Chinese Medicine [Certification SYXK(Beijing) 2020-0013].The temperature of the animal laboratory was 24 ℃ and the humidity was 40%.All animals had free access to food and water.This experiment was approved by the Animal Research Ethics Board of Dongzhimen Hospital (approval No.16-21).
2.2.Drug preparation
Jinsiwei (patent No.ZL200810006733.0) was provided by Dongzhimen Hospital (Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing,China).Jinsiwei was dissolved with 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose to a concentration of 30 mg/mL.Hydrochloric acid donepezil tablets (batch No.140635) were purchased from Eisai Pharmaceutical Co.Ltd.(Suzhou,China).STZ was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St.Louis,MO,USA).
2.3.Establishment of the animal model and grouping
Mice were randomly divided into six groups,including the control group (CG),model group (MG),donepezil group (DG),Jinsiwei high-dose group (JH),Jinsiwei medium-dose group (JM),and Jinsiwei low-dose group(JL).The ICV-STZ administration was carried out according to a previously reported method.13,14The CG was injected with artificial cerebrospinal fluid into the bilateral lateral ventricles on days 1 and 3,and the other groups were injected with STZ that was dissolved in artificial cerebrospinal fluid at a concentration of 3 mg/kg to establish the SAD model.No mice died during the modeling process.The CG and MG were given 0.5%carboxymethyl cellulose by gavage,the DG was treated with donepezil (0.92 mg·kg-1·d-1),and the Jinsiwei groups were given a high dose (20 mg·kg-1·d-1;JH),a medium dose (10 mg·kg-1·d-1;JM),and a low dose(5 mg·kg-1·d-1;JL).The gavage volume was 0.1 mL/10 g,and all animals underwent intragastrical administration continuously for 3 months.
2.4.The Morris Water Maze test
The Morris Water Maze test was carried out according to previously published protocol.15The test was conducted in a quiet and light-controlled room for 6 d.The platform was placed in the third quadrant and hidden 1 cm below the surface of the water.The mice were trained in three daily 120 s sessions for 2 d.Mice were first put on the platform for 10 s and then placed into the water from the center of the edge of the quadrant.Swimming distance and the swimming time to find the platform (escape latency) were recorded.If mice did not find the platform within 120 s,they were placed on the platform for 10 s and escape latency was recorded as 120 s.This procedure was repeated,but mice who did not find the platform were no longer guided from the third day.The platform was taken away on day 6 and the number of platform crossings within 120 s was measured (Shanghai Transfer Information Technology Co.,Ltd.,Shanghai,China).
2.5.Step-down passive avoidance test
The step-down passive avoidance test was performed according to a previous experiment.16The experimental device consisted of a recorder and a testing case that had five separate chambers (Jinan Yiyan Technology Development Co.,Ltd.,Jinan,China),and every chamber had a metal grid floor through which a 36 V current could pass.In addition,there was a cylindrical platform in the center of the chamber by which mice could avoid stimulation.The experiment was performed over 2 d-1 d for training and another for testing.On the first day,each mouse was placed into the chamber and allowed to explore freely for 3 min,then an electrical current passed through the grid floor for 5 min.Under normal conditions,mice would jump onto the central platform to avoid the shock.On the second day,mice were placed onto the platform.The number of times mice fell down (error times) within 5 min was recorded,and the time at which mice jumped off the platform for the first time (step‐down latency) was also recorded.
2.6.Transmission electron microscope observations
First,the mice were put under anesthesia with tribromoethanol (350 mg/kg) and then the tissues of hippocampal CA1 region from mice were dissected rapidly after perfusion and fixation.Second,these tissues were placed in an Eppendorf tube filled with 2.5%glutaraldehyde solution and then kept stationary at 4 ℃for 2 h to be fully fixed.Third,the tissues were irrigated using 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline at 15 min intervals 3 times and were then placed in an Eppendorf tube with 0.1 M phosphate buffered saline solution.Subsequently,the specimens were immediately sent to the electron microscope room to obtain ultrathin sections.Finally,a transmission electron microscope was used to observe the number of synapses in a × 2.0 k visual field.
2.7.Immunohistochemical staining
In brief,six mice from each group were perfused and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde after intraperitoneal anesthesia with tribromoethanol (350 mg/kg).The brains of the mice were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin after fixation,and were then continuously sectioned from the coronal plane (4 μm).The sections were warming(56 ℃,60 min),dewaxing,rehydration,antigen retrieval,blocking endogenous peroxidase,blocking with goat serum,adding primary antibodies (1:500 dilution)against drebrin (ab60933,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),cofilin (ab42824,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),syn(ab32127,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),and NR2B(ab229636,Abcam,Cambridge,UK),and sections were then incubated overnight at 4 ℃.The next day,secondary antibodies were added and color was developed using DAB.Finally,the sections were dehydrated and then mounted with neutral gum.The staining conditions were observed under a microscope with × 20 objective lens,and three fields in the hippocampal CA1 region were selected to take pictures.Image-Pro Plus software was used to calculate the average number of cells with positive protein expression.
2.8.Western blot analysis
Six mice from each group were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and immediately placed on ice plates.The hippocampal tissues of the mice were quickly removed to cryogenic vials and stored in liquid nitrogen.The hippocampal tissues were removed from the liquid nitrogen and placed in an Eppendorf tube.Tissues were cleaved using RIPA buffer,homogenized by ultrasonic treatment,and centrifuged to acquire the supernatant.The protein concentration was measured using the BCA method.Equal amounts of proteins were separated using sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis,and the proteins were then transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes.The membranes were blocked with 5% milk at room temperature for 90 min and subsequently incubated with primary antibodies (1:1000 dilution) against drebrin,cofilin,syn,and NR2B at 4 ℃ overnight.After washing three times with TBST,membranes were incubated with the secondary antibody conjugated with HRP for 1 h.Enhanced chemi-luminescence solution was prepared for visualization.The pictures were taken using automatic chemil-uminescence imaging analyzer.Image J software was used to analyze the results.
2.9.Statistical analysis
Statistical software SPSS 20.0 (IBM Corp.,Armonk,NY,USA) and GraphPad Prism 8.0.1 (GraphPad Software,San Diego,CA,USA) were used for statistical analysis,and the experimental results are expressed as the mean ±standard deviation.One-way analysis of variance was used for all between-group analyses and the least significant difference test was used for pairwise comparisons between groups.Significance was set atP< 0.05.
3.RESULTS
3.1.Efficacy of Jinsiwei on learning and memory impairment in SAD mice
The Morris Water Maze test is a classic and widely used method for assessing spatial learning,memory,and cognitive processes in mice.As shown in Figure 1,the escape latency of the MG was significantly longer than that of the CG over the 5 d (P< 0.01).From day 4,the escape latencies of the DG and JL were significantly shorter than that of the MG (P< 0.01).On day 5,the escape latency of all intervention groups was shorter than that of the MG (P< 0.01 or< 0.05) (Figure 1A).In addition,the swimming distance to find the platform showed similar decrease within all groups during the 5 days of training.However,the swimming distance was significantly longer in the MG than the CG from days 1 to 5 (P< 0.01).Compared with the MG,the DG and Jinsiwei groups had a significantly shorter swimming distance from day 4 (P< 0.01 or< 0.05) (Figure 1B).After removal of the platform on day 6,the number of crossing the platform in the MG was significantly lower than that of the CG (P< 0.01),and all intervention groups crossed the platform more frequently than did the MG (P< 0.01 or< 0.05) (Figure 1C).
The step-down passive avoidance test was used to study the memory retention ability of mice.As shown in Figure 1,the error times of the MG was significantly increased compared with the CG (P< 0.01).Compared with the MG,number of errors in JH and JL were decreased (P<0.05),and the error times of the DG and JM were obviously decreased (P< 0.01) (Figure 1D).After training,the step-down latency in the MG was significantly shorter than that in the CG (P< 0.01).The step-down latencies of the DG and each Jinsiwei group were longer than that in the MG (P< 0.01 or< 0.05)(Figure 1E).
3.2.Efficacy of Jinsiwei on synapses in the hippocampal CA1 in SAD mice
The number of synapses in the hippocampal CA1 was observed using transmission electron microscopy at a resolution of × 2.0 k (Figure 2A).As shown in Figure 2,in the same area,the synapse number in the MG was significantly lower than that in the CG (P< 0.01).The number of synapses in the DG and Jinsiwei groups was significantly higher than that in the MG (P< 0.01)(Figure 2B).
3.3.Efficacy of Jinsiwei on synaptic structure-related proteins
Immunohistochemical staining and western blot analysis showed a significant decrease of drebrin expression in the hippocampus of the MG compared to the CG (P<0.01).The DG,JH,and JM had more positive cells and higher relative protein expression levels of drebrin than the MG after 3 months gavage (P< 0.01 or< 0.05).The number of drebrin-positive cells in the JL was higher than that in the MG (P< 0.05).Although the protein expression of drebrin tended to be higher in the JL,there was no significant difference compared with the MG(Figure 3A,3B,3E).As shown in Figure 3,the positive cells and relative protein expression levels of cofilin were significantly increased by STZ (P< 0.01),which was significantly reversed in the JH,JM,and DG after 3 months administration (P< 0.01 or< 0.05),this effect was not apparent in the JL (Figure 3C,3D,3F).
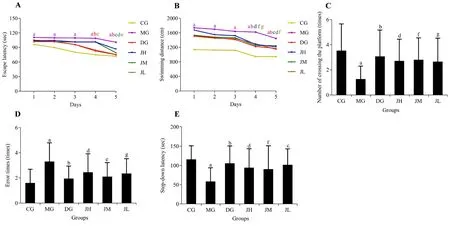
Figure 1 Efficacy of Jinsiwei on Morris Water Maze test and step-down passive avoidance test results in STZ-induced SD mice
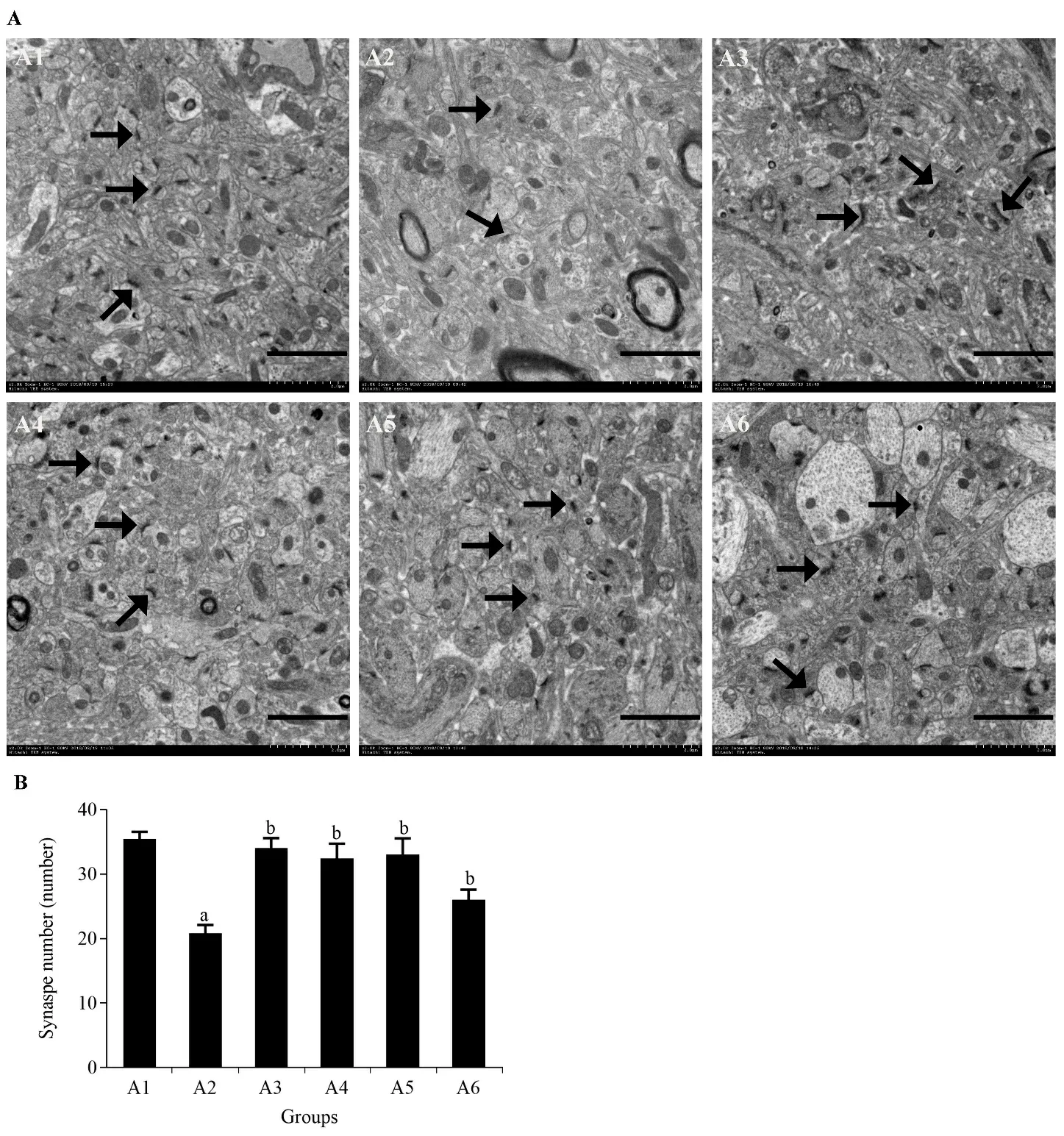
Figure 2 Efficacy of Jinsiwei on the number of synapses in STZ-induced SAD mice

Figure 3 Efficacy of Jinsiwei on the distribution of positive cells and protein expression of drebrin and cofilin in the hippocampal CA1 region of STZ-induced SAD mice
3.4.Efficacy of Jinsiwei on synaptic function-related proteins
Syn and NR2B showed similar group trends,as shown in Figures 4.The positive cells and protein expressions of syn and NR2B were all significantly reduced in the untreated MG compared to the CG (P< 0.01).Subsequently,Jinsiwei and donepezil treatment increased the positive cells and protein expression levels of syn and NR2B after 3 months treatment,among which the changes were more obvious in the JH,JM,and DG(P< 0.01 or< 0.05).However,there was no significant change in the JL (Figure 4A-4F).
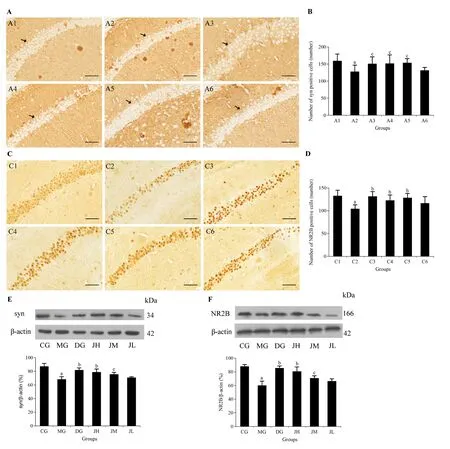
Figure 4 Efficacy of Jinsiwei on the distribution of positive cells and protein expression of syn and NR2B in the hippocampal CA1 region of STZ-induced SAD mice
4.DISCUSSION
AD is a common form of dementia,more than 95% of AD cases are SAD.17Studying the early pathological mechanism of SAD and identifying effective pharmaceutical interventions,which could reduce the social burden and improve the quality of life of patients.Chinese herbal compound is more suitable for the early intervention of AD and long-term use because of its positive therapeutic effect and fewer side effects.In our previous study,liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis showed that Jinsiwei contains more than 83 active components,and the important compounds include ginsenoside Rg1,β-asarone,curcumin,etc.12These major components of Jinsiwei have different neuroprotective effects on AD animal models.Ginsenoside Rg1,as the major ingredient of ginseng,can increase the expression of NR2B to improve learning and memory abilities in rat brain slice model of AD.18β-asarone,the main ingredient of acorus gramineus,exerts neuroprotective effects by increasing the expression of syn in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.19Curcumin has been found that it can increase the expression of postsynaptic density protein 95 to enhance synaptic plasticity.20In addition to the effects of single active ingredients,Jinsiwei has shown a positive effect by regulating the production and degradation of Aβ.21
Accumulating studies have shown that ICV-STZ can disrupt the brain insulin signal pathway and result in the formation of Aβ-derived diffusible ligands (ADDLs).ADDLs neurotoxicity affects the expression of synaptic structural and functional proteins,which leads to synaptic dysfunction and neuron damage,eventually triggering learning and memory impairment.22In this study,mice induced by ICV-STZ showed cognitive and spatial memory dysfunction in the Morris Water Maze task,and synaptic loss occurred after 3 months.After treatment with Jinsiwei for 3 months,the escape latency was largely shortened and the number of crossing platforms was significantly increased,indicating that Jinsiwei indeed improved the learning and memory ability of SAD mice in some extent.Furthermore,the electron microscopy results showed that Jinsiwei rescued the number of synapses in hippocampal CA1 area.
The nervous system receives and transmits informationviasynapses.Synapses are composed of two main parts -the presynaptic membrane and the postsynaptic membrane,which correspond to axon terminals and dendritic spines.Dendritic spines,including the actin cytoskeleton,various receptors,and postsynaptic density,are key structures to maintain synaptic morphology and function.23As an actin-binding protein,drebrin can form a drebrin-actin complex to promote the transformation of dendritic filopodia into dendritic spines and regulate the morphology and plasticity of dendritic spines.Cofilin,an actin depolymerization factor,widely expresses in dendritic spines of brain and regulates actin through cleavage.In this way,old actin is depolymerized and new aggregation is created,resulting in morphologic dynamic changes of dendritic spines,which ultimately influences the synaptic structure.Some studies have suggested that the expression of drebrin in the hippocampus of AD patients is reduced.The density and number of dendritic spines in the brain of AD mice model were significantly reduced as a result of decreased drebrin expression.24,25Moreover,other studies have found that the expression of cofilin was significantly increased in the mice brains of AD model.On the contrary,inhibiting the expression of cofilin can reduce neurotoxicity,increase synaptic connections,and improve the learning and memory function of mice.26Therefore,the protein expression levels of drebrin and cofilin are important indexes reflecting the synaptic structure.Our study found that different doses of Jinsiwei increased the number of drebrin-positive cells and protein expression levels,and reduced the number of cofilin-positive cells and protein expression levels in the hippocampus of STZ-induced SAD model mice.
Normal synaptic function also depends on the involvement of neurotransmitters.Neurotransmitters are released by the presynaptic membrane and then bind to the receptors on the postsynaptic membrane,producing excitatory or inhibitory effects.Syn is a calcium-binding protein sticking synaptic vesicles to the actin filament,controlling the number of synaptic vesicles released from the presynaptic membrane,and thus regulating the secretion of neurotransmitters.The NMDAR is an excitatory amino acid ligand-gated ion channel receptor on the postsynaptic membrane that regulates LTP.LTP is an important basis for synaptic plasticity,learning and memory.NR2B is an important regulatory subunit of NMDAR.The gene encoding NR2B is also known as the smart gene.Studies have demonstrated that the reduction of syn in the hippocampus is positively correlated with the degree of cognitive dysfunction in patients with AD.27Learning and memory ability of young rats was significantly decreased after knocking out the NR2B gene.Conversely,overexpressing NR2B gene revealed superior learning and memory ability in mice.28Therefore,syn and NR2B play essential roles in synaptic function.The results of our study found that the expression of syn and NR2B were significantly increased after the treatment with Jinsiwei.
In conclusion,Jinsiwei can ameliorate learning and memory impairment in STZ-induced SAD model mice.Jinsiwei improves synaptic structure and function by increasing the expression of drebrin,syn,and NR2B,and inhibiting the expression of cofilin.Jinsiwei hold great potential in the treatment of AD to some extent.These findings provide experimental data to support the use of Jinsiwei treating AD patients in clinic.
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2023年1期
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine2023年1期
- Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Effects of the Huangkui capsule (黄葵胶囊) on chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Effectiveness of moxibustion alone on lumbar disc herniation: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Efficacy of acupuncture therapy for post-stroke fatigue: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
- Efficacy of luteolin on the human gastric cancer cell line MKN45 and underlying mechanism
- Tilianin extracted from Xiangqinglan (Herba Dracocephali Moldovicae) inhibits apoptosis induced by mitochondrial pathway and endoplasmic reticulum stress in H9c2 cells after oxygenglucose deprivation/reoxygenation
- Comparing the effects of three decoctions for coronavirus disease 2019 on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-related tolllike receptors-mediated inflammations
